Cryogenics
News: The researchers from Imperial College London have developed a new 3D printing technique using cryogenics.
Definition:
-
- Cryogenics is the science of materials at temperatures below negative 153 degrees C.
- Cryogenics deals with thermal conditions in which gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen and the air in our atmosphere are liquid.
Cryogenic Fluids:
-
- Cryogenics uses helium and nitrogen as the cryogenic fluid that cools a substance.
- Nitrogen has a boiling point of negative 196 degrees C, and helium, negative 269 degrees C.
- So below these temperatures, they are liquid.
- Such fluids need to be stored in vacuum flasks or they could leak and damage their surroundings.
Uses of Cryogenics: Many cryogenic materials have desirable properties. For example:
-
- Hydrogen is one of the best rocket fuels but it can only be used as a liquid, so it needs to be cryogenically cooled.
- Cryogenic hydrogen and cryogenic oxygen power the third stage of ISRO’s LVM3 rocket.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices used in medical diagnostics use cryogenic fluids to cool their magnets.
- The new 3D printing technique developed using cryogenics can replicate biological structures which could be used for tissue regeneration and replicate organs.
Tiantong-1 (Chinese Satellite)
News: China has created world’s inaugural satellite called Tiantong-1 that enables smartphones to make direct calls through it, bypassing the need for traditional mobile towers.
Tiantong-1: Chinese scientists have developed the world’s first satellite capable of enabling smartphone calls directly, without the need for ground-based infrastructure.
Expansive Coverage: The Tiantong-1 satellite series includes three satellites in a geosynchronous orbit at 36,000km, covering Asia-Pacific region from Middle East to the Pacific Ocean.
-
- A geosynchronous orbit is a special position high above the Earth that allows an object to keep pace with the rotation our planet.
Huawei’s Smartphone Innovation: Recently, Huawei Technologies introduced the world’s first smartphone capable of satellite calls, complementing the Tiantong-1 satellite’s capabilities.
Technical Challenge of Passive Intermodulation (PIM) Interference: Achieving direct satellite connectivity for mobile phones faced significant technical hurdles, particularly due to passive intermodulation interference.
-
- PIM is a type of signal interference in a wireless system.
- These interfering signals reduce receiver sensitivity to the point of drastically reducing download speeds or even dropping connections.
- Slight increases in PIM can significantly decrease network performance.
- This type of interference has been a problem in traditional satellite communication networks.
- Chinese scientists tackled this challenge by developing new techniques to suppress PIM effects and advanced technology to detect and address interference issues effectively.
Radiation therapy or Radiotherapy
News: The Radiation Therapy facility has been initiated in the Lady Hardinge Medical College.
Definition: Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-ray or other particles to destroy cancer cells.
Types:
- External beam radiation therapy (teletherapy): Machine directs beams of high-energy radiation toward the tumor.
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy): Doctor places an implant containing radiation in or near the cancer site.
Importance: Radiation therapy is highly effective and well-established treatment for brain, breast, head and neck, cervical cancers, etc., while minimizing damage to healthy tissues from high doses of radiation.
Proton Therapy: Proton therapy, also known as proton beam therapy, is a radiation treatment that precisely delivers a beam of protons to disrupt and destroy tumor cells.
| Variables | Radiation therapy | Proton Therapy |
| 1. Applicability
|
not suitable for treatment near sensitive organs like eyes, brain, spine, etc. |
suitable for treatment near sensitive organs like eyes, brain, etc |
| 2. Risk of damaging the nearby healthy cells |
low |
Very low |
| 3.Cost |
Less expensive |
More expensive |
| 4. Side Effects |
Mostly severe, affecting day to day activities |
Less severe and do not interfere with normal functioning. |
Universe Expansion
News: Recent data from James Webb Space Telescope suggests that while the universe continues to expand at an accelerating pace, this expansion rate may have decelerated in comparison to several billion years ago.
Expansion of the Universe:
-
- Origins: The universe began expanding following the Big Bang event approximately 14 billion years ago.
- Potential Outcomes: Continual expansion could result in an open universe, while cessation of expansion due to gravitational forces might lead to collapse, forming a closed universe.
-
-
-
- Alternatively, if the expansion rate decreases over time, the universe could become flat.
-
-
-
Methods of Studying Expansion:
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
-
-
-
-
- Definition: This comprises photons leftover from the Big Bang, known as its afterglow.
- Observational Tools: Instruments like WMAP, BOOMERanG, and ‘Planck’ in space analyze the CMB. Data from these instruments suggest the observable universe is flat within a 0.4% margin of error.
-
-
-
-
Cosmic Distance Ladder:
- Explanation: This encompasses techniques to measure distances to objects near, far, and very distant from Earth.
- Example: Cepheid variable stars serve as important markers.
-
-
-
-
- Cepheids, also called Cepheid Variables, are stars which brighten and dim periodically.
- This behavior allows them to be used as cosmic yardsticks out to distances of a few tens of millions of light-years.
- Their near-infrared radiation, trackable by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), aids in measurements.
-
-
-
-
- These methods have yielded slightly different values for the Hubble constant. This discrepancy is known as the Hubble tension.
Hubble Tension:
- Refers to a discrepancy in measurements of the rate of expansion of the universe, termed the Hubble constant (H0).
- Significance: H0 represents the rate at which galaxies move away from each other due to universal expansion.
Shrinkflation
News: There’s been a noticeable rise in shrinkflation within the Indian FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) industry lately.
Shrinkflation: ‘Shrinkflation’ occurs when companies reduce the size or quantity of a product while keeping the price same.
- This means that the price tag on the product does not change, but the price per unit of weight or volume increases.
- For example, let’s assume that a bar of a 155 grams dishwashing soap costs Rs 10.
-
-
-
- To cope with higher input costs and/or to cut costs, the company will now trim the size of the same product to 140 grams for the same Rs 10 price.
-
-
-
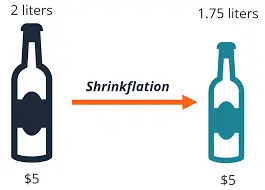
Causes: Retailers often engage in shrinkflation to combat higher production costs.
Impact:
- Shrinkflation is hidden inflation. Instead of increasing the price of a product, producers reduce the size of the product while maintaining the same price.
- It leads to higher frequency of purchases by consumers and reduces their disposable income and purchasing power.
- It also helps producers deal with inflation without impacting demand.
