GS Paper 1
Earth’s Rotation
- News: A recent study published in Nature suggests that global warming-induced melting of polar ice is causing a slowdown in the Earth’s rotation.
- “Rotation” refers to an object’s spinning motion about its own axis. “Revolution” refers the object’s orbital motion around another object.
-
- Earth rotates on its own axis, producing the 24-hour day.
- Earth revolves about the Sun, producing the 365-day year.
- Earth’s Rotation:
- Earth rotates along its axis from west to east.
- It takes approximately 24 hrs to complete on rotation.
- Days and nights occur due to rotation of the earth.
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination.
- Earth rotates on a tilted axis.
- Earth’s rotational axis makes an angle of 23.5° with the normal i.e. it makes an angle of 66.5° with the orbital plane.
- Orbital plane is the plane of earth’s orbit around the Sun.
- Factors Affecting Earth’s Rotation:
-
- Tidal Forces: Gravitational pull from the Moon and the Sun causes tidal bulges, slowing Earth’s rotation due to friction between ocean water and the sea floor.
- Core-Mantle Coupling: Variances in rotation rates between Earth’s inner and outer core impact the magnetic field.
- Glacial Melt: Global warming-induced melting of glaciers and ice sheets redistributes mass, altering Earth’s shape and decelerating its rotation.
Coriolis Force
|
- Earth’s Rotation and Leap Seconds:
-
- Atomic Clocks and UTC: Official time, defined by atomic clocks, is known as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
- Variability in Earth’s Rotation: Earth’s rotation isn’t constant, occasionally slowing due to factors like melting ice caps.
- Leap Second Adjustment: To reconcile discrepancies between atomic time and Earth’s rotation, leap seconds are added or subtracted from UTC.
Climate Engineering and Solar Geoengineering: Types, Techniques and Challenges
GS Paper 2
Sierra Madre
- News: Sierra Madre, an old Philippine ship, is fuelling China-Philippine tensions.
- Definition: It is a 100ft-long landing ship commissioned by the US in 1944 during World War II.
- Landing Ship: Landing ship is specially designed to transport and deploy troops, vehicles, and supplies onto foreign shores for the conduct of offensive military operations.
- Utilization in Conflict:
- It was deployed by the US during the Vietnam War (1954-75).
- It was transferred to the Philippines in 1976.
- Strategic Placement:
- In 1999, this landing ship was left on the Second Thomas Shoal by the Philippines . This move was an attempt at halting further Chinese assertions.
- Second Thomas Shoal is a part of the mostly uninhabited Spratly islands.
- Ongoing Tensions:
- China Demands Removal: China continuously demands the removal of the ship.
- Philippine Resistance: Philippines resists removal to maintain territorial claims and counter Chinese presence in the South China Sea.
- Spratly Islands:
-
- The Spratly Islands consist of more than 100 small islands or reefs in the South China Sea.
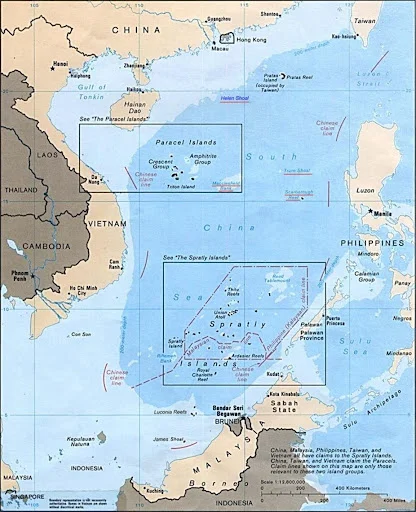
- They are located north of insular Malaysia and are roughly midway between Vietnam and the Philippines.
- These islands are rich in oil and gas reserves along with fishing waters and hence claimed by several countries in the region.
Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance
- News: Recently, the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases and the Global Leaders Group (GLG) on AMR jointly organised a high-level event, ‘Forging partnerships between science and policy’, in Barcelona, Spain.
- Definition:
- The Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR Leaders) consists of world leaders and experts from across sectors working together to accelerate political action on antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- It was established in November 2020.
- Functions:
- Independent Advisory Role: Performs global advisory and advocacy functions independently.
- Promoting Urgency: Maintains urgency, public support, political momentum, and visibility of the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) challenge on the global health and development agenda.
- Approach and Focus:
- One Health Approach: Addresses the AMR challenge by acknowledging the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance:
-
- Definition: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites no longer respond to antimicrobial medicines.
- Public Health Threat: AMR poses a growing threat to public health, as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites develop resistance to drugs intended to combat them.
- Consequences: Resistance renders traditional medicines ineffective, complicating the treatment of even common illnesses.
Coral Reefs: Types, Formation, Threats and Significance | UPSC
UN Panel on Critical Energy Transition Minerals
- News: The United Nations has formed a new panel on “Critical Energy Transition Minerals.”
- Panel’s Aim:
- Development of Global Principles: The panel aims to develop a set of global common and voluntary principles to guide the transition and accelerate the adoption of renewable energies.
- Objectives Aligned with Global Agreements:
- 2030 Agenda and Climate Change Framework: The panel’s objective aligns with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the UN’s Framework Agreement on Climate Change, and its Paris Agreement.
- Twofold Objective:
-
- Just and Equitable Transition: Supporting a fair transition to renewable energies.
- Economic and Social Benefits: Ensuring that countries and local communities benefit economically while upholding social and environmental safeguards.
-
- Composition:
-
- Presently, the panel comprises 23 countries alongside the African Union, with 14 non-governmental organizations representing diverse entities.
-
- Key Members: Both China and the United States are key members of the panel.
- Significance of Critical Energy Transition Minerals:
-
- Vital Components for Clean Energy: Critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements are essential for clean energy technologies like wind turbines, solar panels, electric vehicles, and battery storage.
- Increased Demand: The global transition towards renewable energy to combat carbon emissions has led to a surge in demand for critical minerals, with projections indicating a threefold increase by 2030.
GS Paper 3
Inflation Expectations Survey of Households & Consumer Confidence Survey
- News: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently introduced two new surveys, the ‘Inflation Expectations Survey of Households’ and the ‘Consumer Confidence Survey’.
-
-
- These surveys are aimed at providing crucial insights for the upcoming bi-monthly monetary policy.
-
- Inflation Expectations Survey of Households:
-
-
- This survey will gather subjective evaluations on price movements and inflation based on individual consumption patterns.
- This survey spans 19 cities, including Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Thiruvananthapuram.
- It will gather qualitative responses from households regarding price changes, including general prices and specific product groups, over the next 3 months and one year.
-
- Consumer Confidence Survey:
-
- Aims to gather qualitative responses from households regarding their views on:
- The General Economic Situation,
- Employment Scenario,
- Price Levels,
- Household Income, And
- Spending.
- This survey will also be conducted in 19 cities, including Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, Chandigarh, Chennai, and Delhi.
- Aims to gather qualitative responses from households regarding their views on:
Salmonella
- News: The US has rejected 1/3rd of MDH exports since October over salmonella.
- Definition: Salmonella are a group of bacteria that can cause gastrointestinal illness and fever called salmonellosis.
- Transmission and Contamination:
- Salmonella naturally lives in the intestines of animals and can be found in their feces (poop).
- It can contaminate meat and poultry during slaughter.
- Spread to humans occurs through contact with salmonella-contaminated items in the environment.
- Survival and Resilience:
-
- Ubiquitous Nature: Salmonella is widespread and resilient.
- Environmental Longevity: Can survive for several weeks in dry environments and several months in water.
- Symptoms of Salmonellosis:
-
- Onset and Manifestations: Symptoms typically appear 6 to 72 hours post-infection and include diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
Ethylene (C2H4)
- News: It is being used for artificial ripening of mangoes.
- Nature and Properties: Colourless, flammable gas with a sweet taste and odor.
- Environmental Impact: Acts as a greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming.
- Industrial Importance:
- Chemical Production: Crucial starting material for manufacturing various chemicals, including plastics like polyethylene, polyester fibers, and antifreeze.
- Biological Functions:
- Plant Hormone: Naturally occurring plant hormone involved in physiological processes such as promoting root growth and root hair formation.
- Role in Fruit Ripening: Highly influential in fruit ripening processes, affecting respiration rates and enzymatic activities.
- Effects on Fruit Ripening:
- Color Changes: Influences the synthesis of pigments such as carotenoids (red, orange, and yellow colors ) and anthocyanins (blue or purple colour), leading to color changes during ripening.
- Flavor and Aroma: Stimulates the production of volatile compounds responsible for the flavor and aroma of ripe fruits.
- Regulatory Guidelines:
- FSSAI Directions: Allows the use of ethylene for artificial ripening with a concentration limit of 100 ppm.
- Prohibited Contact: Direct contact of ethylene gas sources with fruits is not permitted according to FSSAI regulations.
IMF’s Stand-by Arrangement (SBA)
-
- News: The IMF Executive Board completed the second review under the Stand-By Arrangement (SBA) for Pakistan.
- Stand-by Arrangement (SBA): The IMF Stand-By Arrangement (SBA) is an economic program of the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Purpose: It provides short-term financial aid to nations grappling with balance of payments issues.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Open to all member countries facing actual or potential external financing requirements, primarily utilized by advanced and emerging market economies.
- Low-income countries may also access the SBA alongside the Standby Credit Facility (SCF).
- Conditionality:
-
- Economic Policy Alignment: Countries seeking SBA funding must align their economic policies to address the underlying issues causing the need for financial assistance.
- Disbursement Criteria: Disbursements are contingent upon the fulfillment of performance targets related to the implementation of suggested structural measures.
- Duration of the Assistance: Typically covers a period of 12–24 months, but not more than 36 months.
Facts for Prelims
Exercise Poorvi Leher
- News: Indian Navy has recently conducted ‘Poorvi Leher’ exercise along east coast to test preparedness.
- Recent Conduct: The Indian Navy executed a Military Exercise called “Poorvi Lehar” along the Eastern Coast of India.
- Objective: The primary goal of the exercise was to evaluate the readiness of the Indian Navy in addressing Maritime Security challenges within the region.
Stridhan
- News: As per a recent ruling of the Supreme Court, a husband has no control over wife’s ‘stridhan’.
- Stridhan:
- Properties gifted to a woman before marriage, at the time of marriage, or upon bidding farewell, and even thereafter constitute her stridhan properties.
- These properties are solely owned by the woman, granting her the full right to dispose of them as she pleases.
- Husband’s Role:
- Lack of Control: The husband holds no authority or control over his wife’s stridhan property.
- Usage in Distress: He may utilize the stridhan property during times of personal distress, but he retains a moral obligation to restore either the property itself or its equivalent value to his wife.
