UPSC GS 1
Gangetic Dolphins
- News: According to a recent report by the Wildlife Institute of India, there are more than 4000 dolphins in the Gangetic River basin.
- National Recognition: The Gangetic River dolphin was declared India’s national aquatic animal in 2009.
- Echolocation and Navigation: The Gangetic River dolphin is blind and uses echolocation to navigate and find prey in river waters.
- Respiratory Characteristics:
-
- As a mammal, the Ganges River dolphin cannot breathe underwater and must surface every 30-120 seconds.
- Due to the sound produced when breathing, the animal is popularly referred to as ‘Souns’, ‘Susu’, ‘Sushuk’, and ‘Seho’.

- Physical Description:
-
- The dolphin has a long, thin snout, a rounded belly, a stocky body, and large flippers.
- Habitat and Dimorphism:
-
- The Gangetic River dolphin lives only in freshwater environments.
- Females are larger than males.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Status: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Government Initiatives for Protection:
-
- Project Dolphin
- Vikramshila Gangetic Dolphin Wildlife Sanctuary (in Bihar)
Funan Techno Canal
- News: The Funan Techo Canal is a proposed 180 km long canal project in Cambodia, which is being funded by China.
- Project Details and Route: The Funan Techo Canal officially known as the Tonle Bassac Navigation Road and Logistics System Project will connect Phnom Penh Autonomous Port with Kep and the Gulf of Thailand.
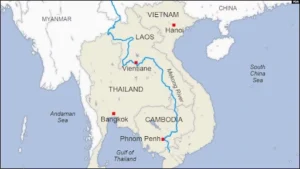
- Strategic Importance: The canal will reduce Cambodia’s reliance on Vietnamese ports, particularly Cai Mep, for international shipping.
Koya Tribe
- News: Andhra’s Koya tribe is facing conflict over sacred Mahua flower.
- Demographics and Location:
-
- The Koya are one of the few multi-racial and multi-lingual tribal communities in India.
- They reside in the forests, plains, and valleys on both sides of the Godavari River, in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- The Koya are believed to have migrated to central India from their original home in Bastar, northern India.
- Language:
-
- The Koya speak Koyi, a language belonging to the Dravidian language family.
- Koyi is closely related to Gondi and has been strongly influenced by Telugu.
- Occupation:
-
- Traditionally, the Koya were pastoralists and shifting cultivators.
- Currently, they have adopted settled cultivation, growing crops such as Jowar, Ragi, Bajra, and other millets.
- Family Structure:
-
- The Koya have a patrilineal and patrilocal family structure.
- The family unit is referred to as “Kutum,” with the nuclear family being the predominant type.
- Monogamy is prevalent among the Koya.
- Religion and Beliefs:
-
- The Koya practice their own ethnic religion and also worship several Hindu gods and goddesses.
- Many Koya deities are female, with the most important being “mother earth.”
- Festivals and Traditions:
-
- The main festivals of the Koya are Bijji Pandum (seeds charming festival) and Kondala Kolupu (festival to appease Hill deities).
- They perform a vibrant and colorful dance called Permakok (Bison horn dance) during festivals and marriage ceremonies.
- Sacred Practices:
-
- The Mahua tree is considered sacred by the Koya.
- Mahua flowers are used for brewing liquor.
UPSC GS 2
Living Will
- News: Justice M S Sonak, who serves on the Goa Bench of the Bombay High Court, recently became the first person in Goa to register a “living will”.
- Living Wills:
-
- Definition: Advance directives, also known as living wills, are legal documents that allow individuals to specify their preferences for medical treatment in the event they become incapacitated and are unable to communicate their wishes.
- Purpose: Living wills give individuals control over how they should be treated in case of incapacitation.
- Clarity for Family Members: Advance directives provide clarity to family members who would otherwise have to make difficult decisions on medical care and life support systems.
- Validity of living wills in India:
-
- The Supreme Court, in a landmark judgment in 2018, accepted and recognised the “right to die with dignity” as part of the fundamental ‘Right to Life’ under Article 21 of the constitution.
- The court observed that every adult individual with the mental capacity to make an informed decision has the right to refuse medical treatment, and life support systems, by executing an advance medical directive or a living will.
- The apex court said that these advance medical directives can be applied only in specific cases, where a patient becomes terminally ill and is not able to convey that the treatment must stop.
- New Guidelines by Supreme Court:
-
- Simplified Documentation Requirements:
- The Supreme Court, led by Justice KM Joseph, implemented revisions to the 2018 guidelines for the registration and enforcement of living wills.
- Witness and Attestation Requirements:
- Under the new guidelines, a living will must be signed and witnessed by two independent individuals.
- Notably, attestation by a notary or a gazetted officer now suffices, replacing the previous mandate for attestation by a judicial magistrate of first class.
- Clarification of Decision-Making Authority:
- The revised guidelines mandate explicit mention of the guardian or close relative authorized to make decisions regarding withdrawal of medical treatment in the event of the maker’s incapacitation.
- Revised Composition and Expertise of Medical Boards:
- Previously, medical boards were required to consist of three doctors with a minimum of 20 years’ experience in various medical fields.
- However, under the updated guidelines, the minimum experience requirement has been reduced to five years, with at least two doctors designated as subject experts.
- Timely Review Processes:
- Both the primary and secondary medical boards are now expected to provide their opinions within 48 hours of receiving a case referral, facilitating quicker decision-making processes.
- Recourse in Case of Disagreement:
- In instances where there is a disparity of opinions between the primary and secondary medical boards, or if both boards refuse permission, the patient’s next of kin reserve the right to petition the High Court.
- The High Court may then establish a new medical board to reassess the case.
UPSC GS 3
Variable Repo Rate
- News: The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) variable rate repo (VRR) auction garnered substantial interest from banks, receiving bids amounting to ₹1,13,915 crore, which significantly exceeded the RBI’s offer of ₹50,000 crore.
- Repo Rate: The Repo Rate is the rate at which banks borrow money from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and it is fixed by the RBI.
- Variable Rate Repo (VRR): VRR is the rate at which the RBI allows banks to borrow, with the rate being determined by the market through auctions.
- Borrowing Duration: The borrowing duration under VRR is more than one day and typically extends up to 14 days.
- Purpose: VRR is a tool used to inject short-term liquidity into the banking system.
Iris-T Missile
- News: According to a recent report, the Bundeswehr, Germany’s armed forces, lost an Iris-T missile, raising serious concerns about the potential compromise of this crucial technology.
- General Description:
-
- The Iris-T is a next-generation short-range air-to-air missile.
- It is part of a six-nation program led by Germany, with Diehl BGT Defence (a German defense company) serving as the industrial prime contractor.
- Program Collaboration:
-
- The IRIS-T program involves collaboration among Germany, Greece, Norway, Italy, Spain, and Sweden.
- This cooperation aims to provide access to advanced technology and expertise, with Diehl Defence as the main contractor.
- Capabilities:
-
- The Iris-T missile is rated for short-range and medium-range air defense.
- The IRIS-T SLM variant is designed to neutralize threats from various enemy aerial systems, including aircraft, cruise missiles, drones, and helicopters, operating at ranges of up to 40 km (25 miles).

- Technical Features:
-
- The Iris-T is characterized by extreme maneuverability suitable for close-in air-to-air combat.
- It is equipped with an innovative infrared seeker, thrust-vector control, and a dogfight optimized motor, enabling it to engage targets from point-blank range to its maximum range.
- Operational Flexibility:
-
- The Iris-T can successfully engage targets behind the launching aircraft.
- It can be used in lock-on before and after launch operations.
Greedflation
- News: Rising food prices in the US might be due to misleading narrative of “greedflation”.
- Definition of Greedflation:
-
- Greedflation simply means (corporate) greed is fuelling inflation.
- Unlike typical inflation scenarios where price increases result from higher input costs or increased demand, greedflation occurs when corporations exploit existing inflation by raising prices far beyond their actual input cost increases.
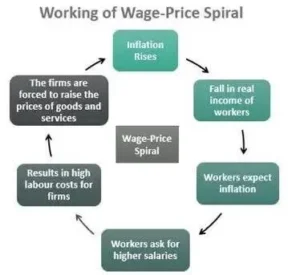
- Profit-Driven Price Increases:
-
- The rising prices under greedflation are driven more by corporate profit-seeking than by traditional economic factors.
- Economic Impact:
-
- This practice maximizes profit margins but also further fuels inflation, creating a cycle that exacerbates economic inequality.
Minuteman III
- News: U.S. test-launches nuclear-capable hypersonic missile capable of striking Moscow within 30 minutes.

- Definition:
-
- The LGM-30G Minuteman III is a solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) first deployed by the United States Air Force (USAF) in the 1960s.
- It serves as the sole land-based component of the U.S. nuclear triad.
- Although initially intended for a ten-year service life, it has been continuously modernized, with its replacement, the Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD), anticipated to be available by 2029.
- This missile was the first in the U.S. arsenal to be equipped with multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs).
- Currently, the U.S. maintains approximately 440 Minuteman III missiles in its arsenal.
- Designed and Manufactured by: Boeing Corporation.
- Features:
-
- Three-Stage, Solid-Fuel Design: The Minuteman III features a three-stage design powered by solid fuel.
- Dimensions: It measures 18.2 meters in length, has a diameter of 1.85 meters, and a launch weight of 34,467 kilograms.
- Range and Payload: The missile boasts a maximum range of 13,000 kilometers and is capable of carrying a payload of three reentry vehicles.
- Current Warhead Configuration: In accordance with arms control agreements between the United States and Russia, it currently carries a single nuclear warhead.
- Reliability and Launch Capabilities: The Minuteman III is known for its rapid launch capability, near 100% testing reliability, and has backup airborne launch controllers to ensure retaliatory capabilities.
Cut-off of UPSC IAS Prelims 2024 Exam
Thismia Malayana
- News: A distinctive plant, Thismia Malayana, which steals nutrients from underground fungi, has been published as a new species in the open-access journal PhytoKeys.
- Definition: Thismia Malayana is a newly discovered species of plant found in the tropical rainforests of Peninsular Malaysia.
- Classification: It belongs to a group of plants known as mycoheterotrophs, which do not perform photosynthesis like most plants.
- Nutrient Acquisition:
-
- Unlike typical plants, mycoheterotrophs such as Thismia malayana act as parasites, stealing carbon resources from fungi on their roots.
- This adaptation exploits the mycorrhizal symbiosis, a mutually beneficial relationship between fungi and a plant’s root system.
- Mycorrhizal Symbiosis:
-
- In mycorrhizal symbiosis, fungi help trees absorb water and nutrients from the soil, while trees provide fungi with sugars produced through photosynthesis.
- This partnership is essential for the health and growth of both organisms.
- Parasitic Behavior:
-
- Thismia malayana deviates from the mutual exchange in mycorrhizal symbiosis by acting as a parasite, siphoning off carbon resources from fungi without offering anything in return.

- Habitat and Adaptation:
-
- Thriving in the low-light conditions of dense forest understories, Thismia malayana’s highly specialized flowers are pollinated by fungus gnats and other small insects.
- Despite its small size, it is typically found hidden in leaf litter and grows near tree roots or old rotten logs.
- Conservation Status: Despite its sensitivity to environmental changes, Thismia malayana has been classified as Vulnerable according to the IUCN Red List.
Musankwa Sanyatiensis
- News: A 210 million-year-old dinosaur fossil, Musankwa Sanyatiensis, uncovered by scientists along the shoreline of Spurwing Island at Lake Kariba has sparked global interest.
- Discovery and Location: Musankwa sanyatiensis is a newly identified dinosaur species discovered from fossils found along the shores of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe.

- Naming:
-
- The dinosaur’s genus name, “Musankwa,” originates from the name of the houseboat scientists utilized during their expeditions to the research site.
- Its species name, “sanyatiensis,” references the Sanyati River, which flows into Lake Kariba.
- Significance:
-
- It marks the first dinosaur to be named from the Mid-Zambezi Basin of northern Zimbabwe in over 50 years.
- Additionally, it is only the fourth dinosaur to be named from Zimbabwe, following previous descriptions.
- Geological Context:
-
- The rocks containing this new specimen date back to the Late Triassic period, approximately 210 million years ago.
- Fossil Specimen:
-
- Musankwa sanyatiensis is represented by the remains of a single hind leg, including thigh, shin, and ankle bones.
- Evolutionary Analysis:
-
- Evolutionary analysis indicates that it belonged to the Sauropodomorpha group, consisting of bipedal, long-necked dinosaurs prevalent during the Late Triassic.
- Interestingly, it appears to be closely related to contemporaneous species found in South Africa and Argentina.
- Physical Characteristics:
-
- Weighing approximately 390 kg, Musankwa sanyatiensis was one of the larger dinosaurs of its era and primarily inhabited swamp areas.
- Lake Kariba:
-
- Lake Kariba is a lake in central Africa, between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe is the world’s largest man-made lake and reservoir by volume.
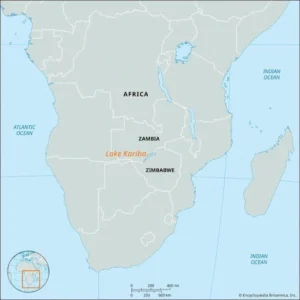
-
-
- Today, the Kariba Dam hydroelectric power station, situated on the lake, serves as a vital source of electricity for both Zimbabwe and Zambia.
Chang’e 6 Mission
- News: Recently, a spacecraft from the Chang’e 6 lunar lander lifted off from the moon’s far side carrying valuable soil and rock samples.
- Definition: China’s moon missions are called Chang’e, named for the goddess of the moon in Chinese mythology.
- Launch: Launched by China’s National Space Administration.
- Aim of the Mission: The goal is to collect lunar samples from the far side of the Moon and return them to Earth.
- International Collaboration: The mission involves international collaboration, with payloads contributed by the European Space Agency (ESA), the French space agency CNES, Italy, and Pakistan.
- Components of Chang’e-6: Chang’e-6 consists of an orbiter, a returner, a lander, and an ascender.

- Lander Equipment: The lander is equipped with multiple sensors, including microwave, laser, and optical imaging sensors, which can measure distance and speed and identify obstacles on the lunar surface.
- Scientific Contribution: The collected lunar samples will be shared with the global scientific community for research purposes.
- Historical Significance: This marks the second time a mission has successfully reached the far side of the moon, with China first achieving this historic feat in 2019 with its Chang’e-4 probe.









