UPSC GS 1
Bharathapuzha River
- News: In a tragic incident, four members of a family drowned in the Bharathapuzha river at Cheruthuruthy.
- About Bharathappuzha River:
- Definition:
- Bharathappuzha is the second longest river in Kerala after the Periyar River, with a length of 209 km.
- Often referred to as the Nile of Kerala, it is also known by names like Nila, Kuttipuram Puzha, and Ponnaniyar.
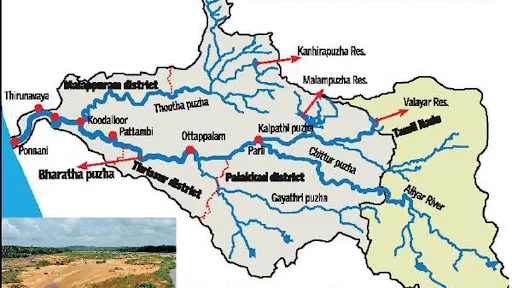
- Course of the River:
- Origin: The river originates in the Annamalai Hills located in the Western Ghats region of Tamil Nadu.
- Flow Path: It flows northwestward through the Pollachi taluk in Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu. The river enters Kerala through the Palghat Gap in the Palghat district. It eventually drains into the Arabian Sea near Ponnani town in Kerala.
- Drainage Basin: The total drainage area of the river is divided between Kerala and Tamil Nadu. The basin receives substantial rainfall during the southwest monsoon and lies in the rain shadow region of the Western Ghats.
- Major Tributaries:
- Gayathripuzha River.
- Kannadipuzha River.
- Kalpathipuzha River.
- Thuthapuzha River.
- Dams: The Malampuzha Dam.
Read also: Critical Minerals in India: A Comprehensive Overview | UPSC
Sun Temple
- News: Singapore President Tharman Shanmugaratnam and the First Lady of the country visited the world heritage site of Sun temple at Konark recently.
- Builder and Era: The Sun Temple was built in the 13th century by King Narasimha Deva I of the Ganga Dynasty as a tribute to the Sun God.
- Architectural Significance: It stands as a testament to the brilliance of Kalinga temple architecture.

- Location and Symbolism: The temple was originally constructed on the sea, creating the illusion of the Sun God rising from the waters during dawn.
- European Reference: European sailors referred to it as the “Black Pagoda” due to the dark appearance of the temple’s roof.
- Structural Features:
- Spatial Units: The temple comprises distinct and well-planned sections, including:
- Jahamogana: The audience hall.
- Natya Mandap: The dance hall.
- Bhoga Mandap: The dining hall.
- Vimana: The original vimana of the temple collapsed in 1837.
- Chariot Design: The temple is designed as the Sun God’s chariot, featuring seven horses pulling it and twenty-four intricately carved wheels.
- Konark Wheels: The wheels are ingeniously designed to serve as sundials, allowing one to determine the time of day by observing the shadows cast by the sun on their spokes.
- Symbolism and Recognition:
-
- Cultural Significance: The 24-spoke Konark wheel represents time (Kalachakra), progress, and the dynamic changes in the cosmos. This iconic wheel is also featured on India’s national flag.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: The Sun Temple was recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1984 for its historical and architectural significance.
Musi River
- News: Hyderabad’s Musi River buildings have earned a place on the 2025 World Monuments Watch.
- Geographical Overview: The Musi River flows through the southern Indian state of Telangana and is a tributary of the Krishna River.
- Origin: The river originates in the Anantagiri Hills near Vicarabad in the Rangareddi district, about 90 kilometers west of Hyderabad.
- Rivulets: It consists of two smaller streams, Esi (8 km) and Musa (13 km), which merge to form the Musi River.
- Confluence: The river meets the Krishna River near Wazirabad in the Nalgonda district.
- Dams: Two significant dams, Himayat Sagar and Osman Sagar, have been constructed on the Musi River.

- Hyderabad Connection: Hyderabad is located along the banks of the Musi River, which serves as a natural divide between the old and new parts of the city.
- About World Monuments Watch (WMW):
-
- Introduction: The World Monuments Watch is a biennial advocacy program launched in 1996 by the World Monuments Fund (WMF), a New York-based organization.
- Purpose: The program highlights buildings and heritage sites at risk from tourism, conflict, climate change, and natural disasters.
- Indian Site Recognition: Gujarat’s Bhuj Historic Water Systems has been recognized by the WMF on its list of 25 global sites under threat due to water crises and climate change.
Gulf of Aden
- News: There is a possibility of an increase in threats in the Gulf of Aden, Red Sea and the sea areas adjacent to East African countries.
- Location:
-
- An extension of the Indian Ocean, situated between the Arabian Peninsula (to the north) and the Horn of Africa (to the south).
- It serves as a connection between the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea, eventually linking to the Indian Ocean.
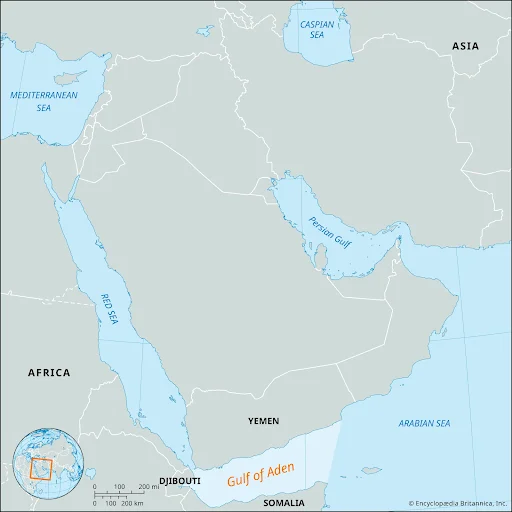
- Naming and Size:
-
- Named after Aden, a coastal port city in Yemen.
- Spanning approximately 900 km in length and 500 km in width, covering an area of about 410,000 sq. km.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- South: Somalia and the Socotra Islands (part of Yemen).
- North: Yemen.
- East: Arabian Sea.
- West: Djibouti.
- Linked to the Somali Sea through the Guardafui Channel in the south and to the Red Sea via the Strait of Bab el-Mandeb in the west.
- Narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura near Djibouti in the west.
- Terrain and Features:
- The Sheba Ridge, an extension of the Indian Ocean ridge system, is the primary relief feature, running along the center of the gulf.
- Has lower saline content compared to the adjacent Red Sea.
- Nearby Cities:
- Prominent cities include Aden, Mukalla, Ahnwar, Balhaf, Berbera, Bosaso, and Djibouti City.
- Major Ports:
- Key ports include Aden in Yemen and Berbera and Bosaso in Somalia.
- Strategic Importance:
- A vital component of the Suez Canal shipping route, which connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Approximately 11% of global seaborne petroleum transits through the Gulf of Aden, en route to the Mediterranean or Arabian Seas.
UPSC GS 2
Lokpal of India
- News: The Foundation Day of the Lokpal of India was held for the first time on 16th January at Manekshaw Centre in the august presence of Shri Justice Sanjiv Khanna (CJI).
- Introduction:
-
- Lokpal is a statutory body established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013.
- Its primary mandate is to investigate allegations of corruption against specific public officials and address related matters.

- Organisational Structure:
- The Lokpal comprises a Chairperson and eight Members, with four designated as Judicial Members.
- The Chairperson can be a former Chief Justice of India, a former Judge of the Supreme Court, or an eminent individual meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Judicial Members are either former Judges of the Supreme Court or former Chief Justices of High Courts.
- At least 50% of the Members must belong to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, minorities, or women.
- Appointment of Members:
- The President of India appoints the Chairperson and Members based on the recommendation of a selection committee.
- The selection committee includes the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Speaker of Lok Sabha, the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, the Chief Justice of India or a nominated Judge, and an eminent jurist.
- Members serve a five-year term or until they reach the age of 70, whichever is earlier.
- The Chairperson’s salary, allowances, and conditions of service are equivalent to those of the Chief Justice of India.
- Members enjoy the same benefits as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
- Jurisdiction:
- Lokpal is authorized to investigate corruption allegations against the Prime Minister, Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and Group A, B, C, and D officials of the Union Government.
- Its jurisdiction extends to chairpersons, members, officers, and directors of boards, corporations, societies, trusts, or autonomous bodies established by Parliament or funded wholly or partially by the Union or State governments.
- It also includes entities receiving foreign contributions exceeding Rs. 10 lakh.
- Complaints must be filed in the prescribed form and relate to offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988. There are no restrictions on who can file a complaint.
- Upon receiving a complaint, the Lokpal may order a preliminary inquiry by its Inquiry Wing or refer the matter for investigation to agencies such as the CBI if a prima facie case is established.
- Complaints involving Central government employees are forwarded to the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC).
- Special Provisions for the Prime Minister:
- Lokpal cannot investigate allegations against the Prime Minister concerning international relations, external and internal security, public order, atomic energy, or space.
- Inquiries against the Prime Minister require approval from at least two-thirds of the Lokpal Members after the full bench considers the matter.
- Powers of Lokpal:
-
- Lokpal can oversee and direct the CBI.
- Investigating officers in cases referred by Lokpal cannot be transferred without its approval.
- Lokpal can authorize the CBI to conduct search and seizure operations related to corruption cases.
- The Inquiry Wing of Lokpal holds the powers of a civil court.
- Lokpal can confiscate assets, proceeds, or benefits acquired through corruption under special circumstances.
- It can recommend the transfer or suspension of public servants involved in corruption allegations.
- Lokpal has the authority to issue directives to prevent the destruction of records during preliminary inquiries.
- As per Section 48 of the Act, Lokpal must present an annual report to the President on its activities, which is subsequently tabled in both Houses of Parliament.
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
- News: The Union Minister of Communications, Sh. Jyotiraditya M. Scindia recently launched the Sanchar Saathi Mobile App and National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0.
- Sanchar Saathi Mobile App:
- Purpose: Sanchar Saathi Mobile App is a user-friendly platform aimed at strengthening telecom security and empowering citizens.
- Functionality: Offers essential tools to secure telecom resources and prevent fraud.
- Key Features:
-
- Chakshu – Reporting Suspected Fraud Communications (SFC): Enables users to report fraudulent calls and SMS directly through the app or from mobile phone logs.
- Mobile Connections in Your Name: Allows citizens to identify and manage all mobile connections issued in their name, ensuring unauthorized connections are detected and addressed.
- Blocking Lost/Stolen Mobile Devices: Provides a mechanism to block, trace, and recover lost or stolen mobile handsets efficiently.
- Verification of Mobile Handset Authenticity: Facilitates users to check the genuineness of mobile devices, ensuring the purchase of legitimate handsets.

- About National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0:
- Background: Builds upon the achievements of NBM 1.0, initiated under the National Digital Communications Policy, 2018.
- Objective: Accelerate India’s digital transformation by expanding broadband infrastructure and connectivity.
- Key Benefits:
-
- Optical Fiber Connectivity: Expand operational optical fiber cable (OFC) networks to 2.70 lakh villages by 2030 with a targeted uptime of 95%, up from the current ~50,000 villages.
- Broadband for Anchor Institutions: Provide broadband access to 90% of critical institutions like schools, primary healthcare centers (PHCs), Anganwadi centers, and Panchayat offices by 2030.
- Fiber Network Mapping: Achieve 100% mapping of fiber networks owned by government PSUs on the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan Platform (PMGS) by 2026. Utilize PMGS for planning additional BharatNet projects.
- Ease of Doing Business: Reduce the average disposal time for Right of Way (RoW) applications from the current 60 days to 30 days by 2030 (down from 449 days in 2019).
- Protection of Underground Telecom Infrastructure: Enhance the adoption of the ‘Call Before u Dig’ (CBuD) mobile app to safeguard underground telecom and utility infrastructure.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Work with Central Ministries, State governments, Union Territories (UTs), and municipalities to effectively implement the New RoW Rules 2024, framed under the Telecommunications Act, 2023.
UPSC GS 3
Information Ratio (IR)
- News: The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has directed mutual funds to disclose a new measure called the Information Ratio (IR) to reflect the risk-adjusted returns (RAR) of equity-oriented schemes.
- Definition: The Information Ratio (IR) is a financial metric used to assess how a portfolio or financial asset performs relative to a benchmark while considering the volatility of its returns.
- Benchmark: The benchmark is typically a market index such as the Nifty 50, but it may also represent a specific industry or market sector.

- Purpose:
- The IR evaluates how effectively a portfolio or asset matches or surpasses the returns of its benchmark.
- It also measures the consistency of a portfolio in outperforming the benchmark returns.
- Key Components:
- Standard Deviation (Tracking Error):
- The ratio incorporates tracking error, which reflects the standard deviation of the portfolio’s excess returns compared to the benchmark.
- A low tracking error indicates consistent performance in exceeding the benchmark, while a high tracking error suggests more volatile returns.
- Uses of Information Ratio:
-
- Performance Measurement: The IR is widely used by fund managers to assess the performance of their portfolios.
- Skill Comparison: It allows for the comparison of the skills and capabilities of fund managers who follow similar investment strategies.
- Investor Insights: The ratio provides investors with a clear understanding of a fund manager’s ability to consistently generate excess returns or even abnormally high returns over time.
- Fee Calculation: Some hedge funds and mutual funds use the IR to determine the performance fees charged to their clients.
See more: Foundation Course For IAS/IPS/UPSC: The Ultimate Guide
Facts for Prelims
Global Risks Report 2025
- News: The World Economic Forum Global Risks Report 2025 reveals a world teetering between technological triumph and profound risk.
- About Global Risk Report: The inaugural edition of the report was released in 2006, where extreme weather events were categorized as “environmental risks.”
- Current Edition: The findings are based on the Global Risks Perception Survey 2024-2025 (GRPS).

- Key Highlights of the Report:
- Time Horizons for Risk Assessment: Risks are evaluated across two time frames:
-
- Short-term (1-2 years): To address immediate challenges.
- Long-term (10 years): To guide policymakers in addressing future threats.
- Risk Categories: Risks are classified under five domains:
- Economic.
- Environmental.
- Geopolitical.
- Societal.
- Technological.
- Top Risks Identified:
- Short-term risks (1-2 years):
- Misinformation and disinformation.
- Extreme weather events.
- State-based armed conflicts.
- Long-term risks (10 years):
- Extreme weather events.
- Biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse.
- Critical changes to Earth’s systems.
- Short-term risks (1-2 years):
- Interconnected Risk Landscape: The global risk environment is influenced by interactions among four critical spheres:
- Technological.
- Geostrategic.
- Climatic.
- Demographic.
- These dynamics are expected to intensify over the next decade, creating a web of complex and interconnected challenges.
- Focus on Climate Pollutants: The report underscores the urgent need to mitigate short-lived climate pollutants, such as:
- Black carbon.
- Methane.
- Hydrofluorocarbons.
- These pollutants have significant adverse effects on both the environment and public health.

