UPSC GS 1
World Wealth Report 2024
- News: World Wealth Report 2024 has been released by the Capgemini Research Institute.
- Coverage: The report covers 71 countries, accounting for more than 98% of global gross national income and 99% of world stock market capitalization.
- Highlights:
-
- Global high-net-worth individuals (HNWI) wealth expanded by 4.7% in 2023, reaching $86.8 trillion.
- The HNWI population increased by 5.1% to 22.8 million globally.
-
- Definition and Segmentation of HNWIs:
-
- HNWIs are individuals with investable assets of $1 million or more, excluding their primary residence, collectibles, consumables, and consumer durables.
- HNWIs are segmented into three categories based on wealth bands:
- Ultra-HNWIs: $30 million or more
- Mid-Tier Millionaires: $5-30 million
- Millionaires Next Door: $1-5 million
-
- Regional Performance in APAC:
-
- Among the best performers in the Asia–Pacific region were India and Australia.
- India recorded HNWI wealth growth of 12.4% and HNWI population growth of 12.2%.
- Australia recorded HNWI wealth growth of 7.9% and HNWI population growth of 7.8%.
-
- Factors Driving Growth:
-
- A resilient economy and robust performance of the equity markets drove wealth growth in both India and Australia.
-
- HNWI Growth in India:
-
- HNWI in India increased by 12.2% in 2023 compared to 2022, bringing the total HNWI population to 3.589 million.
- The financial wealth of India’s HNWIs increased by 12.4% in 2023 to $1,445.7 billion, compared to $1,286.7 billion in 2022.
-
- Economic Indicators in India:
-
- India’s unemployment rate decreased to 3.1% in 2023, down from 7% in 2022.
- The country’s market capitalization increased by 29.0% in 2023, following an increase of 6% in 2022.
- National savings as a percentage of GDP also increased to 33.4% in 2023, compared to 29.9% in 2022.
-
Onge Tribe
- News: Andaman’s Onge tribe king and queen welcome a baby boy, making the population now 136.
- Ancestry and Location:
-
- The Onges are one of the most primitive tribes in India, tracing their ancestry to the Negrito racial group.
- They inhabit Little Andaman Island, the southernmost island in the Andaman archipelago.
-
- Lifestyle and Beliefs:
-
- Traditionally semi-nomadic, the Onges relied on the ocean and forest for their sustenance.
- They do not adhere to strict worship practices or rituals involving sacrifices.
- The Onges consider pearly white teeth a symbol of death, leading them to chew bark to color their teeth red.
-
- Cultural Practices:
-
- Onges use white and ochre clay to decorate their bodies and faces.
- Special occasions see heightened emphasis on body ornamentation.
-

- Historical and Demographic Changes:
-
- Until the 1940s, the Onges were the sole permanent inhabitants of Goubalambabey, their name for Little Andaman.
- Today, they share the 732 sq km island with approximately 17,000 settlers from India, Bangladesh, and the Nicobar Islands.
- The Onge population declined drastically due to contact with British colonists and Indian settlers, dropping from 670 in 1900 to only 96 by the early 2000s.
-
- Modern Settlement:
-
- In 1976, the Onge were relocated to a settlement to provide them with basic hygienic facilities and protection against natural elements.
- They currently reside in a reserve at Dugong Creek on Little Andaman, which is much smaller than their original territory.
-
- Health and Fertility Issues:
-
- The Onge tribe is among the world’s least prolific and most infertile communities.
- Infertility affects over 40% of married couples within the tribe.
-
UPSC GS 2
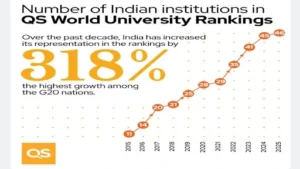
2025 QS World University Rankings
- News: Quacquarelli Symonds has released QS World Rankings 2025.
- Top Rank: Globally, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) retained its position as the best institute in the world for the 13th consecutive year.
- Performance of Indian Universities
- Overall Rankings:
-
- 61% of Indian universities have improved their rankings.
- 24% of Indian universities maintained their positions.
-
- Top Indian Universities:
-
- IIT-Bombay: Secured the top position in India with a 118th rank.
- IIT Delhi: Followed IIT-Bombay in the rankings.
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru: Ranked after IIT Delhi.
- University of Delhi: Made the most significant advancement, jumping 79 places to secure the 328th position.
-
- Institutes of Eminence: Of the 11 Institutes of Eminence in the rankings:
-
- Eight have risen.
- One remains stable.
- One has dropped.
-
- Research and International Collaboration:
-
- India shows significant progress, ranking 2nd in Asia for research and international collaboration.
-
- Improvement and Representation in Asia:
-
- India ranks second in Asia for the most improved universities.
- India also ranks second in Asia for the number of universities represented (with China being first).
-
- QS World University Rankings: The QS World University Rankings is an annual publication by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), a British company specializing in education and study abroad.
- Performance Metrics:
-
- Academic and Employer Reputation
- Faculty Student Ratio
- International Faculty Ratio
- International Student Ratio
- Citations per Faculty
- International Research Network
- Employment Outcomes
- Sustainability
-
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
- News: The Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) has invited suggestions on the draft ‘Central Excise Bill, 2024’ from stakeholders by 26th June 2024.
- Overview of the New Bill:
- Replacement of the Central Excise Act of 1944:
-
- The bill intends to replace the Central Excise Act of 1944 upon its implementation.
-
- Purpose of the Bill:
-
- The main aim of this bill is to remove outdated and redundant provisions following the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- It addresses the long-standing demand from industry players to align excise duty provisions with GST legislation.
-
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC):
- Overview:
-
- CBIC (erstwhile Central Board of Excise and Customs) is a part of the Department of Revenue under the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- CBIC administers all indirect tax-related matters in India.
-
- Functions and Responsibilities:
-
- Policy Formulation: The Board is responsible for formulating policies concerning the levy and collection of Customs duties, Central Excise duties, Central Goods & Services Tax (CGST), and Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST).
- Anti-Smuggling: It is tasked with the prevention of smuggling.
- Administration: CBIC oversees matters related to Customs, Central Excise, CGST, IGST, and Narcotics within its purview.
- Administrative Authority: The Board is the administrative authority for its subordinate organizations, including Custom Houses, Central Excise and Central GST Commissionerates, and the Central Revenues Control Laboratory.
- Tax Collection and Compliance: CBIC ensures that taxes on foreign and inland travel are administered according to the law, and that collection agencies deposit the collected taxes to the public exchequer promptly.
-
- Customs Administration: CBIC handles the collection of customs duty at various points including:
-
- International Airports
- Seaports
- Custom Houses
- International Air Cargo Stations
- International Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
- Land Customs Stations
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
- Container Freight Stations (CFSs)
-
- Organizational Structure
-
- The CBIC is headed by a Chairman, who is appointed by the Indian Government.
- Divisions and Zones: The organization is divided into various divisions and zones, each headed by a Chief Commissioner or Director General.
- GST Intelligence Wing: The CBIC has a GST intelligence wing responsible for detecting and preventing tax evasion.
-
UPSC GS 3
PraVaHa
- News: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software named Parallel RANS Solver for Aerospace Vehicle Aero-thermo-dynamic Analysis (PraVaHa).
- Definition:
-
- PraVaHa is a software system developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) of ISRO for analyzing the aerodynamics and thermodynamics of aerospace vehicles.
- This software is known as a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) tool.
- It is instrumental in simulating the airflow around various aerospace vehicles, including rockets and re-entry vehicles, both with and without wings.
-
- Aim:
-
- PraVaHa is intended to supplant most of the CFD simulations for aerospace vehicle design, which are currently conducted using commercial software.
- The objective is for PraVaHa to become a primary tool in the design of missiles, aircraft, and rockets, providing solutions to complex aerodynamic challenges.
-
- Applications of PraVaHa:
-
- Gaganyaan Program: PraVaHa plays a pivotal role in analyzing the aerodynamics of human-rated launch vehicles, such as the HLVM3, Crew Escape System (CES), and Crew Module (CM).
- Collaborative Development: The software is designed to be both secure and flexible, facilitating collaboration between academic institutions and government laboratories in developmental projects.
- Simulation Capabilities: PraVaHa currently has the capacity to simulate airflow in both perfect gas and real gas conditions.
- Efforts are ongoing to extend its capabilities to include the simulation of chemical reactions, such as those occurring during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere and in scramjet engines.
-
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD):
-
- It is the process of mathematically predicting physical fluid flow by solving the governing equations using computational power.
- In a CFD software analysis, fluid flow and its associated physical properties, such as velocity, pressure, viscosity, density, and temperature, are calculated based on defined operating conditions.
- In order to arrive at an accurate, physical solution, these quantities are calculated simultaneously.
-
- Importance of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD):
-
- Design Studies:
- Initial design studies for launch vehicles require evaluating many different configurations to find the best one.
- CFD allows engineers to simulate and analyze various designs efficiently, helping to identify the optimal configuration for performance and safety.
- Aerodynamic Loads:
- Aerospace vehicles face extreme aerodynamic and thermal loads (pressure and heat) during launch and re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere.
- CFD provides critical insights into these loads, enabling the design of structures capable of withstanding harsh conditions.
- Design Studies:
-
- Flow Understanding:
-
-
- Understanding how air flows around vehicles like rockets or crew modules during re-entry is crucial for designing their shape, structure, and thermal protection systems (TPS).
- CFD helps engineers visualize and analyze these flow patterns, informing decisions that enhance vehicle safety and performance.
-
-
- Unsteady Aerodynamics:
-
-
- The unsteady (changing) part of aerodynamics can cause serious flow issues and significant noise during a mission.
- CFD simulations help predict and mitigate these unsteady aerodynamic effects, contributing to the overall stability and success of aerospace missions.
-
-
Read also: Challenges and Strategies for Women’s Political Representation in India UPSC
UNESCO’s State of Ocean Report 2024
- News: The UNESCO ‘State of Ocean Report, 2024’ offers essential insights into the present condition of global oceans, highlighting the significant challenges posed by climate change and human activities.
- Inception and Purpose:
-
- The UNESCO ‘State of the Ocean Report’ was initiated by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC-UNESCO) during the 2022 United Nations Ocean Conference.
- This report aims to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the ocean’s current condition.
-
- Tracking Progress and Promoting Sustainability:
-
- The report serves as a tool to track the progress of the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–2030).
- It encourages efforts towards creating a sustainable future for our oceans by making the information accessible and actionable.
-
- Expert Insights and Key Topics:
-
- The first edition in 2022 featured insights from over 100 marine science experts on crucial issues such as ocean acidification, pollution, and tsunami warnings.
- These insights help inform and guide global ocean management strategies.
-
- Annual Releases and Alignment with UN Goals:
-
- New editions of the report are released annually on World Oceans Day (June 8).
- Each edition aligns with the seven goals of the UN Ocean Decade, ensuring that the report remains relevant and focused on achieving sustainable ocean development.
-
- Key Highlights of the Report:
- Ocean Warming:
-
- The upper 2,000 meters of the oceans have been warming significantly.
- The rate of warming has increased from 0.32 ± 0.03 watts per square meter (W/m²) to 0.66 ± 0.10 W/m² over the past 20 years.
-
- Energy Absorption:
-
- Oceans are absorbing about 90% of the Earth’s excess energy.
- This absorption leads to deoxygenation (loss of oxygen), which poses a threat to marine ecosystems and the human economies that depend on them.
-
- Ocean Acidification:
-
- The acidity of the ocean is increasing globally, particularly in the open ocean.
- There has been a notable drop in pH since the late 1980s, indicating rising acidification levels.
-
- Sea Level Rise:
-
- Sea levels have been rising steadily since 1993.
- Enhanced monitoring systems are essential to track this phenomenon accurately at all levels.
-
- Marine Carbon Dioxide Removal:
-
- There is growing interest in technologies designed to remove carbon dioxide from the ocean.
- However, the effectiveness and environmental impact of these technologies remain uncertain.
-
Air of the Anthropocene Initiative
- News: The “Air of the Anthropocene” project employs light painting to visualize air pollution in India, Ethiopia, and the UK. This initiative highlights severe health risks and sparks global discussions on air quality.
- Project Overview:
-
- The “Air of the Anthropocene” project is an international effort that combines art and science to visually represent air pollution through light painting.
-
- Collaborative Effort:
-
- Artists and researchers collaborated to create photographic evidence of air pollution.
- They utilized digital light painting techniques alongside low-cost air pollution sensors to achieve this visualization.
-
- Methodology
-
- The “painting with light” team used low-cost air pollution sensors to measure particulate matter (PM) mass concentrations.
- These sensors provided real-time data to control a moving LED array, which flashed more rapidly as PM concentrations increased, visually depicting the severity of air pollution.
-
- Particulate Matter (PM):
-
- PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution), which refers to a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
- Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye.
-
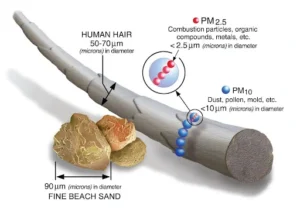
-
-
- Types of Particle Pollution:
- PM10: Inhalable particles with diameters that are generally 10 micrometers and smaller.
- PM2.5: Fine inhalable particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
- Composition: This complex mixture includes both organic and inorganic particles, such as dust, pollen, soot, smoke, and liquid droplets.
- Types of Particle Pollution:
-
Placental Mammals
- News: New research from Stockholm University reveals that the typical mammalian heater organ, brown fat, evolved exclusively in modern placental mammals.
- Placental Mammals:
-
- A placental mammal is an animal that has a placenta.
-
- Function of the Placenta:
-
- The placenta is a vascular organ formed during gestation in female mammals (excluding monotremes and marsupials).
- It is composed of maternal and fetal tissues, facilitating the transport of nutrients from the mother to the fetus and the elimination of fetal waste products.
-
- Gestation and Development:
-
- Placental mammals carry their fetus in the uterus until they are born at an advanced stage.
- The young receive nourishment through the placenta before birth, which delivers nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
- The placenta allows for a long period of fetal growth in the uterus, enabling the fetus to become large and mature before birth.
-

- Classification and Diversity:
-
- Classified under the subclass Eutheria, placental mammals encompass 4,000 identified species.
-
- Evolutionary History:
-
- Fossil evidence indicates that the first placental mammals evolved between approximately 163 million and 157 million years ago during the Jurassic Period (201.3 million to about 145 million years ago).
-
- Comparison with Other Mammals:
-
- Placental mammals include all living mammals except marsupials and monotremes (egg-laying mammals).
- Marsupials and monotremes have a less-developed, less-efficient type of placenta that limits their gestation period.
-
- Marsupials:
-
- They are the group of mammals commonly thought of as pouched mammals (like the wallaby and kangaroo).
- They give live birth, but they do not have long gestation times like placental mammals.
-

-
-
- Instead, they give birth very early and the young animal, essentially a helpless embryo, climbs from the mother’s birth canal to the nipples.
- Marsupials have a short-lived placenta that nourishes their young for just a few days before they’re born, the rest of their nutrition coming from the mother’s teats inside the pouch.
- There are over 330 species of marsupials. Around two-thirds of them live in Australia.
- Marsupials have an extra pubic bone, the epipubic bone, to support their pouch.
-
Read this: None of the Above (NOTA): Significance and Challenges | UPSC
New Species at Clarion-Clipperton Zone
- News: Researchers studying the Pacific Ocean’s deep Clarion-Clipperton Zone have discovered a multitude of species that have never been observed before.
- Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ): It is an abyssal plain between Hawaii and Mexico in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
-
- Abyssal plains are deep-sea areas at depths of 3 500 to 5 500 metres.
-
- Finding:
-
- The animals inhabiting these deep-sea areas have adapted to survive with very little nutrition.
- Consequently, the population is dominated by filter feeders like sponges and sediment feeders such as sea cucumbers.
- Due to the scarcity of food, these animals live far apart and have developed specialized adaptations.
-
- Species Found Are:
- Sea Cucumbers:
-
- Sea cucumbers are part of a larger animal group called echinoderms, which also contains starfish and sea urchins.
- Their body shape is similar to a cucumber, but they have small tentacle-like tube feet that are used for locomotion and feeding.
- Sea cucumbers are found in all marine environments throughout the world, from shallow to deep-sea environments.
-

-
-
- Sea cucumbers are benthic, meaning they live on the ocean floor. However, their larvae are planktonic, meaning they float in the ocean with the currents.
- Sea cucumbers exhibit sexual and asexual reproduction.
- Unlike most terrestrial animals, sea cucumber eggs undergo external fertilization—females release eggs into the water that are fertilized when they come into contact with sperm that males have released.
- A sea cucumber can live for 5 to 10 years.
- Conservation Status: Their collection or trade is banned under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
-
- Pink Sea Pig (Barbie Pigs, enus Amperima)
-
- The species moves very slowly with its tube feet across the plains in search of nutrient-rich sediments.
-

-
-
- The outgrowths on the front end of the underside are remodelled feet used to stuff food into the mouth.
- It acquired its name because of its pink colour and small feet.
-
- Cup-Shaped Glass Sponge:
-
- It is an animal believed to have the longest lifespan of any creature on Earth, 15,000 years.
- It spends its life filtering out nutrients from the never-ending fall of marine snow.
-

World’s Largest Astronomy Camera
- News: Chile will install the world’s largest astronomy camera on the edge of Atacama desert.
- Telescope and Camera Specifications:
-
- The camera will be mounted on the Simonyi Survey Telescope at the Vera C. Rubin Observatory.
- The camera weighs approximately three tonnes and has a resolution of 3.2 gigapixels.
- The observatory features an eight-meter wide-field telescope, a groundbreaking camera, and an automated data processing infrastructure.
-
- Objectives:
-
- Scientific Goals:
- To understand the nature of dark energy and dark matter in the universe.
- To study the possibility of Earth colliding with asteroids or stars and planets close to the sun.
- Data Volume and Catalog:
- The observatory is expected to collect around 20 terabytes of data daily.
- This will result in a 15-petabyte catalog over its decade-long survey.
- Scientific Goals:
-
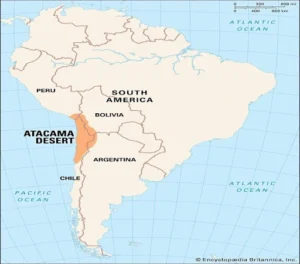
- Atacama Desert:
- Location and Geography:
-
- The Atacama Desert is a 600-mile-long (1,000-kilometer) plateau in the north of Chile.
- It is near the borders of Peru, Bolivia, and Argentina in South America.
- The desert is wedged between the coastal Cordillera de la Costa mountain range and the Andes Mountains.
- The Atacama Desert in Chile is the driest place on the planet.
- Its exceptionally bright skies make it ideal for astronomy.
-
- Climate and Vegetation:
-
- It is the driest nonpolar desert in the world and the only true desert to receive less precipitation than the polar deserts.
- The desert is almost without vegetation, except along slopes moistened by drizzle during the winter or in mesic valleys (moderate supply of moisture) that bisect the otherwise xeric (dry) desert.
-
- Natural Resources:
-
- The Atacama Desert contains the world’s largest supply of sodium nitrate.
-
New Strain of Bird Flu In Human
- News: Recently, the World Health Organization reported the first confirmed human case of the H5N2 type of bird flu in a 59-year-old man in Mexico.
- H5N2:
-
- It is one of several kinds of avian influenza viruses.
- H5N2 belongs to a family of bird flu viruses called H5, which primarily infects wild birds.
- There are a total of nine known subtypes of H5 viruses, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
-
