UPSC GS 1
Jarawa Tribe
- News: For the first time in the history of India’s election process, the 19 members from the Jarawa Tribe in Andaman and Nicobar Islands had been included on the electoral roll of the Special Summary Revision-2025.
- Location and Habitat:
-
- The Jarawas are an indigenous tribal community residing in the Andaman Islands.
- They are primarily found in parts of the Middle Andaman and South Andaman Islands.
- Their habitat includes dense forests, mangroves, and unspoiled beaches, offering a rich natural environment.

- Classification and Origins:
-
- The Jarawas are recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- They are considered descendants of the now-extinct Jangil tribe.
- It is believed that their ancestors were part of the earliest successful human migrations out of Africa.
- Lifestyle and Culture:
- The Jarawas have traditionally been hunter-forager-fishermen, known for their skills in these practices.
- They are renowned as warriors who fiercely protect their territory from intruders.
- Their attire is minimal and functional, adapted to the tropical climate of the Andaman Islands.
- Physical and Nutritional Health:
- Members of the Jarawa Tribe are noted for their robust physiques and excellent nutritional health.
- Historical Context:
- The population of the Jarawas saw a sharp decline following the British colonial presence in the Andaman Islands, which began in 1789.
- Despite significant challenges, including British colonization and World War II, the Jarawas managed to survive.
- Interactions with Outsiders:
- Over time, interactions between the Jarawas and outsiders increased.
- Since 1997, they have initiated contact with settled populations, engaging in trade, interacting with tourists, seeking medical assistance, and even sending their children to schools.
- Current Population:
- The current population of the Jarawa Tribe is estimated to range between 250 and 400 individuals.
Read also: Conference of the Parties (COP 29) | UPSC
Baltic Sea
- News: The Swedish prime minister, Ulf Kristersson recently said the Baltic sea is now a “high risk” zone after a suspected sabotage attack on undersea cables.
- Location and Geographical Context:
- The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea situated in Northern Europe.
- It is a branch of the North Atlantic Ocean.
- The sea stretches northward from southern Denmark almost to the Arctic Circle, separating the Scandinavian Peninsula from the rest of continental Europe.
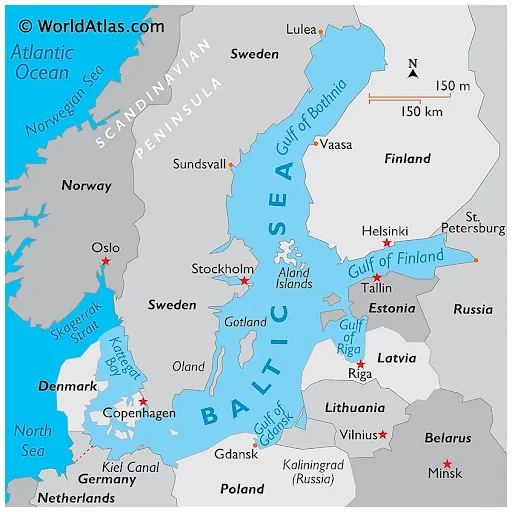
- Connections and Coastline:
-
- It is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits.
- The coastline of the Baltic Sea spans approximately 8,000 km.
- Surrounding Countries:
- The Baltic Sea is bordered by Denmark, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Russia, Finland, and Sweden.
- Size and Dimensions:
- The sea covers an area of around 377,000 sq. km.
- It has a length of approximately 1,600 km and a width of about 193 km.
- Canal Connections:
- It is linked to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal.
- The Kiel Canal connects it to the German Bight of the North Sea.
- Key Gulfs:
- The Baltic Sea features three prominent gulfs:
- Gulf of Bothnia (north).
- Gulf of Finland (east).
- Gulf of Riga (slightly south of the Gulf of Finland).
- The Baltic Sea features three prominent gulfs:
- Unique Characteristics:
- It is often regarded as the world’s largest brackish inland water body.
- Its salinity levels are lower than those of the world’s oceans due to the significant influx of freshwater from surrounding rivers and the sea’s shallow depth.
- Over 250 rivers and streams flow into the Baltic Sea, with the Neva River being the largest contributor.
- Islands and Archipelagos:
- The Baltic Sea is home to more than 20 islands and archipelagos.
- Gotland, located off Sweden’s coast, is the largest island in the sea.
UPSC GS 2
Bal Vivah Mukt Bharat Campaign
- News: Union Women and Child Development Minister Annapurna Devi recently launched the “Bal Vivah Mukt Bharat Campaign”.
- Launch and Objective: The campaign was initiated by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India, to eradicate child marriage across the country by engaging multiple stakeholders.
- Target Areas: It focuses on seven high-burden states—West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Tripura, Assam, and Andhra Pradesh—as well as nearly 300 districts with child marriage rates higher than the national average.
- Goal: States and Union Territories are encouraged to create action plans aimed at reducing child marriage rates below 5% by 2029.
- Child Marriage Statistics: According to government data, child marriage rates decreased from 47.4% in 2006 to 23.3% in 2019-21, reflecting significant progress.

- Key Features of the Campaign:
- Child Marriage Free Bharat Portal: A central component of the initiative is the launch of a dedicated portal to:
- Raise awareness about child marriage.
- Enable individuals to report cases.
- Monitor progress in preventing child marriage.
- Monitoring Mechanisms:
- The portal strengthens the supervision and evaluation of Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPOs) to ensure they actively prevent child marriages and assist affected individuals.
- Complaints lodged on the portal are directly forwarded to the respective CMPOs anywhere in the country.
- All states are instructed to register their CMPOs on the portal to enable real-time tracking of cases.
- Centralized Oversight:
- Nodal officers at the Centre will monitor the portal’s operations and ensure its effectiveness.
- Public Access and Support:
The campaign aims to improve public access to information, making it easier to report incidents and seek assistance through enhanced communication channels. - This initiative represents a significant step in fostering collective efforts to combat child marriage and support vulnerable individuals across India.
E-Daakhil Portal
- News: The Department of Consumer Affairs recently announced the successful nationwide implementation of the E-Daakhil portal, now operational in every state and union territory of India.
- Introduction:
- The E-Daakhil Portal was launched as a cost-effective, quick, and user-friendly mechanism for filing consumer complaints.
- It was introduced by the National Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission on 7th September 2020.

- Purpose: It aims to simplify and expedite the consumer grievance redressal process, eliminating the need for physical presence while filing complaints.
- Features:
- User-Friendly Platform:
- The portal is designed to provide an intuitive, easy-to-navigate interface for consumers.
- Consumers can effortlessly file complaints and access relevant consumer forums.
- Paperless Process:
- E-Daakhil ensures a completely paperless and transparent process, enabling consumers to file and track the status of their cases online.
- Authentication and Accessibility:
- Consumers or advocates can register on the portal by verifying their identity through an OTP sent to their registered mobile number or via an activation link sent to their email.
- Once registered, they can proceed to file complaints seamlessly.
- Convenience:
- The portal allows consumers to lodge grievances from the comfort of their homes, pay the necessary fees online, and monitor the case progress.
- Nationwide Reach:
- E-Daakhil is accessible to consumers across all parts of India, from urban metropolitan cities to remote rural areas.
- User-Friendly Platform:
- Impact: The portal has revolutionized consumer grievance redressal by making the process efficient, transparent, and widely accessible, empowering consumers to seek justice without geographical or logistical barriers.
President’s Colours
- News: General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff recently presented the prestigious President’s Colours to four battalions of the Mechanised Infantry.
- About President’s Colours:
- Definition:
- The President’s Colours is the highest honour bestowed upon a military unit, military training establishment, or State/UT Police Forces in India.
- It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service rendered to the nation during both peace and wartime.
- The honour is also referred to as Rashtrapati ka Nishaan in Hindi.

- Historical Context:
- Ancient Traditions:
- The origins of the President’s Colours trace back to ancient Indian military practices.
- Military units in ancient times carried dhwajas or patakas (flags) bearing the emblems or messages of their kings to demonstrate their allegiance and authority.
- During British Rule:
- The tradition continued under British rule, where military units carried the king’s or queen’s flag during marches.
- Transition to Indian Traditions:
- On November 23, 1950, the King’s Colour of the British Indian regiments was ceremonially retired at Chetwode Hall, Dehradun.
- It was replaced by the Colours of the President of the Republic of India.
- First Presentation:
- The Indian Navy was the first branch of the Indian Armed Forces to receive the President’s Colour. It was presented by Dr. Rajendra Prasad on May 27, 1951.
- Award Presentation:
- Nature of the Award: The President’s Colours is a special flag, also known as Nishaan, awarded to a military unit in a formal ceremony.
- Ceremonial Aspects: Typically, the award is presented by the President, who is the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces. If the President is unavailable, the honour is presented by the respective Service Chief.
- Design of the Flag: The flag features a golden border and displays the insignia of the respective military unit, training establishment, or police force in the centre. It may also include the unit’s motto, significant achievements, and details of notable battles.
- Role in Ceremonial Parades: The President’s Colour occupies a place of honour during ceremonial parades. Soldiers often march with this special flag during key events, such as the unit’s establishment anniversary or other significant occasions.
UPSC GS 3
Sabal 20 Logistics Drone
- News: In a significant move to bolster the Indian Army’s logistical capabilities, the private drone manufacturer EndureAir has delivered its innovative Sabal 20 logistics drone to the Eastern theatre of operations.

- Introduction:
- The Sabal-20 is an electric unmanned helicopter designed for aerial logistics, utilizing advanced variable pitch technology.
- It is developed by the private drone manufacturer EndureAir to meet challenging operational demands.
- Purpose: The drone is tailored to support precise logistics, long-distance deliveries, and high-altitude operations.
- Key Features:
- Tandem Rotor Configuration:
- The drone incorporates a tandem rotor design, ensuring exceptional stability and superior performance in high-altitude conditions.
- It minimizes turbulence risks and provides excellent lifting capacity across varied terrains.
- Payload Capacity:
- It can carry payloads up to 20 kg, equivalent to 50% of its weight, with options for scalability to meet future needs.
- VTOL Capability:
- Equipped with Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) technology, the drone can efficiently operate in confined spaces and rugged terrains.
- Low Noise Design:
- Its low RPM (revolutions per minute) design significantly reduces noise, making it suitable for stealth operations in sensitive missions.
- Autonomous Flight:
- The drone boasts advanced autonomous flight capabilities and intuitive controls, simplifying complex tasks.
- It ensures dependable performance, even beyond the operator’s line of sight.
- Applications: Sabal-20 is specifically crafted to meet diverse logistical needs, offering versatility for operations in challenging environments. It is particularly valuable for tasks requiring precision, efficiency, and reliability.
Network Readiness Index 2024
- News: India has improved its position by eleven slots and is now placed at 49th rank as per the Network Readiness Index 2024 (NRI 2024) report released on 21st November 2024, as against 60th rank scored in the NRI 2023 report.
- Overview:
- The Network Readiness Index (NRI) evaluates the network-based readiness of 133 economies.
- It is based on their performance across four key pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 different variables to assess each economy.
- The report is published by the Portulans Institute, an independent non-profit research and educational organization located in Washington, D.C.

- Key Findings from the 2024 Report:
- India’s Performance:
- India has made significant improvements in both its ranking and score. Its score increased from 49.93 in 2023 to 53.63 in 2024.
- India ranks highly in several indicators, demonstrating its growing technological capabilities.
- Top Rankings for India: India secured 1st rank in the following areas:
- AI scientific publications
- AI talent concentration
- ICT services exports
- India achieved 2nd rank in the following areas:
- FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions
- Mobile broadband internet traffic within the country
- International Internet bandwidth
- India earned 3rd rank in Domestic market scale.
- It placed 4th rank in annual investment in telecommunication services.
- Global and Regional Standing:
- India ranks 2nd among lower-middle-income countries, just behind Vietnam.
- Digital Progress and Strengths:
- The report highlights India’s substantial digital progress, particularly in technological innovation and digital transformation, as one of the nation’s notable strengths.
See more: India-Nigeria Relations: Key Insights for UPSC Exam
Red-breasted Flycatcher (Ficedula Parva)
- News: Red-breasted Flycatcher migrates from Eastern Europe to Hyderabad’s Ameenpur lake.
- Definition: This is a small (11-12 cm) passerine bird of the Old World Flycatcher family. It can be found occasionally feeding on figs (banyan, peepal) in our urban gardens.
- Breeding Grounds: These birds breed in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
- Winter Migration: During winter, they migrate to South Asia, where they find suitable conditions for survival.

- Dietary Habits: Their diet consists mainly of insects, caterpillars, and berries, which provide essential nutrition during their stay in South Asia.
- Features:
-
- Males have a reddish-orange throat that extends till the upper breast, whereas the females are overall brown.
- Males possess a certain grey cast to crown and face, which the female lacks, but both sexes have white sides to the long blackish tail, which they often cock while perched.
- Their wing-tips are downward drooping while it is perched. (Wing tips do not generally droop and are well in-sync with the flanks.)
- These birds can be distinguished from other orders by the arrangement of their toes — three pointing forward and one backward, a design that helps them to cling onto branches efficiently.
- Similar Species: The Taiga flycatcher bears a resemblance to this bird. However, it can be distinguished by the more limited orange throat in breeding males and its prevalence in eastern and northeastern India.
- Conservation Status: The bird is classified as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Historical Significance:
- Ameenpur Lake was once renowned for attracting migratory birds, particularly flamingos, during their seasonal migrations.
- However, due to various environmental factors, the lake’s habitat deteriorated over time, leading to a decline in bird sightings and disappointing birdwatchers.

