UPSC GS 2
Women Councillors
- News: A report by Janaagraha has revealed that Tamil Nadu has the highest number of women councillors.
- Findings of the Report:
- Women’s Representation in Urban Local Bodies:
- Nearly 46% of councillors in India are women, demonstrating significant gender representation in local governance.
- In 19 out of 21 capital cities with active urban local bodies, such as Patna, Shimla, Ranchi, and Bhubaneswar, women’s representation exceeds 60%.
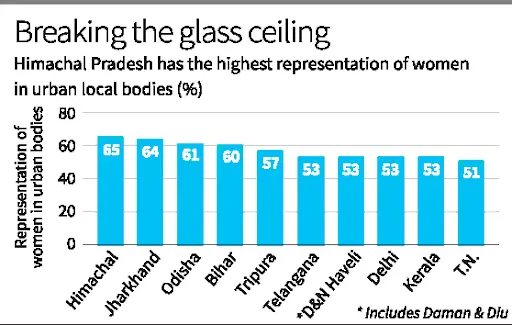
- States Leading in Women Councillors:
- Tamil Nadu ranks highest in the number of women councillors.
- Other leading states in the top 10 include Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Bihar, and Chhattisgarh.
- Policy Initiatives to Promote Women’s Participation:
- Seventeen states have enacted legislation mandating a 50% reservation for women in local bodies, exceeding the constitutional requirement of 33%.
- Political Representation of Women in India:
- Early Years (1952–1971):
- In 1952, women constituted just 4.41% of the Lower House (Lok Sabha).
- This percentage increased to over 6% in the Lok Sabha elections held a decade later.
- However, the representation declined to below 4% in 1971, despite India being led by its first woman Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi, at the time.
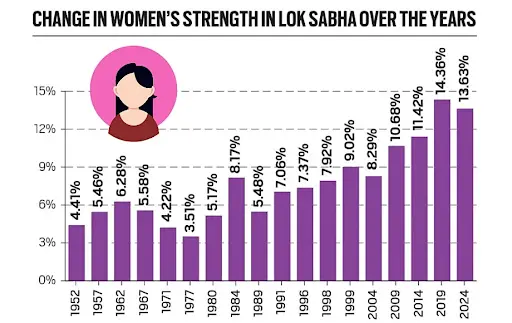
- Recent Trends (2009–2024):
- Women’s representation has gradually increased over the decades, with notable exceptions.
- It surpassed the 10% mark in 2009 and reached a peak of 14.36% in 2019.
- In 2024, 74 women MPs were elected, out of which 43 are first-time parliamentarians.
- The average age of women MPs is 50 years, younger than the overall House average of 56 years.
- Women MPs are as educated as their male colleagues, with 78% having completed undergraduate studies.
- State Legislative Assembly Representation:
- Women’s representation in State Legislative Assemblies remains low across most states.
- Top Performers: Chhattisgarh leads with 14.4% women legislators, followed by West Bengal (13.7%) and Jharkhand (12.4%).
- Global Comparison:
- IPU ‘Women in Parliament’ Report 2021:
- The global average for women in parliaments was 26.1%, significantly higher than India’s representation.
- India ranks below 140 other nations regarding women’s presence in national legislatures.
- Comparative Performance:
- While women’s representation in the Lok Sabha has risen post-independence, reaching ~16% in the 17th Lok Sabha, India lags behind many countries in Africa and South Asia, including Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
Read also: High-Performance Buildings | UPSC
Hamara Samvidhan – Hamara Samman Campaign
- News: The ‘Hamara Samvidhan Hamara Samman’ campaign was organised to commemorate 75th anniversary of the adoption of the Indian Constitution at IIT Guwahati.
- About the Campaign:
- The ‘Hamara Samvidhan – Hamara Samman’ campaign celebrates the 75th anniversary of the adoption of the Indian Constitution and India’s transition to a Republic.
- It aims to deepen public understanding of the Constitution and inspire citizens to recognize and exercise their rights.
- The initiative underscores the Constitution’s role as the supreme legal document that shapes India’s governance structure and ensures the protection of citizens’ rights.
- Launch Details:
- The campaign was officially launched on January 24, 2024, by the Hon’ble Vice President of India.
- The event was held at the Dr. B.R. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
- Objectives of the Campaign:
- Promote awareness of the Indian Constitution among citizens.
- Highlight the Constitution’s significance as a cornerstone of India’s governance.
- Encourage active citizen participation in understanding and safeguarding legal rights.
15 Women Who Contributed In Making The Indian Constitution
|
- Event Highlights:
- Planting Saplings:
- A tree-planting activity was organized under the ‘Ek Ped Maa Ke Nam’ initiative to honor the 15 women members of the Constituent Assembly.
- The saplings symbolized the Constitution’s foundational values of justice, equality, and freedom.
- Samvidhan Katta Magazine:
- A special magazine featuring 75 real-life accounts of how the Constitution impacts everyday life was launched.
- Comic Book:
- A comic book showcasing the stories of 10 beneficiaries of the Tele Law and Nyaya Bandhu programs was unveiled to make constitutional rights relatable and accessible.
- Podcasts:
- Eight podcasts were released to guide citizens on utilizing the Constitution to protect their rights through initiatives like Tele Law and Nyaya Bandhu.
- Tributes:
- Women in the Constituent Assembly, including Late Smt. Leela Roy, were honored for their contributions.
- Special homage was paid to Syed Muhammad Saadulla, Assam’s representative in the Drafting Committee, and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar for his invaluable role in framing the Constitution.
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)
- News: India, in collaboration with the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), is set to host the Global Learning and Development Framework (GLDF) Results Management Training soon.
- Establishment: WADA was founded in 1999 as an international independent organization to lead a global movement towards eliminating doping in sports.
- Governance and Funding: Its governance and funding are based on an equal partnership between the global sports community and governments from across the world.
- Primary Role: WADA’s main responsibility is to develop, harmonize, and coordinate anti-doping regulations and policies across all sports and nations.
- Key Activities:
- Conducting scientific research to advance anti-doping efforts.
- Providing education to raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Strengthening anti-doping capabilities.
- Overseeing the implementation of the World Anti-Doping Code, which standardizes anti-doping policies worldwide.

- Governance Structure:
- Foundation Board:
- The Foundation Board is WADA’s primary policy-making body and consists of 42 members.
- It includes representatives from the Olympic Movement (such as the IOC, National Olympic Committees, International Sports Federations, and athletes) and government officials from all five continents.
- Executive Committee (ExCo):
- Comprising 16 members, the Executive Committee is responsible for managing and running the agency.
- It oversees all operational activities and administers WADA’s assets as delegated by the Foundation Board.
- Formation:
-
- Background: Following revelations that severely impacted the cycling world in 1998, the International Olympic Committee (IOC) called for a World Conference on Doping in Sport.
- First World Conference: The First World Conference on Doping in Sport, held in Lausanne, Switzerland, from February 2–4, 1999, resulted in the Lausanne Declaration on Doping in Sport.
- Creation of WADA: The Lausanne Declaration called for establishing an independent international anti-doping agency.
- WADA was officially founded on November 10, 1999, in Lausanne to promote and coordinate the global fight against doping in sports.
- The agency became operational in time for the Sydney Olympic Games in 2000.
- Legal Status: WADA operates as a Swiss private law, not-for-profit foundation.
- Location: Its official seat is in Lausanne, Switzerland, while its headquarters are based in Montreal, Canada.
UPSC GS 3
Global Soil Conference
- News: The Global Soils Conference 2024 is taking place in New Delhi.
- Organized by: The Indian Society of Soil Science, New Delhi, under the aegis of the International Union of Soil Sciences, Italy.
- In Collaboration With: The Indian Council of Agricultural Research and the National Academy of Agricultural Sciences, New Delhi.
- Theme: The conference’s theme is “Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services.”
- Objective of the Conference:
- Empowering Farmers: The conference seeks to provide farmers with education, support, and modern scientific tools aimed at enhancing the sustainability of agricultural practices.
- Role of Youth and Women: There is a strong emphasis on encouraging young people and women researchers to take the lead in innovating solutions to soil-related challenges.
- Global Partnerships: The event promotes collaboration among scientists, policymakers, NGOs, and other stakeholders, with the goal of developing practical solutions for soil health challenges.

- Focus Areas of the Conference:
-
- Soil as a Global Concern: The conference recognized soil erosion and degradation as major global challenges that threaten sustainable development. It also emphasized the critical importance of soil health for the well-being of humans, animals, and plants.
- Sustainable Land Management: Addressing the global need for sustainable agricultural practices is a key focus. This includes restoring soil health and promoting international collaboration to share innovations and implement scalable solutions for soil conservation.
- SDGs and Soil Health: The conference highlighted the importance of soil conservation in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It stressed the need for resilient ecosystems to ensure food security and sustainable agriculture.
One Day One Genome Initiative
- News: The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC) have launched the ‘One Day One Genome’ initiative.
- Launched by: The initiative has been launched by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) in collaboration with the Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC).
- Purpose: The aim of the initiative is to showcase India’s distinctive microbial diversity and highlight its importance in environmental, agricultural, and human health contexts.
- Lead Organizations: The initiative is led by the Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council-National Institute of Biomedical Genomics (BRIC-NIBMG) under the Department of Biotechnology.

- Key Objectives of the Initiative:
-
- Highlight India’s Microbial Diversity: The initiative emphasizes the unique bacterial species present in India and their significant roles in maintaining ecological balance, supporting agricultural processes, and improving human health.
- Promote Genome Sequencing: It aims to enhance the understanding of microbial potential through genome sequencing, allowing for the discovery of critical enzymes, antimicrobial resistance factors, and bioactive compounds.
- Enhance Accessibility and Innovation: The initiative seeks to make annotated microbial genome data publicly accessible. This move encourages further innovation and research in microbiology and its practical applications.
- Significance of Microorganisms
- Environmental Contributions: Microorganisms play an essential role in driving biogeochemical cycles, soil formation, and organic waste degradation. They also help in mineral purification and methane production, contributing to planetary homeostasis.
- Agricultural Benefits: Microbes facilitate nutrient cycling, nitrogen fixation, and soil fertility. They also assist in pest and weed control, help manage stress responses in crops, and promote plant growth by enhancing nutrient and water uptake.
- Human Health Impact: Microorganisms outnumber human cells in the body and are crucial for digestion, immunity, and mental health. They form symbiotic relationships that help combat infectious diseases.
- What are Microbes?
- Definition: Microbes are microscopic organisms that include bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, and protists. Due to their tiny size, they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Structure: Microbes can be single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea, or multicellular, like some fungi. They are classified into two categories: prokaryotes (organisms without a nucleus, e.g., bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotes (organisms with a nucleus, e.g., fungi and protists).
- Functions: Microbes are integral to ecosystems, functioning as decomposers that break down organic matter. They also contribute to nitrogen fixation, which supports plant growth, and some microbes act as pathogens causing diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
‘Sanyukt Vimochan 2024’
- News: The Indian Army successfully conducted the Multilateral Annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise, ‘Sanyukt Vimochan 2024’ at Ahmedabad and Porbandar on 18-19 November 2024.
- About the Exercise: The Indian Army successfully carried out its annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) exercise, named Sanyukt Vimochan 2024.
- Location: The exercise took place in Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
- Conducted By: It was organized by the Konark Corps of the Southern Command of the Indian Army.
- Participants: The exercise included representatives from nine friendly foreign countries, which encompassed nations from the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), the Indian Ocean Region, and Southeast Asia.
- Aim: The main goal of Sanyukt Vimochan 2024 was to enhance India’s disaster response capabilities. The exercise aimed to improve coordination among various agencies during natural disasters and to strengthen international cooperation in disaster management.

- Tabletop Exercise (TTX):
- Theme: The Tabletop Exercise (TTX) focused on the impact of a cyclone on the coastal region of Gujarat, particularly the Okha-Porbandar coastline.
- Aim: The aim of the TTX was to improve interagency coordination and foster brainstorming of effective strategies for disaster relief.
- Key Outcomes: The exercise highlighted the gaps in the current disaster response mechanisms and helped in the development of more robust and effective joint disaster response protocols.
- Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- Scenario Simulated: The Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration simulated a cyclone scenario, showcasing practical disaster response operations in real-time.
- Event Details: The event involved reconnaissance and surveillance of the affected areas, personnel deployment for rescue operations, casualty evacuation, and the rehabilitation of citizens affected by the disaster.
Cloud Seeding
- News: With the air in Delhi becoming an unbreathable haze of dust and pollutants leaving residents gasping for relief, cloud seeding or artificial rain is being touted as a short-term solution to clear the smog.
- Definition: Cloud seeding, also referred to as artificial rain, is a weather modification technique designed to enhance precipitation by introducing specific substances into clouds to stimulate rainfall.
- How Cloud Seeding is Performed?
- Scientific Basis: The process involves dispersing materials such as silver iodide, potassium iodide, or dry ice into clouds to encourage the formation of rain or snow.
- Mechanism: These substances act as nuclei around which water droplets condense. This increases the likelihood of precipitation as these droplets grow larger and heavier, eventually falling as rain or snow due to gravity.
- Methods of Dispersion:
- Aircraft can release the seeding agents directly into clouds.
- Ground-based generators can release the particles into the atmosphere.
- Rockets are occasionally used to distribute the materials in some regions.
- Purpose: By increasing the size of cloud droplets, cloud seeding facilitates precipitation, making it a useful tool in regions experiencing drought or water shortages.
- Cloud Seeding and Air Pollution Mitigation:
- Impact on Air Quality: Cloud seeding is viewed as a potential method to reduce air pollution by promoting rainfall that can “wash away” particulate matter and other airborne pollutants.
- Mechanism for Cleaning Air: The increased precipitation can help settle dust and pollutants in the atmosphere, providing temporary improvement in air quality.
- Challenges in Cloud Seeding:
- Dependence on Weather Conditions: The effectiveness of cloud seeding relies heavily on the presence of suitable atmospheric conditions, including clouds with sufficient moisture.
- Limitations: Without adequate cloud formation or moisture content, the technique may not yield the desired results.
Lipids
- News: A recent study highlights that low metabolic flexibility to lipids in skeletal muscles may contribute to ectopic lipid accumulation, which in turn triggers metabolic disturbances.
- Definition and Function: Lipids are fatty, oily, or waxy compounds vital for various bodily functions, serving as structural components and energy reserves in living cells.
- Roles in the Body:
- Lipids regulate hormones, support nerve impulse transmission, and cushion vital organs.
- They store energy in the form of body fat and contribute to cell membrane integrity by controlling the passage of substances in and out of cells.
- Chemical Composition: Lipids are primarily made up of hydrocarbons, which are in their most reduced form. This composition makes them an efficient energy source, as their oxidation releases significant amounts of energy.
- Solubility: Due to their non-polar nature, lipids are insoluble in water but dissolve in non-polar solvents like chloroform.
- Types of Lipids:
- Phospholipids: Essential components of cell membranes.
- Sterols: Includes various forms of cholesterol, crucial for maintaining cell structure and producing hormones.
- Triglycerides: Represent over 95% of dietary lipids and serve as the body’s main energy storage form.
- Sources of Lipids: Lipids are abundant in fried foods, animal fats, and dairy products such as butter, cheese, and cream.
- Health Implications:
- Benefits: Lipids are critical for maintaining health by supporting cellular function, energy storage, and organ protection.
- Excessive Consumption Risks: Overconsumption can lead to conditions like atherosclerosis (arterial hardening), hypertension (high blood pressure), and coronary artery disease, posing significant health risks.
Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024)
- News: The Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024) was inaugurated recently at a ceremony organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
- About Bharat NCX 2024:
- Bharat NCX 2024 is a significant initiative aimed at strengthening India’s cybersecurity resilience.
- It is organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS), Government of India, in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
- The event brings together over 300 participants from government agencies, public organizations, and the private sector, focusing on protecting critical information infrastructure through training, live-fire exercises, and strategic simulations.
- Key Features:
- Comprehensive Cyber Defense Training:
- Provides hands-on training in cyber defense strategies and incident response techniques.
- Includes live-fire simulations replicating cyberattacks on IT and operational technology (OT) systems.
- Collaborative Platforms:
- Offers a platform for government and industry stakeholders to work together on enhancing cybersecurity preparedness.
- Strategic Decision-Making Exercise:
- Engages senior management from various sectors in simulated national-level cyber crisis scenarios.
- Aims to improve their strategic decision-making skills in high-pressure situations.
- CISO’s Conclave:
- Features Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) from government, public, and private sectors.
- Includes panel discussions, insights on cybersecurity trends, and exploration of government initiatives to enhance security.
- Cybersecurity Startup Exhibition:
- Highlights innovative cybersecurity solutions developed by Indian startups.
- Demonstrates their contributions to strengthening the nation’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Leadership and Capacity Building:
- Focuses on leadership engagement to tackle emerging cyber challenges.
- Enhances the collective capacity to respond effectively to cybersecurity threats.
Facts for Prelims
World Toilet Day 2024
- News: World Toilet Day is celebrated on 19 November every year.
- Origin and Recognition: World Toilet Day was first established in 2001 and gained official recognition by the United Nations in 2013.
- Focus Areas: It sheds light on the critical issues tied to inadequate sanitation, including public health challenges, environmental consequences, and the loss of human dignity.
- Global Impact:
- Unsafe water and poor sanitation contribute to the deaths of approximately 1,000 children under five each day.
- Implementing better sanitation systems has the potential to save an estimated 1.4 million lives annually.

- Theme for 2024: The theme, “Sanitation for Peace”, emphasizes the importance of access to safe sanitation as a foundation for achieving global harmony.
- Key Message: This year’s observance underscores the role of safe toilets and robust sanitation systems in fostering a healthier, fairer, and more peaceful world.

