UPSC GS 1
Sundhnuksgigar
- News: Sundhnuksgigar volcano in southwest Iceland recently erupted.
- Location: Sundhnuksgigar is located south of Reykjavik (Reykjavík is the capital and largest city of Iceland).
- What are Volcanoes: According to the US Geological Survey, volcanoes are openings or vents where lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.
- Characteristics and Formation:
-
- Volcanoes can be on land and in the ocean.
- They are formed when material significantly hotter than its surroundings is erupted onto the surface of the Earth.
- The material could be liquid rock (known as “magma” underground and “lava” when it breaks through the surface), ash, and/or gases.
-
- Rise of Magma: According to NASA, the rise of magma can take place in three different ways:
-
- Divergent Boundaries: When tectonic plates move away from each other, magma rises up to fill in the space. Underwater volcanoes can form in this process.
- Convergent Boundaries: When tectonic plates move towards each other, part of Earth’s crust can be forced deep into its interior. The high heat and pressure cause the crust to melt and rise as magma.
- Hotspots: Magma rises at hotspots—hot areas inside of the Earth, where magma gets heated up. As magma gets warmer, it becomes less dense, leading to its rise.
-
- Types of Volcanoes: The type of volcano depends on several factors such as the viscosity of the magma, the amount of gas in the magma, the composition of the magma, and the way the magma reaches the surface.
-
- Stratovolcanoes:
- Description: Stratovolcanoes have steep sides and are more cone-shaped.
- Characteristics: They are composed of alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, and other volcanic debris.
- Formation: These volcanoes form from explosive eruptions that eject magma and volcanic materials into the air, leading to the accumulation of layers over time.
- Shield Volcanoes:
- Description: Shield volcanoes have a low profile and resemble a shield lying on the ground.
- Characteristics: They are typically built by the flow of low-viscosity lava that spreads over a wide area, creating gentle slopes.
- Formation: Shield volcanoes form from relatively quiet eruptions where lava flows steadily from a central vent, gradually building up the volcano’s shape over time.
- Cinder Cones:
- Description: Cinder cones have straight sides and are typically less than 200 m high.
- Characteristics: They are made up of fragments of scoria (vesicular rock from basaltic lava) that were expelled from the volcano as gas-rich magma erupted. Cinder cones are often surrounded by dark lava flows erupted from near their base. They can be eroded away easily, and relatively quickly.
- Formation: They form after violent eruptions blow lava fragments into the air, which then solidify and fall as cinders around the volcanic vent.
-
- Why is Iceland so Volcanically Active?
-
- Tectonic Activity
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Iceland sits on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, part of the longest mountain range in the world, in the North Atlantic Ocean. The Eurasian and North American plates are moving apart a few centimeters every year.
- Volcanic Rift Zones: This tectonic activity produces volcanic rift zones, where the Earth’s crust is being pulled apart and fractured. Molten rock, or magma, rises up in these regions, and some reaches the surface, erupting as lava and/or ash.
- Hot Zone
- Geothermal Hotspot: Additionally, Iceland sits over a hot zone or hotspot. This leads to enhanced volcanic activity in the region.
- Tectonic Activity
-
Bela Block Printing
- News: Bela Block Printing, a lesser-known craft of block printing from Kutch, is in dying out slowly.
- Origin and Cultural Significance: This traditional and vibrant textile art form originates from the Kutch district of Gujarat.

- Design Characteristics:
-
- The textile art showcases bold and precise designs on textured fabrics.
- These designs are known for their bold and graphic nature, often featuring large motifs such as animals (elephants, horses) and geometric patterns, with thicker lines than usual.
-
- Colors and Dyes: Vibrant colors are a hallmark of this art form, achieved using natural and vegetable dyes, particularly red and black.
- Craftsmanship and Community: The Khatri community is renowned for practicing this craft.
Moldova
- News: The pro-Russian leader of Moldova’s largest opposition party has called for better relations with Russia and China.
- Location: Moldova is a landlocked country lying in the northeastern corner of the Balkan region of Europe.
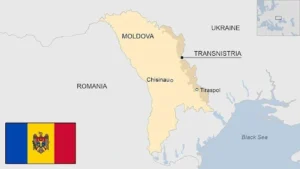
- Bordering Countries:
-
- Ukraine (north, east, and south)
- Romania (west)
-
- Capital City: The capital city is Chișinău, located in the south-central part of the country.
- Economic Status: Moldova is one of the poorest countries in Europe, with its economy heavily reliant on agriculture.
- Demographic Composition: Two-thirds of Moldovans are of Romanian descent.
- Cultural Ties: Moldova and Romania share a common cultural heritage.
UPSC GS 3
Sovereign Credit Rating (SCR)
- News: S&P Global Ratings has raised India’s sovereign rating outlook to ‘positive’ from ‘stable’.
- Definition: A sovereign credit rating is an independent assessment of the creditworthiness of a country or sovereign entity.
- Purpose: This rating assesses a country’s ability and willingness to meet its debt obligations on time.
- Investor Considerations:
-
- Investment Decisions: Investors use SCRs to gauge the risk associated with investing in a country’s bonds.
- Impact of Higher Ratings: Indicate higher creditworthiness, leading to lower risk and interest rates for borrowing.
- Impact of Lower Ratings: Indicate lower creditworthiness, higher risk, and consequently higher borrowing rates.
-
- Economic and Financial Implications:
-
- Attracting Investment: Higher SCRs enhance a country’s ability to attract foreign investment.
- Access to Capital Markets: Better ratings improve access to international capital markets.
- Economic Growth: SCRs influence economic growth by affecting borrowing costs and investment flows.
-
- Factors Influencing SCRs:
-
- Economic Growth: A robust economy can improve a country’s SCR.
- Fiscal Health: Preferable lower fiscal deficits and debt-to-GDP ratios.
- Political Stability: Stability in governance enhances credit ratings.
-
- Leading Credit Rating Agencies:
-
- Global Agencies: Standard and Poor’s (S&P); Moody’s; Fitch Ratings
- Indian Agencies: CRISIL; ICRA; CARE; Fitch Ratings (also operates in India)
-
- Regulation in India: Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs) in India are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Exercise Red Flag 2024
- News: India recently joined the U.S.’s Red Flag air exercise.
- Overview of the Exercise: The Indian Air Force recently participated in a multinational air combat exercise in Alaska, USA, hosted by the United States Air Force.
- Purpose and Design: This exercise, known as Red Flag Alaska 24-2, is designed to create a comprehensive learning environment by simulating realistic combat scenarios.
- Participation by the Indian Air Force: The Indian Air Force (IAF) participated in Red Flag Alaska 24-2, deploying its most advanced fighter jets, including the Rafale.
- Key Training Areas: Red Flag exercises are crucial for aircrews to develop skills in several key areas:
-
- Air combat tactics
- Electronic warfare
- Close air support
- Large-force employment
-
- Rafale Fighter Jets:
-
- The Dassault Rafale is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation.
- Equipped with a wide range of weapons, the Rafale is intended to perform various missions, including:
- In-depth strike
- Anti-ship strike
- Nuclear deterrence missions
- Introduced in 2001, the Rafale is currently being produced for the French Air Force.
- International Purchases: The Rafale has been selected for purchase by several international air forces, including the Indian Air Force, the Egyptian Air Force, the Qatar Air Force.
-
Global Food Policy Report 2024
- News: Global Food Policy Report 2024: Food systems for healthy diets and nutrition has been released by International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI).
- Overview and Establishment:
-
- The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) was established in 1975.
- It provides research-based policy solutions to sustainably reduce poverty and end hunger and malnutrition in developing countries.
-
- Organizational Affiliation: IFPRI is a research centre of Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centers, which is the world’s largest agricultural innovation network.
- Strategic Research Areas: IFPRI’s research focuses on five strategic areas:
-
- Fostering Climate-Resilient and Sustainable Food Supply
- Promoting Healthy Diets and Nutrition for All
- Building Inclusive and Efficient Markets, Trade Systems, and Food Industry
- Transforming Agricultural and Rural Economies
- Strengthening Institutions and Governance
-
- Headquarters: The headquarters of IFPRI is located in Washington, D.C.
- Global Food Policy Report 2024:
-
- Dietary Patterns: The 2024 report highlights that at least 38% of the Indian population consumed unhealthy foods, while only 28% ate a balanced diet.
- Malnutrition Trends: In India, the proportion of the population suffering from malnutrition increased from 15.4 % in 2011 to 16.6 % by 2021.
- Overweight Prevalence: The prevalence of overweight adults increased from 12.9% in 2006 to 16.4 % in 2016.
- Packaged Food Consumption: The share of packaged (highly processed and calorie-dense) foods in household food budgets nearly doubled during this period, increasing to 12 % from 6.5 %.
- Increasing Consumption of Unhealthy Foods: The consumption of calorie-dense and nutrient-poor foods in India was not only high but also increasing, while the consumption of vegetables and other micronutrient-rich foods remained low.
- Rise of Processed Foods in South Asia: In India and other South Asian countries, the consumption of processed foods is on the rise. After cereals and milk, snacks and prepared foods accounted for the majority of Indian food budgets.
- Cost of Micronutrient-Rich Foods: The report highlighted that in the South Asian region, micronutrient-rich foods were expensive, whereas cereals, fats and oils, sugar, and sugary and salty snacks were relatively inexpensive.
-
Recombinant Proteins
- News: Researchers at the Department of Biochemistry, Indian Institute of Science, have developed a novel method for the production of recombinant proteins.
- Definition and Production:
- Recombinant Proteins:
-
- Recombinant proteins are artificially produced by introducing specific genes (Recombinant DNA) into host organisms, such as bacteria or yeast.
- These genes instruct the host organisms to manufacture the desired protein.
-
- Types of Recombinant Proteins: Various types exist based on their applications and production methods.
-
- Well-known types include interferons, recombinant hormones, tumor necrosis factors, etc.
- Examples: human insulin for diabetes, human growth factors for growth hormone deficiency, Factor VIII for hemophilia, and therapeutic monoclonal antibodies for treating cancer and viral infections like SARS-CoV-2.
-
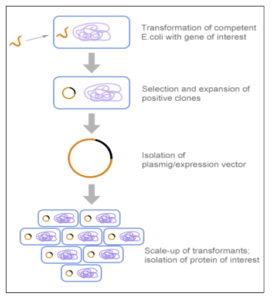
- Production Process:
-
- Insertion and Transfer:
- Insert a modified gene into a suitable vector (like a plasmid).
- Transfer the vector into host cells (like bacteria or yeast).
- Cell Growth and Harvesting:
- Grow these cells in a culture until they reach high concentration.
- Harvest the cells to obtain the recombinant protein.
- Insertion and Transfer:
-
- Applications
-
- Biomedical Research: Utilized to understand health and disease mechanisms.
- Biotherapeutics: Employed in the development of biotherapeutic products.
- Protein-Based Polymers: Utilized in drug delivery systems.
- Disease Treatment: Used to produce antibodies and enzymes.
- Tissue Engineering: Provides protein scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.
-
- Role and Function of Proteins:
-
- Proteins are large, complex molecules that serve as key building blocks of life.
- Proteins facilitate most biological processes in a cell, including gene expression, cell growth, proliferation, nutrient uptake, intercellular communication, and apoptosis.
- The blueprint for protein synthesis is stored in DNA, which serves as a template for regulated transcriptional processes to produce messenger RNA (mRNA).
-
26th Committee on Environmental Protection (CEP-26)
- News: India successfully concluded hosting of 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM-46) and 26th Committee on Environmental Protection (CEP-26) in Kochi, Kerala.
- Important Outcomes of the Events:
-
- Establishment of Maitri-II: To strengthen cooperation in the preservation and management of Antarctica, India has decided to set up an Antarctic research station named Maitri-II.
- CEP Priorities: The Committee agreed to focus on:
- Management of implications of sea ice change
- Enhancing environmental impact assessments of major activities
- Protecting the emperor penguin
- Developing an international framework for environmental monitoring in Antarctica
- Management Plans Adoption:
- The Parties adopted 17 revised and new management plans for Antarctic Specially Protected Areas (ASPAs).
- Several modifications and additions were made to the list of Historic and Monument sites.
- Renewable Energy and Biosecurity:
- The ATCM encouraged efforts to increase the use of renewable energy.
- Robust biosecurity measures were recommended to minimize the risks of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza.
- Awareness Initiatives:
- A commemorative MyStamp featuring the ATCM-46 logo was released.
- A mural titled ‘Species-rich Antarctica’ was unveiled to enhance awareness of Antarctica.
- Tourism Framework:
- A significant outcome was the adoption of a decision to develop an ambitious, comprehensive, flexible, and dynamic framework for regulating tourism and non-governmental activities in Antarctica.
- The Parties also discussed consultative status requests from Canada and Belarus, but no consensus was reached.
-
- About Committee for Environmental Protection (CEP):
-
- Establishment: The CEP was established in 1991 under the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty (the Madrid Protocol).
- Purpose: The CEP advises the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) on matters related to environmental protection and conservation in Antarctica.
- CEP-26 Agenda Focus:
- Assessing the current state of the Antarctic environment.
- Evaluating the environmental impact of activities in the region.
- Managing and reporting on environmental protection efforts.
- Developing strategies to respond to climate change impacts in Antarctica.
- Creating and updating management plans for protected areas, including marine spatial protection.
- Implementing measures to conserve Antarctic biodiversity and protect native species.
-
GS Foundation 1 Year: Structured Prep, Expert Guidance & More
Cryonics Practice for Freezing Human Body
- News: Recently, a cryonics company in Australia has successfully preserved its first client through freezing, with the aspiration of reviving them in the future.
- Cryonics:
-
- The practice of freezing an individual who has died, with the intention of reviving them in the future, is known as cryonics.
- The term “cryonics” is derived from the Greek word “krýos,” meaning “icy cold.”
-
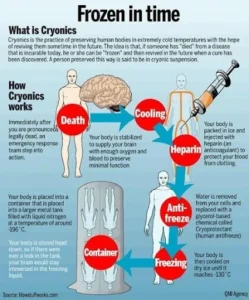
- Objective and Purpose:
- Saving Lives: Cryonics aims to save lives by preserving individuals at extremely low temperatures until future medical technologies can restore them to full health.
- State of Cryopreserved Patients:
- Cryopreserved Patients: Individuals in this state are referred to as “cryopreserved patients,” as Cryonicists do not consider them truly dead.
- Cryonic Preservation Process:
-
- Cryonic preservation can only be performed after an individual has been legally declared dead.
- The process begins shortly after death, with the body being packed in ice (-196°C) and transported to a cryonics facility.
-
- Steps:
-
- Blood Replacement: At the facility, blood is drained and replaced with antifreeze and organ-preserving compounds known as cryoprotective agents.
- Vitrification: In this vitrified state, the body is placed in a chamber filled with liquid nitrogen and preserved at -196 °C.
-
Hoolock Gibbons
- News: The Northeast Frontier Railway will construct canopy bridges for Hoolock Gibbons to move across a railway track bifurcating its prime habitat in eastern Assam.
- Hoolock Gibbon: India’s Only Ape:
-
- The Hoolock Gibbon is the only ape found in India.
- It is native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.
-
- Habitat and Characteristics:
-
- Gibbons, the smallest and fastest of all apes, live in tropical and subtropical forests in the southeastern part of Asia.
-
- Classification:
-
- The Hoolock Gibbon is categorized into Western Hoolock Gibbon and Eastern Hoolock Gibbon.
-

- Distribution:
- Western Hoolock Gibbon:
-
- The Western Hoolock Gibbon has a much wider range, found in all the states of the northeast of India.
- Its range is restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra river and east of the Dibang river.
- Outside India, it is found in eastern Bangladesh and north-west Myanmar.
-
- Eastern Hoolock Gibbon:
-
- The Eastern Hoolock Gibbon inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, as well as southern China and northeast Myanmar.
-
- Conservation Status:
-
- The Western Hoolock Gibbon is listed as Endangered in the IUCN Red List.
- The Eastern Hoolock Gibbon is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List.
-
Facts for Prelims
Key Polity Terms
|
