UPSC GS 1
Pallikaranai Marshland
- News: The Tamil Nadu Government plans to build a high level bridge between Kamatchi Hospital in Pallikaranai and Thoraipakkam to protect the Pallikaranai marshland.
- Introduction:
-
- The Pallikaranai Marshland is a significant freshwater and partly saline wetland located about 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- It stands as one of the last remaining natural wetlands in Chennai city.
-
- Ecological Importance:
-
- The Pallikaranai Marshland serves as an essential aquatic buffer for the flood-prone regions of Chennai and Chengalpattu districts.
- It plays a crucial role in draining an area of 250 sq.km, encompassing 65 wetlands, through two outlets: Okkiyam Madavu and the Kovalam Creek, ultimately discharging into the Bay of Bengal.
-
- Topography:
-
- Parts of the Marsh are below the mean sea level, qualifying as low-lying basins.
-
- Ramsar Site:
-
- The Pallikaranai Marshland is recognized as one of the Ramsar sites in India, highlighting its international importance as a wetland.
-
- Biodiversity:
-
- The diverse ecosystem of the Pallikaranai Marshland supports bird species, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, fish, molluscs, crustaceans.
- Notable species: Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis) and birds such as the glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus) and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
-

- Climate and Hydrology:
-
- Although the Pallikaranai Marshland has a tropical bio-climate, the influence of the Bay of Bengal significantly affects it.
- The marsh witnesses dramatic changes in its hydrology and biodiversity annually, attributed to the maritime influence and the vagaries of the North East Monsoon.
-
See this: A List of Major Freedom Fighters of India (1857-1947)
UPSC GS 2
Geoportals
- News: The Central Government has launched two Geoportals namely ‘Bhuvan Panchayat (Ver. 4.0)” portal for rural land record and “National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM Ver. 5.0)” developed by Indian Space research Organization (ISRO).
- Aim: ISRO has been developing geospatial databases, geoportals and decision support systems for governance, sustainable development and disaster management support in India as per the requirements of Ministries and Departments of Government of India.
- Introduction to Bhuvan Panchayat Geoportal 4.0:
-
- Definition: Bhuvan Panchayat Geoportal 4.0 is an online geospatial data and services dissemination platform designed to integrate and utilize space-based information for governance and research initiatives, particularly in spatial planning up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Developer: This WebGIS platform has been developed by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) under the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Features and Capabilities:
- Visualization and Analysis: The platform enables the visualization and analysis of geospatial data.
- Web Map Service (WMS): It supports the sharing of web map services for various thematic data products.
- Data Products: All thematic data products are generated at a 1:10,000 scale under the Space-based Information Support for Decentralized Planning (SISDP) project.
- Applications: Bhuvan Panchayat Geoportal 4.0 supports the integration of space-based information into:
- Governance: Enhancing decision-making processes at the local government level.
- Research Initiatives: Facilitating research and analysis in spatial planning and development.
- Spatial Planning: Providing critical geospatial data for planning and development activities up to the Gram Panchayat level.
-
- Introduction to the National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) Portal:
-
- Definition: This portal is a comprehensive geospatial database designed to support situational assessment and effective decision-making during disasters and emergency situations across India.
- Features and Capabilities
- Comprehensive Geospatial Database: The NDEM portal provides a uniform, structured, multi-scale geospatial database for the entire country.
- Situational Assessment: Facilitates situational assessment to aid in decision-making during emergencies and disasters.
- Geo-Portal for Disaster Management: Acts as a national-level geo-portal to provide space-based information integrated with Decision Support System (DSS) tools and services from disaster forecasting organizations.
- Disaster Phases Coverage: Addresses all natural disasters in all phases, including preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation, contributing to effective Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR).
- Integration with Other Systems:
- Disaster Forecasting: Amalgamates data and services from various disaster forecasting organizations for value addition.
- Integrated Control Room for Emergency Response (ICR-ER): Functions as a Disaster Recovery and Data Provider node for the ICR-ER, established by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), New Delhi.
-
Scheme for Partial Reimbursement of Exploration Expenses for Holders of Exploration Licences (EL)
- News: To accelerate mineral exploration, the Ministry of Mines has launched the Scheme for Partial Reimbursement of Exploration Expenses for Holders of Exploration Licences (EL).
- Introduction:
-
- This scheme aims to provide financial support to licence holders for the exploration of critical minerals.
-
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Mines
- Reimbursement Details: Scheme offers a 50% reimbursement on expenses incurred during the exploration of critical minerals, with a maximum cap of Rs 20 crore.
- Increased Cap: The maximum cap can be increased to Rs 24 crore if the exploration licence holder hands over a G2 (general exploration) block for auction for the grant of a mining lease within three years from the execution of the exploration licence and it is successfully auctioned.
- Funding Source: National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET): Incentives for all selected licensees will be provided from the Rs 5,000 crore NMET fund.
- Repayment Terms:
-
- EL holders must repay the received amount within ten years, in equal annual instalments, starting from the beginning of mineral production.
- If a lump sum payment is received, the full amount must be repaid within one month.
-
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act)
|
- Unlimited Applications: There is no limit on the number of applications or the scheme’s outlay.
- Optional Participation: The scheme allows optional participation for EL holders granted licences through auction after the scheme’s introduction.
- Proposal Submission: Holders must submit an exploration expense reimbursement proposal within six months of receiving their EL.
- Impact on Obligations: Decisions on reimbursement will not impact the obligations of EL holders as per the terms of their EL set by the State Government at the time of auction.
- Exploration Stages and Reimbursement: The exploration exercise is divided into six stages, each eligible for 50% reimbursement with specific maximum outlays:
-
- Geological Mapping and Sampling: Up to Rs 1.50 crore.
- Geophysical Investigations: Up to Rs 3 crore.
- Exploratory Drilling: Up to Rs 10 crore.
- Chemical and Petrological Analysis: Up to Rs 2.50 crore.
- Mineral Beneficiation: Up to Rs 1.50 crore.
- Research Collaborations and Consultancy Services: Up to Rs 1.50 crore.
- Logistics Expenses: Up to Rs 1.50 crore annually, with a maximum of Rs 30 lakh per year.
-
- Critical minerals:
-
- These are raw materials essential for economic and national security, often used in high-tech industries and renewable energy technologies.
- They are typically rare, difficult to mine and substitute, and often vulnerable to supply chain disruptions due to limited global production and geopolitical factors.
- Example: copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt
-
UPSC GS 3
Steriphopus Wangala
- News: Steriphopus Wangala is a newly discovered species of spiders in Meghalaya.
- Introduction: Steriphopus wangala is a newly discovered species of spider from the West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya.
- Naming and Cultural Significance: This spider has been named after the Wangala Festival, also known as the 100 Drums Festival, which is a harvest festival celebrated by the Garo community.
- Taxonomy and Family: Steriphopus wangala belongs to the Palp-Footed Spider family. This family is distinguished by their first pair of legs, which are disproportionately powerful and heavily sclerotized.

- Physical Characteristics: The species is characterized by its distinctive reddish-brown color.
- Wangala Festival:
-
- Introduction: The Wangala Festival, also known as the 100 Drums Festival, is a significant and popular festival celebrated by the Garo community in Meghalaya.
- Significance and Timing:
- The Wangala Festival marks the end of the agricultural season.
- It is a time for the Garos to thank the spirits and deities for a bountiful harvest and seek their blessings for the upcoming year.
- This festival also signifies the onset of winter.
- Religious and Cultural Practices:
- During the Wangala Festival, the tribals offer sacrifices to please their main deity, Saljong, the Sun God.
- This is a crucial aspect of the festival, reflecting the community’s deep spiritual connection and gratitude.
-

-
-
- Highlights of the Festival:
- The highlight of the Wangala Festival is the rhythmic beat of a hundred drums, a significant element of Garo culture.
- These drums are traditionally made out of tree trunks and play a central role in the celebrations.
- The ceremony performed on first day is known as “Ragula” is performed inside the house of the chief. On the second day is known as “Kakkat”.
- Dance and Music:
- Towards the end of the festival, which lasts for several days, the largest group of dancers converges on the main celebration area.
- Accompanied by multiple drums, they perform ceremonial and traditional dances.
- The dance is characterized by dancers moving in sync with the rhythmic drumming, creating a vibrant and lively atmosphere.
- Highlights of the Festival:
-
Juno Probe
- News: New findings from NASA’s Juno probe provide a fuller picture of how widespread the lava lakes are on Jupiter’s moon Io.
- JUNO (Jupiter Near-Polar Orbiter):
-
- JUNO is a NASA spacecraft designed specifically to orbit and study the planet Jupiter.
- Launched on August 5, 2011, by an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, JUNO embarked on a mission to enhance our understanding of the largest planet in our solar system.
-
- Launch and Journey: The spacecraft began its 5-year journey to Jupiter upon its launch in 2011.
- Arrival and Orbit: JUNO arrived at Jupiter in 2016 and has since been orbiting the planet every 11 days in a highly elliptical orbit (4,400 by 2,700,000 km or 2,700 by 1,700,000 miles) over the planet’s poles.
Jupiter Moons
|
- Main Goal:
-
-
- The primary mission goal is to learn more about Jupiter’s origins and how the planet has changed over time.
- JUNO is the first orbiter to peer beneath Jupiter’s dense clouds.
-
- Solar-Powered: JUNO is powered by solar energy, which is noteworthy given the spacecraft’s distance from the Sun.
- Extended Mission: Although JUNO’s primary mission concluded in July 2021, it has been granted an extended mission that is expected to continue until 2025.
- Exploration of Jupiter’s Moons: During the extended mission, JUNO is exploring some of Jupiter’s most intriguing moons, including Ganymede, Europa, and Io.
- Further Investigations: JUNO will also conduct more detailed investigations of Jupiter’s atmosphere and rings.
Motor Neuron Diseases (MNDs)
- News: The third annual conference on MND ‘Awareness, Care and Management’ at Nimhans recently stated that symptomatic and supportive treatments help manage the condition better.
- Introduction:
-
- Motor Neuron Diseases (MNDs) are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy motor neurons, the cells responsible for controlling skeletal muscle activity such as walking, breathing, speaking, and swallowing.
- These neurons are located in the brain and spinal cord and play a crucial role in muscle movement.
-
- Symptoms and Onset:
-
- MND can manifest at any age, but symptoms typically appear after the age of 50.
- Early signs of MND include muscle weakness and slurred speech, which eventually lead to paralysis.
- MNDs tend to affect more males than females.
-
- Causes of MND:
-
- The exact cause of MND is not known, but it is generally believed to result from a combination of environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors.
- Most MND cases develop without an obvious cause, but around 1 in 10 cases is familial, meaning the condition is inherited due to a genetic mutation.
-
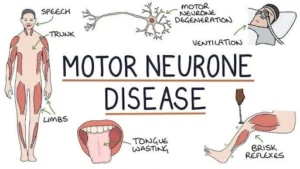
- Types of Motor Neuron Diseases: The group of diseases classified as MNDs includes:
-
- Progressive Bulbar Palsy
- Primary Lateral Sclerosis
- Progressive Muscular Atrophy
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- Kennedy’s Disease
- Post-Polio Syndrome
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): The most common type of MND, affecting both the upper and lower motor neurons, and impacting muscles of the arms, legs, mouth, and respiratory system.
- On average, individuals with ALS live for 3-5 years after diagnosis, though some live for 10 years or longer with supportive care.
-
- Treatment for MNDs:
-
- There is currently no cure or standard treatment for MNDs.
- However, symptomatic and supportive treatments can help improve comfort and maintain the quality of life for those affected.
-
ABHYAS
- News: India has successfully tested ‘Abhyas’ high-speed expendable aerial target.
- Introduction to ABHYAS:
-
- ABHYAS is a High Speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT).
- It is designed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Aeronautical Development Establishment in Bengaluru.
- It has been developed in collaboration with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and Larsen & Toubro.
-

- Features of ABHYAS:
-
- Realistic Threat Simulation: ABHYAS provides a realistic threat scenario for weapon systems practice, enhancing training and testing capabilities.
- Autonomous Flying: The system is designed for autonomous flying with the help of an autopilot.
- Ground Control System: Integration and control are managed via a laptop-based Ground Control System, facilitating aircraft integration and pre-flight checks.
- Data Recording: ABHYAS includes a feature to record data during flight for detailed post-flight analysis.
- Booster Design: The booster for ABHYAS has been designed by the Advanced Systems Laboratory.
- Navigation System: The navigation system has been developed by the Research Centre Imarat.
-
Read also: Understanding and Addressing the Risks of Spurious Liquor | UPSC
Raimona National Park
- News: Mainland Serow, vulnerable mammal species, sighted in Raimona National Park.
- Definition:
-
- Raimona National Park is a significant protected area located in the state of Assam, India, along the Indo-Bhutan border.
- This national park is renowned for its rich biodiversity and unique geographical setting.
-
- Geographical Boundaries:
-
- Northern Boundary: Shares the Indo-Bhutan international border with Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary in Bhutan.
- Western Boundary: Defined by the Sankosh River, which also marks the inter-state boundary between West Bengal and Assam from the Indo-Bhutan border.
- Eastern Boundary: Marked by the Saralbhanga River (also known as Swrmanga), which flows southward from Sarphang district of Bhutan.
-

- Vegetation: Moist sal forests, sub-Himalayan high alluvial semi-evergreen forests, savannah forests, moist-mixed deciduous forests, riparian fringing forests to khoir-sisoo forests.
- Fauna: The park is home to a variety of wildlife including tiger, clouded leopard, golden langur, Indian gaur, Asian elephant, spotted deer, wild buffalo, and hornbill.
- Flora: Orchid Species, Tropical Rainforest Species, Riverine Grasslands.
Rhisotope Project
- News: South African scientists have injected radioactive material into live rhinoceros horns to make them easier to detect at border posts in a pioneering project aimed at curbing poaching.
- Radioactive Rhino Project:
-
- The Radioactive Rhino Project, initiated in 2021 in South Africa, aims to combat rhino poaching by making rhino horns easier to detect at border posts and rendering them useless for human consumption.
-
- Project Objectives:
-
- Detection Enhancement: The project aims to enhance the detectability of rhino horns at international borders.
- Useless for Consumption: The horns are treated to be useless for traditional medicine or other human consumption purposes.
-

- Implementation:
-
- Radioactive Chips: Two tiny radioactive chips are inserted into the horns of 20 rhinos.
- Material: The low-dose radioactive material is designed to be detectable by radiation sensors at international borders.
- Safety: The material does not harm the animals or the environment.
- Duration: The radioactive material is expected to last five years on the horn, offering a cost-effective solution compared to dehorning every 18 months.
- Microdot Spraying: Additionally, 11,000 microdots are sprayed on each treated horn for further identification.
-
- Monitoring and Follow-Up:
-
- Blood Samples: Scientists will take follow-up blood samples to ensure the rhinoceroses are effectively protected.
-
Facts for Prelims
Duckworth-Lewis Method
- News: Frank Duckworth, 84, passed away on June 21.
- Definition:
-
- English statistician Frank Duckworth developed the DL method with Tony Lewis.
- The original method was first used in international cricket in 1997.
- It was formally adopted by the ICC as the standard for setting revised targets in truncated games in 2001.
-
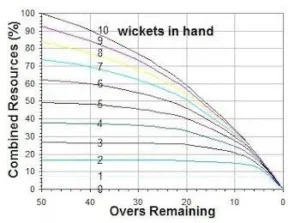
-
-
- The DL method replaced the rain rule that was used previously to calculate targets in interrupted matches, most infamously during the 1992 ODI World Cup semi-final between England and South Africa in Sydney.
- In 2014, it was renamed the Duckworth-Lewis-Stern method after the retirement of Duckworth and Lewis and the modifications made to the system by Australian statistician Steven Stern.
-

