Introduction
- India’s recent expulsion of six Canadian diplomats, along with the withdrawal of its High Commissioner, reflects a significant escalation in tensions between the two countries.
- This diplomatic standoff has raised concerns about potential economic repercussions, including uncertainties around the $75 billion in Canadian pension fund investments in India, stalled trade negotiations, and disruptions to remittance flows from Canada to India.
Khalistan Movement and Its Role in Straining Relations
- A major source of friction between the two nations has been the Khalistan movement, which advocates for the creation of a separate Sikh state in India.
- This issue gained renewed attention following the assassination of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a pro-Khalistan leader in Canada, with Prime Minister Justin Trudeau accusing Indian agents of being involved.
- India denied the allegations, countering that Canada has provided shelter to Khalistani extremists, which has further deepened the diplomatic rift.
Historical Tensions: The Khalistan Issue in India-Canada Relations
During Punjab Militancy:
-
- 1982: In 1982, India asked Canada for extradition of a Khalistani terrorist (Talwinder Parmar) wanted in India for killing of police officers, Canada, under Pierre Trudeau, Justin Trudeau’s father, made an excuse and refused.
- 1984: The aftermath of Operation Bluestar, a military operation to remove militants from the Golden Temple, fueled support for the Khalistan movement among the Sikh diaspora.
- 1985: The bombing of Air India’s Kanishka flight by Babbar Khalsa, a Khalistani separatist group, resulted in the deaths of 331 civilians, further straining relations.
Read also: The Gig Economy in India: Growth, Challenges & Insights | UPSC
Post-2015 Developments:
-
- 2015: Justin Trudeau’s association with individuals sympathetic to the Khalistan cause began to strain bilateral relations.
- 2017: Punjab’s Chief Minister, Captain Amarinder Singh, declined to meet Canadian Defence Minister Harjit Singh Sajjan, accusing him of supporting separatists.
- 2018: India expressed displeasure when Jaspal Atwal, convicted of attempting to assassinate an Indian Cabinet minister in 1986, was invited to a dinner during Trudeau’s visit to India. Trudeau received a lukewarm welcome, greeted at the airport by India’s Minister of State for Agriculture rather than PM Modi.
- 2019: Canada’s public report on terrorism initially mentioned Sikh extremism and the Khalistan issue but was revised in 2019 to remove these references before the Vaisakhi festival.
- 2020: Trudeau’s public support for the farmers’ protests in India was criticized by New Delhi, which accused him of encouraging extremist elements.
- 2022: The alliance between Trudeau’s Liberal Party and the New Democratic Party (NDP), led by Jagmeet Singh, further strained ties, as Singh openly endorsed the Khalistan Referendum held in Canada.
- 2023: During the G20 Summit in New Delhi, PM Modi expressed serious concerns about continued anti-India activities by extremist elements in Canada.
Political Challenges and Decline
- Plebiscite in Kashmir (1948): Canada supported a United Nations-backed plebiscite in the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir in 1948, which strained diplomatic ties with India, as India viewed the issue as a matter of internal sovereignty.
- Nuclear Tests (1998): The Canada Deuterium Uranium (CANDU) reactor enabled the use of unenriched uranium for nuclear energy, benefiting developing nations like India. However, it also facilitated access to plutonium, raising concerns about nuclear weapons proliferation.
- The United States and Canada collaborated with India to develop the CIRUS reactor, commissioned in July 1960 under Homi Jehangir Bhabha’s leadership.
- Although Canada, under Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau, emphasized the programme’s peaceful intent, he warned that nuclear cooperation would cease if India tested a nuclear device.
- In 1974, India conducted a nuclear test at Pokhran using plutonium from the CIRUS reactor, calling it a “peaceful nuclear explosion.”
- However, Canada viewed it as a breach of trust, withdrawing support for India’s nuclear programme and recalling officials working on another reactor.
- India’s decision not to sign the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) further created a diplomatic divide that took years to mend.
- Khalistan Movement: One of the most persistent challenges in India-Canada relations has been the Khalistan issue. Canada has often been criticized by India for its perceived leniency towards Khalistani supporters within its borders. Some key examples include:
- Air India Bombing (1985): The bombing of Air India Flight 182, carried out by Khalistani extremists in Canada, resulted in the deaths of 331 people. India accused Canada of not doing enough to prevent such activities on its soil, a perception that continues to haunt the bilateral relationship.
- Invitation to Jaspal Atwal (2018): Jaspal Atwal, convicted for an assassination attempt on an Indian minister, was controversially invited to a dinner event with Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during his 2018 visit to India. This incident, coupled with Trudeau’s perceived soft stance on Khalistani elements, aggravated tensions between the two countries.
- Trudeau’s Support for Farmers’ Protests (2020): During the 2020-21 farmers’ protests in India, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau expressed public support for the protestors, which India viewed as an interference in its domestic affairs. This led to a formal diplomatic protest from India, accusing Canada of supporting extremist elements under the guise of human rights.
Current Diplomatic Fallout: Key Concerns
- Geopolitical Implications: The diplomatic standoff has geopolitical implications for India. If the allegations are proven, India’s G20 reputation could suffer. The crisis affects nations with ties to both India and Canada, including G7 members (US, UK, Germany, France, Italy, Japan) and Five Eyes allies (US, UK, Australia, New Zealand). These countries, also key Indian partners through the Quad and bilateral ties, now face a delicate balancing act.
- Impact on Trade Agreements: Talks on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between the two countries have stalled due to the diplomatic crisis, potentially derailing efforts to strengthen trade ties.
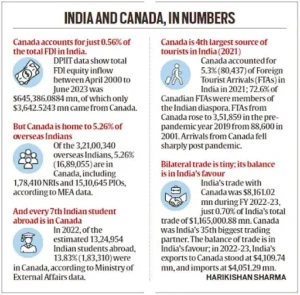
- Effect on Trade Relations: Canada accounts for about 1% of India’s trade and supplies 25% of its pulses and 5% of its fertilizers. The fallout threatens bilateral trade, with both countries standing to lose.
- Uncertainty for Canadian Investments: From 2020 to 2023, Canada ranked as the 18th-largest foreign investor in India, with investments amounting to $3.31 billion. Canadian pension funds, including CPPIB and CDPQ, have invested over $75 billion in Indian firms, such as Paytm and Kotak Mahindra Bank. The crisis raises concerns over the stability of these investments.
- Impact on Remittances: In 2023, India received $125 billion in remittances, with Canada being among the top 10 sources. Disruptions in people-to-people connections could impact these financial flows.
- Effect on Student Mobility: Canada is a preferred destination for Indian students, with over 427,000 Indian students currently enrolled. The diplomatic fallout may affect student mobility and educational opportunities.
Strategic Importance of India-Canada Relations
Indo-Pacific Cooperation:
-
- Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy highlights India as a vital partner in promoting stability and security in the region, with both nations sharing democratic values and a commitment to a rules-based international order.
- Canada’s view of India as a critical ally contrasts with its growing concerns over China’s increasing influence and authoritarianism in the Indo-Pacific.
- India’s participation in multilateral forums like the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad), where it cooperates with countries like the US, Japan, and Australia, aligns with Canada’s interests in maintaining a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
Economic and Trade Engagement:
-
- In 2022, India was Canada’s ninth-largest merchandise trading partner in the Indo-Pacific region, the 13th-largest merchandise trading partner globally and the 14th-largest destination for merchandise exports.
- Canada’s export of pulses to India, accounting for 25% of India’s pulse imports, remains a crucial component of the trade relationship.
- Additionally, Canada contributes to India’s fertilizer supply, which is critical for India’s agricultural sector.
- Canadian companies like Brookfield Asset Management and Fairfax Financial have significant stakes in Indian companies and infrastructure, exemplifying deep economic integration.
- Over 400 Canadian companies operate in India, while more than 1,000 are actively exploring business opportunities in sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and clean energy.
Development Cooperation:
-
- Canada has been an active partner in India’s development initiatives through its support for projects in health, education, and social welfare.
- Grand Challenges Canada, a non-profit organization, has funded 75 projects across India, investing $24 million in 2018-19 alone. These projects focus on innovations in healthcare, gender equality, and maternal and child health, aligning with India’s development goals.
- Furthermore, Canada has contributed to India’s efforts in climate change adaptation and renewable energy development, including providing technical and financial support for solar power projects under the International Solar Alliance, which India spearheaded.
Energy Sector Collaboration:
-
- India and Canada’s energy collaboration was formalized through the Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (NCA) in 2010. This agreement paved the way for India’s procurement of uranium, which is crucial for its nuclear energy program.
- Two countries have signed a long-term uranium supply agreement, ensuring that India could source uranium from Canada to fuel its growing nuclear energy needs. The deal, valued at $350 million, was a significant step toward enhancing India’s energy security.
- Additionally, Canadian companies like SNC-Lavalin have been involved in India’s nuclear power projects, providing technical expertise and infrastructure development support.
Science, Technology, and Space Cooperation:
-
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) have signed Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) to collaborate on space exploration and satellite technology.
- Antrix, ISRO’s commercial arm, has successfully launched several Canadian satellites into space, including NLS-14 and NLS-15 on the PSLV-C49 mission in 2020.
Education and Student Exchange:
-
- Since 2018, India has been the largest source of international students in Canada, with over 427,000 Indian students currently pursuing higher education in Canadian universities and colleges.
- The Canada-India Institutional Cooperation Project and Scholarship Programs have further bolstered academic exchange and fostered research collaborations between Indian and Canadian universities.

Indian Diaspora:
-
- Canada is home to one of the largest Indian diasporas in the world, with 1.6 million people of Indian origin making up more than 3% of Canada’s total population.
- Members of the Indian community in Canada have made notable contributions to the country’s economy, politics, and society. For example, 22 Members of Parliament of Indian origin serve in Canada’s House of Commons, including high-profile figures like Defence Minister Harjit Singh Sajjan and Minister of International Development Bardish Chagger.
Additional Challenges in India-Canada Relations
- Khalistani Separatism: One of the most prominent challenges in India-Canada relations is the issue of Khalistani separatism. Canada’s balancing act of accommodating Sikh political aspirations domestically, while maintaining diplomatic ties with India, has strained relations.
- Attacks on Indian Consulates and Diaspora: The Indian consulates and diaspora in Canada have been targeted by Khalistani supporters and other extremist groups, further souring bilateral relations.
- Vandalism of Hindu Temples (2023): Several Hindu temples in Canada were vandalized by pro-Khalistani groups in 2023, sparking outrage in India. The BAPS Swaminarayan Temple in Toronto was one of the key sites attacked, with anti-India slogans spray-painted on its walls.
- Trade Barriers: Despite strong economic potential, trade between India and Canada faces several obstacles, including complex regulations, bureaucratic hurdles, and market protectionism.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) Stalemate: Negotiations have been ongoing for several years, but little progress has been made. Canada’s concerns over India’s regulatory environment, such as its stringent labor laws and intellectual property rights issues, have slowed the process. Similarly, India has raised concerns over market access barriers, particularly in agriculture and services sectors.
- Bilateral Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement (BIPPA): This is another stalled negotiation which has remained in limbo due to disagreements over investor protections and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Protectionist Measures: Canada’s protectionist policies, particularly in its agricultural sector, have restricted access for Indian goods, such as spices and textiles. Meanwhile, India has imposed high tariffs on Canadian imports, including dairy products and lumber, further hindering the expansion of bilateral trade.
- Canada-China Relations: Canada’s relationship with China has been another point of friction in its ties with India.
- Huawei and 5G Network Controversy: Canada’s initial hesitation in banning Huawei from participating in its 5G network development, despite pressure from its Western allies, including India, raised concerns.
- China’s Influence in Canadian Politics: One significant example of Chinese interference in Canada’s elections came to light in 2021, when reports emerged that Chinese operatives had attempted to influence the outcome of the 2019 federal election. This revelation led to widespread concern about the integrity of Canada’s political system and raised questions about the country’s ability to safeguard its democracy from foreign influence.
Read also: 11 Classical Languages of India – Complete UPSC Guide
Way Forward
- Constructive Engagement with the Sikh Diaspora: India needs to engage constructively with the Sikh diaspora, counter misinformation, and highlight the positive developments in Punjab.
- New Cooperation Framework: Both countries should explore pragmatic areas of cooperation, such as trade, infrastructure, and energy, to rebuild ties.
- Dehypenation of Political and Economic Issues: India and Canada must separate political disputes from trade relations to resume negotiations on the Free Trade Agreement.
- Civil Society and Track II Diplomacy: Encouraging dialogue through civil society initiatives can foster better understanding and conflict resolution.
- Responsible Media Reporting: Media should ensure balanced reporting to accurately reflect the complexities of bilateral relations and the progress being made toward reconciliation.

