GS Paper 1
Auroras
- News: The Chandrayaan-2 orbiter and Aditya-L1 spacecraft have captured images of solar flares occurring behind auroras.
- Understanding Auroras:
- Auroras are natural phenomena characterized by vibrant, swirling lights that illuminate the night sky.
- They manifest in various colors, including blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- They are commonly observed near the poles of both the northern and southern hemispheres.
- In the north, this display is called the aurora borealis; in the south, it is known as the aurora australis.

- Causes of Auroras:
- Auroras occur as a result of solar activity originating from the Sun’s surface.
- The Sun emits a continuous stream of charged particles known as the solar wind, along with magnetic fields.
-
- Solar winds are ejections of charged particles from the Sun’s atmosphere, mostly composed of protons and electrons.
-
- When the solar wind interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field (magnetosphere ), some charged particles are trapped and directed towards the planet’s poles.
- Upon entering the Earth’s upper atmosphere, these particles collide with gases, producing luminous displays.
- When solar wind particles collide with oxygen, a green colour light is produced.
- Interaction with nitrogen produces shades of blue and purple.
- Expanding Auroras:
-
- Under certain conditions, auroras extend beyond polar regions and reach midlatitudes.
- This phenomenon typically occurs during periods of heightened solar activity, marked by solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- A solar flare is a tremendous explosion on the Sun that happens when energy stored in ‘twisted’ magnetic fields (usually above sunspots) is suddenly released.
- Coronal Mass Ejections, or CMEs, are explosive bursts of solar plasma and magnetic field that fly away from the Sun.
- The increased intensity of the solar wind during these events can trigger geomagnetic storms, disrupting the Earth’s magnetic field and allowing auroras to be visible at lower latitudes.
GS Paper 2
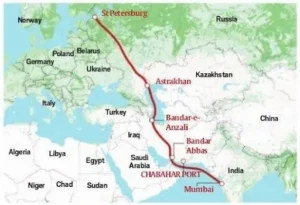
Chabahar Port Pact
- News: India and Iran have signed the Chabahar port operation pact.
- Parties: The signing of a new 10-year Contract between India Ports Global Ltd (IPGL) and the Ports & Maritime Organisation of Iran (PMO) recently took place.
- Key Facts:
- Under the Contract, IPGL will commit to further equipping and operating the port for the duration of the Contract.
- At the end of the 10-year period, both sides would further extend their cooperation in Chabahar.
- IPGL will invest approximately 120 million USD in equipping the port.
- India has also offered an IN credit window equivalent to USD 250 million, for mutually identified projects aimed at improving Chabahar-related infrastructure.
- Chabahar Port:
- The Chabahar Port is an India-Iran flagship project that serves as an important transit port for trade with Afghanistan and Central Asian countries, which are landlocked countries.
- India has been involved in upgrading its facilities to make it a viable transit route for Indian goods bound for Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- A memorandum of understanding for the development of the Chabahar port by India was signed in May 2015.
- Significance for India:
- Trade and Cooperation: Chabahar port operation pact is expected to enhance trade, marine cooperation, and transshipment.
-
-
- Aims to boost trilateral trade between India, Iran, and Afghanistan.
-
-
- Regional Connectivity: Chabahar port is a crucial trade link connecting India with Afghanistan and Central Asian countries.
-
-
- Its development is key to improving regional connectivity and promoting economic growth.
-
-
- Strategic Importance: Located in Iran’s Sistan-Baluchistan province, Chabahar is a deep-water port with substantial strategic value.
-
-
- Provides India with an alternative route to access Afghanistan and Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan.
-
-
- India’s Commitment: The agreement highlights India’s dedication to investing further in Chabahar port, enhancing its efficiency and capacity.
-
-
- India plans to use the port for humanitarian aid shipments, showcasing its commitment to regional development beyond commercial interests.
-
-
Read also: Kalapani Land Dispute between India and Nepal: Origin, Challenges and Resolution | UPSC
Vibrant Village Programme
- News: India’s Vibrant Village Programme seeks boost from private sector.
- Definition: Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under Ministry of Home Affairs launched in Feb 2023.
- Aim:
- Comprehensive development of villages of blocks on northern border thus improving the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- This will help in encouraging people to stay in their native locations in border areas.
- This will aid in reversing the outmigration from these villages adding to improved security of the border.
- Target Areas: This initiative envisages comprehensive development of identified villages in Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, and UT of Ladakh.
- Components:
- The programme includes both components of Central Sector Schemes (CS) and Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSSs) in the identified focused areas of intervention.
- Creation of opportunities for livelihood generation through:
- Promotion of tourism and cultural heritage.
- Skill development and entrepreneurship.
- Development of cooperative societies including agriculture/horticulture and cultivation of medicinal plants/herbs.
- Providing road connectivity to unconnected villages.
- Development of housing and village infrastructure.
- Enhancing energy access including renewable energy.
- Improving television and telecom connectivity.
- Implementation Strategy:
-
- The scheme aims to identify and develop economic drivers in northern border villages by leveraging local resources.
- It includes developing growth centres using the “Hub and Spoke Model” to:
- promote social entrepreneurship,
- empower youth and women through skill development and entrepreneurship, and
- harness tourism potential by promoting local culture and heritage.
- Sustainable eco-agribusinesses will be developed using the “One Village-One Product” concept through community organizations, cooperatives, SHGs, and NGOs.
- The district administration, with Gram Panchayats, will create Vibrant Village Action Plans to ensure 100% saturation of Central and State schemes.
GS Paper 3
Zero-Day Vulnerability (ZDV)
- News: A new zero-day vulnerability has recently been identified in Google Chrome, sparking concerns among everyday users and cybersecurity experts.

- Definition: A zero-day vulnerability is a system or software vulnerability unknown to the vendor and for which no patch or means of mitigation are available at the time it is discovered.
- Zero-Day Attack: A zero-day attack occurs when threat actors develop and release malware that targets the zero-day vulnerability.
- Zero-Day Exploit: A zero-day exploit is the method hackers use to attack systems with a previously unidentified vulnerability.
- Risks: Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a high risk to organizations because:
- Heightened Risk Factors: ZDVs present a significantly increased risk to users as they are discovered before security researchers and software developers are aware of them.
- Cybercriminal Exploitation: Cybercriminals take advantage of ZDVs to exploit vulnerabilities and profit from their malicious activities, emphasizing the need for urgent action to address the issue.
- Extended Exposure: Systems vulnerable to ZDVs are exposed until the vendor releases a patch to rectify the identified flaw, leaving users vulnerable to potential attacks for an extended period.
Sea Anemone
- News: Researchers from the ICAR-National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources (NBFGR) have observed a significant occurrence of anemone bleaching near Agatti Island.
- Definition: The sea anemone (Actiniaria) is part of a family of aquatic animals distinguished by soft bodies and the ability to sting.
- Taxonomic Classification: Sea anemones, soft-bodied marine invertebrates, belong to the phylum Cnidaria, sharing kinship with corals, jellyfish, and sea pens.
- Habitat: They inhabit oceans worldwide, ranging from shallow waters to deep sea environments, with a majority thriving in coastal tropical regions.

- Diversity in Appearance:
-
- Exhibiting a diverse array of colors, shapes, and sizes, they establish symbiotic relationships with green algae, akin to corals.
- However, rising sea surface temperatures disrupt this association, leading to bleaching events.
-
- Symbiotic Bonds: A symbiotic relationship is one in which organisms, people, or things exist together in a way that benefits them all.
-
-
- The symbiotic relationship between an anemone and a clownfish (Amphiron ocellaris) is a classic example of two organisms benefiting the other.
- The anemone provides the clownfish with protection and shelter.
- The clownfish provides the anemone nutrients in the form of waste while also scaring off potential predator fish.
-
- Ecological Significance: Their presence in benthic ecosystems (lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean) plays pivotal roles in biogeochemical processes.
Soil Nailing
- News: Soil nailing can prevent landslips in the Nilgiris.
- Definition: Soil nailing is a geotechnical engineering technique aimed at reinforcing soil in specific areas to enhance its strength and stability.
- It involves inserting reinforcing elements into the soil to provide structural support.
- Basic Technique of Soil Nailing:
- The technique involves drilling multiple holes into walls or slope faces, followed by the insertion of nails into these pre-drilled holes.
- Subsequently, the holes are filled with grouting materials like concrete or shotcrete.
- Additionally, a drainage system is installed behind the soil nails to prevent water accumulation and associated pressure.
- Applications of Soil Nailing: Slope stabilization for infrastructure projects such as roadways and railways, providing excavation support for basements, tunnels, and trenches, as well as mitigating landslides.
- Limitations of Soil Nailing:
-
- Despite its effectiveness, soil nailing may not be suitable for all soil types, particularly loose soils.
- Furthermore, its successful implementation requires skilled personnel, and the long-term performance is contingent upon the quality of materials used.
PS4 Engine
- News: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently successfully tested PS4 Engine made with the help of additive manufacturing technology commonly known as 3D printing.
- Engine Specifications:
- The PS4 engine is a liquid rocket engine designed to utilize earth-storable bipropellant combinations.
- It employs Nitrogen Tetroxide as an oxidizer and Mono Methyl Hydrazine as fuel, operating in a pressure-fed mode.
- Application in PSLV:
-
- Primarily employed as the fourth stage engine in the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the PS4 engine boasts a thrust of 7.33 kN in vacuum conditions.
-
- Significance of 3D Printed PS4 Engine:
- Reduction in Complexity: The transition to 3D printing technology has significantly reduced the complexity of the PS4 engine, consolidating the number of parts from 14 components to a single-piece design.
- Savings in Raw Materials: Utilizing additive manufacturing has led to a remarkable 97.5% reduction in raw material usage per engine.
- This translates to a drastic reduction in metal powder consumption, from 565 kg in conventional manufacturing processes to merely 13.7 kg with 3D printing.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Production: The adoption of 3D printing has streamlined the production process, resulting in a 60% reduction in overall production time for the PS4 engine.
See more: Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Investment Models: Types, Advantages and Challenges | UPSC
Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) Technology
- News: Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change made it mandatory for all coal-based Thermal Power plants (TPP) to install Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) Technology.
- Definition:
- The Flue-Gas Desulfurization (FGD) process utilizes a set of technologies to remove sulfur dioxide (SO2) from the flue gas emissions of coal-fired power plants.
- FGD systems were developed as a response to the exhaust – flue gases – from fossil fuel-burning plants, principally coal-burning, that posed both an environmental and human health hazard.
- Flue Gas: It is produced when fossil fuels such as coal, oil, natural gas, or wood are burned for heat or power. It may contain pollutants such as particulates, sulfur dioxide, mercury, and carbon dioxide.
- Types:
- Dry FGD: In the process of dry scrubbing injection systems, lime is used as a reagent to react and remove gaseous pollutants.
- Wet FGD: The process of wet scrubbing typically utilizes an alkaline-based slurry of lime to scrub gases.
- Importance of FGD Technology for India:
- India’s energy generation installed capacity stands at 425 GW.
- The thermal sector holds a predominant position within the overall installed capacity, encompassing coal (48.6 per cent), gas (5.9 per cent), lignite (1.6 per cent), and a minimal share (<0.2 per cent) from diesel.
- India is the largest emitter of SO2 in the world, according to a 2019 Greenpeace study.
- In 2019, India emitted 21% of global anthropogenic (human-made) SO2 emissions nearly double that of the second-ranked global emitter, Russia.
- In fact, across India, only a combined capacity of 16.5 Gigawatts (GW) of coal plants have installed FGDs and Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion (CFBC) boilers equivalent to 5.9 GW.
- The CREA analysis found that 92 per cent of the country’s coal power plants function without FGDs.
Peregrine Falcon
- News: About 378,000 viewers watched peregrine falcons on the St Albans Cathedral website via a webcam in 2023.
- Distribution:
- One of the most widespread birds in the world.
- Found on all continents except Antarctica and on many oceanic islands.
- Habitat Preferences:
- Prefer open habitats such as grasslands, tundra, and meadows.
- Most common in tundra and coastal areas.
- Rare in sub-tropical and tropical habitats.

- Behavior:
- Active during the day.
- Primarily solitary when not breeding and establish and defend territories.
- Ecological Role:
- High-level predators.
- Play an important role in regulating populations of their prey, particularly pigeons and doves.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List status: Least Concern.
Facts for Prelims
Sahitya Akademi Fellowship
- News: Author Ruskin Bond receives Sahitya Akademi Fellowship.
- Sahitya Akademi Fellowship:
- It is the highest honor bestowed by the Akademi on a writer, reserved for ‘the immortals of literature’.
- Notable literary works by Ruskin Bond include “Vagrants in the Valley,” “Once Upon a Monsoon Time,” “Angry River,” “Strangers in the Night,” “All Roads Lead to Ganga,” among others.
- Sahitya Akademi Awards:
- These awards are annually presented by Sahitya Akademi, India’s National Academy of Letters, under the Ministry of Culture, instituted by the GoI to preserve and promote literature through accolades.
- Sahitya Akademi Awards stand as the second-highest literary honor following the Jnanpith award, established in 1954.
- Annually, 24 awards are conferred, covering 22 languages in the 8th Schedule, along with English and Rajasthani, with an equal number of awards for literary translations.
- Additionally, Sahitya Akademi engages in a Literary exchange program with various countries to enhance the global presence of Indian literature.
