UPSC GS 1
Rani Velu Nachiyar
- News: The PM Modi remembered the courageous Rani Velu Nachiyar on her birth anniversary recently.
- Birth and Early Life:
- Rani Velu Nachiyar was born on January 3, 1730, in Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu, India.
- She holds the distinction of being the first queen to actively resist British rule, taking up arms against colonial powers long before the Sepoy Mutiny.
- Title and Skills:
- Tamils honor her with the title “Veeramangai,” meaning brave woman.
- She was trained extensively in weaponry, martial arts like Valari and Silambam (stick fighting), horse riding, and archery.
- A polyglot, she was proficient in several languages, including French, English, and Urdu.

- Marriage and Family:
-
- She married Muthuvaduganathaperiya Udaiyathevar, the king of Sivagangai, and they had a daughter together.
- After the British soldiers killed her husband, she stepped into the battlefield to avenge his death.
- War Against the British:
- She forged alliances with Hyder Ali and Gopala Nayaker, leading a successful campaign against the British forces.
- Her victory against the colonial powers marked her as a prominent figure in India’s early resistance against British rule.
- Administrative Legacy:
- In 1780, she entrusted the administration of her kingdom to the Marudu brothers, granting them powers to govern effectively.
Read also: Decline in Democracy and Voter Participation | UPSC
Savitribai Phule
- News: The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi paid tributes to Savitribai Phule Ji on her birth anniversary.
- Early Life and Background:
- Savitribai Phule was born on January 3, 1831, in a small village in Satara district, Maharashtra.
- She was an Indian social reformer, poet, and an influential voice in the Indian freedom struggle.
- Savitribai actively participated in the women’s liberation movement, advocating for social equality and education.

- Education and Role as a Teacher:
-
- She received her training at Ms. Farar’s Institution in Ahmednagar and Ms. Mitchell’s school in Pune.
- She became the first female teacher in India, paving the way for women’s education.
- In 1848, she and her husband, Jyotirao Phule, opened India’s first school for women in Pune.
- Despite societal resistance, by 1851, she managed 18 schools for children from different castes, educating 150 girls.
- Educational Contributions: Savitribai and Jyotirao Phule established two educational trusts:
- The Native Female School, Pune.
- The Society for Promoting the Education of Mahars, Mangs, and other oppressed castes.
- In 1852, the British government recognized their efforts in education and honored Savitribai as the best teacher.
- Advocacy Against Discrimination:
- Savitribai worked alongside her husband against caste-based discrimination.
- She was instrumental in shaping the Satyashodhak Samaj (1873), an institution that fought for social equality.
- Women’s Rights and Empowerment:
- She launched the Mahila Seva Mandal in 1852, creating awareness about women’s rights and promoting inclusivity by involving all castes.
- Savitribai championed the rights of widows, opposing customs that forced them into lives of hardship and advocating for widow remarriage.
- She organized barbers’ strikes in Mumbai and Pune to protest the practice of shaving widows’ heads.
- Savitribai also campaigned against dowry and other oppressive social practices.
- Support for Vulnerable Groups:
- In 1863, Savitribai and Jyotirao started Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha, India’s first home to prevent infanticide, providing support for pregnant Brahmin widows and victims of rape.
- Literary Contributions: Savitribai authored two poetry collections:
- Kavya Phule (1854).
- Bavan Kashi Subodh Ratnakar (1892).
- Her poem “Go Get Education” encouraged the oppressed and backward classes to pursue education for empowerment.
- Legacy and Commemoration:
- Her birth anniversary, observed as Savitribai Phule Jayanti, celebrates her pioneering contributions to education and social equality.
UPSC GS 2
Central Groundwater Board (CGWB)
- News: There are 440 districts with excessive nitrates in their groundwater as of 2023, an increase from 359 such districts in 2017, according to a recent report by the Central Groundwater Board (CGWB).
- Definition:
-
- The Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) functions under the Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.
- It is a multidisciplinary scientific organization tasked with managing, exploring, monitoring, assessing, augmenting, and regulating groundwater resources in the country.

- Mandate:
-
- Develop and disseminate technologies for sustainable and scientific groundwater development and management.
- Monitor and implement national policies for groundwater conservation, exploration, augmentation, pollution control, and distribution.
- Ensure adherence to economic, ecological, and equity principles in groundwater usage.
- Organizational Structure:
- The CGWB is headed by a Chairman and supported by five members.
- It comprises experts from various fields, including Hydrogeologists, Geophysicists, Chemists, Hydrologists, Hydrometeorologists, and Engineers.
- Major Activities of CGWB:
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management (NAQUIM): Preparing aquifer maps and management plans for sustainable groundwater use.
- Groundwater Exploration: Identifying areas with groundwater potential and delineating aquifers.
- Geophysical Surveys: Mapping zones with groundwater-bearing potential.
- Groundwater Resource Assessment: Conducting periodic evaluations of the country’s groundwater resources.
- Monitoring Groundwater: Observing groundwater levels and quality through a network of monitoring wells.
- Data Dissemination: Sharing groundwater-related data and knowledge.
- Groundwater Modelling: Using advanced tools for simulating and managing groundwater systems.
- GIS and Remote Sensing Applications: Utilizing geospatial technologies for groundwater studies.
- Groundwater Regulation: Collaborating with the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) and State organizations to regulate groundwater development and management.
- Coordination with State Governments: Establishing standard methodologies for groundwater studies.
- Research and Development: Conducting studies and operationalizing new technologies for groundwater investigation and management.
- Water Conservation: Promoting artificial recharge and conservation of groundwater resources.
- Capacity Building: Enhancing knowledge and skills through training and knowledge transfer initiatives.
- Headquarters: Bhujal Bhawan, Faridabad, Haryana.
28th National Awards for e-Governance
- News: The Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions recently issued the guidelines for the 28th National Awards for e-Governance (NAeG) 2025.
- About National e-Governance Awards Scheme: This scheme is considered one of the most competitive and esteemed digital governance award schemes in India.
- Objective: Its primary goal is to acknowledge and encourage outstanding implementation of e-Governance initiatives.
- Award Components: Gold Awardees will receive:
- A trophy, a certificate, and an incentive of ₹10 lakh, which can be utilized for implementing projects or addressing resource gaps in public welfare initiatives.
- Silver Awardees will be granted:
- A trophy, a certificate, and an incentive of ₹5 lakh for similar purposes.

- Number of Awards: A total of 16 awards will be presented under the NAeG 2025:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- Award Categories for 2026:
- Government Process Re-engineering through Technology for Digital Transformation.
- Innovation Using AI and Emerging Technologies to Deliver Citizen-Centric Services.
- Best Practices and Innovations in Cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Initiatives for Enhanced Service Delivery, focusing on efforts by Districts, Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), and Gram Panchayats.
- Replication and Scaling of Successful National Awarded Projects, such as those recognized by NAeG, Prime Minister’s Excellence Awards, or other Central Ministries.
- Digital Transformation Using Data Analytics in Digital Platforms by Central Ministries, States, or Union Territories.
- Nodal Ministry: The scheme is overseen by the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions.
Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) Report
- News: School enrolment has seen a significant drop for the academic session 2023-2024, especially post Covid-19 pandemic, according to the Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) report.
- About UDISE+:
- The United District Information System for Education (UDISE+) is one of the largest Management Information Systems initiated by the Department of School Education and Literacy (DoSEL) under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- It encompasses data from over 14.72 lakh schools, 98.08 lakh teachers, and 24.80 crore students across India.
- Purpose and Functionality:
- Data Compilation Portal: UDISE+ is an online portal developed to maintain comprehensive records of school-related data, including details on teachers, enrolment, infrastructure, and other metrics for all recognized schools in the country.
- Data Collection Process: School-specific information is collected using a Data Capture Format (DCF). Each school is provided with a unique login ID and password, enabling them to compile data online.
- Verification Process: The Head Teacher or Head Master compiles the data, which then undergoes a three-stage validation and verification process:
- Block/Cluster level.
- District level.
- State level.
- Final certification is provided by the State Project Director (SPD), and the data is then considered approved by the respective state.
- Significance: UDISE+ is recognized as the only pan-India and most reliable database for school education in the country.
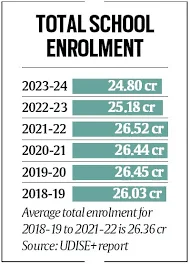
- Highlights of UDISE+ Report 2023-24:
- Enrolment Trends:
- Total student enrolment in 2023-2024 stood at 24.8 crore, a decline from 25.18 crore in 2022-2023.
- Historical data shows an average enrolment of around 26.36 crore between 2018-2019 and 2021-2022.
- Enrolment has dropped by over 1 crore since the pandemic, marking a significant decline between 2022-2023 and 2023-2024.
- Gender Representation:
- Boys constituted 51.9% of total enrolments, while girls accounted for 48.1%.
- Minority Representation: Minorities comprised around 20% of total enrolments. Among minorities:
- Muslims formed 79.6%,
- Christians 10%,
- Sikhs 6.9%,
- Buddhists 2.2%,
- Jains 1.3%,
- Parsis 0.1%.
- Category-wise Enrolment:
- Scheduled Caste (SC) students: 4.47 crore in 2023-2024, down from 4.59 crore in 2022-2023.
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 11.2 crore in 2023-2024, compared to 11.45 crore in 2022-2023.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility:
- Basic Facilities: Over 90% of schools are equipped with essential amenities such as electricity and gender-specific toilets.
- Technological Readiness: Advanced infrastructure remains limited:
- 57.2% of schools have functional computers.
- 53.9% have internet access.
- 52.3% are equipped with ramps and handrails, highlighting gaps in accessibility and technological advancement.
UPSC GS 3
Tinnitus
- News: IIT-Bombay researchers develop affordable device to diagnose tinnitus.
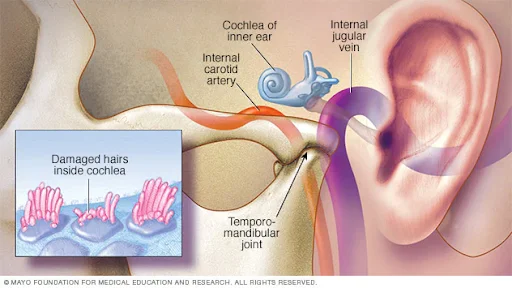
- Definition: Tinnitus refers to the perception of sound without any external source, meaning the affected individual is the only one who hears it.
- Causes:
- Age-related hearing loss.
- Ear injuries.
- Issues with the circulatory system.
- Symptoms: One may hear phantom sounds in one ear, in both ears, and in head. The phantom sound may ring, buzz, roar, whistle, hum, click, hiss, or squeal.
- Treatment Options:
- Hearing aids.
- Sound-masking devices.
- Medications.
- Techniques to help individuals manage and cope with the persistent noise.
- Newly Developed Tinnitus Device:
- Comprehensive Management: The device, paired with dedicated application software, provides a holistic approach to tinnitus management.
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: It accurately identifies the nature and frequency of the sound experienced by the patient, aiding in targeted treatment.
- Customizable Multimodal Treatment: Offers a personalized treatment plan tailored to each patient’s specific condition and needs.
- Tracking and Monitoring: The software includes tools to track disease progression, allowing clinicians to monitor patient improvement over time.
Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: A four-day faunal survey conducted at the Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary has added significant findings to the sanctuary’s biodiversity records.
- Location: Situated in the southern part of the Western Ghats, in the Kollam district of Kerala.
- Area and Biosphere Reserve:
- Covers approximately 172 sq. km.
- Forms an integral part of the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve.
- Topography: The sanctuary is predominantly hilly, interspersed with numerous ravines.
- Drainage: Major rivers include:
- Shendurney River.
- Kazhuthuruthy River.
- Kulathupuzha River.
- These rivers converge to form the Kallada River.
- Flora:
- Tropical evergreen forests.
- Semi-evergreen forests.
- Moist deciduous forests.
- Unique Feature:
- The sanctuary gets its name from Gluta travancorica, a tree species locally known as ‘Chenkurunji.’
- This species is endemic to the region and found in abundance within the sanctuary.
- Fauna:
-
- Prominent species include elephants, tigers, leopards, gaurs (Indian bison), sambar deer, barking deer, wild boars, and bonnet macaques.
- It also hosts Nilgiri langurs and lion-tailed macaques, both endemic to the Western Ghats.
- Birds:
- Over 200 bird species have been recorded, including:
- Great Indian hornbill.
- Malabar pied hornbill.
- Grey-headed bulbul.
- White-bellied treepie.
- Various woodpeckers, flycatchers, and raptors.
Stellaria bengalensis
- News: After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala recently, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
- About Stellaria Bengalensis:
- Taxonomy and Family: Stellaria bengalensis is an annual herb belonging to the genus Stellaria under the family Caryophyllaceae.

- Habitat and Location:
- This plant was discovered growing on muddy soil slopes at altitudes ranging between 2,245 and 2,450 meters.
- It is found in the Sangser forest area of Kalimpong.
- Physical Features:
- An annual herb that grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Notable for its white flowers.
- Lacks bracts.
- Features shorter petals that are enclosed within the sepals.
- Seeds are sharp and pointed.
- Life Cycle:
- Flowering and fruiting are observed from May to September.
- Distribution and Related Species:
- In India: India has approximately 22 species of Stellaria, primarily distributed across the Himalayan region.
- Related Species: Another species, Stellaria mcclintockiae, was earlier identified in the Nelliyampathy Hills of Kerala.
- Conservation Status: The species has been provisionally classified as “data deficient” under the criteria of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
See more: The Gig Economy in India: Growth, Challenges & Insights | UPSC
Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)
- News: The Union Cabinet extended the one-time special subsidy on fertilizer Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) at a rate of ₹3,500 per metric tonne till from January 1, 2025 till further orders.
- About Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP):
- Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is among the most widely utilized fertilizers worldwide, supplying key nutrients—nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P)—that are crucial for plant development.
- It ranks as the second most extensively used fertilizer in India, following urea.

- Importance for Agriculture:
- Nutrient Benefits:
- DAP is rich in phosphorus, which plays a vital role in stimulating root establishment and growth.
- Without adequate phosphorus, plants may struggle to grow to their normal size or experience delayed maturity.
- Solubility:
- It is highly soluble in water, enabling it to dissolve quickly in soil and release plant-available forms of phosphate and ammonium.
- Additional Applications:
- Fire Retardant:
- A mixture of DAP with other components is used to create fire barriers, often spread ahead of a wildfire to prevent its spread.
- Industrial Use:
- Employed in metal finishing processes.
- Serves as a flux for soldering metals like tin, copper, brass, and zinc.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- Added to wine to sustain yeast fermentation during the production process.
- Used in milk to support the formation of cheese cultures.

