GS Paper 3
Hopen Island
News: Hopen Islands have reported the first instance of a walrus succumbing to avian influenza, marking a concerning development in the spread of the disease.
Location and Geography: Hopen Island is situated in the southeastern part of the Svalbard archipelago, falling within Norway’s territory.
- The island primarily consists of rocky terrain and continuous permafrost, with a narrow beach encircling its perimeter.
Fauna:
- Hopen Island harbors a significant population of polar bears, particularly during the winter months when the surrounding waters freeze into sea ice.
- These bears rely on the sea ice for hunting seals, a crucial food source in their diet.
- The sub-population of Ursus maritimus (polar bears) found on Hopen Island exhibits genetic distinctiveness.
- This genetic variation is closely associated with the Barents Sea region, reflecting adaptations to local environmental conditions.
- Among the birds that breed here are black-legged kittiwakes, thick-billed guillemots, and black guillemots.

Walnus:
- Pinniped Mammals: Walruses belong to the Pinniped family, along with seals and sea lions.
- Distinctive Features: They are recognized by their large size and prominent tusks. Their skin is covered with a sparse layer of coarse hairs.
- Adaptation to Terrestrial and Marine Environments: Walruses possess the ability to both swim in the ocean and move on land and sea ice.
- Diet and Habitat: Their diet primarily consists of mollusks, but they also consume worms, snails, soft-shell crabs, shrimp, and sea cucumbers.
- Habitat Range: They inhabit Arctic and sub-Arctic regions near the North Pole, including the Pacific, Atlantic, and Arctic Oceans.
- Current Threats: The primary threat to walruses is climate change, which affects their habitat and food sources.
- Conservation Status: According to the IUCN Red List, walruses are classified as Vulnerable.
- Keystone Species: Walruses play a crucial role as keystone species in Arctic marine ecosystems, influencing the balance and health of their habitats.
Avian Influenza:
- Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian (bird) influenza (flu) Type A viruses.
- These viruses naturally spread among wild aquatic birds worldwide and can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species.
- Bird flu viruses do not normally infect humans. However, sporadic human infections with bird flu viruses have occurred.
Nifty Non-Cyclical Consumer Index Fund
News: Groww Mutual Fund has launched India’s first non-cyclical index fund.
Definition: This is an open-ended equity scheme following a non-cyclical consumer theme.
Investment Strategy:
- Long-Term Capital Growth: The mutual fund is structured to facilitate long-term capital growth by investing in securities from the Nifty Non-Cyclical Consumer Index (TRI).
Unique Offering:
- First of Its Kind in India: It stands as India’s inaugural index fund allowing investors to access prominent stocks within consumer industries like FMCG and Textiles.
Index Composition and Objective:
- Index Focus: The fund aims to achieve its objectives by investing in the Nifty Non-Cyclical Consumer Index (TRI), which comprises 30 companies.
- Defensive Stocks: Non-cyclical stocks, also referred to as defensive stocks, are included in this index, providing stability during market downturns.
Characteristics of Non-Cyclical Stocks:
- Steady Demand: Non-cyclical stocks maintain a stable demand as they provide essential goods and services such as food, water, and utilities.
- Insulation from Cyclical Fluctuations: Their demand remains unaffected by cyclical economic shifts, contributing to their reliability as investments.
MQ-9B Predator Drones
News: The US has approved a potential sale of 31 MQ-9B Predator drones to India.
Overview of MQ-9B Predator Drones
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV): The MQ-9B Predator drone is a versatile UAV capable of both remote-controlled and autonomous flight operations.
-
- It’s a variant of the MQ-9 “Reaper” series.
-
Features:
- Hunter-Killer UAV: Developed by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI), the MQ-9B is the first hunter-killer UAV designed for prolonged surveillance at high altitudes.
- Custom Sensor Integration: It features integrated signals and communications intelligence systems and can be equipped with various custom sensors tailored to mission requirements.
- SkyGuardian and SeaGuardian: The MQ-9B comes in two versions: SkyGuardian and SeaGuardian.
- Extended Endurance: Capable of remaining airborne for approximately 35 hours, it boasts extended operational durations.
- Automatic Operations: The drone facilitates automatic take-offs and landings, making it easier to deploy and retrieve.
- Integration into Civil Airspace: It seamlessly integrates into civil airspace, enhancing situational awareness for both military and civil authorities, particularly in maritime environments.
- Carrying Capacity and Fuel Capacity: With a carrying capacity of up to 5,670 kg and a fuel capacity of 2,721 kg, the MQ-9B Predator drones boast substantial operational capabilities.
Importance:
- Role at Borders: These UAVs play a vital role in border security by providing real-time reconnaissance, target acquisition, and tracking capabilities through high-quality video feeds.
- Precision Strike Capability: Equipped with precision strike missiles, the MQ-9B enhances capabilities in surveillance, warfare, electronic warfare, and expeditionary missions.
- Operational Support: Additionally, they support armed forces by efficiently transporting essential supplies, enhancing security, and operational efficiency.
Drip Pricing
News: The Center has recently alerted the public about the practice of “drip pricing,” emphasizing its tendency to unexpectedly reveal hidden charges to consumers.
Definition: It is a marketing tactic where only a portion of a product or service’s total cost is initially disclosed, with the full price revealed progressively as the consumer proceeds through the purchase process.
Implementation Strategy:
- Concealing Essential Fees: This strategy often involves hiding crucial fees such as taxes or booking charges, or omitting necessary add-ons like internet access or essential amenities.
- “Headline Price” Misrepresentation: The advertised price in print, emails, or on websites, referred to as the “headline price,” may not accurately reflect the final cost that consumers will incur.
Motivation for Businesses:
- Attracting Customers with Lower Initial Prices: Companies employ drip pricing to entice customers by starting with a lower advertised price, with the hope that they will proceed with the purchase despite additional costs revealed later.
Impact on Consumer Behavior:
- Challenge in Price Comparison: Drip pricing complicates the process of comparing prices for consumers, making it harder for them to make informed decisions.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Sellers who offer more transparent pricing may find themselves at a disadvantage compared to those engaging in drip pricing tactics.
Carbon Farming
News: Carbon Farming is fundamental to life on earth and plays a crucial role in various processes.
Definition: Carbon farming is an agricultural technique that integrates carbon capture and storage management into farming practices.
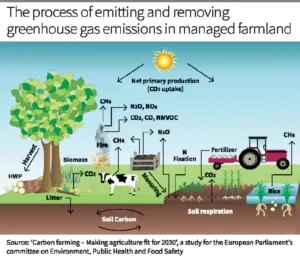
Objectives: The primary goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance soil carbon content, and improve agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
Tailored Practices: Carbon farming employs diverse strategies customized to fit various agricultural landscapes and climatic conditions, ensuring versatility and broad applicability.
Benefits:
- Rotational Grazing: Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration: Rotating livestock across pastures helps maintain soil health and increases carbon sequestration in the soil.
- Agroforestry Practices:
- Silvopasture: Integrating trees, pasture, and livestock enhances carbon sequestration and diversifies farm income.
- Alley Cropping: Planting rows of trees or shrubs between crops provides shade, reduces erosion, and enhances carbon storage.
- Conservation Agriculture:
- Zero Tillage: Reducing soil disturbance maintains soil structure and organic content.
- Crop Rotation and Cover Cropping: Alternating crops and using cover crops improve soil health and biodiversity.
- Crop Residue Management: Practices like stubble retention and composting enhance soil organic matter.
- Integrated Nutrient Management:
- Organic Fertilizers and Compost: Promotes soil fertility and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Agro-Ecological Approaches:
- Crop Diversification and Intercropping: Improves ecosystem resilience, aids in pest control, and balances nutrient levels.
- Livestock Management:
- Methane Reduction and Carbon Storage: Optimizing feed quality, managing animal waste, and rotational grazing reduce methane emissions and increase carbon storage.
- Additional Carbon Sinks Management:
- ‘4 per 1000’ Initiative: Emphasizes the role of additional carbon sinks in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting carbon farming’s potential in effective carbon sequestration.
Challenges of Carbon Farming:
- Geographical and Climatic Limitations: Optimal carbon sequestration requires suitable conditions, posing challenges in hot, dry regions with water scarcity.
- Soil and Biodiversity Constraints: Hindered carbon sequestration due to inadequate soil quality and biodiversity.
- Arid Region Constraints: Water scarcity limits plant growth, impacting carbon sequestration and impracticality of water-intensive practices.
- Economic and Financial Barriers: Adoption costs may deter small-scale and resource-poor farmers from embracing carbon farming.
Policy Support and Community Engagement: Robust policy support and community engagement are essential for effective adoption and scalability of carbon farming practices.
Swing Trading
News: Swing trading is a strategy that capitalizes on market volatility to generate profits.
Definition: Swing trading is a style of trading where investors keep their positions for longer than a single day, typically holding onto stocks for several days or weeks.
Aim:
- The primary goal of swing trading is to profit from short- to medium-term fluctuations in stock prices.
- Traders aim to enter and exit positions quickly, typically holding stocks for 2 days to a few weeks.
- Swing traders capitalise on both upward and downward movements in the market, seeking to take advantage of trends and momentum.
Woking of Swing Trading:
- A swing trader will look for stocks with high volume (a lot of trading activity) and volatility (price movement).
- They select stocks based on fundamental analysis and technical indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) to understand historical performance and potential future movements.
- The entry into a swing trade involves setting up stop-loss orders (to limit potential losses) and target prices (to capture profits) based on support and resistance levels.
- Swing traders buy at support (lower price level) and sell at resistance (higher price level) anticipating the stock’s price to swing back and forth within these bounds.
Benefits:
- Less Time-Consuming: Swing trading provides traders with the flexibility to participate in the market while requiring less time commitment compared to day trading.
- Short- to Medium-Term Gains: Traders can capitalize on short- to medium-term opportunities, allowing them to benefit from market fluctuations without the need for constant monitoring.
- Swift Position Adjustments: Traders can adjust their positions promptly in response to changing market conditions, offering agility in decision-making.
Challenges:
- Requirement for Insight: Swing trading demands a thorough grasp of market dynamics, encompassing technical analysis and market sentiment.
- Potential Long-Term Opportunity Oversights: Traders risk missing out on long-term investment prospects while concentrating on short- to medium-term gains.
C295 Transport Aircraft
News: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has taken delivery of second C295 transport aircraft.
Next-Generation Tactical Airlifter: The C295 is a modern tactical airlifter designed to operate in the light and medium segments, offering versatility in various missions.
Manufacturer: Manufactured by Airbus, a prominent European multinational aerospace corporation known for its innovative aircraft designs.
Features:
- Versatile Mission Capabilities: Tailored for a wide range of missions including troop and cargo transport, maritime patrol, surveillance, reconnaissance, signals intelligence, medical evacuation, air-to-air refueling, VIP transport, and airborne firefighting.
- Flight Endurance and Payload Capacity: Boasting a flight endurance of up to 13 hours, the C295 can carry payloads of up to nine tonnes, enhancing its operational efficiency.
- All-Weather Functionality: Capable of operating under diverse weather conditions, ensuring reliability in various environments.
- Rear Ramp Door: Equipped with a rear ramp door for swift deployment and paradropping of troops and cargo, facilitating quick reaction in critical situations.
Acquisition by India:
- India finalized the acquisition of 56 C295 aircraft to replace the legacy Avro fleet of the Indian Air Force (IAF) at a cost of Rs 21,935 crore.
- Airbus will deliver the initial 16 aircraft in ‘fly-away’ condition by 2025, while the remaining 40 aircraft will be manufactured and assembled by Tata Advanced Systems (TASL) in India, establishing an industrial partnership.
Artificial General Intelligence
News: During a recent interview, the CEO of OpenAI, reaffirmed his dedication to allocating substantial financial resources towards advancing the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Definition: AGI refers to a machine or software capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can do.
- This includes reasoning, common sense, abstract thinking, background knowledge, transfer learning, and the ability to differentiate between cause and effect.
Objective: AGI aims to replicate human cognitive capabilities, allowing it to tackle unfamiliar tasks, learn from new experiences, and apply its knowledge in novel ways.
Distinction from Narrow AI (Artificial Intelligence) :
- Scope and Capabilities: Narrow AI, prevalent in current applications, is designed to perform specific tasks such as image recognition, translation, or playing games like chess.
- While Narrow AI excels within its predefined parameters, AGI aspires to achieve a broader, more generalized form of intelligence, resembling the versatility of human cognition. For example:
- Healthcare Revolution: AGI could transform healthcare by redefining diagnostics, treatment planning, and personalized medicine through comprehensive data analysis.
- Finance and Business Enhancement: In finance and business, AGI has the potential to automate tasks and improve decision-making by providing real-time analytics and precise market predictions.
