UPSC GS 1
Sri Singeeswarar Temple
- News: A set of copper plate inscriptions with two leaves dating back to the 16th Century CE have been discovered at the Sri Singeeswarar temple at Mappedu village in Tiruvallur district recently.
- Sri Singeeswarar Temple: Sri Singeeswarar Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, located in Mappedu Village near Perambakkam in the Thiruvallur District of Tamil Nadu.
- Construction: The temple was established in 976 AD by Aditya Karikalan II, father of the renowned Chola emperor Rajaraja Cholan, who built the Thanjavur Big Temple.

- Enhancements: In 1501, during the reign of King Krishnadevaraya, Dalavai Ariyanadha Mudaliar, his viceroy, utilized his influence to construct the Rajagopuram (main tower), the compound wall, and a 16-pillared mandapam.
- Architectural Style:
-
- Design: The temple showcases Dravidian architecture, characterized by elaborate sculptures and intricate carvings.
- Rajagopuram: The towering entrance gateway consists of five tiers.
-
- Presiding Deity: The temple enshrines Lord Shiva in the form of Singeeswarar.
- Lingam: In the sanctum, Singeeswarar is represented as a slightly larger-than-usual Shiva Lingam, revered by devotees.
Read also: One Nation One Election: Impact on Indian Democracy | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
5th National Water Awards 2023
- News: President Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 in New Delhi today.
- Inception: The inaugural National Water Awards were launched by the Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation in 2018.
- Objectives:
-
- These awards aim to recognize and celebrate the efforts of individuals and organizations nationwide in achieving the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat.’
- They also strive to raise awareness among the public regarding the significance of water and encourage the adoption of optimal water usage practices.
-

- Categories: The 5th National Water Awards, held in 2023, included awards across nine categories:
-
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (excluding schools or colleges)
- Best Civil Society
-
- Winners: In the Best State category, Odisha was awarded the first prize, followed by Uttar Pradesh in second place. Gujarat and Puducherry shared the third position.
- Recognition: Each award recipient will receive a citation, a trophy, and cash prizes in specific categories.
ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
- News: The 15th edition of the ITU (International Telecommunications Union) Kaleidoscope Academic Conference began recently in New Delhi.
- Definition: ITU Kaleidoscope 2024 is an international conference organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which is the United Nations’ specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICT).
- Purpose of the Kaleidoscope Conferences:
-
- Kaleidoscope conferences are part of ITU’s broader initiative to promote dialogue among the academic, research, and industry sectors in ICT.
- The goal is to drive innovation and collaboration in the development of global standards.
-
- Theme: Innovation and Digital Transformation for a Sustainable World
- Goals of Kaleidoscope 2024: The primary goals of Kaleidoscope 2024 include:
-
- Promoting collaboration between academia and industry to facilitate the development of international ICT standards.
- Showcasing the latest research and innovations that could shape the future of telecommunications.
- Addressing global challenges to ensure that advancements in ICT yield broader societal benefits.
-

- Features of ITU Kaleidoscope 2024:
-
- Technical Paper Presentations: Academics and researchers will present their findings on relevant topics, with selected papers published in the conference proceedings.
- Keynotes and Panel Discussions: Industry leaders, policymakers, and academic experts will engage in discussions about current trends, challenges, and opportunities in ICT.
- Workshops and Tutorials: These hands-on sessions will allow participants to explore specific technologies and applications in greater detail.
-
- Key Themes for ITU Kaleidoscope 2024:
-
- 5G and Beyond: Examining the development of 5G networks and the future of mobile connectivity, including the integration of 6G, new spectrum management, and IoT technologies.
- AI and Machine Learning: Investigating the role of artificial intelligence in telecommunications, including network automation and enhanced service delivery.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy: Addressing security challenges within global ICT systems, focusing on personal data protection, infrastructure security, and trust frameworks.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Highlighting ICT’s contribution to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in education, healthcare, and smart cities.
- Quantum Communications: Exploring the effects of quantum computing and quantum cryptography on secure communications networks.
- Digital Inclusion: Ensuring equitable access to digital technologies, tackling the digital divide, and promoting inclusive growth through ICT.
-
UPSC GS 3
Satellite Spectrum
- News: Union Communications Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia has clarified that spectrum for satellite communication (satcom) would be allocated “administratively”, rather than through an auction of airwaves.
- Definition:
-
- Satellite spectrum pertains to the array of radio frequencies utilized by satellites for communication with ground stations, other satellites, and various terrestrial devices.
- These frequencies belong to the electromagnetic spectrum, specifically within the radio wave category, and are designated for a range of satellite services, including communication, broadcasting, navigation, and Earth observation.
- Unlike terrestrial spectrum, which is used for mobile communication, satellite spectrum has no national territorial limits.
-
- Regulation:
-
- The management of satellite spectrum usage is overseen by international organizations such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- The ITU plays a crucial role in coordinating and allocating frequencies to minimize interference among diverse satellite systems and other communication methods.
-
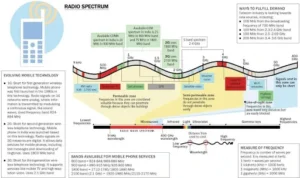
- Satellite Frequency Bands:
-
- L-band (1-2 GHz): Utilized for GPS and mobile satellite services.
- S-band (2-4 GHz): Employed for weather radar, air traffic control, and mobile satellite services.
- C-band (4-8 GHz): Frequently used for satellite TV broadcasting and data communications.
- X-band (8-12 GHz): Primarily allocated for military applications involving radar and communication.
- Ku-band (12-18 GHz) and Ka-band (26-40 GHz): Designed for satellite television, internet services, and high-throughput data transmission.
-
- What is Airwaves/Spectrum?
-
- Airwaves refer to radio frequencies found within the electromagnetic spectrum that facilitate the wireless transmission of information for various services, including telecommunications.
-
- Management and Allocation:
-
- The government oversees the management and allocation of airwaves, granting access to companies or sectors for their specific use.
- To distribute airwaves, the government conducts auctions for a predetermined amount of spectrum within designated frequency bands, enabling operators to provide communication services to consumers.
-
Naseem-Al-Bahr
- News: The Indian Navy and Royal Navy of Oman successfully conducted the ‘Naseem Al Bahr’ joint naval exercise off Goa’s coast recently, strengthening mutual cooperation.
- Definition: The Indo-Oman Naval Exercise, known as Naseem Al Bahr, took place off the coast of Goa from 13 to 18 October 2024.
- Exercise Participants:
-
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand; Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Royal Navy of Oman (RNOV): Vessel Al Seeb
-

- Phases of the Exercise: The exercise comprised two main phases:
-
- Harbour Phase (13-15 October 2024):
- This phase included professional interactions between the participating navies, featuring Subject Matter Expert Exchanges and planning conferences.
- Additionally, sporting events and social engagements were organized to foster relationship building.
- Sea Phase (16-18 October 2024):
- Joint maritime operations involved gun firings at inflatable surface targets and close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- The ships executed complex naval maneuvers and conducted Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopters from INS Trikand performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- The Indian Navy’s Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data.
- Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb for a day to enhance interoperability.
-
- Key Outcomes:
-
- Enhanced Interoperability: The exercise fostered mutual understanding and the sharing of best practices between the two navies.
- Strengthened Collaboration: It reinforced India’s commitment to cooperation with friendly nations in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Successful Engagement: The exercise effectively achieved its objectives of building stronger naval ties and operational cohesion between the Indian Navy and the Royal Navy of Oman.
-
Coelogyne Tripurensis
- News: A significant discovery has been made in Tripura’s Jampui Hills with the identification of a new orchid species named Coelogyne tripurensis.
- Description: Coelogyne tripurensis is a newly identified species of orchid.
- Discovery Location: It was found in the moist broadleaf forests of the Jampui Hills in Tripura, located at the westernmost edge of the Indo-Myanmar Biodiversity Hotspot.

- Genus Information:
-
- This genus comprises approximately 600 species, with its native range including the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and the Southwest Pacific Islands.
- Most species in this genus are primarily epiphytic, though some are rarely lithophytic or terrestrial.
- Coelogyne species are highly regarded by horticulturists due to their significant ornamental value and relatively straightforward cultivation requirements.
-
- Taxonomic Section:
-
- The new species is categorized under the section Fuliginosae, which is notable for its unique characteristics, such as striking flowers, a distinctive labellum, and prominent keels.
- Species in this section exhibit considerable phenotypic plasticity, making them difficult to classify precisely.
-
Yars Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM)
- News: Russia has tested Yars missiles in drills near Moscow, signaling nuclear deterrence amid Ukraine conflict and raising concerns of nuclear escalation.
- Overview of RS-24 Yars:
-
- The RS-24 Yars, also known as Topol-MR, is a Russian intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) introduced in 2007 to enhance the country’s nuclear deterrence capabilities.
- It is an advanced version of the Topol-M missile, featuring improvements in range, mobility, and warhead capacity.
- The Yars plays a crucial role in Russia’s strategic nuclear forces, forming a backbone of its long-range strike capability.
-

- Key Features of the Yars Missile: The Yars missile can be deployed in two primary configurations:
- Silo-Based: Launched from hardened underground silos for better protection against enemy attacks.
-
- Mobile Launchers: Mounted on large transporter-erector-launchers (TELs), which provide mobility and make detection and destruction by adversaries more difficult.
- Range: The Yars has a range of up to 11,000 km (approximately 6,835 miles), enabling it to strike targets far beyond Russia’s borders, including most of Europe, the United States, and other strategic locations.
- Warhead: The Yars is equipped with multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing it to carry multiple nuclear warheads that can strike different targets, enhancing its lethality and complicating interception by missile defense systems.
- Accuracy and Guidance: It benefits from advanced guidance systems, ensuring high accuracy. Its MIRVs can deliver warheads with precision, making strikes against strategic enemy targets more effective.
-
- Strategic Importance:
-
- The Yars missile is a critical component of Russia’s nuclear triad, which includes land-based ICBMs, submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers.
- This triad provides Russia with a diversified and resilient nuclear deterrent, ensuring a capability to retaliate in the event of an attack.
-
Read also: Bulldozer Justice: A Controversial Approach to Law & Order | UPSC
Zeilad Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: The Rongmei Naga Council Manipur (RNCM), a powerful Naga citizens’ group, has strongly opposed the proposed oil exploration at Zeilad Wildlife Sanctuary in Manipur‘s Tamenglong district.
- Definition: Zeilad Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Tamenglong district of Manipur, near the Indo-Myanmar border. It was established in 1982 and spans an area of 21 sq. km.
- Geographical Setting: Positioned within the basin of the Barak River, the sanctuary features a hilly landscape.
- Lakes: The sanctuary is home to a cluster of seven lakes, including Zeilad, Guiphuapzei, Nrouzei, Tuangpuizei, Goulungzei, and Napsemzei, with Zeilad Lake being the largest and most prominent.
- Vegetation: The forest consists of semi-evergreen and wet hill forests, providing a suitable habitat for diverse species.
- Flora: Michelia champaca, Schima wallichii, Toona ciliata, Gmelina arborea, Mangifera indica, Messua ferrea, and Castanopsis hystrix.
- Fauna: Tigers, leopards, leopard cats, small Indian civets, common langurs, Hoolock gibbons, Great Indian Hornbills, barking deer, and flying squirrels.
- Birds: Great Indian Hornbill
- Aquatic Fauna: Marine species found in the lakes include fish, tortoises, and pythons.
- Ecological Significance

