UPSC GS 1
Campi Flegrei
- News: A strong earthquake recently hit Italy’s Campi Flegrei supervolcano region.
- Location and Description: Campi Flegrei, also known as Phlegrean Fields, is an active volcanic area situated near Naples, Italy.
- Subsea Presence: Approximately one third of Campi Flegrei is located beneath the Tyrrhenian Sea, positioned between mainland Italy and the island of Sardinia.
- Characteristics:
-
- Campi Flegrei is not characterised by a single volcano.
- It is more of a volcanic system, with several centres situated within a caldera.
- A caldera is a large depression formed when a volcano erupts and collapses.
- The caldera spans approximately 12-15 km (7.5-9.3 miles) in diameter. It was formed around 39,000 years ago following a massive eruption that depleted its magma chambers.
-

- Significance: Campi Flegrei is recognized as the largest active caldera in Europe, surpassing Vesuvius in size and activity level.
-
- Despite its relatively quiet period, it holds potential for significant volcanic events.
-
- Eruption History: The last eruption of Campi Flegrei occurred in 1538, resulting in the creation of Monte Nuovo, a new mountain.
-
- While this eruption was relatively minor, it demonstrates the ongoing activity of the volcanic system.
-
- Classification as a Supervolcano
-
- Definition: A supervolcano is a volcano that has had an eruption with a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) of 8, the highest recorded value.
- Volume of Deposits: For such eruptions, the volume of deposits exceeds 1,000 cubic kilometers (240 cubic miles), indicating immense scale and potential global consequences.
-
Narva River
- News: Recently, a new dispute has arisen between Russia and Estonia, focusing on the removal of navigation markers along the Narva River.
- Location: The Narva River forms part of the border between Russia and Estonia and discharges into the Baltic Sea.
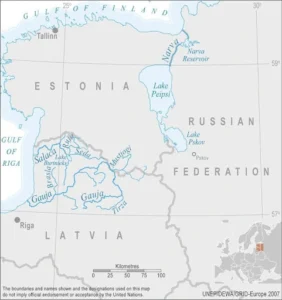
- Connection: The river connects Lake Peipsi with the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea.
RBI’s Record Surplus Transfer to Central Government: Opportunities and Challenges UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Article 329(b)
- News: Recently, the Election Commission (EC) invoked Article 329(b) of the Constitution, which prohibits judicial intervention in the functioning of the commission during the course of an ongoing election process.
- Indian Constitution: Enshrined in Part XV of the Indian Constitution, articles 324-329 specifically discuss elections.
- Clauses: Article 329 of the Indian Constitution has two clauses that define the role of the judiciary in electoral matters.
-
- Article 329(a): States that the judiciary cannot challenge the constitutionality of laws relating to the boundaries of electoral districts or the allocation of seats.
- Article 329(b): Amended by the Constitution (19th Amendment) Act, 1966.
- Specifies that no election to either House of Parliament or the Legislature of a State shall be called into question except by an election petition.
- Such petitions must be presented to the appropriate authority and follow the manner prescribed by or under any law made by the appropriate Legislature.
-
- Representation of the People Act, 1951:
-
- Empowerment of High Courts: The Representation of the People Act, 1951, implements Article 329(b) by empowering high courts to hear and decide election petitions.
- Supreme Court Appeal: Decisions on these petitions can be challenged in the Supreme Court.
-
- Judicial Precedent:
-
- Ponnuswamy Judgment (1952): The Supreme Court, in the Ponnuswamy judgment, stated that it could not interfere in the election process once it was notified by the Election Commission of India.
- K. Venkatachalam vs. A. Swamickan (1999): The SC held that Article 329(b) is inapplicable if the matter pertains to Articles 191 and 193, which deal with disqualifications and penalties related to parliamentary and legislative assembly membership, respectively.
-
Squad Minilateral Grouping
- News: Recently, the US secretary of defence met his Australian, Filipino, and Japanese counterparts to institutionalize and launch the ‘Squad’ as a new four-way security arrangement in the Indo-Pacific.
- Emergence: The Squad has recently emerged as a minilateral security grouping in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Member Nations: The Squad consists of the United States, Australia, Japan, and the Philippines.
- Structure and Formality: The level of formality and structure of the Squad in comparison to existing arrangements like the Quad (US, Japan, India, Australia) remains unclear.
- Understanding Minilateralism: Minilateralism is a concept in international relations involving small groups of nations collaborating to address various issues, including security, economic, and technological challenges, or to pursue mutual goals.
- Characteristics:
-
- Informal: Minilateral frameworks are informal in nature.
- Flexibility: They offer flexibility in decision-making and action.
- Voluntary Participation: Participation in minilateral groups is voluntary.
- Varied Interests: Member nations may have varied situational interests.
- Shared Values or Capabilities: Collaboration is based on shared values or relevant capabilities.
-
UPSC GS 3
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR)
- News: A SEBI committee has suggested changes to the BRSR, or Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting, framework.
- Overview: The Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) framework was launched by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 2021.
-
- It evolved from the earlier Business Responsibility Report (BRR), which was introduced in 2012.
-
- Objective: The primary aim of the BRSR framework is to encourage listed companies to adopt sustainable business practices and to disclose information related to their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
- Mandate: The BRSR mandates the top 1,000 listed entities by market capitalisation to file their BRSR as part of their Annual Report with SEBI.
- BRSR Principles: The BRSR framework is based on nine key principles that guide businesses towards responsible and sustainable practices:
-
- Ethical Governance: Businesses should conduct and govern themselves with integrity and in a manner that is ethical, transparent, and accountable.
- Sustainable Goods and Services: Businesses should provide goods and services in a manner that is sustainable and safe.
- Employee Well-being: Businesses should respect and promote the well-being of all employees, including those in their value chains.
- Stakeholder Responsiveness: Businesses should respect the interests of and be responsive to all their stakeholders.
- Human Rights: Businesses should respect and promote human rights.
- Environmental Protection: Businesses should respect and make efforts to protect and restore the environment.
- Responsible Policy Advocacy: Businesses, when engaging in influencing public and regulatory policy, should do so in a manner that is responsible and transparent.
- Inclusive Growth: Businesses should promote inclusive growth and equitable development.
- Consumer Responsibility: Businesses should provide value to their consumers in a responsible manner.
- By adhering to these principles, businesses can ensure they are contributing positively to society and the environment, while also maintaining transparency and accountability in their operations.
-
Astronomical Transients
- News: Indian-American astronomer Shrinivas Kulkarni was recently awarded the 2024 Shaw Prize in Astronomy for his significant contributions to understanding the physics of astronomical transients.
- Definition: Astronomical transients are celestial objects or phenomena whose brightness changes significantly over a relatively short period of time. This period is short in the context of astronomical timescales, which span millions or billions of years.
- Characteristics: The changes in brightness of astronomical transients can be dramatic, ranging from objects becoming briefly brighter than anything else in the sky to objects fading from view entirely.
- Importance of Study: Studying astronomical transients helps scientists understand:
-
- Stellar evolution
- Formation of black holes
- The early universe
-
- Examples of Astronomical Transients:
-
- Supernovae: These are exploding stars that can briefly outshine entire galaxies.
- Active Galactic Nuclei: These are super-massive black holes at the centers of galaxies that emit tremendous amounts of energy.
- Fast Radio Bursts: These are mysterious millisecond-long bursts of radio waves that originate from unknown sources.
-
- Understanding and observing these transients provide crucial insights into the dynamic and evolving nature of the universe.
Zimbabwe Gold (ZiG)
- News: To address its long-standing economic instability, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe (RBZ) has launched a new gold-backed currency called the ZiG.
- Introduction: Zimbabwe Gold (ZiG) is a new gold-backed currency launched by Zimbabwe.
- Backing and Value: The value of ZiG is supported by Zimbabwe’s reserves of gold and other precious metals.
- Circulation:
-
- ZiG has been in circulation since April 5, 2024.
- It is the sixth currency currently used in Zimbabwe.
-

- Purpose and Transition:
-
- ZiG replaced the Zimbabwean dollar, which had suffered from severe hyperinflation.
- Banks in Zimbabwe have been converting the previous national currency, the Zimbabwean dollar, into ZiGs.
- The aim of this conversion is to promote simplicity, certainty, and predictability in monetary and financial matters.
-
Strain Rate
- News: Copper becomes unexpectedly hard under extreme strain rate.
- Definition: Strain is the measure of how much a material deforms when stress is applied. It quantifies the change in shape or size of an object relative to its original dimensions.
- Units: Strain is dimensionless as it is expressed as the ratio of meters divided by meters, resulting in no physical units.
- Strain Rate: Strain rate is the rate at which deformation occurs in a material subjected to strain over a specific period. It indicates how quickly a material is deformed over time.
- Formula: Strain Rate = Change in Strain / Change in Time
- Units: The unit of strain rate is per second (s⁻¹).
- Importance: Strain rate is a crucial factor in materials science and engineering because it affects the mechanical properties and behavior of materials. Understanding strain rate helps in predicting how materials will respond under different conditions.
- Copper Properties
-
- Electrical Conductivity: Copper is a good conductor of electricity.
- Ductility: Copper is ductile, meaning it can be drawn out into a thin wire.
- Alloys of Copper:
- Stainless Steel: Iron, chromium, nickel, carbon, silicon, and manganese.
- Morel Metal: Copper and nickel.
- Duralumin: Copper and aluminium.
- Brass: Copper and zinc.
- Bronze: Copper and tin.
-
- Copper Ore and Mining: Copper ore is found in both ancient and younger rock formations.
- Mining Challenges: Mining for copper is costly because most copper ores contain a small percentage of the metal.
- Copper Ore in India: India has low-grade copper ore with less than 1% metal content, compared to the international average of 2.5%.
- Major Suppliers: The major part of India’s copper supply comes from the USA, Canada, Zimbabwe, Japan, and Mexico.
Eucalyptus
- News: Protest is brewing in Kerala over the recent decision of the state forest department to allow planting of eucalyptus trees in the reserve forest areas of the state.
- Overview: Eucalyptus is a large genus comprising more than 660 species of shrubs and tall trees in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae). These trees are among the tallest in the world.
- Native Habitat:
-
- Eucalyptus is native to Australia, Tasmania, and nearby islands.
- There are over 700 species of eucalyptus in these regions.
- In Australia, they are commonly known as gum trees or stringybark trees.
-

- Features:
-
- Shallow Roots: Excellent at accessing water near the surface.
- Fast Maturity: Allows for rapid reproduction.
- Leathery Leaves: Vertical leaves minimize water loss.
- Fibrous Bark: Helps regulate temperature and may deter pests.
-
- Growing Conditions: Eucalyptus thrives in deep, fertile, well-drained loamy soil with adequate moisture.
- Uses:
-
- Pulpwood: Major source for paper production.
- Firewood: High burning efficiency makes it a good source.
- Essential Oils: Leaves produce oils with antiseptic and medicinal properties, used for cold treatment and as a pain reliever for aching joints.
- Wood: Tough and durable, used in furniture and fences.
-
- Eucalyptus in India:
-
- Common Species: Eucalyptus tereticornis and Eucalyptus hybrid are the most widely planted species.
- Regions: Widely grown in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Mysore, Kerala, and the Nilgiri Hills.
-
- Concerns:
-
- High Water Usage: Can lead to soil fertility depletion.
- Potential Allelopathy: May suppress the growth of other plants.
- Toxic Foliage: Leaves are toxic to animals and humans if ingested.
- Flammable Oil: Oil can give off flammable fumes, which can be ignited by lightning or sparks.
-
INS Kiltan
- News: The Royal Brunei Navy warmly welcomed the Indian Naval Ship Kiltan upon its arrival in Muara, Brunei.
- Overview:
-
- Introduction: INS Kiltan is a cutting-edge indigenous warship poised for commissioning into the Indian Navy.
- Project 28: It is the third vessel in the Kamorta-class corvettes built under Project 28.
- Naming and Origin: Named after an island in the Aminidivi group within the strategically vital Lakshadweep and Minicoy Islands.
- Design: It is designed by the Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design and constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
-
- Advanced Features:
-
- Carbon Fibre Composite Superstructure:
- The first major Indian warship with a superstructure made from carbon fibre composite material.
- Enhances stealth, reduces weight, and lowers maintenance costs.
- Weapons and Sensors:
- Heavyweight Torpedoes and ASW Rockets: Essential for submarine defense.
- Medium-Range Gun and CIWS: Includes a 76 mm caliber gun and two multi-barrel 30 mm guns with dedicated fire control systems for close-in protection.
- Missile Decoy Rockets (Chaff): Enables evasion maneuvers.
- Advanced ESM System, Sonar, and Radar: Enhances detection and tracking capabilities.
- Future Upgrades:
- Planned installation of a short-range Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system.
- Will be equipped with an integral ASW helicopter.
- Significance:
- Joins the lineage of indigenous warships like the Shivalik Class and Kolkata Class, alongside sister ships INS Kamorta and INS Kadmatt.
- Enhances the Indian Navy’s combat capabilities by providing a comprehensive operational picture.
- Carbon Fibre Composite Superstructure:
-
Online Cybercrimes
- News: A significant number of Indians are becoming victims of internet-based financial fraud, believed to be orchestrated by criminals operating from three neighboring Southeast Asian countries: Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia.
- Context: In its examination of trends observed from January to April, the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C) discovered that 46% of reported financial fraud cases during this period, resulting in a cumulative loss of approximately Rs 1,776 crore, were linked to these three nations in Southeast Asia.
- Types of Crime:
- Trading Scam: Fraudsters advertise on social media offering free trading tips, often using images of well-known stock market experts and fake news articles.
-
- Victims are directed to join WhatsApp groups or Telegram channels to receive investment advice.
- They are persuaded to install specific trading applications and register to receive further guidance.
- Victims deposit money into specified bank accounts to “buy shares” and are shown fake profits in digital wallets.
- However, they are unable to withdraw the money until they accumulate a substantial amount, often after paying additional “taxes”.
-
- Digital Arrest Scam: Victims receive calls claiming they are involved in illegal activities or have received illegal goods.
-
- Fraudsters pose as law enforcement officials, demanding money for “compromise” and “closure of the case”.
- Victims may be digitally arrested, forced to stay visible until demands are met.
-
- Investment Scam (Task-Based): Victims receive WhatsApp messages offering large sums of money for social media rating tasks.
-
- After completing initial tasks, victims receive small sums and are asked to deposit larger amounts for promised returns.
- Victims are blocked if they refuse, but those who participate are asked to complete additional tasks to receive their money.
-
- Romance/Dating Scam: Victims are targeted by individuals posing as foreign women on dating and social media sites.
-
- Victims are lured into relationships or marriage proposals, followed by requests for financial assistance.
- Scammers appear genuine, caring, and believable, gaining victims’ trust quickly.
-
