UPSC GS 1
Cyclone Remal
- News: Cyclone Remal has hit West Bengal, causing destruction.
- Name Origin: The name ‘Remal’ was given by Oman and means ‘sand’ in Arabic.
- Origin: The cyclone originated in the Bay of Bengal (BoB).
- Factors Contributing to the Formation of Cyclone Remal:
-
- Depression Formation: A depression, characterized by circulating winds and atmospheric instability, formed over the central Bay of Bengal, serving as the genesis of Cyclone Remal.
- Warmer Water Temperatures: The Bay of Bengal experienced water temperatures 2–3°C warmer than average, providing the energy needed for cyclones to form and intensify.
- Madden Julian Oscillation: This band of clouds moving eastward, along with the winds and warm ocean waters south of the Bay of Bengal, played a role in initiating the cyclone due to their rotational effect.
- Geographical Amplification: The shallow bathymetry and funnel-shaped geography of the northern Bay of Bengal amplified the intensity of the cyclone as it approached the coast.
-
- Previous Cyclones: Cyclones such as Yaas (2021), Amphan (2020), Fani (2019), and Aila (2009) have previously caused massive damage in the Sundarbans and other parts of West Bengal.
- How are Cyclones Named?
-
- Global Naming Authorities: Cyclones that form in every ocean basin across the world are named by the regional specialised meteorological centres (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs).
-
- There are six RSMCs in the world, including the India Meteorological Department (IMD), and five TCWCs.
-
- Role of India Meteorological Department (IMD):
-
- IMD as an RSMC: The IMD names cyclones developing over the north Indian Ocean, including the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, following a standard procedure.
- Advisory Role: The IMD is also mandated to issue advisories to 12 other countries in the region on the development of cyclones and storms.
-
- Global Naming Authorities: Cyclones that form in every ocean basin across the world are named by the regional specialised meteorological centres (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs).
-
- History and Procedure of Naming Cyclones in the North Indian Ocean:
-
-
-
- Initiative by WMO/ESCAP: In 2000, a group of nations under the WMO/ESCAP (World Meteorological Organisation/United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific), comprising Bangladesh, India, the Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, decided to start naming cyclones in the region.
- Finalization of Names: After each country sent in suggestions, the WMO/ESCAP Panel on Tropical Cyclones (PTC) finalized the list of names.
-
-
-
Kharkiv and Kyiv Region
- News: Russia has launched a ground offensive into Ukraine’s Kharkiv region.
- Location of Kharkiv City:
-
- Geographical Position: Kharkiv city is situated in northeastern Ukraine.
- River Confluence: It lies at the confluence of the Uda, Lopan, and Kharkiv rivers.
-
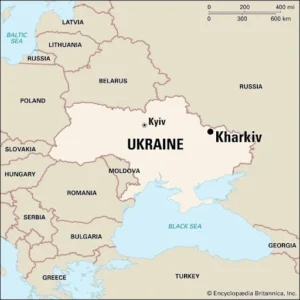
- Location of Kyiv, the Capital:
-
- Capital City: Kyiv serves as the capital of Ukraine.
- Geographical Position: It is located on the Dnieper River in north-central Ukraine.
-
Mount Ibu
- News: Indonesia’s Mount Ibu erupted again, sending ash 4 km high, as streaks of purple lightning flashed around its crater.
- Location and Characteristics:
-
- Geographical Position: Mount Ibu is situated on the northwest coast of Halmahera island, Indonesia.
- Elevation: Rising to 1,377 meters above sea level, it is a prominent stratovolcano.
- Dimensions: The volcano spans 16 km from east to west and 13 km from north to south.
-
- Activity and Status:
-
- Volcanic Activity: Mount Ibu is among Indonesia’s most active volcanoes, consistently experiencing frequent eruptions.
- Eruption Records: In 2023, Mount Ibu recorded a total of 21,100 eruptions, highlighting its significant volcanic activity and making it the second most active volcano in Indonesia.
-
- Stratovolcano: Stratovolcano, volcanic landform characterized by a conical shape formed by layers of volcanic material deposited during successive volcanic eruptions.
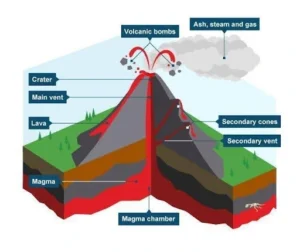
-
-
- Stratovolcanoes tend to slope gently at the base but rise quickly near the summit to form tall mountain peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
-
UPSC GS 2
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
- News: Byju’s faces another setback as the Bengaluru National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) deferred the hearing of the “oppression and mismanagement plea” filed by investors.
- Overview of the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT):
- Establishment: The NCLT is a quasi-judicial body established under the Companies Act, 2013 in 2016.
- Recommendation: It was formed based on the recommendation of the Balakrishna Eradi committee on laws relating to the insolvency and winding up of companies.
- Functions of the NCLT:
-
- Corporate Disputes: Resolves civil corporate disputes arising under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Case Hearings: Empowered to hear and decide on cases related to mergers and acquisitions, oppression and mismanagement, winding up of companies, and other corporate law matters.
- Insolvency Resolution: Acts as an adjudicating authority for the insolvency resolution process of companies and Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
-
- This process aims to revive financially distressed companies or ensure their orderly liquidation.
-
-
- Centralization and Streamlining: The NCLT centralizes and streamlines the process by merging the jurisdictions of:
-
- The Company Law Board (CLB): Handled company-related matters before the NCLT.
- The Board for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR): Dealt with sick and financially distressed industries.
- The Appellate Authority for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (AAIFR): Handled appeals related to BIFR decisions.
- High Courts: Previously dealt with winding up, restructuring, and reduction of share capital.
-
- Composition of the NCLT:
-
- Structure: Consists of a President and such number of Judicial and Technical Members as may be required.
-
- Powers of the NCLT:
-
- Procedural Flexibility: Not limited or bound by the rules laid down in the Code of Civil Procedure; guided by principles of natural justice, subject to the Act and Central Government rules.
- Order Enforcement: Can enforce any order it gives in the same manner as a court.
- Order Scrutiny: Has the power to scrutinize its own orders.
- Procedure Regulation: Has the authority to regulate its own procedure.
-
- Principal Bench: Located in New Delhi.
Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge (GATK)
- News: The new Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources, and Traditional Knowledge, approved by WIPO member states marks a significant milestone in international law.
- Adoption and Objectives:
- Adoption: Adopted in May 2024 under the aegis of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- Aim:
-
- To address the complex relationship between intellectual property (IP), genetic resources, and associated traditional knowledge
- It seeks to ensure fair compensation and benefit-sharing for developing countries whose genetic resources and traditional knowledge are utilized by companies from developed countries.
-
- Key Provisions:
- Disclosure Requirement:
-
- Genetic Resources: Where a patent application involves genetic resources, the applicant must disclose the country of origin or source.
- Traditional Knowledge: If traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources is involved, the applicant must disclose the Indigenous Peoples or local community that provided it.
-
- Scope:
-
- Genetic resources, found in entities such as medicinal plants and agricultural crops, are often utilized in patented inventions, although they themselves cannot be patented.
-
- Implementation: Once ratified by 15 contracting parties, the Treaty will establish an international legal framework requiring patent applicants to disclose the origin of genetic resources and the associated traditional knowledge used in their inventions.
- About World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO):
-
- Agency Type: Specialized agency of the United Nations.
- Location: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Establishment: Established by the WIPO Convention in 1967.
- Mission: To lead the development of a balanced and effective international intellectual property system that enables innovation and creativity for the benefit of all.
- Membership: WIPO currently has 193 member states.
- Function: Provides a global policy forum where governments, intergovernmental organizations, industry groups, and civil society come together to address evolving IP issues.
-
Arab League
- News: The Arab League called for UN peacekeeping forces in the Palestinian territories during a summit in Bahrain’s Manama.
- Establishment and Membership
-
- Formation: The League of Arab States (LAS), initially called the League of Arab States, was established in Cairo, Egypt, on March 22, 1945, with six founding members.
- Expansion: It began with six members and has since grown to include 22 member states, spanning the Middle East and parts of Africa.
-
- Objectives and Mission:
-
- Origins: Originally driven by Pan-Arabism, aiming to foster unity among Arab nations, especially in response to the emergence of Israel.
- Mission: The league’s broad mission is to promote cooperation among member states across various domains, including political, economic, social, and cultural issues.
-
- Members:
-
- Total Members: It has a total 22 members.
- Founding members: Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen
- Other members: Libya, Sudan, Tunisia, Morocco, Kuwait, Algeria, Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Mauritania, Somalia, the Palestine Liberation Organization, Djibouti, and Comoros.
- Observer Status: Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Venezuela have been granted observer status by the League, allowing them to participate in certain capacities.
-
- Structure and Operations:
-
- Decision-Making: Decisions within the league are typically made on a majority basis, although enforcement power is limited.
- Voting System: Each member state holds one vote on the Council, with decisions being binding only on those states that have voted in favor.
- Headquarters: Situated in Cairo, Egypt, the league operates from its central headquarters.
- Official Language: Arabic serves as the official language of the League of Arab States.
-
- Manama Declaration:
-
- Arab League Summit: The Manama Declaration stemmed from discussions during the 33rd Arab League Summit convened in Manama, the capital of Bahrain.
- Participants: Representatives from the 22-member Arab League participated in the summit.
- Key Provisions:
- Call for UN Peacekeeping Forces: The declaration advocated for the deployment of United Nations peacekeeping forces in the occupied Palestinian territories.
- Emphasis was placed on the importance of continued protection until a two-state solution is achieved.
- Support for Palestinian Unity: The Manama Declaration urged all Palestinian factions to unify under the umbrella of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- This call for unity aimed to strengthen Palestinian representation and cohesion in pursuing their aspirations.
-
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) Vs Consumer Price Index (CPI): Composition, Methodology, and Uses
UPSC GS 3
Cost Inflation Index (CII)
- News: The Central Board of Direct Taxes, CBDT has notified the Cost Inflation Index, CII for the financial year 2024- 25 for calculating long-term capital gains.
- Purpose: The CII is a tool used in India’s income tax system to account for inflation when calculating capital gains tax on the sale of long-term assets.
- Publication: Published by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
- Legal Basis: Notified under the Income-tax Act, 1961 every year.
- Function:
-
- Helps individuals ascertain the inflation-adjusted current price of an asset.
- Assists in calculating capital gains from a transfer or sale of capital assets by accounting for inflation.
-
- This adjustment reduces the apparent capital gain and, consequently, the amount of capital gains tax an individual has to pay.
-
-
- Benefits of CII:
-
- Real Value Reflection: Provides a fair reflection of an asset’s real appreciation in value, considering inflation.
- Tax Relief: Prevents taxpayers from being penalized for inflation-driven price increases, thereby reducing their tax burden.
-
- Capital Gain
-
- Definition: Capital gain refers to the profit acquired from the sale or transfer of any capital assets, including land, property, stocks, shares, trademarks, patents, etc.
- Classification: Normally, an asset is required to be retained for more than 36 months (24 months for immovable property and unlisted shares, 12 months for listed securities) to qualify as ‘long-term capital gains’.
-
Graphite
- News: India is in talks with Sri Lanka to acquire a graphite mine block.
- Graphite Overview:
- Composition: Graphite is a mineral composed almost entirely of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure.
- Forms: It is a naturally occurring form of crystalline carbon and is a stable form of carbon. Colloquially known as black lead or plumbago due to its resemblance to metal lead.
- Formation: Formed by the metamorphosis of sediments containing carbonaceous material. Graphite can be found naturally or produced synthetically.
- Properties of Graphite
-
- Electrical Conductivity: Due to its free-moving electrons within the layers, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
- Lubrication: The weak bonding between the layers of graphite allows them to slide easily over each other, making it a good lubricant.
- Heat Resistance: Exceptionally resistant to heat, graphite can withstand up to 3,000°C without melting, decomposing, or losing its structural integrity.
- Thermal Conductivity: An excellent conductor of heat, as the loosely bound layers allow heat to easily travel between them.
- Chemical Inertness: Relatively inert, graphite does not readily react with many other substances at room temperature.
-
- Applications of Graphite:
-
- Used in pencils and lubricants.
- Serves as electrodes in batteries and brushes for electric motors.
- Utilized in heat sinks and composite materials.
- Integral in the cores of nuclear reactors.
-
- Global Production:
-
- Major Producers: Graphite is mined extensively in China, India, Brazil, North Korea, and Canada.
- Sri Lankan Graphite: Known for its purity, Sri Lankan graphite is considered among the purest in the world with more than 98% carbon content.
-
Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) Aircraft
- News: The emergence of electric vertical take off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft has captured the attention of innovators, urban planners, and commuters.
- Definition: Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft are a new class of aircraft designed to take off and land vertically like a helicopter, but are powered by electric motors instead of combustion engines.
- Advantages: This design makes eVTOL aircraft quieter, more efficient, and potentially more environmentally friendly than traditional helicopters.
- Potential Applications
-
- On-Demand Air Taxi Services: eVTOLs could revolutionize intra- and intercity transportation by providing fast and efficient air taxi services.
- Air Ambulances: They could be used for rapid medical response and transportation in emergencies.
- Search and Rescue: eVTOL aircraft can be deployed for search and rescue operations due to their vertical take-off and landing capabilities.
- Cargo Delivery: They offer a new solution for delivering goods quickly and efficiently, especially in areas with limited access.
-
- Development and Future Prospects
-
- Current Status: eVTOL aircraft are still under development, with various prototypes and testing phases ongoing.
- Future Potential: Once fully developed, eVTOLs have the potential to significantly impact and improve various aspects of transportation and logistics.
-
Inverted Duty Structure (IDS)
- News: Central Government is targeting inverted duty structures in washing machines, solar glass, air purifiers.
- Definition: Inverted Duty Structure (IDS) occurs when import duties on input goods are higher than on finished goods, meaning the GST rate paid on purchases exceeds the GST rate payable on sales.
-
- Example: A bakery buys flour and sugar, both taxed at 18%, to produce cookies, which are sold with a 5% GST. This creates an IDS as the bakery pays more tax on the ingredients than it collects on the final product.
-
- Implications:
-
- Higher Tax Payments: Businesses end up paying the government more in taxes than they collect from customers.
- Costly Products: Expensive inputs increase the cost of products, making them less competitive in the export market.
- Working Capital Issues: Resources remain blocked in the form of Input Tax Credit (ITC) due to high input tax, creating working capital problems for taxpayers.
-
India’s Tourism Sector
- News: India has got 39th position in the World Economic Forum’s Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI).
- World Economic Forum’s Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI):
-
- The Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024 is the second edition of an index that evolved from the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index (TTCI) series by World Economic Forum.
- Travel and Tourism Development Index measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of the T&T sector, which in turn contributes to the development of a country.
-
- Key Findings of the Index are:
- Top Five Countries: US, Spain, Japan, France and Australia.
- India’s Recovery and Positive Aspects in the TTDI:
- India’s rank on the World Economic Forum’s Travel & Tourism Development Index 2024 has risen to 39th place, with global tourism activities returning to pre-pandemic level,
-
- Natural Resources: India ranks sixth globally, highlighting its abundant natural attractions.
- Cultural Resources: India secures the ninth position, underscoring its rich cultural heritage and historical sites.
- Non-leisure Resources: India ranks ninth, indicating the diverse range of non-leisure activities available to tourists.
- Competitiveness Rankings:
- Price Competitiveness: India is placed 18th, showcasing its affordability as a travel destination.
- Air Transport: India ranks 26th in air transport competitiveness, reflecting improvements in its aviation sector.
- Ground and Port Infrastructure: India secures the 25th position, signifying the adequacy of its ground and port infrastructure for tourism.
- India’s Leading Position in South Asia:
- Largest Travel and Tourism Sector: India boasts the largest travel and tourism sector in South Asia, contributing significantly to the regional economy.
- Top Lower-Middle-Income Economy: India is recognized as the top-ranked lower-middle-income economy among the 119 nations assessed in the study.
-
