GS Paper 1
Vallabhacharya
News: The 545th birth anniversary of Mahaprabhu Vallabhacharya has been recently celebrated.
Early Life:
- Vallabhacharya was born into a Brahmin family in Champaran, which is now located in the Raipur district of Chhattisgarh.
- His birth anniversary is observed in India on Krishna Paksha Ekadashi of the Vaishakha month of the Hindu calendar as Vallabhacharya Jayanti.

Role in the Bhakti Movement:
- He emerged as one of the pioneers of the Bhakti movement.
- He was a contemporary of Sri Chaitanya Mahaprabhu, contributing significantly to the revival of devotional practices in Hinduism.
Founding Pushtimarg Sect:
- Vallabhacharya established the Krishna-centered Pushtimarg sect, which translates to “the path towards grace,” within the Vaishnavism tradition.
- He propagated the philosophy of Shuddhadvaita.
Philosophical Tenets:
- Pushtimarga Emphasis: Within Pushtimarg, Vallabhacharya emphasized Bhakti, or devotional love and surrender, as the primary means for devotees to attain salvation, focusing on devotion to Lord Krishna.
- Shuddhadvaita Philosophy: Vallabhacharya’s philosophy of Shuddhadvaita posits pure non-dualis.
- It asserts that the individual soul (atman) is not distinct from the supreme reality (Brahman) but is rather a part of it.
- Unlike Advaita philosophy by Shankaracharya, it rejects the concept of maya (illusion).
Literary Contributions: Vallabhacharya’s significant literary works include
- Anubhashya on Brahma Sutra,
- Subhodhini Vyakhya of Bhagavat,
- Siddhanta-Rahsya,
- Bhagavat Leela Rahasya,
- Ekanta-Rahsya,
Catatumbo Lightning
News: Catatumbo lightning emerges from the convergence of multiple factors, creating the distinct conditions necessary for its occurrence.
Definition: “Catatumbo lightning” is a natural phenomenon specific to the Catatumbo River area at Lake Maracaibo in Venzuela.
- It is named after the Catatumbo River that feeds into the lake.
Location: It occurs over the mouth of the Catatumbo River where it empties into Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela. This area is called as “the lightning capital of the world”.
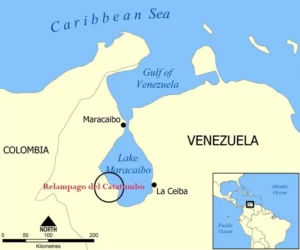
- Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela is the largest lake in Latin America.
- It is also among the oldest water bodies on the planet.
- Its proximity to the Andes Mountains and the Caribbean Sea creates a unique geographical setup that plays a crucial role in the frequency of lightning in the region.
Frequency and Duration: Catatumbo lightning is renowned for its remarkable frequency and duration, with occurrences spanning up to 160 nights annually.
Mechanism of Lightning:
- Catatumbo lightning materializes when warm, moisture-laden air originating from the Caribbean Sea converges with cooler air descending from the Andes mountains.
- This collision of air masses generates towering cumulonimbus clouds, setting the stage for the electrifying display.
- Within these big clouds, vigorous winds and temperature differentials provoke the accumulation of electrical charges.
- When the electrical potential reaches a critical threshold, the stored energy discharges in the form of awe-inspiring lightning bolts.
8 May | UPSC Current Affairs | GS 3: Hopen Island, Drones, Carbon Farming & More
GS Paper 2
Global Biofuel Alliance
News: The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has announced that the Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) has launched a work plan.
Definition: The Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) is a multi-stake holder alliance of Governments, International Organizations and Industries.
Launch: GBA was launched on the sidelines of the 2023 G20 summit in New Delhi,
Aim:
- The alliance is aimed at facilitating international cooperation and intensifying the use of sustainable biofuels.
- It also seeks to facilitate global biofuels trade and technical support for national biofuel programmes.
Members Nations:
- The GBA was spearheaded by India, the United States, and Brazil.
- 9 initiating members–India, the US, Brazil, Argentina, Bangladesh, Italy, Mauritius, South Africa, and the UAE.
- Observer countries: Canada and Singapore.
International Organisations:
- World Bank, Asian Development Bank, World Economic Forum, International Energy Agency, International Energy Forum, International Renewable Energy Agency, and International Civil Aviation Organization have agreed to join the alliance.
Functions: GBA aims to increase biofuel usage by:
- Facilitating capacity-building exercises along the biofuel value chain.
- Providing technical support for national biofuel programs.
- Promoting sharing of policy lessons.
- Advancing biofuel technology.
- Encouraging wider stakeholder participation to enhance the use of sustainable biofuels.
Importance for India:
- The alliance will focus on collaboration and will provide additional opportunities to Indian industries in the form of exporting technology and equipment.
- It will also help accelerate India’s existing biofuels programs such as PM-JIVAN Yojna, SATAT, and GOBARdhan scheme, thereby contributing to increased farmers’ income.
- It will also help in creating jobs and overall development of the Indian ecosystem.
Biofuel:
- Definition: Biofuel is a renewable energy source that is derived from plant, algal, or animal biomass.
- Most biofuels are used as transportation fuels, but they may also be used for heating and electricity generation.
- Global Growth Projection: The International Energy Agency anticipates a remarkable surge in biofuel production by 2050, estimating a 3.5-5 times increase, primarily fueled by global Net-Zero objectives.
- India’s Contribution to Biofuel Procurement:
- In 2022, worldwide biofuel procurement soared to a record-breaking 171.2 billion liters, with India’s share standing at a modest 2.7%, equivalent to 4.6 billion liters.
- Despite this, India maintains its status as the third-largest ethanol producer globally, trailing behind only the United States (US) and Brazil in production volume.
GS Paper 3
India VIX (Volatility Index)
News: India VIX has surged to a 15-month
Volatility Index:
- The Volatility Index measures the market’s anticipation of volatility in the near term.
- During moments of market volatility, the market typically moves sharply up or down, and the VIX tends to climb.
- VIX falls as volatility falls.
- VIX is not the same as a price index like the NIFTY.
- The price index is calculated by taking the price movement of the underlying equities into account.
- The Volatility Index is calculated as an annualized percentage using the order book of the underlying index options.
India VIX:
- India VIX reflects investors’ perceptions of market volatility in the near term, i.e. it portrays market volatility over the next 30 calendar days.
- The higher the India VIX number, the greater the predicted volatility, and vice versa.
- The India VIX is calculated by the NSE from the order book of NIFTY options.
- India VIX mirrors the state of risk among investors.
- When the India VIX is high, the market expects considerable shifts, indicating a volatile time.
- However, if the India VIX is low, it signifies that the market is anticipating minute changes.
FWD 200B
News: India’s First Indigenous Bomber UAV has been unveiled in Bengaluru.
Definition: It is India’s first indigenous bomber UAV aircraft.
Manufacture: FWD-200B is developed by Flying Wedge Defence, one of the pioneers in India’s defence and aerospace technology sector.

Aim:
- To position India as a global drone manufacturing and technology hub.
- Equipping India with the right air defence resources and enhancing national security.
Features:
- It is classified as a MALE Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (medium-altitude, long-endurance).
- FWD-200B is equipped with optical surveillance payloads and integrated with precision air strike capabilities resembling missile-like weapons.
- It has a payload capacity of 100 kgs.
- It operates at a maximum speed of 200 knots (370 kmph) and can stay in the air for 12 to 20 hours straight.
Importance:
- FWD-200B will reduce India’s reliance on costly bomber unmanned aircraft imports and boost the Make in India initiative.
Child Labour in India: Magnitude, Causes, Impacts and Solutions | UPSC
Goldene
News: Researchers have developed Goldene, a single-atom-thick sheet of gold, opening new avenues in nanotechnology.
- Goldene:
- Goldene marks the pioneering achievement as the first free-standing 2D metal.
- It is a mere one atom thick, approximately 100 nanometers thin—about 400 times slimmer than the thinnest commercially available gold leaf.
- Applications:
- Electronics Industry: Goldene’s ultrathin nature promises transformative applications in the electronics industry, enabling the development of next-generation electronic devices with enhanced performance and miniaturization.
- Catalysis and Energy Production: Goldene holds potential in catalytic processes for carbon dioxide conversion, hydrogen production, and water purification, offering efficient and sustainable solutions for addressing environmental and energy challenges.
Sahyadri Tiger Reserve
News: Maharashtra will translocate tigers to Sahyadri reserve.
Location: The Sahyadri Tiger Reserve is located in the Sahyadri Ranges of Western Ghats in Maharashtra.
Formation:
- Established through the amalgamation of the Chandoli National Park and Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary, the reserve was notified to safeguard its rich biodiversity.
Distinctive Landscapes:
- A prominent feature of the reserve is its abundance of barren rocky and lateritic plateaus, locally referred to as “Sadas,” contributing to its unique topography.
Vegetation:
- The reserve has moist evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist and dry deciduous vegetation, providing habitats for diverse flora and fauna.
Faunal Diversity:
- Tigers, leopards, and various lesser cats, alongside predators like wolves, jackals, and wild dogs.
Provision For Translocation:
- Tranquilisation of tigers for translocation is granted under Section 12 of the Wildlife Protection Act. It allows tranquillisation for the following purposes:
- Education, scientific research & scientific management, including translocation to an alternative suitable habitat and population management without killing or poisoning any wild animals;
- Collection of specimens for recognised zoos or museums and similar institutions;
- Derivation, collection or preparation of snake venom for the manufacture of life-saving drugs.
- Prior permission for translocation is required from the Central Government for Schedule I animals and from the State Government for any other wild animal.
Other Tiger Reserves in Maharashtra: Maharashtra is also home to other tiger reserves:
- Melghat Tiger Reserve,
- Bor Tiger Reserve,
- Nawegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve,
- Pench Tiger Reserve,
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve,
Widal Test
News: In India, healthcare providers widely employ the Widal test to diagnose typhoid fever, utilized across both public and private healthcare sectors.
Definition: The Widal blood test is used to diagnose typhoid fever (enteric fever).
- As with other infections, our immune system produces antibodies in the blood against the bacteria, causing enteric fever.
- The Widal test rapidly detects and quantifies these antibodies.
- It’s a point-of-care test and doesn’t need special skills or infrastructure.
| Typhoid
⮚ Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection that is caused by is caused by Salmonella typhiand other related bacteria. ⮚ Typhoid spreads through contaminated food and water. ⮚ Its symptoms are high fever, stomach pain, weakness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation, and a rash. ⮚ Some people, called carriers, may remain symptom-free and shed the bacteria in their stool for several months to years. ⮚ The subsequent treatment usually consists of tablets, typically in urban areas, or injections in rural ones. ⮚ As per the World Health Organisation, 90 lakh people are diagnosed worldwide with typhoid every year and 1.1 lakh die of it. |
Why is the Widal Test Inappropriate for Testing Typhoid in India?
- Single Test Insufficiency:
- A single positive Widal test result doesn’t definitively diagnose typhoid, while a negative result doesn’t rule it out.
- Confirming an active infection requires testing at least two serum samples taken 7-14 days apart, but this is often impractical.
- Baseline Antibody Levels:
- In regions with high and sustained typhoid prevalence, baseline levels of antibodies against the bacteria may already be present in the blood.
- Without knowing these baseline levels, accurately interpreting the test is challenging, especially considering different cut-off values specified by various test kit manufacturers.
- Cross-Reactivity and False Results:
- Reagents used in the Widal test can cross-react with antibodies from infections caused by other pathogens or in individuals vaccinated against typhoid, potentially leading to false positives.
- Additionally, prior antibiotic therapy can influence antibody levels, resulting in false negatives.
- Erroneous Test Results Impacting Burden Assessment:
- The Widal test’s tendency to produce inaccurate results obscures the true burden of typhoid fever in India, hampering effective disease management and prevention efforts.
- Issues Contributing to Test Inaccuracy:
- A lack of awareness of the proper time at which to collect a blood sample, along with a lack of standardisation of kits and poor quality-control compound the problem.
- High Cost of Testing and Treatment:
- Each Widal test typically costs several hundred rupees, placing a financial strain on patients, particularly in resource-constrained settings.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Concerns:
- The irrational use of antibiotics is a major cause of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- Some strains of Salmonella are also resistant to multiple drugs.
- Continued irrational use of the Widal test, which facilitates unnecessary use of antibiotics, will make it more difficult to control this preventable disease.
Way Forward:
- Efforts should be directed towards developing superior point-of-care tests to replace the Widal test, enhancing accuracy and reliability in diagnosing typhoid fever.
- Prioritizing measures to guarantee adequate and safe food and water supplies, along with functional sanitation systems.
- Adopting a ‘hub and spoke’ model in healthcare delivery can optimize resources, with peripheral sites collecting samples and district hospitals and medical colleges serving as hubs for sample processing.
-
- These facilities can also double as research centers to generate regional prevalence and susceptibility data.
-
- The Indian Council for Medical Research should continue to publish annual reports highlighting typhoid bacteria’s resistance patterns, aiding in informed decision-making for treatment protocols.
- Efforts should be made to increase sample testing coverage and reporting to provide comprehensive susceptibility data across different regions.
- Given the presence of symptom-free carriers, continuous environmental surveillance and data-sharing are imperative to effectively monitor and mitigate the spread of typhoid fever.
