UPSC GS 2
Schedule 6 of the Indian Constitution
- News: Sonam Wangchuk and other activists from Ladakh have demanded that Schedule 6 of the Indian Constitution be made applicable to the Union Territory.
- Objectives of the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution: The Sixth Schedule aims to safeguard the administration and governance of tribal areas in select northeastern states while protecting the rights and identity of tribal communities:
- Administration of Tribal Areas: Provides for the administration of tribal regions in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram through autonomous bodies.
- Protection of Tribal Land and Resources: Ensures that tribal land and resources are not transferred to non-tribal individuals or communities.
- Preservation of Tribal Identity: Seeks to prevent the exploitation or marginalization of tribal communities by non-tribal populations while promoting their cultural and social identity.
- Provisions of the Sixth Schedule:
-
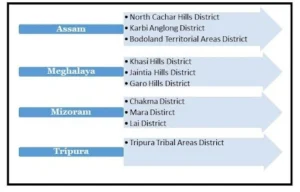
- Article 244(2): The provisions under the Sixth Schedule apply specifically to the administration of tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions:
- Tribal regions in these four states are administered as autonomous districts.
- If different Scheduled Tribes reside within a district, the Governor may create autonomous regions by dividing the district accordingly.
- Reorganization Powers:
- The Governor has the authority to organize or reorganize autonomous districts, modify their boundaries, or change their names as necessary.
- Constitution of District Councils and Regional Councils:
- Each autonomous district will have a District Council with a maximum of 30 members.
- Up to four members are nominated by the Governor, and the remaining are elected through adult suffrage.
- In regions designated as autonomous, a separate Regional Council will be constituted.
- Legislative Powers of District and Regional Councils:
- Councils can make laws on matters like land management, forests (excluding reserved forests), and inheritance of property.
- Regulation of Trade and Money-Lending:
- Councils have the authority to regulate money-lending and trade by non-tribal residents in their districts.
- Governor’s Assent:
- All laws enacted by the Councils require the approval of the Governor.
- Administration of Justice in Autonomous Areas:
- The District and Regional Councils can establish Village and District Council Courts to handle disputes involving Scheduled Tribe members.
- The Governor determines the extent to which the High Court will have jurisdiction over cases handled by these Council Courts.
- Council Courts cannot adjudicate cases involving offenses punishable by death or imprisonment of five years or more.
- Financial and Administrative Powers of Councils:
- Councils can collect land revenue and impose taxes on professions, trades, vehicles, and animals.
- Councils have the power to grant licenses and leases for mineral extraction within their jurisdictions.
- Councils can establish and manage primary schools, markets, roads, dispensaries, fisheries, and transport services.
- Exemptions from Parliamentary and State Laws:
- Acts passed by Parliament or state legislatures either do not apply or apply with modifications in autonomous districts and regions.
- Appointment of Commission:
- The Governor has the authority to appoint a commission to investigate and report on any aspect of the administration of autonomous districts or regions.
-
- Tribal Areas Governed Under the Sixth Schedule:
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- News: The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
Read also: South India’s Ageing Population: Healthcare & Social Services | UPSC
- Definition:
-
- The IAEA is the leading global intergovernmental platform for scientific and technical collaboration in the nuclear field.
- It is recognized as the “Atoms for Peace and Development” organization within the UN framework, promoting safe, peaceful, and secure applications of nuclear technology.
-
- Establishment and Reporting: Founded as an autonomous entity through the IAEA Statute, it operates independently of the United Nations. However, it reports to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.

- Membership: Currently, 178 countries are members of the IAEA.
- Organizational Structure
-
- General Conference: All member states participate in the annual General Conference to approve the budget, debate policies, and review the agency’s programs.
- Board of Governors: Comprising 35 members, the Board meets around five times a year. It oversees key functions, approves safeguards agreements, and appoints the director general.
- Secretariat: The day-to-day operations are managed by the Secretariat, led by the director general.
-
- Functions of the IAEA:
-
- The IAEA collaborates with member states and partners worldwide to ensure the peaceful, secure, and safe use of nuclear science and technology.
- It conducts inspections, monitors nuclear activities, analyzes information, and takes measures to ensure nuclear materials are not diverted for weapons-related purposes.
- The IAEA enforces comprehensive safeguards under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), acting as the first defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Facilitates the sharing of scientific and technical knowledge among member states.
- Enhances global, national, and regional capabilities to respond to nuclear or radiological emergencies to minimize their impact.
-
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
e-Shram: One- stop solution Portal
- News: Union Labour Minister Mansukh Mandaviya has launched ‘e-Shram – One Stop Solution‘ for workers in the unorganized sector.
- Objective: eShram aims to provide unorganised workers with seamless access to various Social Security Schemes through the eShram portal.
- Purpose: The main goal of the eShram One Stop Solution is to streamline the registration process for unorganised workers and enhance their access to government welfare schemes. This platform serves as a link connecting workers to the multitude of benefits provided by the government, ensuring a simpler and more transparent registration experience.
- Data Integration: The initiative involves consolidating and integrating information from multiple Central Ministries and Departments into a unified repository.
- Integrated Welfare Schemes: Key welfare schemes, including One Nation One Ration Card, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, National Social Assistance Programme, National Career Service, and Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan, have been integrated with the eShram portal.

- What is the eShram Portal?
-
- Launch and Purpose: The eShram portal was introduced by the Ministry of Labour and Employment in 2021 to establish a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers.
- Registration Process: Registration on the portal is fully Aadhaar verified and Aadhaar seeded, allowing any unorganised worker to register based on self-declaration.
-
- Occupational Scope: The portal permits unorganised workers to register themselves under a self-declaration process across 400 occupations categorized into 30 broad occupation sectors.
India-China Agreement
- News: India and China reached an agreement on patrolling arrangements along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) after a series of discussions and deliberations at both diplomatic and military levels.
- Important Points of the Agreement:
- Announcement of Agreement:
-
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar announced the development on October 21, 2024, crediting “patient and persevering diplomacy” for the progress.
- The agreement reflects joint efforts by both countries to de-escalate border tensions.
-
- Restoration Agreement:
-
- India and China have agreed to restore the Line of Actual Control (LAC) to its pre-May 2020 status, allowing both nations to resume patrolling.
- This marks a major diplomatic breakthrough in resolving the prolonged border standoff that began in 2020.
-

- Restoration of Patrols:
-
- Both Indian and Chinese troops will now resume patrolling along the LAC following the arrangements that existed before 2020.
- This resolves the deadlock that had disrupted patrols in critical areas for more than four years.
-
- Troop Deployment During the Standoff:
-
- At the height of the standoff, both nations deployed more than 50,000 troops along the LAC, along with heavy firepower and military equipment.
- The new agreement seeks to reduce tensions in this heavily fortified region.
-
- Geopolitical Impact:
-
- The timing of the agreement, just before Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s planned visit to the BRICS summit in Russia, could boost India’s diplomatic standing.
- However, concerns linger about China’s long-term intentions, especially regarding Taiwan.
-
- Outstanding Issues at Depsang Plains and Demchok:
-
- Although many friction points have been addressed, the strategic regions of Depsang Plains and Demchok remain unresolved.
- Talks are ongoing to address these contentious areas.
-
Secularism
- News: The Supreme Court affirmed that secularism is a core part of the Constitution’s Basic Structure while hearing petitions challenging the addition of “socialist” and “secular” to the Preamble.
- Judgment on Secularism and the Constitution:
-
- Secularism as a Constitutional Value: The bench emphasized that secularism is reflected in the Constitution’s commitment to equality and fraternity.
- Previous Rulings on Secularism: The court referred to earlier judgments where secularism was upheld as a core element of the Constitution.
- Reaffirmation of Basic Structure Doctrine: The Supreme Court reiterated that secularism is a fundamental and permanent part of the Basic Structure of the Indian Constitution.
-

- Challenge to the 42nd Amendment:
-
- Inclusion of “Socialist” and “Secular”: The 42nd Amendment, introduced during Indira Gandhi’s tenure, added the terms “socialist” and “secular” to the Preamble. It also changed the phrase “unity of the nation” to “unity and integrity of the nation.”
- Historical Context of the Amendment: Before the amendment, the Preamble described India as a “sovereign, democratic republic. The new terms were added during the Emergency period through the 42nd Amendment.
-
- Kesavananda Bharati Case and the Preamble:
-
- Preamble as Part of the Constitution: The 1973 Kesavananda Bharati case, decided by a 13-judge bench, established that the Preamble is an essential part of the Constitution.
- Amendability of the Preamble: The judgment confirmed that although the Preamble can be amended, no amendment can alter the Constitution’s Basic Structure.
-
UPSC GS 3
Hornets
- News: A species of hornet that often munches on foods containing alcohol can hold its liquor, without any side effects, at levels that no other known animal can tolerate.
- Hornets:
- Social Structure: Hornets are social wasps that form large, well-organized colonies.
- Global Distribution: There are around 20 species of hornets, naturally found in Asia, Europe, and Africa, with one species introduced to North America.

- Family Vespidae: Hornets belong to the family Vespidae, which also includes other wasps like yellow jackets, paper wasps, potter wasps, and pollen wasps.
- Appearance: Typically black or brown with yellow or yellowish patterns.
- Danger Perception: Hornets are often considered more dangerous than other wasps due to their size, though they are not necessarily more aggressive.
- Venom: Their sting delivers more venom than any other stinging insect.
- Largest Species: The Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia), also known as the northern giant hornet, is the largest wasp species in the world and is native to Asia.
- Nest Locations:Hornets typically build their nests in elevated areas.
- Food Preferences: Their diet is rich in sugar and protein.
- Prey: Hornets hunt various insects, including honeybees and other social wasps, chewing them into a paste to feed their larvae.
C. elegans Worm
- News: Molecular biologist Gary Ruvkun has won the fourth Nobel Prize resulting from C. elegans research.
- Nobel Prize Contributions of C. elegans: Research involving Caenorhabditis elegans has played a pivotal role in four Nobel Prize-winning discoveries:
- 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: The study of C. elegans revealed the process of programmed cell death (apoptosis), essential for understanding diseases like AIDS, stroke, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: Research on C. elegans led to the discovery of RNA interference (RNAi), a process that silences specific genes, revolutionizing therapeutic approaches in genetics and medicine.
- 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: The worm contributed to the development of fluorescent proteins (“cellular lanterns”), which allowed scientists to visualize molecular activities in real-time and enhanced molecular biology techniques.
- 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: Molecular biologist Gary Ruvkun credited C. elegans for its role in his groundbreaking research on microRNAs, small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression.
- About Caenorhabditis elegans: C. elegans is a small, 1-millimeter-long nematode that has become a cornerstone of biological research. It has significantly impacted four Nobel Prize-winning studies across diverse fields.
- Organism Characteristics:
- It is a free-living, transparent roundworm, widely recognized as a model organism in molecular and developmental biology.
- Key Attributes:
-
- Genome: C. elegans has about 20,000 genes, with many counterparts in humans, facilitating comparative genetic studies.
- Life Cycle: Its development from egg to adult occurs within 3 days, making it ideal for rapid experimentation.
- Reproductive Modes: The species includes both hermaphrodites capable of self-fertilization and males for sexual reproduction.
- Role in Apoptosis Research: It was instrumental in identifying the genetic mechanisms governing programmed cell death.
- Applications: Research on C. elegans has advanced our understanding of neurobiology, aging, development, and genetics.
-
- Experimental Advantages of C. elegans Several unique features make C. elegans an ideal organism for scientific experiments:
-
- Simplicity: The worm consists of precisely 959 somatic cells, with their developmental paths fully mapped from fertilization to death.
- Transparency: Its translucent body enables researchers to easily observe developmental processes under a microscope within a few days.
- Genome Sequencing Milestone: C. elegans was the first animal to have its genome fully sequenced in 1998, preceding other models like fruit flies and mice.
- Self-Fertilization Capability: Hermaphroditic individuals possess both eggs and sperm, allowing for efficient reproduction without a mate.
-
Nilgiri Tit (Hypolycaena nilgirica)
- News: Butterfly enthusiasts from the Nilgiris have recorded for the first time in India, the Nilgiri tit (Hypolycaena nilgirica) utilising a large terrestrial orchid plant as a host.
- Nilgiri Tit Butterfly:
-
- Taxonomy: The Nilgiri Tit Butterfly belongs to the family Lycaenidae and was first described in 1884 from Coonoor in the Nilgiris. It has also been recorded in Sri Lanka.
- Distribution: In India, it has been found in various locations, including Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary in Idukki district, and Silent Valley National Park in Palakkad district, Kerala.
-

- Appearance:
-
- Male: The male butterfly exhibits a dark reddish purple-brown coloration on its upper side, featuring two black spots capped in orange near the tails.
- Female: The female is characterized by a pale brown hue.
-
- Habitat: The Nilgiri Tit Butterfly typically inhabits forests and lush home gardens, particularly those that host orchids.
- Reproductive Behavior:
-
- It lays its eggs on the inflorescence (complete flower head) of the larval host plant, Eulophia epidendraea, a terrestrial orchid species. This is the first documented instance of the butterfly utilizing this specific plant as a host.
- The terrestrial orchid can be found on rocky slopes in humid areas.
-
- Conservation Status: The Nilgiri Tit Butterfly is classified under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act, highlighting its conservation importance.
Candy Leaf (Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) Bertoni)
- News: At the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) in Guwahati, Research Scholars did pioneering research on Stevia’s medicinal properties, effects on cellular signalling mechanisms to prove Assam’s Stevia’s therapeutic qualities.
- Definition: Stevia rebaudiana is a plant species in the genus Stevia of the family Asteraceae. It is commonly known as candyleaf, sweetleaf or sugarleaf.
- Non-Caloric Sweetener with Health Benefits: Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana), known primarily for its non-caloric sweetening properties, also possesses therapeutic qualities, as indicated by recent research.

- Impact on Multiple Systems: Stevia shows promise in managing endocrine, metabolic, immune, and cardiovascular disorders by modulating cellular signaling pathways.
- Inhibition of Protein Kinase C (PKC) Phosphorylation:
-
- Research reveals that Stevia suppresses PKC phosphorylation, a critical pathway linked to inflammatory, autoimmune, endocrine, and cardiovascular diseases.
- By inhibiting PKC activity, Stevia mitigates downstream inflammatory responses, addressing the root cause of many chronic health conditions.
-
- Management of Various Conditions: Stevia’s therapeutic potential extends to:
-
-
- Endocrine and metabolic disorders: Diabetes (type 1, type 2, and pre-diabetes)
- Autoimmune diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis
- Cardiovascular diseases: Hypertension and vasculopathy
- Chronic inflammation-related conditions: Chronic kidney diseases
-
- Key Molecular Interactions: Active compounds in Stevia engage with AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a crucial regulator of energy balance and inflammation, pointing to the need for further studies to unlock its full therapeutic potential.
- Stevia Cultivation in Assam: Assam has become a significant exporter of Stevia, with its cultivation recognized by the North Eastern Council as a driver of economic growth in the region, meeting rising global demand.
Read also: The Gig Economy in India: Growth, Challenges & Insights | UPSC
S-4*
- News: Amidst de-escalation with China and a diplomatic spat with Canada, India has quietly launched its fourth indigenously built nuclear-powered ballistic missile (SSBN) submarine.
- Codename and Indigenous Content:
-
- The fourth SSBN is codenamed S4*.
- It incorporates approximately 75% indigenous components and is equipped with K-4 ballistic missiles.
-
- Missile System:
-
- The K-4 missiles have a range of 3,500 km and are launched via vertical launch systems.
- In comparison, INS Arihant, the first of this class, carries K-15 missiles with a range of 750 km.
- INS Arighaat and INS Aridhaman, both enhanced versions of Arihant, are equipped solely with K-4 ballistic missiles.
-

- Recent Developments:
-
- The launch of S4* follows the commissioning of INS Arighaat in August 2024.
- INS Aridhaman is scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- Both INS Arihant and INS Arighaat are already deployed on deep-sea patrols.
-
- Naming System:
-
- India’s first leased nuclear attack submarine, INS Chakra, was designated as S1.
- Successive vessels were named INS Arihant (S2), INS Arighaat (S3), and INS Aridhaman (S4).
- The S4* submarine, the latest and final one in this series, awaits a formal name.
-
- Global Operators: Only a few nations—the United States, Russia, China, the United Kingdom, France, and India—operate SSBNs, equipped with submarine-launched nuclear ballistic missiles.
- Strategic Role: SSBNs are designed to ensure a reliable second-strike capability, forming a critical element of nuclear deterrence through the principle of mutual assured destruction.
- Endurance and Operational Range: These submarines offer unlimited range and endurance, with operational limits defined by crew fatigue, food supplies, and maintenance needs rather than fuel.

