UPSC GS 1
Mount Kanlaon
- News: Hundreds of people were sheltered in evacuation centres after Mount Kanlaon erupted in the central Philippines.
- Location: Mount Kanlaon is a stratovolcano located in the north-central portion of the island of Negros, Philippines.
- Description:
-
- It is the highest mountain on the island of Negros and the 42nd tallest peak on an island in the world.
- The volcano comprises a number of pyroclastic cones and craters.
-
What are Pyroclastic Cones?
|
- Volcanic Activity:
-
- Mount Kanlaon is one of the active volcanoes in the Philippines and is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- The summit of Kanlaon volcano, at an elevation of 2,435 meters, contains a broad, elongated caldera with a crater lake, and a smaller but more active crater to the south.
-
- Geological Features:
-
- The base of Kanlaon covers an area of 30 km by 14 km.
- It is underlain by tropical volcanic materials composed of sheeted lava flows, lahar deposits, airfall tephra, and apron pyroclastic materials.
-
- Biological Diversity:
-
- Mount Kanlaon is biologically diverse and is home to a number of species of flora and fauna.
- The slopes serve as headwater catchments for major river systems on the entire Negros Island.
-
- Eruption History:
-
- Kanlaon has erupted several times since 1886, typically comprising phreatic explosions of small to moderate size that produce minor ashfalls near the volcano.
-
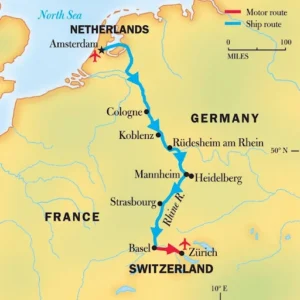
Rhine River
- News: Parts of the river Rhine in south Germany remained closed to cargo shipping after heavy rain in south Germany increased water levels.
- About Rhine River
- Geographical Features:
-
- The Rhine River is the 12th longest river in Europe and the longest in Western and Central Europe.
- Known as Rhein in Germany, Rhine in France, and Rijn in the Netherlands, it runs for over 1,232 kilometers (766 miles) from its source in the Swiss Alps in Switzerland.
-
- Course and Countries:
-
- The river flows through six countries: Switzerland, the Principality of Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, France, and the Netherlands before emptying into the North Sea at Rotterdam, Netherlands.
- The Rhine forms a natural border between Germany and France.
-
- Drainage Area and Tributaries:
-
- The river drains an area of about 185,000 square kilometers.
- Notable tributaries of the Rhine River include Aare, Tamina, Moselle, Erft, Rein da Tuma, Plessur, Rotach, and Wiese.
-
- Commercial Importance:
-
- The Rhine is Europe’s most important commercial waterway, facilitating trade among Switzerland, France, Germany, and the Netherlands.
-
- Major Cities:
-
- Major cities along the Rhine include Basel (Switzerland), Cologne, Bonn, Duisburg, Mainz, Leverkusen, and Neuss (Germany), Strasbourg (France), and Rotterdam and Utrecht (Netherlands).
-
- Industrial Significance:
-
- The river supports industrial transportation and industrial production, with approximately 20% of the world’s chemical industries manufacturing along its banks.
-
Dnipro
- News: Recently, a Russian missile attack targeted the central city of Dnipro, resulting in injuries to seven individuals, including two children, and causing damage to civilian infrastructure.
- Location and Geography:
-
- Formerly known as Dnipropetrovsk, Dnipro is a city of regional significance situated in the Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, located in the eastern portion of Ukraine.
- It covers an area of 409,718 square kilometers and is positioned along both banks of the Dnieper River, near its confluence with the Samara River.
- The city center stands on the right bank, forming part of the Dnieper Upland, while the left bank is part of the Dnieper Lowland.
- Dnipro is the country’s fourth-largest city after Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Odesa.
-
- Population and Status:
-
- As of 2021, the city had a population of 980,948 inhabitants.
-
- Industrial Significance:
-
- Dnipro is considered one of Ukraine’s principal industrial centers.
- It hosts several facilities dedicated to heavy industries, producing a diverse range of products including launch vehicles, rolled metal, cast iron, machinery, agricultural equipment, and various chemicals.
-
- Key Facts about Dnieper River
-
- Geographical and Linguistic Diversity: The Dnieper River is the fourth-longest river in Europe, known as Dnepr in Russian, Dnipro in Ukrainian, and Dnyapro in Belarusian.
- Situated in Eastern Europe, the Dnieper River and its tributaries drain much of Belarus and Ukraine.
- Course: Originating in Russia’s low Valday Hills, west of Moscow, the river runs a total length of 1,368 miles through western Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine before emptying into the Black Sea.
- It passes through numerous urban centers, including Smolensk and Dorogobuzh in Russia, Mogilev in Belarus, and Kiev, Cherkasy, Dnipro, and Zaporizhia in Ukraine.
- Historically, the river served as an important barrier dividing Ukraine into right and left banks.
-
- Tributaries: The Dnieper River boasts approximately 32,000 tributaries, including the Sozh, Desna, Trubizh, Bilozerka, Drut, Berezina, and Prypiat Rivers.
UPSC GS 2
NOTA
- News: In Madhya Pradesh’s Indore constituency, the “None of the Above” (NOTA) option has made history by securing a record-breaking 2,18,674 votes, emerging as the runner-up.
- Definition:
-
- NOTA is a ballot option allowing electors to express their negative opinions and lack of support for the contenders in an election.
-
- Implementation and Availability:
-
- In September 2013, the Supreme Court ruled in favour of including the ‘none of the above’ option in ballots, mandating the ECI to incorporate a button for NOTA in all EVMs.
- The button for NOTA is available at the bottom of all the EVMs.
- NOTA was first available during the Assembly elections in Delhi, Chhattisgarh, Mizoram, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh in 2013.
-
- NOTA and Rule 49-O:
-
- While NOTA has been in force since 2013, Rule 49-O of the Conduct of Election Rules, 1961, allows electors to decide not to vote.
- Under Rule 49-O, if a voter chooses not to vote, the presiding officer notes it in the remarks section next to their name in the voter list, along with their signature or thumb impression.
- However, this violates the secrecy of the vote, unlike the anonymity provided by NOTA.
-
- What Happens If NOTA Gets The Most Votes?
-
- Votes cast as NOTA are counted but are considered ‘invalid votes.’
- Even if NOTA receives the highest number of votes in a constituency, the candidate with the second-highest number of votes is declared the winner.
- Therefore, votes for NOTA do not alter the outcome of the election.
-
UN Global Supply Chain Forum
- News: The inaugural UN Global Supply Chain Forum, jointly organized by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) and the Government of Barbados, took place successfully from May 21 to 24, 2024, in Barbados.
- Objective: This significant event convened over 1,000 participants from across the globe to address critical issues such as global disruptions, geopolitical tensions, climate change, and the enduring impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on international trade.
- Participants and Key Focus Areas: The forum witnessed the active participation of trade and transport ministers from various Small Island Developing States (SIDS), representatives from UN agencies, officials from major global ports including the Port of Seattle, and key leaders in the shipping and logistics sectors.
- Initiatives and Outcomes:
-
- The forum introduced a pivotal document titled the “Manifesto for Intermodal, Low-Carbon, Efficient and Resilient Freight Transport and Logistics.”
- This manifesto aims to transform freight transport systems to align with global climate goals and enhance socio-economic resilience.
- The event also marked the launch of the UN Trade and Development Trade-and-Transport Dataset, developed in collaboration with the World Bank.
- This comprehensive dataset encompasses global data on over 100 commodities and various transport modes, facilitating an in-depth analysis of trade and transport costs.
- The forum introduced a pivotal document titled the “Manifesto for Intermodal, Low-Carbon, Efficient and Resilient Freight Transport and Logistics.”
-
Phenome India Project
- News: The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) announced the successful conclusion of the first phase of its longitudinal health monitoring project, the ‘Phenome India-CSIR Health Cohort Knowledgebase’ (PI-CheCK).
- About Phenome India-CSIR Health Cohort Knowledgebase:
- Introduction:
-
- Phenome India-CSIR Health Cohort Knowledgebase (PI-CheCK) is a project initiated by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) on December 7, 2023.
- This is the first pan-India longitudinal health monitoring study focusing on cardio-metabolic diseases.
-
- Participants:
-
- Nearly 10,000 individuals, including CSIR employees, pensioners, and their spouses, from 17 states and 24 cities are involved in the study.
-
- Data Collection:
-
- The study gathers extensive data, including clinical questionnaires, lifestyle and dietary habits, anthropometric measurements, imaging/scanning data, and detailed biochemical and molecular data.
-
- Purpose:
-
- The initiative aims to develop India-specific risk prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases, including diabetes, liver diseases, and cardiac diseases.
-
- Significance:
-
- Understanding Disease Risk: The study is critical for understanding the risk and prevalence of cardio-metabolic disorders in the Indian population, which may differ from Western populations due to ethnic diversity and distinct lifestyle patterns.
- Promoting P4 Healthcare: CSIR is utilizing this project to advance Predictive, Personalized, Participatory, and Preventive (P4) healthcare, tailored to the unique phenotypic and genetic profiles of the Indian population.
-
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
- Introduction:
-
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is India’s largest research and development (R&D) organization.
- It was established in September 1942.
- CSIR operates as an autonomous body under the Societies Registration Act of 1860.
- The organization receives its funding from the Ministry of Science and Technology.
-
- Focus Areas:
-
- CSIR is dedicated to scientific research and development across a diverse range of fields, including aerospace, biology, chemistry, earth sciences, engineering, and medical sciences.
-
- Organizational Structure:
-
- President: The Prime Minister of India serves as the President (Ex-officio).
- Vice President: The Union Minister of Science and Technology holds the position of Vice President (Ex-officio).
-
- Governing Body:
-
- Leadership: The Director-General heads the governing body.
- Members: The governing body includes other ex-officio members, such as the finance secretary responsible for expenditures.
- Term Length: Members typically serve terms of three years.
-
- CSIR Advisory Board:
-
- Composition: The CSIR Advisory Board consists of a 15-member panel, including distinguished experts from various scientific and technological fields.
- Role: The board advises the governing body on matters related to science and technology.
- Member Tenure: Each member’s term lasts for three years.
-
Read also: Mystery of the Far Side of the Moon | UPSC
UPSC GS 3
The Blaze Star
- News: The “Blaze Star” or the T Coronae Borealis (T CrB) is expected to brighten significantly between now and September 2024.
- Introduction:
-
- Blaze Star, officially known as T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), is a dim star situated 3,000 light-years away from our solar system in the constellation Corona Borealis (the “Northern Crown”).
-

- Recurrent Nova:
-
- Blaze Star is a rare example of a recurrent nova, with eruptions occurring approximately once every 80 years.
-
- Stellar Components:
-
- The nova involves a binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and a red giant.
- The white dwarf draws material from the red giant, leading to periodic explosive increases in brightness.
- The explosion occurs when the red giant’s surface temperature escalates dramatically, causing it to shed material onto the white dwarf, which then ignites a thermonuclear explosion.
-
- Upcoming Event:
-
- The upcoming stellar explosion is expected to be visible to the naked eye and shine as brightly as Polaris, the North Star, for about a week.
- NASA predicts this event to occur sometime between now and September 2024.
-
- Historical Eruptions:
-
- Notable eruptions of T CrB were recorded in 1946 and 1866, with earlier documented observations dating back to 1787 and 1217.
-
- Frequency and Impact:
-
- Novae like T CrB occur once every few decades to a century, differing from supernovae in scale, frequency, and consequences.
- Unlike supernovae, novae do not destroy the star system but allow it to reset and repeat the cycle.
-
Reverse Transcriptase
- News: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the enzyme reverse transcriptase became a cornerstone in laboratories worldwide. It was the gold standard for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 virus through diagnostic tests.
- Discovery:
-
- Reverse transcriptase was discovered independently by Howard Temin and David Baltimore in 1970, as published in the journal Nature.
- This enzyme can reverse the usual flow of genetic information by converting RNA into DNA.
-
- Impact on Genetic Research:
-
- This discovery changed the understanding of genetic information flow and revolutionized research methods, allowing scientists to study genes more effectively.
-
- Application in Diagnostics and Treatment
-
- Diagnostics: The enzyme is crucial in molecular diagnostics, converting viral RNA into DNA to measure viral loads, especially in diseases like hepatitis B and HIV.
- Treatment of HIV: Reverse transcriptase inhibitors became a fundamental part of treating HIV/AIDS, significantly improving patient survival rates.
-
- About Bacterial Reverse Transcriptase and Gene Creation:
-
- Discovery: The first bacterial reverse transcriptase was identified in 1989, revealing that bacteria have genetic mechanisms similar to those in humans.
- Function in Klebsiella pneumoniae: When attacked by bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria), Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria utilize reverse transcriptase to create DNA from non-coding RNA, leading to the production of a protein named ‘Neo.’
- Defense Mechanism: Researchers have named this protein ‘Neo,’ which stands for “never-ending open-reading frame.”
- Neo can induce a state of deep sleep in the bacterial cell, halting its multiplication. This also prevents the infecting virus from multiplying, effectively stopping the infection.
-
- Implications and Future Directions:
-
- Potential in Biotechnology and Medicine: The role of reverse transcriptase in bacterial defense opens new avenues for biotechnological and medical innovations, particularly in combating antimicrobial resistance.
- Research Opportunities: Further exploration of reverse transcriptases could unveil new mechanisms of genetic evolution and viral resistance strategies, offering novel therapeutic and biotechnological applications.
-
Parengyodontium Album
- News: Recent research has unveiled the discovery of a marine fungus named Parengyodontium album capable of decomposing plastic polyethylene (PE) in oceanic environments.
- Plastic Polyethene Breakdown: Parengyodontium album is a marine fungus renowned for its capability to degrade plastic polyethene (PE), the most prevalent plastic found in the ocean.
- Discovery and Researchers: This remarkable fungus was discovered by marine microbiologists from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ).
- Bioremediation Process: In the bioremediation process facilitated by Parengyodontium album, the carbon derived from PE is converted into the fungal biomass of P. album, serving as its energy source.
- Importance of Photodegradation:
-
- Initial photodegradation of PE by UV sunlight plays a crucial role in this process, rendering the fungus valuable in degrading floating oceanic plastic litter.
-
- Global Plastic Production and Ocean Pollution:
-
- With humans producing over 400 billion kilograms of plastic annually, a substantial portion ends up in the ocean, posing environmental challenges.
-
- Fungal Degradation Potential:
-
- Fungi are regarded as the ‘masters of degradation’ due to their utilization of a variety of digestive enzymes for plastic degradation.
- Researchers anticipate the existence of more plastic-degrading fungi in the deeper parts of the ocean, further emphasizing the potential of organisms like Parengyodontium album in mitigating plastic pollution.
-
- Bioremediation Process:
-
- Bioremediation uses microorganisms to degrade organic contaminants in soil, groundwater, sludge, and solids.
- The microorganisms break down contaminants by using them as an energy source or cometabolizing them with an energy source.
-
Facts for Prelims
Key Polity Terms:
- Caveat emptor: let the buyer beware
- Locus Standi : right of a party to bring a legal action
- Amicus curiae: friend of the court, special expert appointed by the court to help in a particular case.
