UPSC GS 1
Morocco
- News: In a significant move to bolster its defense export capabilities, India is eyeing Morocco as a pivotal gateway to both Africa and Europe.
- Location:
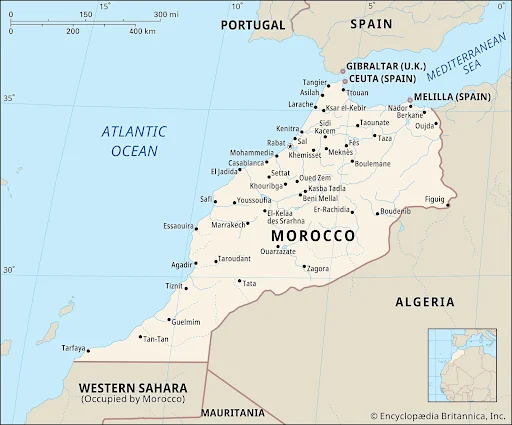
- Morocco is situated in the Maghreb region, spanning the Northern and Western Hemispheres.
- It shares borders with Western Sahara to the south and Algeria to the east.
- The country has coastlines along both the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north, making it the only African nation with coasts on both these water bodies.
- Casablanca, Morocco’s largest city and a major port on the Atlantic Ocean, serves as an industrial and commercial hub.
- Two Spanish enclaves, Ceuta and Melilla, are located on Morocco’s northern coast.
- Climate:
- Northern Morocco, particularly regions north of Western Sahara and along the coasts, experiences a Mediterranean climate.
- This climate is characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
- River:
- The Moulouya River is Morocco’s most prominent water source.
- It originates in the Atlas Mountains and flows into the Mediterranean Sea.
- Highest Point:
- Jebel Toubkal, located in the Atlas Mountains, is Morocco’s highest peak and the tallest point in the region.
- Political System:
- Morocco operates as a constitutional monarchy with a bicameral legislative system.
- Economy:
- The country’s economy is largely dependent on the export of raw materials.
- Language:
- Arabic and Tamazight (Berber) are the official languages of Morocco.
- Arabic is spoken by approximately two-thirds of the population.
- Capital City: Rabat serves as the capital of Morocco.
Read also: Inland Waterways in India – Key for UPSC Preparation
Kerch Strait
- News: A Russian oil tanker carrying thousands of tonnes of oil products split apart recently during a heavy storm spilling oil into the Kerch Strait.
- Geographical Location:
-
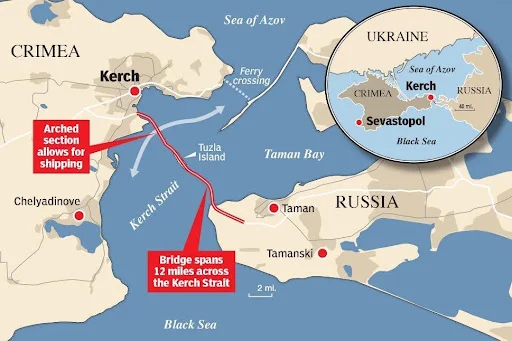
- The Kerch Strait is situated in Eastern Europe and serves as the sole waterway connecting the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov.
- It separates the Kerch Peninsula (part of the Russian-occupied Crimean Peninsula) on the west from the Taman Peninsula in Russia, located to the east.
- Historical Names:
- The strait was referred to as the Strait of Cimmerian Bosphorus during the Roman era.
- In Greek, it was known as the Cimmerian Strait.
- Physical Features:
- The Kerch Strait is approximately 3 km long, 15 km wide, and has a depth of 18 meters.
- Its narrowest point, located at the northern end of the Chushka Landspit, is only 3 to 5 kilometers wide.
- The city of Kerch, situated on the Crimean side, lies near the midpoint of the strait.
- Significance:
- It is a critical global shipping route, enabling the movement of vessels between the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea.
- The strait has been a focal point of geopolitical conflict, particularly between Russia and Ukraine, following Moscow’s annexation of Crimea in 2014.
- Kerch Strait Bridge:
- The Kerch Strait Bridge, also called the Crimean Bridge, connects mainland Russia with the Crimean Peninsula.
- Completed in 2018, it comprises both road and rail links, stretching 19 kilometers, making it the longest bridge in Europe.
- The bridge stands as a prominent symbol of Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and underscores the strategic and political significance of the region.
UPSC GS 2
CHARAK
- News: Under the guidance of the Ministry of Coal, Singrauli based Coal India arm Northern Coalfields Limited (NCL) has rolled out ‘CHARAK’- “Community Health: A Responsive Action for Koylanchal”, an innovative health-centric CSR Initiative.
- Definition:
-
- The CHARAK Initiative, which stands for Community Health: A Responsive Action for Koylanchal, is an innovative health-focused Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) project.
- It is dedicated to providing free medical treatment to patients from economically weaker sections in the Singrauli region who are suffering from identified life-threatening diseases.

- Scope of Treatment:
-
- The initiative offers free treatment for specified life-threatening diseases.
- Treatment is available at the dedicated hospital (NSC) or specialized empanelled hospitals across the country.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Residents of Singrauli and Sonbhadra districts are eligible.
- Families with an annual income of less than Rs. 8 lakhs from all sources can avail of the benefits under this scheme.
- Diseases Covered The scheme addresses a wide range of serious health conditions, including:
- Malignancy.
- Tuberculosis (TB) and related complications.
- HIV and associated complications.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Organ transplant.
- Burns with contractures resulting in permanent disability.
- Liver disorders.
- Sudden hearing loss.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).
- Acute surgical emergencies.
- Neurological and neurovascular disorders.
- Accidental trauma.
- Serious handicaps.
- Multisystem disorders.
- Connective tissue disorders.
- Sudden vision loss.
- Impact: The CHARAK Initiative exemplifies the role of CSR in addressing critical healthcare challenges and improving access to quality medical treatment for vulnerable populations.
UPSC GS 3
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)
- News: The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and New & Renewable Energy recently launched the Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF).
- Objective: The scheme aims to provide credit facilities to small farmers, helping them avoid distress sales by offering financial assistance post-harvest.

- Corpus: A fund of Rs. 1,000 crore has been allocated for financing farmers who pledge their commodities through electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs) issued by Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA)-accredited warehouses.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.
- Implemented by: Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA).
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural loans up to Rs. 75 lakhs.
- Non-agricultural loans up to Rs. 200 lakhs.
- Eligible Institutions:
- Scheduled banks.
- Cooperative banks.
- Eligible Beneficiaries:
- Small and marginal farmers (SMFs).
- Women farmers.
- SC/ST/PwD farmers.
- Other farmers, MSMEs, traders, farmer producer organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Risks Covered:
- Credit risk.
- Warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- 85% guarantee for loans up to Rs. 3 lakhs for small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST, and PwD borrowers.
- 80% guarantee for loans between Rs. 3 lakhs and Rs. 75 lakhs for the same category of borrowers.
- 75% guarantee for loans availed by other eligible beneficiaries.
- Impact:
- The scheme is expected to enhance access to post-harvest finance, especially for small farmers, improving their economic stability.
- By boosting lending against e-NWRs, the scheme will play a critical role in increasing farmers’ incomes and supporting economic growth.
INS Nirdeshak
- News: The Indian Navy is all set to commission its latest survey ship, Nirdeshak, at Naval Dockyard, Visakhapatnam soon.
- Definition: INS Nirdeshak is the second ship under the Survey Vessel (Large) Project of the Indian Navy. Its primary roles include conducting hydrographic surveys, aiding navigation, and supporting various maritime operations.

- Design and Construction:
- The vessel has been constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Reflecting the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India), over 80% of its components are indigenous.
- Legacy:
- INS Nirdeshak is a modern reincarnation of its predecessor, the erstwhile INS Nirdeshak, which served the Navy with distinction for 32 years before being decommissioned on December 19, 2014.
- The name ‘Nirdeshak’, meaning ‘Pathfinder’, highlights its mission to chart maritime territories with precision.
- Key Specifications:
- Displacement: Approximately 3400–3800 tons.
- Length: 110 meters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding speeds of 18 knots.
- Endurance: Designed to remain operational at sea for over 25 days.
- Propulsion System:
- Powered by two marine diesel engines.
- Features fixed-pitch propellers for efficient propulsion.
- Construction Technology:
- Built using ‘Integrated Construction’ technology, ensuring efficiency and durability.
- Adheres to the high standards of the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS).
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: INS Nirdeshak is outfitted with advanced systems for accurate underwater mapping and navigation:
-
- Hydrographic Data Acquisition and Processing Systems for real-time data analysis.
- Advanced Satellite-Based Navigation and Communication Systems for seamless coordination.
- Sub-surface Sensors for detailed mapping of underwater terrain.
- Deployment capabilities for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs).
- These sophisticated systems ensure the vessel can conduct high-precision hydrographic surveys, making it an indispensable asset for the Indian Navy.
SLINEX 2024
- News: The bilateral naval exercise SLINEX 2024 (Sri Lanka–India Exercise) will be conducted from 17 to 20 Dec 24 at Visakhapatnam under the aegis of the Eastern Naval Command.
- Definition:
-
- SLINEX is a bilateral naval exercise between India and Sri Lanka aimed at fostering maritime cooperation.
- First introduced in 2005, this series of exercises has significantly strengthened the naval partnership between the two nations.
- The 2024 edition is focused on reinforcing the strong maritime ties while ensuring a safe, secure, and rules-based maritime environment.

- Structure of the 2024 Edition: The exercise will be conducted in two distinct phases:
- Harbour Phase: Activities include professional exchanges and social interactions to enhance mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Sea Phase: This phase will joint exercises, including Special Forces operations, gun firings, communication drills, seamanship practices, navigation evolutions, and helicopter operations.
- Participating Units:
- Indian Navy: INS Sumitra, a Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel from the Eastern Fleet.
- Sri Lankan Navy: SLNS Sayura, an Offshore Patrol Vessel.
- Key Highlights and Scope Expansion: SLINEX has progressively expanded in scope, allowing both navies to:
-
- Enhance interoperability through realistic and complex drills.
- Exchange best practices in naval operations and maritime security.
- By integrating professional expertise and fostering camaraderie, SLINEX continues to play a pivotal role in the India-Sri Lanka defense partnership.
First Diabetes Biobank
- News: India has inaugurated its first diabetes biobank in Chennai. It will help advance research on diabetes among the Indian population.
- Key Features of the Biobank:
-
- The diabetes biobank serves as a repository for biological samples from diverse populations to facilitate scientific research.
- Its primary functions include collecting, processing, storing, and distributing biospecimens to support ongoing and future studies.
- The biobank houses blood samples related to various types of diabetes, including Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
- Understanding Diabetes:
- Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas cannot produce insulin or when the body is unable to use insulin effectively.
- Insulin is a vital hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels.
- An inability to produce or utilize insulin properly leads to high blood glucose levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia.
- Prolonged hyperglycemia can cause severe damage to various organs and tissues, contributing to critical health conditions.
- Diabetes is a major contributor to health complications such as blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputations.
- Epidemiological Study on Diabetes in India:
- Between 2008 and 2020, a large-scale study was conducted, sampling 1.2 lakh individuals across India.
- The study included 33,537 participants from urban areas and 79,506 from rural areas across 31 states and Union Territories.
- Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- An autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- This leads to the production of little or no insulin.
- Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require daily insulin administration to manage their blood glucose levels.
- The condition is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults and was previously referred to as juvenile diabetes.
- Common symptoms include:
- Excessive urination (polyuria)
- Extreme thirst (polydipsia)
- Constant hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Vision changes
- Fatigue
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- Caused by the body’s ineffective use of insulin, even though insulin production might still occur.
- Accounts for over 95% of diabetes cases globally.
- Key contributors include excess body weight and physical inactivity.
- Symptoms are generally less severe compared to Type 1, often resulting in delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Gestational Diabetes (GDM):
- Refers to elevated blood glucose levels that develop during pregnancy.
- GDM can cause complications for both the mother and the child.
- In most cases, it resolves after childbirth, but women with GDM and their children are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Hydroxymethanesulphonate
- News: Scientists have found aerosol particles that exist in a supercooled state during very cold winters allow the formation of hydroxymethanesulphonate.
- Definition:
- Hydroxymethanesulphonate (HMS) is classified as a secondary aerosol formed through specific chemical reactions.
- Its formation involves the interaction of formaldehyde and sulfur dioxide (SO₂) in the presence of liquid water.

- Role of Liquid Water:
-
- Liquid water within aerosol particles is a key requirement for HMS formation.
- Even under extremely cold temperatures, liquid water can exist in a supercooled state within aerosol particles, allowing the chemical reaction to occur.
- Environmental Conditions Favoring HMS Formation:
- Low Temperatures: Lower temperatures reduce the volatilization of ammonium, thereby decreasing aerosol acidity. This stabilization of sulfite ions promotes HMS formation.
- High Ammonium Ion Concentrations: Elevated ammonium levels help neutralize acidity within aerosols, creating optimal conditions for HMS formation.
- Supercooled Liquid Water: The presence of liquid water in a supercooled state enables the reaction to proceed even at sub-zero temperatures.
- Impact on Health and Environment:
- Air Quality: HMS contributes to secondary aerosol formation, which increases PM2.5 levels in the atmosphere. These fine particles degrade air quality, particularly in cold urban regions such as Fairbanks, Alaska.
- Climate Impact: HMS influences cloud formation and the radiative properties of aerosols, thereby playing a role in climate regulation and processes.
- Health Concerns: The rise in PM2.5 levels due to HMS exacerbates respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. This impact is particularly severe in areas already burdened by high levels of air pollution.
Little Bunting
- News: A little bunting bird, never before seen in Rajasthan, has been spotted in Mount Abu by birdwatcher Sahil Zutshi.
- Taxonomy:
- The Little Bunting is a passerine bird that belongs to the bunting family, Emberizidae.
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla

- Distribution:
- This bird breeds across the taiga regions, spanning the far northeast of Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East.
- It is a migratory species, wintering in the subtropical regions of northern India, southern China, and northern parts of Southeast Asia.
- Physical Features:
- The Little Bunting is a small bird, measuring about 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches) in length.
- Its underparts are white with distinct dark streaks on the breast and sides.
- The bird is characterized by a chestnut-colored face, a white malar stripe, and black crown stripes.
- It has a white eye-ring and a fine dark border outlining its chestnut cheeks, giving it a resemblance to a small female reed bunting.
- Males and females look similar in appearance.
- Vocalization:
- The bird’s call is a distinctive “zik,” while its song is a melodious rolling sequence: “siroo-sir-sir-siroo.”
- Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Little Bunting is classified as a species of Least Concern.

