GS Paper 2
WTO Talks End With No Consensus on Agriculture Support

Context: Negotiations at the World Trade Organisation’s (WTO) 13th Ministerial Conference finally concluded on March 2, 2024 in Abu Dhabi.
However, the Conference failed to achieve any outcome on public stockholding (PSH) for food security and domestic support for farmers in developing countries, including India, which has been demanding a permanent solution on these issues.
| Relevance:
· Prelims: Agriculture, International Affairs · Mains: Effect of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India’s interests |
Analysis
Public Stockholding and Food Security
- India and 80 other countries have been negotiating a permanent solution for public stockholding (PSH) of food instead of temporary measures.
- The PSH policy makes it possible for the government to procure crops like rice and wheat from farmers at MSP, store and distribute these food grains to the poor and is thus essential for India’s food security strategy.
- However, PSH and other measures like subsidies and minimum support prices (MSP) are viewed as trade-distorting domestic measures by the developed world and have been a long-pending mandated issue at the WTO.
- Currently, under global trade norms, a WTO member country’s subsidy bill should not breach the limit of 10 per cent (for developing countries) and five per cent (for developed countries) of the value of production-based on the reference price of 1986-88. These allowances are called de minimis
- Apart from increasing this de minimislimit, India has asked for amendments in the formula to calculate the price support subsidies given to farmers for government procurement.
- Currently, it is calculated as the reference price for 1986-88. This, the developing countries, said, is a flawed calculation.
- India has asked that the reference price should be either the three-year average price based on the preceding five-year period excluding the highest and the lowest entry for that product; or adjusted for excessive inflation.
- On the objections to the 10 per cent limit by many countries including India, as an interim measure, the WTO members at the Bali ministerial meeting in December 2013 had agreed to put in place a mechanism popularly called Peace Clause and committed to negotiating an agreement for a permanent solution.
- Under the Peace Clause, WTO members agreed to refrain from challenging any breach in the prescribed ceiling by a developing nation at the dispute settlement forum of the WTO.
- This clause will stay till a permanent solution is found to the food stockpiling issue.
- India also asked for SSM (special safeguard mechanism), which aims at protecting poor and marginal farmers from any surge in imports or a steep decline in prices.
No Agreement on Fisheries Text
- The agenda for the WTO members was to discuss how to curb harmful fisheries subsidies that contribute to overcapacity and overfishing. No agreement could not be reached on this pillar.
- The Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies (AFS) was signed in 2022 at the 12th Ministerial Conference (MC12) of the WTO but covered prohibiting subsidies for only illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and overfished stocks, two of the three pillars under which negotiations have evolved. The third pillar concerns subsidies that contribute to overfishing and overcapacity.
- India is one among those that have yet to ratify the agreement on fisheries. India has argued that developed countries have depleted marine resources through industrialised overfishing and deep-water fishing.
Transition Period
- Another thorny issue was the transition period. Members of the least-developed countries (LDC) and developing countries, with a global share of marine catch not greater than 0.8 per cent (de minimis) would be excluded from the core prohibition on subsidies.
- Countries not falling into either of the other groups would have to demonstrate fulfilling the sustainability-based conditions outlined in the draft text in their regular notifications of fisheries subsidies.
- India’s global share of marine catch is greater than 0.8 per cent (between 4-5 per cent) and thus becomes excluded from the prohibitions.
- India has sought a blanket exemption from subsidy cuts for all its fishers for a ‘transition period’ of 25 years to address their development needs and ensure their livelihoods. Meanwhile, the developed nations want to limit this period to no more than seven years.
UPSC Daily News: Minerals, Avian Flu, Core Industries and More
GS Paper 3
Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP)
Context: Weeks after a township of Myanmar near the Indian border was captured by the rebel Arakan Army, an Indian delegation led by Rajya Sabha member K. Vanlalvena met with the Arakan Army inside Myanmar and held talks about the road network that is vital for the Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) – a flagship Indian project aimed at firming up overland and water connectivity with Southeast Asia.
| Relevance:
· Prelims: Geography (Location) · Mains: Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc. |
Analysis
- The Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project is a bilateral agreement between India and Myanmar.
- It, among others, involves the connecting of Aizwal in Mizoram with the deep-water Sittwe Port in Myanmar.
- A Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) initiative, the project seeks to ease India’s access to Southeast Asia through Myanmar and provide an alternate route between the landlocked Northeast and the rest of India, a purpose currently only served by the narrow Siliguri corridor.
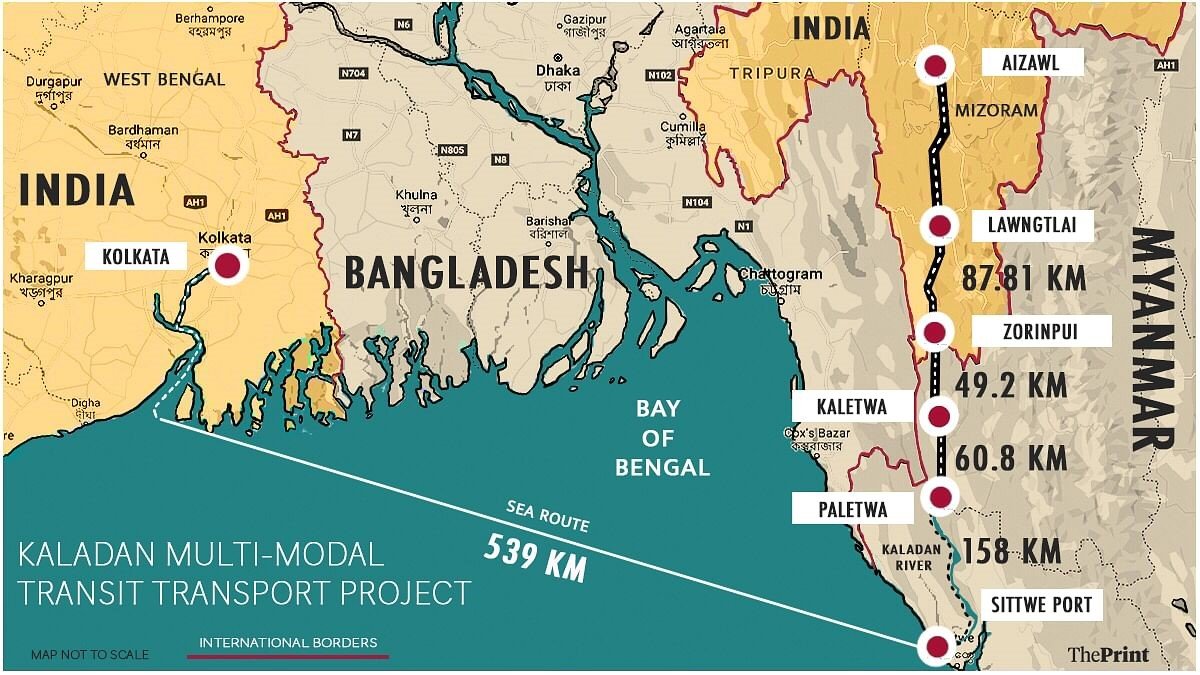
- KMTTP connects Kolkata to Sittwe port, which is further linked to Paletwa in Myanmar through a waterway route along the river Kaladan.
- Both the port at Sittwe and the inland water terminal at Paletwa are developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) — an autonomous organisation under the Union shipping ministry.
- From Paletwa, a 110 km road is being built to connect to Zorinpui at Mizoram on the Indo-Myanmar border.
- Zorinpui is further connected to Lawngtlai through a 100 km road.
- From Lawngtlai, an existing highway connects it to Aizawl, which in turn is linked to other northeastern cities including Guwahati.
- The project was launched under the ‘Look East Policy’, which dates back to 1991, and is being pursued by the present government under ‘Act East Policy’, its remodeled version of the policy.
Kaladan River
- The Kaladan river originates in central Mizoram and is known as the Chhimtuipui river in Indian territory.
- After meandering along the Indo Myanmar Boarder at North East India, River Kaladan flows through the southern part of Mizoram (India) and finally empties itself at Sittwe, the sea port in Myanmar into Bay of Bengal.
- The Kaladan is navigable within Myanmar from its confluence point at Sittwe to Paletwa.
- Beyond that point, the shallow waters and sharp curves make navigation infeasible.
- Consequently, road transport is proposed from Paletwa to the Indian border in Mizoram.
Act East Policy
- The Objective of ”Act East Policy” is to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationship with countries in the Asia-Pacific region through continuous engagement at bilateral, regional and multilateral levels thereby providing enhanced connectivity to the States of North Eastern Region including Arunachal Pradesh with other countries in our neighbourhood.
- While India’s earlier Look East Policy was driven by economic interests, the Act East Policy is driven by economic and security interests.
- While Look East Policy was limited to South East Asia but Act East Policy is extended to both South East Asia and East Asia as well.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
Context: The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister has approved the establishment of International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) with headquarters in India.
| Relevance:
· Prelims: Environment, Ecology and Biodiversity · Mains: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment. |
Analysis
- Out of the seven big cats (Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar and the Cheetah), five big cats viz. Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard and Cheetah are found in India.
- The cheetah was declared extinct in 1952. In 2022, the Government of India embarked on an ambitious programme to introduce African cheetahs to the Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
- IBCA aims at securing the future of big cats and landscapes they thrive. The pioneering and long standing tiger and other big cat conservation good practices evolved in India may-be replicated in many other range countries.
- IBCA has been conceived as a multi-country, multi-agency coalition of 96 big cat range countries (which house one or more of these big cats), non-range countries, scientific organizations and business groups willing to contribute to the cause of big cats.
What are Big Cats?

- Scientists categorize big cats based on two specific qualities: they belong to the genus Panthera and have a special two-piece hyoid bone in their throat that allows them to roar.
- The five cats of the Pantheragenus are Tiger (Panthera tigris), Lion (Panthera leo), Jaguar (Panthera onca), Leopard (Panthera pardus) and Snow Leopard (Panthera uncia).
- All Pantheraspecies, except for the Snow Leopard, make a loud roar.
- The Snow Leopard has shorter vocal folds and cannot roar and used to be classed in its own Uncia genus.
- However, genetic studies showed it was closely related to the other Panthera species and belonged in the same genus.
Jaguars Vs Leopards
- Jaguars and leopards are two distinct species (Panthera oncaand Panthera pardus).
- The two big cats live in geographically diverse areas of the world.
- Jaguars are found in the Americas, stretching from the scrublands and forests of Mexico down to the tropical rainforests of South America.
- Leopards live in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia, preferring deserts, grasslands, and rainforests.
- One of the easiest ways to visually differentiate a jaguar and a leopard is to look at the pattern of their coats.
- Jaguar coats have black dots in the rose-shaped spots, while leopards do not.
- Body shape can help as well, as jaguars have a thicker head and bulkier body compared to the sleeker leopard.
Are Cheetahs and Cougars Considered Big Cats?

- Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus – Vulnerable) are the only living species that belong to the genus Acinonyx,while cougars (Puma concolor – Least Concern) belong to the genus Puma.
- Both cats also lack a hyoid bone, setting them apart once again from the roaring big cats.
- Despite these biological differences, cheetahs and cougars (puma/mountain lion) have characteristics that make them very strong candidates for the big cat club. They are, clearly, very big cats, are critical species for a healthy ecosystem.
Important Characteristics of Big Cats
- All cats, including big cats, are members of the Felidae family.
- The lion has the loudest roar, which can be heard 8-10 kilometres away.
- The largest cat in the Americas, the Jaguar has the strongest bite force of all wild cats.
- The Amur tiger (Siberian tiger) is the largest of the big cat species.
- The term black panther is most frequently applied to black-coated leopards of Africa and Asia and jaguars of Central and South America.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE): Structure and Mandate
- Context: The Bureau of Energy Efficiency recently celebrated its 22nd Foundation Day on 1 march 2024.
| Relevance:
· Prelims: Important Organisations and Institutions related to Environment · Mains: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment. |
Analysis
Do You Know What is BEE?
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Power, and is established under provisions of the Energy Conservation Act 2001.
- Its aim is to promote efficient use of energy and its conservation, with the primary objective of reducing energy intensity of the Indian economy.
What is National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE)?
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE), one of the eight national missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), is being implemented by the BEE.
- The primary objective of the mission is to develop regulations and policies that are instrumental in strengthening the market for energy efficiency.
What are the Initiatives that come under NMEEE?
- NMEEE consist of four initiatives to enhance energy efficiency in energy intensive industries which are as follows:
- Perform Achieve and Trade Scheme (PAT)– Implementing a market assisted compliance mechanism to accelerate implementation of cost effective improvements in energy efficiency in large energy-intensive industries
- Market Transformation for Energy Efficiency (MTEE)– Accelerating the shift to energy efficient appliances in specific application through innovative measures to make the products more affordable.
- Energy Efficiency Financing Platform (EEFP)– Facilitating Financial Institutions to invest in Energy Efficiency Projects and Programmes
- Framework for Energy Efficient Economic Development (FEEED)– Developing fiscal instruments to leverage financing for Energy Efficiency through risk mitigation.
Tyler Prize for the Planetary Boundaries Framework
Context: The 2024 Tyler Prize for environmental achievement will be awarded to Johan Rockstrom for his pioneering work to the development of the Planetary Boundaries framework.
The prestigious Tyler Prize is often described as Nobel Prize for environment.
| Relevance:
· Prelims: Ecology, Environment and Biodiversity · Mains: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment. |
Analysis
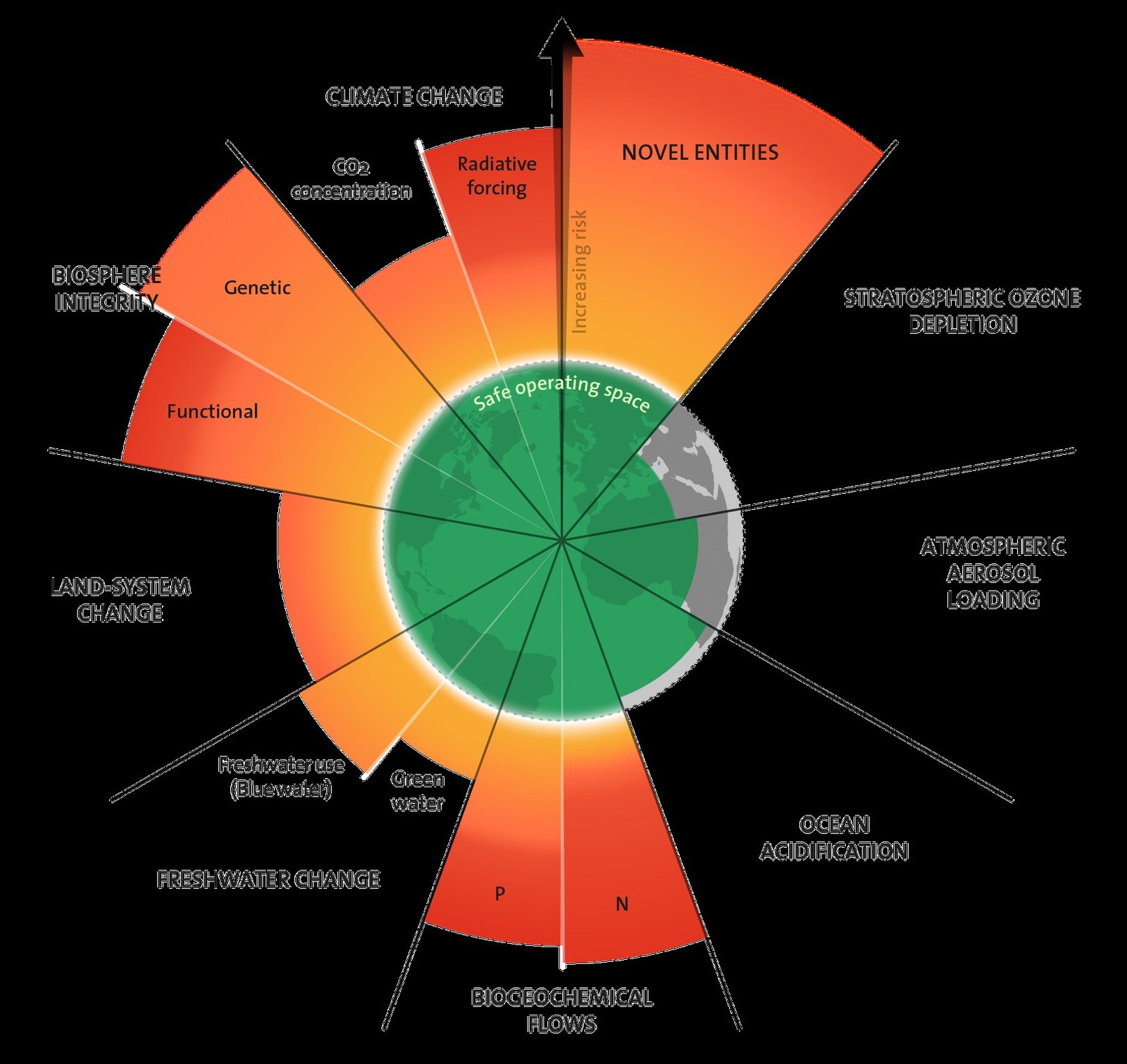
- The Planetary Boundaries framework presents a set of nine planetary boundaries within which humanity can continue to develop and thrive for generations to come.
- The framework tried to identify the Earth-system processes and associated thresholds which, if crossed, could generate unacceptable environmental change.
- The framework, published in 2009, defines these systems as:
- Climate change;
- Rate of biodiversity loss (terrestrial and marine);
- Interference with the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles;
- Stratospheric ozone depletion;
- Ocean acidification;
- Global freshwater use;
- Change in land use;
- Chemical pollution; and
- Atmospheric aerosol loading.
Facts for Prelims
News Broadcasting & Digital Standards Authority (NBDSA)
- The News Broadcasting & Digital Standards Authority (NBDSA) has directed three TV news channels to remove videos of certain programmes on communal issues as they violated the Code of Ethics and other guidelines. Penalties have also been imposed on two of them.
- Formerly known as News Broadcasters Association (NBA), the NBDSA represents the private television news, current affairs and digital broadcasters.
- It is the collective voice of the news, current affairs and digital broadcasters in India. It is an organization funded entirely by its members.
