GS Paper 1
Atacama Desert
- News: Recent research reveals a vast and diverse group of bacteria thriving beneath the arid sands of the Atacama Desert.
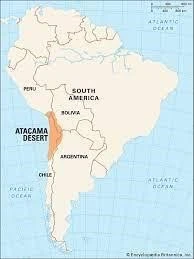
- Geographical Location:
-
- Located in northern Chile, bordered by the Andes Mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
- Shares borders with Argentina, Peru, and Bolivia.
-
- Extreme Environmental Conditions:
-
-
- Known as the driest desert globally.
- Exhibits extreme dryness, highest UV radiation levels on Earth, and highly saline and oxidizing soils.
- Hosts 12 volcanoes, primarily situated in the western outliers of the Andes.
-
- Climate and Geography:
-
-
- Receives an average rainfall of about 1 mm per year due to its location between the Andes (blocks the humid air from the Amazons) and Coastal Mountain ranges.
- Formerly part of the Pacific Ocean seabed, featuring caked salt deposits called playas, stretching for miles and up to 1.6 feet thick.
-
- Natural Resources:
-
-
- Has largest natural supply of Sodium Nitrate, suitable for fertilizer and explosive production.
- Soil samples resemble those from Mars, making it a testing ground for NASA’s instruments for missions to the red planet.
-
- Astronomical Significance:
-
-
- One of the few locations with over 300 days of clear skies annually and minimal light pollution.
-
- Cultural Heritage:
-
- Houses the Chinchorro Mummies, the oldest artificially mummified human remains ever discovered.
Debunking the Myth: UPSC Civil Services Exam is Not Just for the Super-Intelligent
GS Paper 2
Spices Board India
- News: Spices Board of India has asked companies for quality check information.
- Introduction to Spices Board
- Established under the Spices Board Act, 1986, on February 26, 1987.
- Operates under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
- Formed by merging the Cardamom Board and the Spices Export Promotion Council.
- Mandate and Responsibilities
- Oversight of 52 spices listed in the Spices Board Act, 1986.
- Development of small and large cardamom sectors.
- Promotion and regulation of spice exports.
- Quality control measures for exported spices.
- Research activities focused on cardamom conducted through the Indian Cardamom Research Institute.
- Through these functions, the Spices Board works towards enhancing the development, promotion, and quality assurance of India’s diverse spice industry.
Article 244(A)
- News: Residents of the Diphu Constituency in Assam advocate for the enforcement of Article 244(A) of the Constitution.
- Background of Article 244(A): Inserted into the Constitution by the 22nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1969.
- Provisions of Article 244(A):
-
- Allows for the establishment of an autonomous State comprising select tribal areas within Assam.
- Grants the autonomous state its own local Legislature, which may be either elected or partially nominated and elected, along with a Council of Ministers or both, for local governance.
-
- Enhanced Powers for Tribal Areas: Offers greater authority to tribal areas compared to the Sixth Schedule, particularly regarding law and order administration within the region.
- Determination of Powers and Functions: Specifies that the specific powers and functions of this autonomous state will be delineated by legislation enacted by the Parliament.
GS Paper 3
Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: Supreme Court stays construction of four dams inside Haryana’s Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Location
-
- Situated in the Shivalik foothills of the Himalayas in Haryana.
- Bordered by the Yamuna River to its east.
-
- Geographical Features
-
- Valleys in the sanctuary contain seasonal rivulets known locally as ‘soats,’ which typically remain dry for most of the year.
-
- Historical Landmarks
-
- Houses the historic Kalesar Fort, constructed during the reign of Aurangzeb.
- Notable for its Dak bungalows, colonial-era administrative architectural bungalows.
-
- Flora
-
- Rich in diverse flora, including sal, khair, shisam, tun, sain, and amla trees.
-
- Fauna
-
- Home to a variety of wildlife, including leopards, sambar deer, barking deer, hyenas, jackals, Indian porcupines, Indian pangolins, and langurs.
- Hosts a range of bird species such as the red junglefowl, grey partridge, Indian peafowl, and white-throated kingfisher.
-
Maximum Residue Limit (MRL)
- News: The Food Safety Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) increased the maximum residue limit (MRL) of pesticides in herbs and spices by 10 times.
- Maximum Residue Limit (MRL): Defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) as the highest legally tolerable level of pesticide permitted in food or animal feed.
- Setting of MRLs:
-
-
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) establishes MRLs for pesticides in food and feed crops to ensure food safety and facilitate international trade.
- CAC was established jointly by the FAO and the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1963.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) establishes MRLs for pesticides in food and feed crops to ensure food safety and facilitate international trade.
-
- Objective of MRLs:
-
-
- MRLs are instituted to safeguard consumer health and ensure food safety.
-
- MRLs in India:
-
-
- Specified under the Food Safety and Standards (Contaminants, Toxins and Residues) Regulation, 2011, by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- Determined based on field trial data obtained through the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC) under the Ministry of Agriculture.
-
- Implications of Increasing MRL Limits:
-
- Potential Benefits:
- Enhanced pest control measures may lead to increased agricultural yield.
- Ensures food security by safeguarding crops against pests.
- Potential Benefits:
- Concerns:
-
- Elevated dietary exposure to pesticide residues.
- Overuse of pesticides may contribute to the development of pesticide resistance in pests.
- Possibility of import bans on Indian food items due to elevated pesticide content, affecting international trade relationships.
Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) 2024
- News: It is released annually by the Global Network Against Food Crises (GNAFC).
- Background of the GRFC
-
- Published annually by the Global Network Against Food Crises (GNAFC).
- Established in 2016 as an international alliance to combat food insecurity.
-
- Member Organizations
-
- Includes the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the World Food Programme (WFP), UNICEF, IFPRI, and other governmental and non-governmental organizations.
-
- Highlights of GRFC 2024
-
- Scope of Analysis: Analyzed a population of 1.3 billion across 59 countries in 2023.
- Revealed that nearly 282 million individuals faced high levels of acute food insecurity.
- Scope of Analysis: Analyzed a population of 1.3 billion across 59 countries in 2023.
-
- Trends in Food Insecurity: 2023 marked the fifth consecutive year of escalation in acute food insecurity. Despite varied causes and durations, food deprivation persisted.
- Drivers of Food Crises: Conflict, extreme weather events, and economic shocks identified as primary drivers. Conflict pushed 135 million people in 20 countries into hunger.
-
-
- Extreme weather events impacted over 72 million individuals in 18 countries.
-
-
- Countries Facing Severe Food Crises: Ten most affected countries in 2023:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo, Nigeria, Sudan, Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Yemen, Syrian Arab Republic, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Myanmar.
- These nations urgently require comprehensive intervention strategies to address food insecurity challenges.
