UPSC GS 1
Ram Prasad Bismil
- News: Birth anniversary celebrated recently on June 11.
- Early Life:
-
- Ram Prasad Bismil Born in 1897 in Shahjahanpur, Uttar Pradesh.
- Joined the Arya Samaj at a young age.
-

- Ideology and Actions:
-
- Advocated revolutionary methods for India’s freedom struggle, contrasting with Gandhian principles.
- Involved in distributing prohibited literature during the Mainpuri Conspiracy.
-
- Formation of Organizations:
-
- Co-founded the Hindustan Republican Association with Sachindra Nath Sanyal and Jadugopal Mukherjee.
- Established the revolutionary organization “Matrivedi.”
-
- Notable Incidents:
-
- Participated in the Kakori Robbery Case alongside Chandra Shekhar Azad and Ashfaqulla Khan.
-
- Literary and Cultural Contributions:
-
- Renowned for his patriotic poem “Sarfaroshi ki Tamanna.”
-
- Execution and Legacy:
-
- Executed on December 19, 1927, for his role in the Kakori Conspiracy Case, leaving behind a legacy of bravery and sacrifice.
-
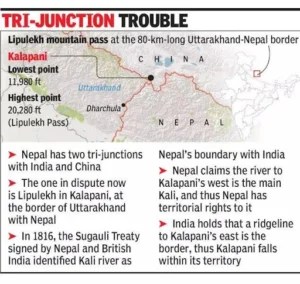
Lipulekh Pass
- News: Indian traders demand resumption of border trade with China through Lipulekh pass.
- Location:
-
- Located near the tri-junction of India, China (Tibet), and Nepal.
- Situated in Uttarakhand, specifically in the Pithoragarh district.
-
- Significance:
-
- Major pass in the Kumaun region, situated in the Kali Valley.
- Has served as an ancient trade route for centuries.
-
- Historical and Cultural Importance:
-
- Used by traders, pilgrims, and travelers for cultural exchange over the ages.
-
- Role in Pilgrimage:
-
- Reduces travel time significantly for the Kailash Mansarovar Pilgrimage.
-
Gender Gap Report 2024
- News: India has ranked 129 on Global Gender Gap Index Report 2024.
- Global Gender Gap Index
-
- The Global Gender Gap Index is an annual report by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
- It evaluates gender-based disparities in access to resources and opportunities across countries worldwide.
- Established in 2006, it is the most long standing index for monitoring progress in bridging gender gaps over time.
-
- Key Parameters: The index assesses the gender gap across four main dimensions:
-
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
-
- Scoring System: Countries are ranked on a scale from 0 to 1:
-
- Score of 1: Indicates complete gender equality.
- Score of 0: Indicates a total absence of equality.
-
- Key Highlights: India’s Gender Gap Status in 2024
-
- Overall Ranking and Score: India has closed 64.1% of its gender gap in 2024, but its ranking has declined from 127th last year to 129th. Among South Asian economies, India is the third lowest.
- Comparative Rankings with Neighbors
- Bangladesh: 99th position
- Nepal: 117th position
- Sri Lanka: 122nd position
- Bhutan: 124th position (score: 0.651)
- Pakistan: 145th position (score: 0.570)
- India’s Ranking in Key Parameters:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity: 142nd
- Health and Survival: 142nd
- Educational Attainment: 112th
- Political Empowerment: 65th
- Political Empowerment Sub-Index:
- Head-of-State Indicator: India ranks within the top 10 with a score of 40.7%.
- Federal Representation: However, India’s scores for women’s representation at the federal level, in ministerial positions (6.9%) and in parliament (17.2%), remain relatively low.
- Economic Parity:
- India’s economic parity stands at 39.8%, indicating that, on average, women earn Rs 39.8 for every Rs 100 that men earn.
- Educational Attainment:
- Lower Parity: India’s score in ‘Educational Attainment’ also contributed to a lower parity status compared to the previous assessment cycles.
- Wide Gender Gap: The shares of women are high in primary, secondary and tertiary education enrolments but they have only been modestly increasing.
- The gap between men and women’s literacy rate is 17.2 percentage points wide, leaving India ranked 124th on this indicator.
-
- Key Highlights Worldwide:
-
- Global Gender Gap: The global gender gap now stands at 68.5%, a 0.1% point improvement on last year, primarily due to modest gains in economic participation and opportunity.
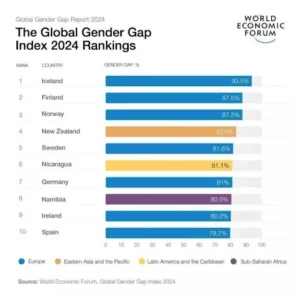
- Top-Ranking Countries: Iceland ranked as the most gender-equal country in the world for the 15th consecutive year and the only country to have closed 93.5% of its gender gap.
-
-
-
-
- It was followed in the top 10 by Finland, Norway, New Zealand, Sweden, Nicaragua, Germany, Namibia, Ireland and Spain.
- While no country has yet achieved full gender parity, the top ten ranking countries have closed at least 80% of their gap.
-
-
See this: India – Africa Relations: History, Sigificance, Challenges and Solutions | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
General Anti-Avoidance Rule (GAAR)
- News: The Telangana High Court has ruled against a taxpayer against whom the revenue department had invoked General Anti-avoidance Rule (GAAR).
- Definition:
-
- The General Anti-Avoidance Rule (GAAR) is an Indian law designed to curb tax evasion and prevent tax leaks.
- Implemented on 1st April 2017, GAAR falls under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
-
- Purpose:
-
- GAAR aims to deter aggressive tax planning, specifically targeting transactions or business arrangements created solely to avoid paying taxes.
- Its goal is to minimize revenue losses for the government caused by these tax avoidance strategies.
-
- Application:
-
- GAAR applies to transactions that are technically legal but lead to reduced tax liability.
- This type of tax planning, where the primary purpose is tax reduction, is what GAAR seeks to regulate.
-
- Categories of Tax Reduction: Tax reduction can be divided into three categories:
-
- Tax Mitigation: This involves using fiscal incentives provided by tax legislation, complying with its conditions, and considering the economic consequences.
- Tax mitigation is allowed under the Act and remains acceptable even after GAAR’s implementation.
- Tax Evasion: This occurs when individuals or entities do not pay the taxes they owe, which is illegal and subject to prosecution.
- Acts of illegality, wilful suppression of facts, misrepresentation, and fraud fall under tax evasion and are prohibited by law.
- GAAR does not cover tax evasion, as existing laws already address it.
- Tax Avoidance: This includes legal actions taken to reduce tax liability, though not illegal, are considered undesirable as they undermine effective tax collection.
- GAAR targets transactions where the main purpose is to avoid tax by using legal means that would not have been pursued without the tax benefit.
- Tax Mitigation: This involves using fiscal incentives provided by tax legislation, complying with its conditions, and considering the economic consequences.
-
- GAAR’s Impact:
-
- GAAR treats tax avoidance and tax evasion similarly, scrutinizing any transaction that reduces tax liability.
- By addressing transactions intended solely for tax reduction, GAAR aims to ensure that such practices are curtailed.
-
UPSC GS 3
Vidyut Rakshak
- News: Indian Army has unveiled “Vidyut Rakshak”.
- Definition:
-
- A system designed specifically for the Indian Army to monitor, protect, and control generators.
- Utilizes Internet of Things (IoT) technology for enhanced functionality.
-
- Developed by: Army Design Bureau (ADB)

- Functionality:
-
- Monitors parameters of all existing generators, regardless of type, make, rating, or age.
- Predicts and prevents faults through advanced analytics.
- Automates manual operations, reducing dependency on manpower.
-
Quantum Mechanics
- News: Recently, the United Nations declared 2025 the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology to celebrate the contributions of quantum science to technological progress.
- Introduction to Quantum Mechanics: Branch of physics dealing with particles at atomic and subatomic levels.
- Key Concepts:
- Superposition: Particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously until observed.
- Entanglement: Particles can be interconnected, where the state of one instantly affects another regardless of distance.
- Quantum Computing: Utilizes qubits in superposition to perform multiple calculations simultaneously.
- Quantum Cryptography: Applies quantum principles to create secure communication systems.
- Wave-Particle Duality: Small objects exhibit characteristics of both particles (matter) and waves (energy disturbance).
- Uncertainty Principle: States that position and speed of particles (e.g., photons, electrons) cannot be simultaneously known with perfect accuracy.
Nagarahole Tiger Reserve
- News: An elephant that was part of the historic Mysuru Dasara celebrations died of electrocution near Karnataka’s Nagarahole Tiger Reserve recently.
- Introduction to Nagarahole Tiger Reserve:
-
- Located in the districts of Mysore and Kodagu in Karnataka.
- Covers an area of 847.981 sq km.
- Named after the river ‘Nagarahole,’ which means ‘snake stream’ in Kannada, flowing through the habitat and joining the Kabini river.
- Forms part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
-
- Geographical Features:
-
- Contiguous with Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) to the south.
- Adjacent to Bandipur Tiger Reserve to the southeastern parts.
- Features Kabini and Taraka reservoirs in the west and southeastern parts respectively.
-
- Historical Background:
-
- Origin as a protected area dates back to the Wodeyar dynasty, used as a hunting reserve.
- Established as a wildlife sanctuary in 1955 by Coorg State.
- Upgraded to a national park in 1988.
- Designated as a Tiger Reserve under Project Tiger in 1999.
-
- Vegetation and Flora:
-
- Predominantly southern tropical, moist, mixed deciduous vegetation.
- Eastern portion transitions into dry deciduous type.
- Includes swampy fallows called ‘hadlu’ dominated by grasses and sedges, preferred by wild herbivores.
- Features commercially important trees like rosewood, teak, sandalwood, and silver oak.
-
- Fauna:
-
- Supports diverse wildlife including carnivores like Tiger, Leopard, Asiatic wild dog, and Sloth bear.
- Herbivores such as Asiatic Elephant, Gaur, Sambar, Chital, Muntjac, Four-horned antelope, Wild pig, Mouse deer, and South-western langur thrive in the reserve.
-
Microalgae
- News: CSIR-IICT scientists identify microalgae as a potential protein supplement.
- Characteristics
-
- Microscopic Algal Species: Microalgae are tiny algal species, differing from the larger, macroscopic algae.
- Unicellular Nature: They are predominantly unicellular, though some form colonies with more complex structures.
- Size Range: Their sizes vary widely, from just a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers.
- Lack of Plant Structures: Unlike higher plants, microalgae lack roots, stems, or leaves.
- Photosynthetic Ability: They are mostly photosynthetic due to the presence of photosynthetic pigments.
- Habitat Diversity: These versatile organisms can inhabit a range of aquatic environments, including freshwater, brackish water, marine, and hypersaline conditions.
- Examples: Examples of unicellular microalgae include green algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates.
-
- Importance of Microalgae
-
- Primary Producers: Microalgae serve as primary producers in ecosystems.
- Aquatic Food Webs: They play a crucial role in supporting various organisms and influencing nutrient cycles within aquatic food webs.
- Oxygen Production: Their photosynthetic activity contributes significantly to oxygen production in the environment.
- Symbiotic Relationships: They can establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms, such as providing nutrients to corals (zooxanthellae) through photosynthesis.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Certain microalgae species, like Nostoc, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria, have the ability to fix nitrogen.
- Resource of Nutrients: Microalgae are a valuable source of essential nutrients, including lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and pigments, offering significant nutritional and health benefits.
- Dietary Supplements: Notably, Spirulina and Chlorella are popular types of microalgae consumed as dietary supplements, known for their rich nutrient profiles and health-promoting properties.
-
- What is Algae?
-
- Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that have the ability to conduct photosynthesis.
- Certain algae are familiar to most people; for instance, seaweeds (such as kelp or phytoplankton), pond scum or the algal blooms in lakes.
- However, there exists a vast and varied world of algae that are not only helpful to us, but are critical to our existence.
-
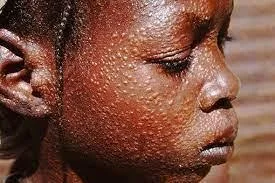
Kala-azar
- News: World Health Organization (WHO) launched a new framework on June 12 to guide health authorities, policy makers and other stakeholders to eradicate the disease in eastern Africa.
- Kala-azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
-
- Kala-azar, also known as visceral leishmaniasis (VL), is a severe form of leishmaniasis caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani.
- The disease is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected female sandfly, primarily Phlebotomus argentipes in India.
-
- Symptoms:
-
- Fever: Irregular bouts of fever.
- Weight Loss: Significant and substantial weight loss.
- Organ Swelling: Swelling of the spleen and liver.
- Severe Anaemia: If left untreated, severe anaemia can develop, which may lead to death within two years.
-
- Diagnosis
-
- Clinical Signs: Diagnosis is based on clinical signs.
- Parasitological Tests: Involves testing for the presence of the parasite.
- Serological Tests: Use of tests such as the rK39 diagnostic kit.
-
- Prevalence
-
- Kala-azar is endemic in 75 countries across Asia, Africa, and the Americas. In 2020, India accounted for 18% of the global burden of this disease.
-
Pterosaur
- News: Paleontologists have discovered a new species of pterosaur after analysing 100-million-year-old fossilised bones uncovered in western Queensland, Australia.
- Pterosaurs: Mesozoic Era Flying Reptiles
-
- Pterosaurs are a group of flying reptiles that thrived throughout the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era, spanning from approximately 252.2 million to 66 million years ago.
- Despite not being classified as dinosaurs, pterosaurs, like dinosaurs, belong to the archosaur clade, which also includes birds and crocodiles.
- Notably, pterosaurs were the first reptiles capable of flight and the earliest vertebrates known to have achieved powered flight.
-

- Distinctive Characteristics
-
- Flight Adaptations: Pterosaur wings were formed by an advanced membrane of skin extending from the thorax to an elongated fourth finger.
- Diversity in Morphology: Early pterosaur species possessed long, fully-toothed jaws and elongated tails. In contrast, later species exhibited significantly reduced tails, and some were edentulous (lacked teeth).
- Neck and Feeding Adaptations: Many pterosaurs had elongated necks, and some species had throat pouches akin to those of modern pelicans, which were likely used for catching fish.
-
- Evolutionary Significance:
-
- The evolution of flight in pterosaurs occurred independently of the development of flight in birds and bats.
- Pterosaurs are not closely related to either birds or bats, making their flight capabilities an example of convergent evolution, where similar traits evolve separately in unrelated lineages.
-
- Notable Species:
-
- Included Quetzalcoatlus, the largest known flying vertebrate, from the late Cretaceous period.
-
- Extinction:
-
- Extinct around 65.5 million years ago during the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event.
- Birds, descendants of dinosaurs, eventually filled the ecological niche once dominated by pterosaurs.
-
Tmesipteris Oblanceolate
- News: The fern species Tmesipteris oblanceolata from New Caledonia has been found to have more than 50 times more DNA in each cell than humans.
- Genome Size:
-
- Tmesipteris oblanceolata contains 160 billion base pairs, making it the largest known eukaryotic genome.
- Approximately 50 times larger than the human genome.
-

- Previous Record Holder:
-
- Before Tmesipteris oblanceolata, the largest known genome belonged to the Paris japonica flower, with 149 billion base pairs.
-
- Habitat and Distribution:
-
- Grows epiphytically on fallen trunks in the forests of New Caledonia.
- Belongs to a genus of vascular plants with only about 15 known species.
- Found on the island nation of New Caledonia (overseas French territory situated in the Southwest Pacific) Oceania and several Pacific Islands, including Eastern Australia.
-
- Physical Description:
-
- Typically, 15 to 30 cm long, mostly unbranched.
- Features shorter leaves at the base.
- Leaves have tops that appear abruptly cut off, described as “truncata.”
-
Donanemab
- News: Donanemab, currently undergoing trials, has demonstrated significant potential in slowing cognitive decline in individuals with early Alzheimer’s disease.
- Definition:
-
- Donanemab is a monoclonal antibody that targets amyloid, a sticky protein that accumulates in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
-
- Efficacy:
-
- More effective in individuals with low to moderate tau levels at the trial’s onset compared to those with high tau levels.
-
- Tau Protein:
-
- Tau (t-tau) protein reflects the intensity of neuronal damage in neurodegeneration, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease:
-
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive and irreversible neurological disorder.
- Beta-amyloid, a protein vital for brain function, becomes toxic in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Forms clumps that disrupt brain cell connections, leading to cognitive issues such as memory loss.
- Protein deposits interfere with neuron communication.
- Early Symptoms: Initial signs include forgetfulness, difficulty finding words, problem-solving challenges, confusion, and disorientation.
- Causes: Involves genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
-

