UPSC GS 1
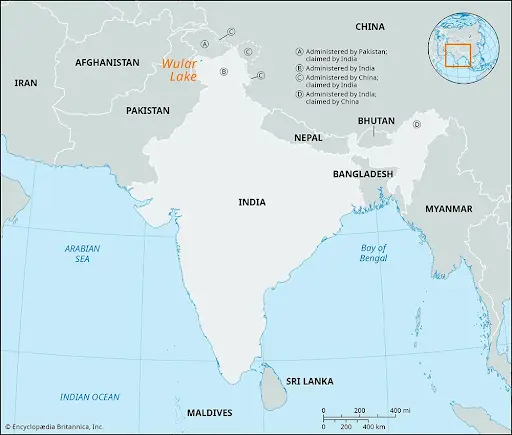
Wular Lake
- News: The Wular lake is slowly choking up due to ingress of silt-laden waters gushing in the form of streams from mountains in its catchments.
- Location and Size:
- Largest freshwater lake in India and the second-largest in Asia.
- Located in Bandipore district, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Spread over 200 sq. km, with a length of 24 km and a breadth of 10 km.
- Situated at an altitude of 1,580 meters on the foothills of Haramuk Mountain.
- Formation:
- The lake basin was formed due to tectonic activity.
- It is believed to be a remnant of the ancient Satisar Lake.
- Feeding River:
- Wular Lake is fed by the Jhelum River.
- Island Feature:
-
-
- The lake has an island at its center called ‘Zaina Lank,’ which was built by King Zainul-Abi-Din.
-
- International Importance:
-
-
- Designated as a Wetland of International Importance under the Ramsar Convention in 1990.
-
- Ecological Significance:
-
-
- An important area for wintering, staging, and breeding birds.
- Notable bird species include the black-eared kite, Eurasian sparrow hawk, short-toed eagle, Himalayan golden eagle, and Himalayan monal.
-
- Fish Habitat:
-
- Wular Lake plays a significant role in fish production, contributing to 60 percent of the total fish output in Jammu and Kashmir.
Classical Language
- News: Centres for promotion of classical Telugu, Odia, Kannada and Malayalam now demand autonomy for proper functioning.
- Criteria for Declaring a Language as Classical in India
- Long Historical Record: The language must have a documented history of at least 1,500-2,000 years in early texts.
- Cultural Heritage: It should have a body of ancient literature that is highly regarded as a cultural heritage by its speakers across generations.
- Original Literary Tradition: The language’s literary tradition should be original and not borrowed from another community.
- Distinct from Modern Forms: The classical language should be distinct from its modern form, often showing a discontinuity between the classical version and later developments or offshoots.
- Recognized Classical Languages in India: India has six classical languages — Tamil, Sanskrit, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, and Odia
- Tamil (2004): First language to be accorded classical status.
- Sanskrit (2005):
- Telugu (2008):
- Kannada (2008):
- Malayalam (2013):
- Odia (2014): Latest language to be recognized.
- Benefits of Classical Language Status:
- Awards for Scholars: Two major international awards are given annually to scholars of eminence in the classical language.
- Centre of Excellence: A Centre of Excellence for Studies in the Classical Language is established.
- University Support: The University Grants Commission (UGC) is requested to create Professional Chairs in Central Universities to promote and study the classical language.
Read also: A List of Major Freedom Fighters of India (1857-1947)
UPSC GS 2
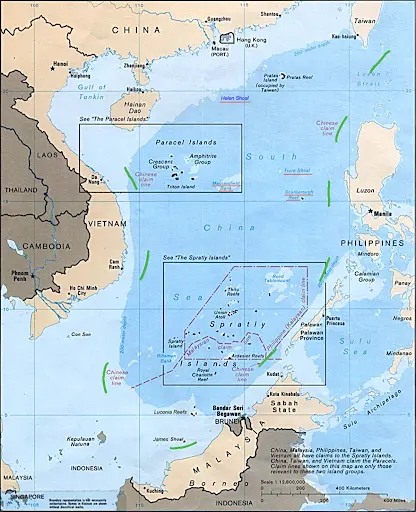
South China Sea Dispute
- News: Recently, the Philippine government accused China of carrying out “repeated aggressive, unprofessional and illegal” actions in the South China Sea.
- South China Sea:
-
- The South China Sea is a marginal sea in western Pacific Ocean that borders the Southeast Asian mainland.
- The South China Sea is situated just south of the Chinese mainland.
- It is bordered by the countries of Brunei, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
- Importance of the South China Sea:
-
- There are 11 billion barrels of oil and 190 trillion cubic feet of natural gas in deposits under the South China Sea.
- Sea is home to rich fishing grounds, a major source of income for millions of people across the region.
- More than half of the world’s fishing vessels operate in this area.
- The main route to and from Pacific and Indian ocean ports is through the Strait of Malacca and the South China Sea.
- As one of the busiest maritime routes in the world, it serves as a vital artery for international trade, facilitating the flow of 64% of total goods discharged worldwide.
- South China Sea trade accounts for 5.72 % of all trade in goods for the United States.
-
- Nine-dash Line:
- The nine-dash line demarcates China’s territorial claims in the sea on Chinese maps.
- It was initially the “eleven-dash line” but in 1953.
- China asserts a claim to 90% of the South China Sea, based on the historical U-shaped nine-dash line drawn on a map in the 1940s and encompassing several islands, esp. the Paracels and Spratlys.
- The line runs 2,000 km from the Chinese mainland to within a few hundred kilometres of the Philippines, Malaysia and Vietnam.
- Marginal Sea:
-
- These are semi-enclosed seas.
- They are partially enclosed bodies of water that are adjacent to larger oceans or major landmasses.
- They have shallower depths, relative isolation from open oceans, and unique hydrographic conditions.
Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB)
- News: Amit Shah has inaugurated NCB’s zonal office in Chhattisgarh’s Raipur.
- Role and Authority:
-
- The NCB is the nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency in India, operating under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It was constituted on 14th November 1985 under the provisions of the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985.

- Key Functions and Powers:
- Coordination: Coordinates actions by various state governments, offices, and authorities under multiple laws such as the NDPS Act, Customs Act, and Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- International Obligations: Implements India’s commitments to international conventions and protocols concerning countermeasures against illicit drug trafficking.
- Global Cooperation: Assists foreign authorities and international organizations to facilitate coordinated action in the prevention and suppression of drug trafficking.
- Inter-Ministry Coordination: Coordinates efforts of various ministries, departments, and organizations related to combating drug abuse.
- Enforcement Role: The NCB functions as an enforcement agency through its zonal offices, which are responsible for:
-
- Collecting and analyzing data on drug seizures.
- Studying trends and modus operandi of drug traffickers.
- Disseminating intelligence and working closely with customs, state police, and other law enforcement agencies.
- Headquarters:
- The NCB’s headquarters is located in Delhi.
UPSC GS 3
Unified Lending Interface (ULI)
- News: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced the upcoming launch of the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) in ‘due course’ to transform the lending ecosystem of India.
- What is ULI?
- ULI is a credit digital public infrastructure (DPI) platform, designed and developed by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH).
- Aim:
- It aims to enable a seamless and consent-based flow of digital information, including land records from various states, from multiple data service providers to lenders.

- Working of ULI:
- Currently, the data needed for credit appraisal is scattered across multiple entities such as governments, banks, account aggregators, and credit information companies.
- However, these data sets are in separate systems, creating hindrance in frictionless and timely delivery of rule-based lending.
- ULI’s architecture addresses this challenge with a plug and play approach that enables quicker access to information from diverse sources.
- The platform will have common and standardised application programming interfaces (APIs) to ensure access to information from diverse sources.
- Benefits:
-
- Facilitate a seamless flow of digital information, including land records of various states, from multiple data service providers to lenders.
- Cater to a large unmet demand for credit particularly for agricultural and medium small and micro enterprises (MSME) borrowers.
- Reduce the turnaround time or TAT for processing and sanctioning loans without requiring extensive documentation.
- Reduce the complexities for the parties involved in the process i.e. lenders and borrowers.
- Importance:
- As per RBI, the ‘new trinity’ of JAM-UPI (Unified Payments Interface)-ULI will be a revolutionary step forward in India’s digital infrastructure journey.
- The JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhar and Mobile) trinity is a tool used by the government to transfer cash benefits directly to the bank account of the beneficiary.
- Just like the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) changed the payments ecosystem, similarly RBI expects ULI to transform the lending landscape of India.
BHISHM Cubes
- News: PM Modi recently presented four BHISHM (Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita & Maitri) Cubes to the Ukrainian government during his historic visit to Kyiv.
- BHISHM Cubes: Overview
- Purpose:
- The BHISHM Cubes are compact, portable medical units designed to provide first-line care in emergency situations, particularly in conflict zones or disaster-stricken areas.
- BHISHM stands for Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita & Maitri, symbolizing India’s spirit of cooperation and friendship.

- Features of BHISHM Cubes
- Medical Capabilities:
-
- BHISHM Cubes are stocked with essential medicines and equipment to handle a wide range of injuries such as trauma, bleeding, burns, and fractures.
- Surgical Capabilities:
- Each Cube is equipped with the tools necessary for a basic Operation Room (OR), capable of performing 10-15 surgeries per day, covering both minor and complex procedures.
- Patient Management:
- A single BHISHM Cube can manage approximately 200 cases, addressing various medical needs where local facilities may be overwhelmed or inaccessible.
- Self-Sufficiency:
- The Cube can generate its own power and produce limited amounts of oxygen, allowing it to operate independently in remote or war-torn areas.
- Ukraine Deployment:
- A team of Indian medical experts has been deployed to Ukraine to provide initial training to local personnel.
- This training is crucial to ensure the effective operation of the BHISHM Cubes and to maximize their life-saving potential in challenging environments.
Alpkarakush Kyrgyzicus
- News: The remains of a dinosaur named Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus were recently unearthed in Kyrgyzstan, marking the first-ever find of a theropod dinosaur in the region.
- Discovery:
- A new species of large theropod dinosaur, Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus, was recently discovered in the Middle Jurassic Balabansai formation in the Fergana Depression, northern Kyrgyzstan.
- Time Period:
- This dinosaur roamed the Earth during the Callovian age of the Jurassic period, approximately 165 to 161 million years ago.

- Size and Physical Traits:
- Estimated body length: 7 to 8 meters.
- Notable feature: A distinct, protruding ‘eyebrow’ on the postorbital bone, suggesting the presence of a horn above the eye.
- Classification:
- Belongs to the Metriacanthosauridae family, a group of medium-to-large allosauroid theropods.
- Characteristics of this family:
- High-arched skulls.
- Elongated, plate-like neural spines.
- Slender hindlimbs.
- Significance:
- This species is the first large Jurassic predatory dinosaur unearthed in the region between central Europe and East Asia.
- Theropods are one of the most prominent groups of dinosaurs, which include well-known predators like Tyrannosaurus, Allosaurus, and modern birds.
Sonoluminescence
- News: Sonoluminescence has been in the news.
- Phenomenon: Sonoluminescence is a unique occurrence where small gas bubbles in a liquid emit brief flashes of light when subjected to intense sound waves. This phenomenon was first discovered in 1934 by two German engineers while studying sonar.
- How Sonoluminescence Works:
- Sound Wave Interaction:
- The process starts when a small bubble in a liquid is trapped by powerful sound waves.
- The bubble alternates between rapid expansion and contraction due to the sound waves’ high and low-pressure phases.
- Extreme Conditions:
- During the contraction phase, the bubble compresses so rapidly that its internal temperature rises to several thousand kelvins.
- The gases inside the bubble become ionized from the heat, resulting in a flash of light energy that lasts for an incredibly short time—about a trillionth of a second.
- Natural Occurrence:
- Pistol Shrimp:
- Sonoluminescence also occurs in nature. The pistol shrimp (family Alpheidae) creates a similar effect with its specialized claw.
- The shrimp snaps its claw shut rapidly, producing a high-velocity water jet that forms a low-pressure bubble.
- When this bubble collapses, it emits a loud sound, intense heat, and a flash of light, akin to the sonoluminescence observed in labs.
- Applications:
- Scientific Curiosity:
- Though the phenomenon remains largely of academic interest, sonoluminescence has captivated scientists due to its mysterious nature and the extreme conditions it produces.
- Potential applications have been discussed in areas like thermonuclear fusion and acoustic imaging, though much research is still ongoing.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
- News: India’s first quantum computer is set for launch under National Quantum Mission.
- Objective:
- After a delay of nearly four years, the National Quantum Mission aims to propel India’s advancements in quantum technologies, specifically across four verticals—quantum computing, communication, measurement, and sensing.
- Funding & Structure:
- Allocated funding: Nearly ₹6,000 crore.
- Establishment of four Section 8 companies under premier institutions like IITs and IISc, which will lead activities in the identified verticals.

- Mission Timeline:
- Launched in 2023, the mission is planned to span eight years (2023-2031) under the leadership of the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Key Focus Areas:
- Quantum Computing:
- Development of intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 physical qubits.
- Platforms utilized: Superconducting and photonic technology.
- Quantum Communication:
- Establishment of satellite-based secure quantum communication networks, covering a range of 2000 km within India and extending to other countries.
- Quantum Measurement and Sensing:
- Development of highly sensitive magnetometers in atomic systems and precision atomic clocks for applications in timing, communications, and navigation.
- Quantum Materials Development:
- Support for the design and synthesis of quantum materials such as superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials to fabricate advanced quantum devices.
- Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs):
- Four T-Hubs will be set up in premier research and academic institutes to foster both fundamental and applied research, and drive research and development (R&D) activities forward.
- Sectors Benefited:
- The mission’s advancements will find applications in diverse sectors such as healthcare, diagnostics, defence, energy, and data security.
- How Quantum Computers Work:
- Qubits and Superposition:
- Quantum computing uses the qubit as the basic unit of information, instead of the conventional bit.
- Qubits allow for the coherent superposition of ones and zeros, enabling quantum computers to perform computations differently from classical computers.
INS Mumbai
- News: Indian Navy’s Destroyer ‘INS Mumbai’ has visited Sri Lanka.
- Commissioning:
- INS Mumbai is the third ship in the Delhi-class of guided missile destroyers, indigenously built and commissioned into the Indian Navy on 22 January 2001.
- Built at Mazagon Dock Limited, Mumbai.
- Awards & Recognition:
-
- INS Mumbai has been adjudged the ‘Best Ship’ thrice and the ‘Most Spirited Ship’ twice, a rare accomplishment for any warship.

- Operational History:
- Op Parakram (2002): Part of the naval operations during heightened tensions between India and Pakistan.
- Op Sukoon (2006): Led the evacuation of Indian, Nepalese, and Sri Lankan citizens from war-torn Lebanon.
- Op Rahat (2015): Played a crucial role in the evacuation of Indian and foreign nationals from Yemen.
- Upgradation & Deployment: After completing a mid-life upgrade, INS Mumbai rejoined the Eastern Naval Command in Visakhapatnam on 8 December 2023.
- Key Features:
- Displacement: Over 6,500 tons.
- Crew: Manned by 350 sailors and 40 officers.
- Dimensions: 163 meters in length and 17 meters at the beam.
- Speed: Powered by four gas turbines, capable of exceeding speeds of 32 knots.
- Armament & Technology: Equipped with state-of-the-art weapons, including Surface-to-Surface Missiles, Surface-to-Air Missiles, Anti-Submarine rockets, and torpedoes. The ship possesses lethal firepower to engage various threats.
- Aviation Capabilities: Operates all types of helicopters in the Indian Navy’s inventory, serving as extended surveillance and reconnaissance platforms.

