Virtual Reality vs. Augmented Reality vs. Mixed Reality
- Context: When Apple unveiled its Vision Pro in June 2023, it called the device a “revolutionary spatial computer”.
- It also told the developers to call their apps ‘spatial computing apps’ — not augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), or mixed reality (MR) apps.
- But most tech enthusiasts preferred calling it a ‘mixed reality headset’.
Analysis
- Despite having many things in common, virtual, augmented, and mixed reality are not the same.
- Reality can be thought of as a construct that each of us makes based on what we perceive from our senses, whether what we perceive comes from the digital or the physical world.
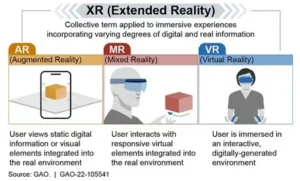
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
- Virtual Reality is a simulated and immersive experience projected by a device into the user’s sight.
- In VR experiences, the physical or real-world environment is entirely blocked out.
- Imagine walking inside the Taj Mahal, while still sitting in your room. This is an example of VR.
- VR experiences are located at the fully virtual extreme of the virtuality continuum.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
- Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that allows the superposition of digital elements into the real-world environment.
- Typically, there is limited to no direct interaction between the digital and physical world components.
- AR experiences are close to the physical world end of the virtuality continuum.
- AR only requires a smartphone with a camera and an AR app. One great example of this in action is IKEA’s recent AR app that allows anyone to imagine how any room or space would feel with some of the brand’s furniture.
Read Also: Planetarydaries Framework: Concept and Significance | UPSC
What is Mixed (Merged) Reality (MR)?
- Mixed reality is a hybrid of VR and AR and aims to offer the best of both worlds.
- Mixed Reality (MR) is a technology that allows not only the superposition of digital elements into the real-world environment but also their interaction.
- Just like VR, MR uses a headset to launch the experience. But mixed reality devices are different from typical VR hardware because they use mounted translucent glasses like Google Glass that let us stay grounded in the real world—the virtual reality is mixed with actual reality.
- Like AR, MR overlays digital content and simulations on top of what we would normally see. But mixed reality experiences let you physically interact with the simulation in ways that AR can’t.
- Instead of depending solely on remote controllers or phone screens, we can interact with the immersive content using natural body and finger gestures.
- Thus, in MR experiences the user can interact with both digital and physical elements. MR differs from AR—where digital and physical elements don’t interact— and VR—where the physical or real world is completely blocked out.
- MR experiences cover the center of the virtuality continuum.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
- Extended reality (XR) is an umbrella term that includes AR, MR, VR, and any technology that blends the physical and the digital world.
References:
- https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/beyond-ar-vs-vr-what-is-the-difference-between-ar-vs-mr-vs-vr-vs-xr#:~:text=Augmented%20reality%20(AR)%3A%20a,a%20fully%2Dimmersive%20digital%20environment.
- https://www.toptal.com/designers/ui/augmented-reality-vs-virtual-reality-vs-mixed-reality
- https://medium.com/predict/mixed-reality-or-spatial-computing-346e62148026
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/apple-should-mind-mixed-realitys-rich-history-in-its-vision-pro-doublethink/article67968358.ece
Practice Questions
- Which of the following statements accurately distinguishes between Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR)?
(a) Virtual Reality completely replaces the user’s physical environment with a simulated one, while Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the real world, and Mixed Reality combines elements of both.
(b) Virtual Reality overlays digital content onto the real world, Augmented Reality immerses users in a simulated environment, and Mixed Reality enhances the user’s perception of reality by blending real and virtual worlds.
(c) Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality are interchangeable terms describing the same technology, whereas Mixed Reality refers to a combination of physical and digital elements in a virtual environment.
(d) Virtual Reality enhances the user’s perception of reality by blending real and virtual worlds, Augmented Reality replaces the user’s physical environment with a simulated one, and Mixed Reality overlays digital content onto the real world.
Answer: a
Explanation:
- Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely simulated environment, where they can interact with digital elements and environments that do not exist in the physical world.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of reality by adding virtual elements to their surroundings.
- Mixed Reality (MR) merges virtual and real environments seamlessly, allowing users to interact with virtual objects while still being aware of and able to interact with the real world.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Relevance: When Apple unveiled its Vision Pro in June 2023, it called the device a “revolutionary spatial computer”. But most tech enthusiasts preferred calling it a ‘mixed reality headset’.
Subject: Current Affairs | Science and Technology
Tags: Factual | Easy Difficulty
- Differentiate between Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality. Also highlight their varied applications across sectors? (Answer in 250 words)
- Despite having many things in common, virtual, augmented, and mixed reality are not the same and thus have varied applications across sectors.
Virtual Reality (VR):
- Virtual Reality immerses users in a simulated environment, typically through a headset or goggles, completely replacing the real world with a digitally created one.
- VR technology blocks out the user’s physical surroundings and transports them to a computer-generated world. Users can interact with this artificial environment as if it were real. In India, VR finds application in various sectors:
- Education: Many among India’s leading online education platforms offer VR modules that provide immersive learning experiences, allowing students to explore complex concepts in science, history, and more.
- Entertainment: VR gaming arcades have gained popularity in Indian cities, offering thrilling immersive gaming experiences that transport players to virtual worlds.
- Training: Indian defense forces utilize VR simulations for military training purposes, providing soldiers with realistic combat scenarios without real-world risks.
Augmented Reality (AR):
- Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of reality.
- Unlike VR, AR does not replace the physical environment but adds virtual elements to it. AR applications in India span various sectors:
- Retail: Lenskart, one of India’s largest online eyewear retailers, offers an AR feature that allows customers to try on glasses virtually using their smartphones, enhancing the online shopping experience.
- Healthcare: Healthcare startup Practo introduced an AR app that enables users to visualize medical conditions in 3D, aiding doctors in explaining diagnoses and treatment plans to patients more effectively.
- Tourism: Google’s AR navigation feature, launched in India, overlays directions and points of interest onto the real world through a smartphone camera, making navigation in unfamiliar places more intuitive for travelers.
Mixed Reality (MR):
- Mixed Reality combines elements of both VR and AR, allowing users to interact with virtual objects while still being aware of and able to interact with the real world. MR applications in India include:
- Manufacturing: Tata Steel employs MR solutions to optimize production processes, enabling engineers to visualize and interact with machinery and data overlays in real-time, enhancing efficiency and safety.
- Architecture: Indian architectural firms like Zaha Hadid Architects utilize MR technology to create immersive virtual models of buildings and urban spaces, facilitating better design visualization and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Marketing: Mahindra uses MR showroom experiences to allow potential car buyers to interact with virtual car models, customize features, and explore interiors, enhancing the marketing and sales process.
- In conclusion, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality offer distinct immersive experiences and have diverse applications across sectors in India, ranging from education and entertainment to healthcare and manufacturing. Each technology brings unique benefits and opportunities for innovation, contributing to the advancement of various industries in the country.

