UPSC GS 1
Poumai Naga Tribe
- News: The Poumai Naga tribe has taken a significant stride towards wildlife conservation by banning hunting, trapping, and killing of wild animals and birds within their territory.
- Poumai Naga Tribe: The Poumai Naga tribe is an indigenous ethnic group, primarily residing in the Senapati district of Manipur, with some presence in parts of Nagaland.
- Population and Distribution:
-
- About 95.7% of the total Poumai population lives in the Senapati district of Manipur.
- It is one of the oldest and largest Naga tribes in Manipur.
-

- Language:
-
- The Poumai people communicate in their native language called “POULA.”
-
- Religion:
-
- Christianity is the dominant religion practiced by the Poumai community.
-
- Traditional Skills:
-
- In ancient times, the Poumai were well-known for their:
- Pouli (Pottery)
- Poutai (Pou salt) production
- These crafts were highly regarded in tribal areas across Manipur and Nagaland.
-
- Occupation:
-
- The primary occupation of the Poumai Naga is agriculture.
- Shifting cultivation, once common, is now rarely practiced in Poumai villages.
-
- Popular Festivals:
-
- Thounii – This is the New Year’s celebration that takes place after harvesting.
- Laonii- It is celebrated after the completion of paddy transplantation. This is an opportunity to interact with and renew bonds with brothers and sisters, as well as for male sanctification
-
Read also: White Revolution 2.0: New Dairy Frontier for India’s Growth | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi
- News: The Ministry of Tourism recently launched a national responsible tourism initiative by the name of ‘Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi’ on September 27th, World Tourism Day,.
- World Tourism Day: The theme for this year’s World Tourism Day is ‘Tourism & Peace’.
- Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi:
- Aim:
-
- Through this initiative, Ministry of Tourism aims to elevate the overall experience for tourists in destinations, by having them meet ‘tourist-friendly’ people who are proud Ambassadors & Storytellers for their destination.
-
- Launch Destinations: Ministry of Tourism piloted Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi in 6 tourist destinations across India namely:
-
- Orchha (Madhya Pradesh), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh) Bodh Gaya (Bihar), Aizawl (Mizoram), Jodhpur (Rajasthan), and Sri Vijaya Puram (Andaman & Nicobar Islands).
-
- Key Features:
-
- The vision of Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi is to welcome one and all to experience Incredible India through Incredible Indians.
- Driven by ‘Athithi Devo Bhava’, cab drivers, auto drivers, staff at railway stations, airports, bus stations, etc were provided training and awareness on the importance of tourism, general cleanliness, safety, sustainability.
- Special emphasis is being placed on the training of women and youth to enable them to develop new tourism products & experiences like heritage walks, food tours, craft tours, nature treks, homestay experiences, etc.
- Tourism-specific training is being followed by general training in digital literacy and digital tools to ensure that the experiences they create are discoverable and visible to tourists, nationally and globally.
-
Commission for Air Quality Management
- News: The Supreme Court recently pulled up the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) over its alleged lack of effort to curb stubble burning in neighbouring states, which has been a significant contributor to Delhi’s air pollution during winter months.
- Definition:
-
- The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) is a statutory body formed under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas, Act 2021.
- It has the authority to take comprehensive measures to curb air pollution in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- The Commission is headquartered in the NCR, with the power to set up offices in adjoining regions.
-
- Composition: The Commission consists of:
-
- A chairperson with experience of not less than 15 years in the field of environmental protection and pollution control or having administrative experience of not less than 25 years.
- A representative of the Secretary in the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, who shall be an officer not below the rank of Joint Secretary.
- 5 ex officio Members who are either Chief Secretaries, or Secretaries in-charge of the department dealing with environment protection in the NCT of Delhi and the States of Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh;
- One full-time Member who is or has been a Joint Secretary to the Government of India;
- Other members including experts from fields such as environment, public health, agriculture, and meteorology.
-
- Jurisdiction: The CAQM’s jurisdiction covers:
-
- The entire National Capital Region (NCR), including Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan
- Any other adjoining areas as notified by the central government
-
- Powers and Functions: The CAQM has broad powers to:
-
- Monitor, coordinate, and regulate activities contributing to air pollution
- Formulate policies and issue directives to curb pollution from industrial emissions, vehicular pollution, stubble burning, construction activities, and road dust
- Impose fines and penalties on violators of environmental regulations
-
- Overriding Powers: The CAQM has overriding authority over other bodies, such as:
-
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
- State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs)
- Its aim is to ensure coordinated efforts to tackle pollution in the region.
-
- Advisory and Coordination Role:
-
- The Commission advises central and state governments on air quality matters.
- It coordinates with state authorities, agencies, and local bodies to enforce environmental laws and implement air quality improvement measures.
-
- Penalties:
-
- Individuals who fail to comply with the Commission’s orders or violate provisions of the Act face penalties, including:
- Fines
- Imprisonment
-
UPSC GS 3
Rice
- News: The Centre recently lifted the ban on export of Non-Basmati White Rice.
- Definition: Rice is one of the most important food crops and feeds more than 60% population of India.
- Growing Conditions:
-
- It is a kharif crop which requires high temperature, (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm.
- In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
- Rice is grown under so diverse soil and climatic conditions including alkaline and acidic soils.
- Rice vegetates from 90 to 200 days, depending on the varieties and agro-ecological situations.
-
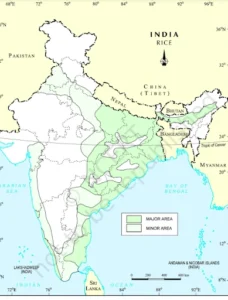
- Types of Rice:
- Long Grain Rice/Basmati Rice:
-
- It belongs to the category of ‘Indica Rice’ or long grained rice.
- Due to its full-bodied flavor and versatility, the long grain rice is also known as an ‘all-purpose rice’ or ‘ basmati rice’, and is an ideal choice for an everyday meal.
- Basmati rice is mainly cultivated in climates that are warm, like those in India, Pakistan and Thailand.
-
- Medium Grain Rice:
-
- This type of rice has a creamy color and a slightly chewy texture.
- The kernels of this kind of rice are shorter and wider as compared to that of long grain rice and also do not always remain fluffy.
- It is an ideal form to be used in desserts, breads, etc.
-
- Short Grain Rice:
-
- Belonging to the ‘Japonica’ (round grained) category of rice, the grains of this type of rice have short and plump kernels.
- This rice is identified as having a smooth, creamy texture, ideal for making rice pudding and other sweet dishes involving the use of rice.
- It is mainly grown in cold weather areas, such as Japan, Korea and China.
-
- Rice Production in India:
-
- Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions.
- Major 5 states in rice production are West Bengal, UP, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Tamil Nadu. The west Bengal produces 15% of total quantity of rice produced in the country.
- Rice contributes 42 % of total food grains production and 45 % of the total cereal production in the country.
-
- India in Global Rice Production:
-
- China is the largest producer of rice. It produced over 208 million tonnes in 2022. This is more than a quarter of the total rice produced globally.
- India is the second largest producer and the biggest exporter of rice followed by Bangladesh, Indonesia, and Vietnam.
- India, along with China, accounts for over half of the world’s rice production. China, however, is also the biggest consumer of rice, leaving little for exports.
- Among the various rice growing countries of the world, India has the largest area under rice.
- According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), India accounted for 33 per cent (17 million tonnes) of the world’s total rice exports (53 million tonnes) during the calendar year 2023.
-
Bharat 6G Alliance
- News: Telecom Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia recently initiated a meeting with the seven working groups of the Bharat 6G Alliance.
- Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA):
-
- The Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA) is a collaborative platform with the goal of establishing India as a global leader in the telecom sector.
- It focuses on promoting indigenous technology, achieving universal and affordable connectivity, and leading the development and deployment of 6G technology in the country.
-
- Composition of the Alliance: B6GA consists of a diverse range of stakeholders, including:
-
- Public and private companies
- Academia
- Research institutions
- Standards development organizations
-

- Global Collaboration:
-
- The platform seeks to form coalitions and synergies with other 6G Global Alliances.
- It promotes international collaboration and knowledge exchange to accelerate advancements in 6G technology.
-
- Objectives:
-
- Foster indigenous development of telecom solutions.
- Position India as a leading supplier of IP, products, and solutions for affordable 5G and 6G technologies.
- Enable India to create and deploy future telecom solutions on a global scale.
-
- Support for Indian Ecosystem:
-
- One of the primary goals of B6GA is to unite Indian startups, companies, and the manufacturing ecosystem.
- It aims to establish consortia that will drive the design, development, and deployment of 6G technologies in India.
-
- Market Access and Leadership:
-
- B6GA facilitates market access for Indian telecom products and services.
- The alliance works to ensure India emerges as a global leader in the 6G technology space.
-
Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: The Ratapani Sanctuary might get the status of a tiger reserve.
- Location:
-
- Located in the Raisen and Sehore districts of Madhya Pradesh, Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary covers an area of 825.90 sq km.
- This sanctuary is set within the Vindhya Hills, with a rocky forest landscape that includes aquatic environments.
-
- Geographical Features:
-
- Runs parallel to the northern side of the Narmada River
- The Kolar River forms the western boundary of the sanctuary
- Bhimbetka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located within the sanctuary, featuring rock shelters and ancient rock paintings.
- It also has other historical and religious destinations like Ginnourgarh Fort, POW camp, Keri Mahadeo, Ratapani dam, Jholiyapur dam etc.
-
- Flora: The forest in Ratapani is dry deciduous and moist deciduous type, with one of the finest teak (Tectona grandis) as the main tree species. About 55 percent of area is covered by teak.
- Fauna: Tigers, leopard, sloth bear, hyena, spotted deer, sambar deer, chinkara, black buck, monkeys, sloth bears, Paradise Flycatcher( the state bird of Madhya Pradesh).
Sea Robins
- News: A recent study has revealed new insights into evolutionary adaptations by examining the unique “walking” abilities of sea robins.
- About Sea Robins:
-
- Sea robins belong to the Triglidae family of ray-finned fish.
- They inhabit diverse habitats, from shallow salt marshes to deep ocean waters.
- Sea robins are found in warm and temperate seas across the world.
-

- Benthic Specialists:
-
- Most Triglidae fish are benthic, meaning they spend much of their time at the ocean bottom.
- They hunt in the sand for fish, crustaceans, and other invertebrates.
- Their benthic lifestyle has led to the evolution of unique traits, including leg-like appendages.
-
- Physical Characteristics:
-
- Sea robins are elongated fish with armoured bony heads and two dorsal fins.
- They possess six leg-like appendages, which help them “walk” along the ocean floor.
- The name “sea robin” comes from their large, wing-like pectoral fins, which they fan out when excited or threatened.
- These fins help them appear larger and blend in with the sandy ocean bottom.
- Their fins open and close while swimming, resembling a bird in flight.
- Some species have scaly bodies, while others are covered in bony plates.
-
- Colour and Pattern:
-
- Sea robins are usually brightly coloured, with some species exhibiting ornate patterns on their pectoral fins.
-
- Vocal Abilities:
-
- Sea robins are vocal and can produce audible sounds using their swim bladders and specialized muscles attached to them.
-
Read also: Bombay High Court Strikes Down Centre’s Amended IT Rules | UPSC
Global Innovation Index (GII) 2024
- News: Recently, the Global Innovation Index (GII) was released by the World Intellectual Property Organization.
- Global Innovation Index (GII):
-
- The GII is a reliable tool for governments to evaluate the social and economic changes driven by innovation within their countries.
- It assesses the performance of innovation ecosystems in 133 economies and tracks the latest global innovation trends.
-
- Released by: The GII is published by the Geneva-based World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- Indicators: It is based on 81 indicators classified into seven pillars: institutions, human capital and research, infrastructure, market sophistication, business sophistication, knowledge and technology outputs, and creative outputs.
- India’s Rise in the Global Innovation Index 2024:
-
- India’s Global Ranking: India climbed to 39th position among 133 global economies in the 2024 Global Innovation Index, highlighting its growing innovation capabilities.
- Regional and Economic Leadership: India is the top performer in Central and Southern Asia and ranks first among lower-middle-income economies worldwide.
- Science and Technology Cluster Ranking: India secured 4th place in WIPO’s Science and Technology Cluster Ranking. Major cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru, and Chennai are listed among the world’s top 100 science and technology clusters.
- Global Standing in Intangible Asset Intensity: India ranks 7th globally in intangible asset intensity, reflecting its growing innovation strength.
- Consistent Growth in Innovation: India has steadily improved its position in the Global Innovation Index, rising from 81st in 2015 to 39th in 2024.
- Innovation Outputs and Inputs in 2024:
- India ranks 33rd in innovation outputs, showing improvement from last year.
- It ranks 44th in innovation inputs.
- India performs better in innovation outputs than inputs, showcasing the strength of its innovative results.
-

