UPSC GS 1
Shale Gas
- News: Shale gas generation potential has been found in eastern South Karanpura oalfield in Jharkhand.
- About Shale Gas:
-
- Shale gas is a type of natural gas trapped within shale rock formations, found in microscopic or submicroscopic pores.
- It is composed of naturally occurring hydrocarbon gases derived from the decomposition of organic matter such as plant and animal remains.
- Typically, shale gas contains 70–90% methane (CH4), making it a key hydrocarbon targeted by exploration companies.
-
- Extraction Process:
-
- Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking): Deep vertical holes are drilled into the shale rock, followed by horizontal drilling to maximize gas extraction.
- Fracking fluids (a mixture of water, sand, and chemicals) are pumped at high pressure into the drilled holes. This process opens up fractures in the rock, allowing trapped gas to flow into collection wells. Once extracted, the gas is piped away for commercial use.
-
- Promising Shale Gas Reserves in India:
-
- Cambay Basin
- Gondwana Basin
- Krishna-Godavari (KG) Basin
- Cauvery Basin
- Indo-Gangetic Basin
- Assam & Assam-Arakan Basin
-
- Applications of Shale Gas:
-
- Electricity Generation: A cleaner alternative to coal in power plants.
- Domestic Use: Employed for heating and cooking in households.
- Industrial Use: Utilized in chemical industries as a feedstock and fuel.
-
Read also: 11 Classical Languages of India – Complete UPSC Guide
UPSC GS 2
National Sports Governance Bill, 2024
- News: Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports has put in public domain the Draft National Sports Governance Bill, 2024 for inviting comments/suggestions of general public and the stakeholders, as part of pre-legislative consultation process.
- Objectives:
-
- Promote Sports and Athlete Welfare: Create frameworks to advance sports and enhance athlete well-being, ensuring governance follows ethical principles.
- Institutional Capacity and Standards: Align governance of sports federations with global best practices, Olympic values, and ethical guidelines.
- Sports Dispute Resolution: Establish a unified and fair mechanism to address sports-related conflicts and grievances efficiently.
-
- Key Features:
- Sports Regulatory Board of India:
-
- A central regulatory authority responsible for recognizing and overseeing National Sports Federations (NSFs).
- Offers autonomy and flexibility in governing sports bodies without rigid rules for NSF recognition.
-
- Governance Structure for Sports Bodies:
-
- Indian Olympic Association (IOA), Paralympic Committee of India (PCI), and NSFs to align with global standards.
- Executive Committees limited to a maximum of 15 members, with leadership positions open to qualified Indian citizens.
- Encourages full-time, salaried management led by a CEO to ensure professionalism.
- Mandates adherence to Olympic, Paralympic, and relevant international regulations.
-
- Ethical and Governance Standards:
-
- Enforces mandatory ethical practices through dedicated Ethics and Dispute Resolution Commissions.
- Promotes transparency, integrity, and fairness in administrative procedures.
- Compliance with international standards essential for hosting global sports events.
-
- Athletes Commissions:
-
- Mandatory creation of Athletes Commissions within the NOC, NPC, and all NSFs to represent athlete interests in policy-making.
- Government will provide financial assistance to support these commissions.
-
- Athlete Representation:
-
- Athletes of Outstanding Merit (SOMs) will constitute 10% of voting members in General Bodies, ensuring their voices are heard.
- SOMs will also hold seats in Executive Committees to provide athlete insights in governance.
- Gender diversity will be prioritized in athlete representation.
-
- Safe Sports Policy:
-
- Focuses on ensuring athlete safety, with a special emphasis on minors and women.
- Implements the Prevention of Sexual Harassment (POSH) Act, 2013, to address harassment and abuse in sports.
-
- National Sports Promotion Organisations (NSPOs):
-
- Sets guidelines for recognizing and regulating NSPOs, empowering NGOs and private entities to contribute to sports development.
-
- Appellate Sports Tribunal:
-
- Establishes a dedicated tribunal to resolve sports-related disputes, reducing the need to rely on civil courts.
- Provides a single-window system for quicker, more cost-effective dispute resolution.
-
- Ad-hoc Normalisation Committees:
-
- Authorizes the Sports Regulatory Board to set up ad-hoc committees to temporarily manage federations in cases of non-compliance or suspension.
-
- Global Anti-Doping and Ethical Compliance:
-
- Prioritizes ethical conduct and strict anti-doping compliance, with severe penalties for violations.
- Requires all bodies to follow the IOC Code of Ethics and relevant national laws.
-
- Public Accountability and Transparency:
-
- Makes the NOC, NPC, and NSFs accountable under the RTI Act, except for performance and medical-related information.
-
- Inclusivity and Gender Representation:
-
- Ensures at least 30% female representation in governing bodies to promote gender equality in sports.
-
- Sports Election Panel:
-
- Empowers a dedicated Sports Election Panel to conduct fair elections for IOA, PCI, and NSFs, led by experienced election officers.
-
- Restrictions on National Symbols:
-
- Limits the use of the Indian flag or national insignia to recognized sports bodies only.
- Unauthorized usage may attract penalties, including imprisonment of up to one year, a fine of ₹10 lakh, or both.
-
Tele MANAS
- News: The Union Health Ministry celebrated the completion of two years of National Tele Mental Health Programme, Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking across States (Tele MANAS) on World Mental Health Day.
- Key Launches and Features:
- Tele MANAS App & Video Call Facility:
-
- Provides mental health support with resources on self-care, identifying distress signals, and managing early signs of stress and anxiety.
- Interactive features include mind challenges, games, and mindfulness exercises to enhance user engagement.
- Offers free, confidential, 24/7 access to trained mental health professionals across India.
-
- Video Consultation Feature:
-
- Upgraded from the audio-only facility, this feature enables brief physical or Mental State Examinations (MSE) during consultations.
- Initially launched in Karnataka, Jammu & Kashmir, and Tamil Nadu, with plans for nationwide expansion.
-
- Call Handling Milestone:
-
- Since its launch, Tele MANAS has managed over 1.45 million calls, reflecting strong user engagement and accessibility.
-
- Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States (Tele-MANAS) Initiative
-
- Network of Excellence: Operates through 23 tele-mental health centres of excellence, providing support across the country.
- Aim: Deliver free tele-mental health services nationwide, 24/7, with a special focus on remote and under-served areas.
- Initiated by: Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- Nodal Centre: National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS).
- Technology Support: Provided by the International Institute of Information Technology-Bangalore (IIITB).
- Functioning and Helpline:
- A toll-free 24/7 helpline (14416) is available for callers to choose services in their preferred language.
- Calls are routed to Tele-MANAS cells in respective states or union territories for appropriate support.
- Two-Tier System:
- Tier 1: State-level Tele MANAS cells, including trained counsellors and mental health specialists.
- Tier 2: Specialists from the District Mental Health Programme (DMHP) or Medical Colleges for physical consultations, with access to e-Sanjeevani for audio-visual interactions.
-
10-Point Plan
- News: Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced a comprehensive 10-point plan to strengthen India-ASEAN relations during the 21st India-ASEAN Summit in Vientiane, Laos.
- 10-Point Plan for India-ASEAN Relations:
-
- ASEAN-India Year of Tourism (2025): India will contribute USD 5 million for joint tourism activities.
- Celebration of a Decade of Act East Policy: Events include Youth Summit, Start-up Festival, Hackathon, Music Festival, and Delhi Dialogue.
- Women Scientists Conclave: Organized under the ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund to promote women in science.
- Increased Scholarships for ASEAN Students: Scholarship capacity at Nalanda University will be doubled. New scholarships will be introduced in Indian Agricultural Universities.
- Review of Trade in Goods Agreement: Scheduled for completion by 2025 to enhance bilateral trade.
- Disaster Resilience Initiatives: India will contribute USD 5 million to support disaster resilience projects.
- Health Ministers’ Track: New mechanism to improve health resilience and collaboration among ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN-India Cyber Policy Dialogue: Regular cyber policy dialogues to enhance digital and cyber security.
- Green Hydrogen Workshop: A workshop will explore sustainable energy possibilities through green hydrogen.
- ‘Plant a Tree for Mother’ Campaign: ASEAN leaders are invited to participate in this climate resilience initiative.
-
- Key Themes of Cooperation:
-
- Regional Security: Focus on peace, stability, maritime safety, and free navigation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Maritime Security: Commitment to peaceful resolutions in the South China Sea, following UNCLOS and the Declaration on the Conduct of Parties.
- Defense Cooperation: Areas of focus include cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, and joint military exercises.
- Digital Transformation and Emerging Technologies: Key areas include AI, Blockchain, IoT, Robotics, Quantum Computing, and 6G technology. Joint efforts will focus on digital public infrastructure, fintech, and cybersecurity.
- Trade Relations: India’s trade with ASEAN has doubled in the past decade, now exceeding USD 130 billion.
-
UPSC GS 3
Murine Typhus
- News: A 75-year-old man from Kerala who recently travelled to Vietnam and Cambodia has been diagnosed with the bacterial disease murine typhus.
- Overview:
-
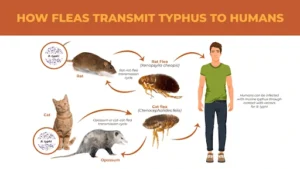
- Murine typhus is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Rickettsia typhi, which is transmitted by fleas.
- It is also referred to as endemic typhus, flea-borne typhus, or flea-borne spotted fever. Rodents such as rats, mice, and mongoose act as the primary reservoirs for the disease.
- Fleas infected with Rickettsia typhi can remain carriers throughout their lifespan and may also infest domestic animals like cats and dogs, contributing to the disease’s spread.
-
- Transmission of Murine Typhus:
-
- Mode of transmission: Infected flea feces entering through skin abrasions or cuts.
- Other exposure: Contact of mucous membranes (such as the eyes or mouth) with infected flea feces.
- Non-human-to-human spread: The disease does not transmit directly from person to person or from people to fleas.
- Geographical presence: It is commonly found in tropical and subtropical coastal areas where rodent populations are abundant. In India, murine typhus has been reported in regions like the Northeast, Madhya Pradesh, and Kashmir.
-
- Symptoms of Murine Typhus:
-
- Incubation period: Symptoms typically appear 7 to 14 days after exposure.
- Early symptoms:
- Fever
- Headaches
- Muscle and joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomach aches
- Later symptoms: In some cases, skin rashes develop a few days after the onset of initial symptoms.
- Duration: Symptoms generally resolve within two weeks, but complications can prolong the illness for months if untreated.
-
- Treatment for Murine Typhus:
-
- Antibiotic therapy: Doxycycline is the preferred treatment for the disease.
- Importance of early diagnosis: Timely identification is crucial to prevent severe complications.
- Risk of fatality: Although rare, the disease can become life-threatening if left untreated for more than one or two weeks.
- Vaccine status: No vaccine is currently available for murine typhus.
-
- Prevention of Murine Typhus:
-
- Regularly wash pets like cats and dogs to prevent flea infestations.
- Monitor for signs of fleas and seek flea treatment if necessary.
- Keep rodents and small mammals out of the household environment.
- Maintain good hygiene to avoid exposure to flea feces.
-
Rare Diseases
- News: The Delhi High Court has issued directions aimed at improving the availability of so-called “orphan drugs”, which are medications used to treat “rare diseases”.
- Orphan Drugs and Rare Diseases:
-
- Orphan drugs are medications used to treat rare diseases.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) defines rare diseases as debilitating, lifelong conditions that affect 1 or fewer people in 1,000.
- In India, around 55 rare diseases are recognized, including:
- Gaucher’s disease
- Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs)
- Only 5% of rare diseases have available therapies, and less than 10% of patients receive disease-specific care due to high treatment costs.
-
- Classification of Rare Diseases in India: Rare diseases in India are grouped into three categories based on the complexity and duration of treatment:
-
- Group 1: Diseases that can be treated with one-time curative procedures.
- Group 2: Conditions that require long-term or lifelong treatment, but at a relatively lower cost.
- Group 3: Diseases where effective treatments are available, but they are expensive and require lifelong therapy.
-

- National Policy and Funding for Rare Diseases:
-
- In 2021, the government launched the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD).
- Financial assistance up to Rs 50 lakh is provided for treatment at identified Centres of Excellence (CoEs).
- The CoEs include AIIMS in Delhi, PGIMER in Chandigarh and the Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research at Kolkata’s SSKM Hospital.
- The Govt has also opened a Digital Portal for Crowdfunding & Voluntary Donations with information about patients and their rare diseases, the estimated cost of treatment, and bank details of the CoEs.
- Donors can choose the CoE and patient treatments they wish to support.
- Each CoE also has its own Rare Disease Fund, which is used with approval from its governing authority.
-
- Cost of Orphan Drugs:
-
- Many medicines and therapies for rare diseases are patented, which makes them very expensive.
- Companies importing these drugs face 11% customs duty and 12% GST. The Delhi High Court has set a 30-day deadline for processing tax exemptions under customs, GST, and Income Tax laws.
- The Department of Pharmaceuticals issued an order in 2019 exempting orphan drugs from price controls.
-
- Patents Act of 1970:
-
- If treatments or medicines for rare diseases are not available, the government can, under the Patents Act of 1970, allow a third party to manufacture them against payment of a royalty to the patent holder.
- The government can also acquire patents to ensure the availability of medicines if the patent holder does not provide them.
-
Read also: Artificial Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Guide | UPSC
Dragon Drones
- News: Videos have emerged on social media of the Ukrainian military dropping ‘Dragon’ drones on the Russian army in the Russia-held region of Kharkiv in Ukraine.
- What are Dragon Drones?
-
- Dragon drones are high-precision drones that release thermite, a mixture of aluminium and iron oxide.
- Thermite, developed over a century ago to weld railroad tracks, can trigger a self-sustaining reaction when ignited.
- It burns through nearly everything, including clothes, trees, and military-grade vehicles, and can even burn underwater.
- On human contact, thermite causes severe burns and bone damage, often fatal.
- The combination of thermite and drones makes these weapons highly effective and difficult to counter.
-

- History of Thermite Use:
-
- World War I: German zeppelins dropped bombs containing thermite, marking an early use of this substance in warfare.
- World War II:
- Both Allied and Axis forces used thermite-laden bombs in aerial campaigns.
- Allies dropped approximately 30 million 4-pound thermite bombs on Germany and another 10 million on Japan.
- Thermite hand grenades were employed to disable artillery pieces without explosions.
-
- Modern Conflicts: Thermite is now used by espionage agents and special operations teams due to its intense burning capability without causing explosions.
- Legal Aspects of Thermite Use in War:
-
- Thermite is not banned under international law, but restrictions exist.
- The Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (Cold War-era guidance by the United Nations) bars the use of incendiary weapons like thermite against civilian targets.
- Protocol III of the Convention allows thermite use only against military targets, due to its potential to cause severe burns and respiratory injuries.
-
Komodo Dragons
- News: The Indonesian government plans to implement partial closures of Komodo National Park in 2025 to alleviate the growing pressure on its unique ecosystem caused by rising tourist numbers.
- About Komodo Dragon:
-
- Scientific Name: Varanus komodoensis
- Family: Varanidae (Monitor lizards)
- Distribution: Found on Komodo Island and a few neighboring islands in the Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia.
-
- Key Features:
-
- Size: Grows up to 3 meters (10 feet) in length and can weigh around 135 kg (300 pounds).
-
- Appearance:
-
- Adults have a stone-gray color with large, distinct scales.
- Juveniles are more vibrant in color, often with noticeable patterns.
-

- Tongue: Yellow and forked.
- Reproduction:
-
- Primarily reproduces sexually.
- In the absence of males, females can produce offspring via parthenogenesis (asexual reproduction).
-
- Venomous Bite:
-
- The bite contains toxins that induce blood loss and shock in prey, leading to immobilization.
-
- Behavior:
-
- Capable of running swiftly and is known to attack and occasionally kill humans.
- Lifespan is around 30 years.
-
- Conservation Challenges:
-
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
- Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and mitigating human-wildlife conflict.
-
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.

