Central Industrial Security Force (CISF)
News: CISF has taken over Parliament security from Delhi Police.
Definition: CISF is an armed force of the Union Government established under an Act of Parliament, “Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968”.
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
Aim: CISF provides security to the premises staff along with the security of property and establishments.
Security Mandate: CISF provides security to:
- Strategic Establishments: Department of Space, the Department of Atomic Energy, the Airports, the Delhi Metro, the ports, the historical monuments.
- Basic Areas of Indian Economy: Petroleum and natural gas, electricity, coal, steel and mining.
- Private Sector Units and important government buildings in Delhi.
Protected Persons:
- CISF provides security for individuals categorized as Z Plus, Z, X, and Y.
Features:
- It is one of the 7 Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) under the MHA.
-
- Other six are: Border Security Force, Indo-Tibetan Border Police, Sashastra Seema Bal, Assam Rifles, National Security Guard, Central Reserve Police Force.
-
- CISF is the only force with a customized and dedicated fire wing.
- CISF is a compensatory cost force which means it bills its clients for the services it provides.
Vitrectomy
News: Aam Aadmi Party leader and Rajya Sabha MP Raghav Chadha recently underwent vitrectomy.
Overview of Vitrectomy Surgery:
- Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing the vitreous humour, a gel-like substance filling the space between the lens and the retina in the eye.
Common Reasons for Surgery:
- Retinal detachment, where the retina separates from the back of the eye, is a primary reason necessitating vitrectomy surgery to prevent potential blindness.
- In cases of eye trauma, foreign objects may require removal via vitrectomy.
- Complications like cataract surgery, may also warrant vitrectomy to resolve issues.
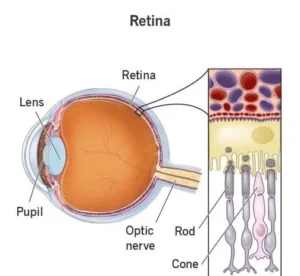
Retina:
- The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball.
- Images that come through the eye’s lens are focused on the retina.
- The retina then converts these images to electric signals and sends them along the optic nerve to the brain.
- Retina contains rods and cones. Rods are responsible for night vision and seeing in low light conditions.
- Cones are responsible for color vision and seeing in bright light conditions.
 New Collective Quantified Goal on Climate Finance (NCQG)
New Collective Quantified Goal on Climate Finance (NCQG)
News: Negotiations on New Collective Quantified Goal on climate finance take centerstage at the 29th Conference of the Parties (COP29).
Establishment:
- At the 2009 Copenhagen UN Climate Change Conference, developed countries pledged to mobilize $100 billion annually by 2020 to help developing countries.
- This goal was extended to 2025 at COP21.
- At COP21, a new goal New Collective Quantified Goal on Climate Finance (NCQG) was proposed to set for post-2025.
Aim: NCQG proposes to increase the ceiling on climate finance beyond the $100 billion yearly target.
Need for NCQG:
- The amount of $100 billion was inadequate compared to the climate finance needs of developing countries, which range from $1-2.4 trillion per year until 2030.
- Moreover, the goal of $100 billion has not been achieved in a single year since its announcement.
-
- The latest estimates show that developed countries mobilised $89.6 billion in 2021 for developing countries.
-
Challenges in Achieving The Target of $100 Billion Annually:
- Geographic Imbalance in Climate Finance: 80% of total global climate finance between 2011 and 2020 was concentrated in the OECD countries and East Asia Pacific region.
-
-
- This revealed a significant geographical concentration of funds.
-
-
- Fund Allocation: Adaptation accounted for only 8% of total climate funding in 2019-2020, with the majority of funds going toward mitigation.
- Type of Climate Finance: Almost 94% of current climate investment is either debt or equity, with only 6% in the form of aid.
Blood Minerals
News: Apple faces allegations of using ‘blood minerals’ from war-torn Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Meaning: Blood Minerals refer to minerals that are sourced from conflict-affected regions where violence & human rights violations (like child labour) are interlinked with mineral extraction.
Examples: Tantalum, tin, tungsten, and gold (3TG) are major examples of blood minerals
Extraction: The extraction and trade of these minerals have been linked to funding armed groups and fuelling conflicts in several countries in Central Africa.
Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) System
News: DRDO has successfully flight tested the Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) system from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha.
Definition: SMART is a next-generation missile-based light-weight torpedo delivery system designed and developed by DRDO.
Aim: To enhance the anti-submarine warfare capability of the Indian Navy far beyond the conventional range of lightweight torpedoes.
Features:
- It is a canister-based missile system that comprises several advanced subsystems including two-stage solid propulsion and precision inertial navigation.
- It carries an advanced lightweight torpedo missile as a payload along with a parachute-based release mechanism.
- It can be launched from both coasts and warships.
- This missile-based mechanism to launch lightweight torpedoes can target submarines hundreds of kilometres away, beyond the conventional range of lightweight torpedoes.
- It will be particularly employed in the absence of other assets for immediate action when an enemy submarine is detected.
- It also consists of several state-of-the-art mechanisms such as symmetric separation, ejection and velocity control.
Balanced Fertilisation
News: Balanced fertilisation is likely to be a key policy goal for the government taking over after the Lok Sabha elections.
Definition:
- The requirements of nutrients such as Nitrogen, Phosphate and Potash are soil and crop specific.
- The use of the right ratio of nutrients as per soil or crop requirement is known as “balanced fertilization”.
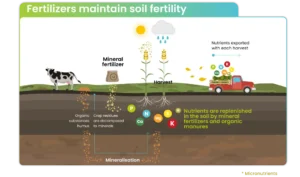
Essential Fertilisers:
- They are basically food for crops, containing nutrients necessary for plant growth and grain yields.
- Nutrients used for Balanced fertilisation:
-
-
- Primary Nutrients: Nitrogen- N, phosphorus-P and potassium-K,
- Secondary Nutrients: Sulphur-S, calcium, magnesium
- Micro Nutrients: Iron, zinc, copper, manganese, boron, molybdenum
-
