UPSC GS 1
Mata Ni Pachedi Paintings
- News: Mata ni Pachhedi art form from Ahmedabad has got the geographical indication (GI) tag.
- Definition:
-
- Mata ni Pachedi is an ancient religious textile folk art form from Gujarat, inspired by the Kalamkari style of painting. Here are the key aspects of this art form:
-
- Region: Gujarat, India.
- Community: The Vaghari community is traditionally known for creating these artworks.
- Purpose: These paintings are used in religious rituals and ceremonies.

- Creators: Historically, only men paint these artworks.
- Subject Matter: The central figure in these paintings is often the divine feminine (goddess), surrounded by images of devotees, flora, and fauna.
- Tools and Materials: Artists use a kalam (pen) made from bamboo sticks to draw the intricate designs.
- Colors: The traditional color palette includes maroon, black, and white, creating a distinctive and recognizable style.
Garnet
- News: New research reveals that Australia’s distinctive pink sand originates from Antarctic mountains.
- Definition:
-
- Garnet is a mineral known for its deep red color and various industrial uses.
-
- Color and Appearance:
-
- Garnet is typically deep red in color, but can also occur in shades of orange, yellow, green, and even black.
- It crystallizes at high temperatures and can be opaque, transparent, or translucent.
-

- Formation:
-
- Garnets form in metamorphic rocks such as schist, amphibolite, and eclogite, as well as in some igneous rocks like granite and peridotite.
- They develop deep within the Earth’s crust under conditions similar to those where diamonds are formed.
-
- Types:
-
- There are six main types of garnet, each with slightly different chemical compositions. Garnets can also be found in combinations, such as pyrope-almandine or pyrope-spessartine.
-
- Production: Australia is a significant producer of garnets, accounting for almost half of the world’s supply. Other major producers include India, USA, and China.
- Uses:
-
- Garnet is highly valued for its hardness and abrasive properties, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
- Manufacturing of blasting media and abrasives for sandblasting and waterjet cutting.
- Production of grinding wheels, mosaic cutting stones, and decorative wall plasters.
- Use in ceramics, polishing of picture tubes, and glass polishing.
- Application as an antiskid surface for roads and air strips due to its durability.
-
Container Port Performance Index (CPPI) 2023
- News: As many as nine ports of India have made it to the global top 100 rankings in the latest edition of Container Port Performance Index.
- Definition: The Container Port Performance Index (CPPI) is a highly regarded benchmark that evaluates the performance of ports based on parameters such as productivity, efficiency, and reliability.
- Released by: The World Bank and S&P Global Market Intelligence.
- Purpose: The CPPI serves as a reference point for various stakeholders, including national governments, port authorities, development agencies, supra-national organizations, and private operators involved in trade, logistics, and supply chain services.
- CPPI 2023 Highlights:
- Top Ports: Yangshan port in China and Salalah port in Oman were ranked as the top two ports globally.
- Indian Ports Performance:
- Visakhapatnam Port: Ranked 19th globally, a significant improvement from its 115th rank in 2022. It achieved a turnaround time (TRT) of 21.4 hours, 27.5 moves per crane hour, and minimized berth idle time.
- Mundra Port: Ranked 27th, up from the 48th position in 2022.
- Additional Indian Ports in Top 100: Seven more Indian ports secured ranks in the top 100 global ports:
-
- Pipavav: Ranked 41
- Kamarajar: Ranked 47
- Cochin: Ranked 63
- Hazira: Ranked 68
- Krishnapatnam: Ranked 71
- Chennai: Ranked 80
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPA): Ranked 96
-
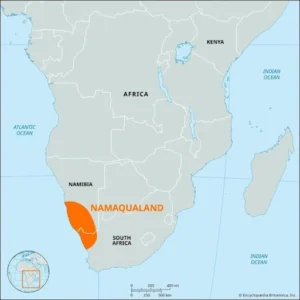
Namaqualand
- News: Scientists recently uncovered the world’s oldest inhabited termite mounds along the Buffels River in Namaqualand, which date back an astonishing 34,000 years.
- Geographic Location:
-
- Namaqualand is a desert region in southwestern Africa.
- Stretching from north to south, it spans from the Karas region of Namibia to the Northern Cape province of South Africa.
- From west to east, it extends from the Namib Desert to the Kalahari, covering an area of 400,000 square kilometers.
-
- Subregions:
-
- Great Namaqualand: This is the Namibian section located north of the Orange River.
- Little Namaqualand: This is the South African section located south of the Orange River.
-
- Climate and Vegetation:
-
- Namaqualand is characterized by its very dry climate.
- For much of the year, succulents are almost the only plants visible on the vast plains.
- These plants can store water for long periods and are well-adapted to surviving droughts.
- Most of the region’s rain falls in the winter. If there is sufficient rainfall, wildflowers bloom and cover Namaqualand for a few weeks during springtime.
-
- Inhabitants: The area was traditionally inhabited by the Nama people until the German occupation of the region in the 19th century.
- Natural Resources:
-
- Namaqualand is rich in natural resources, particularly copper, which the Nama people mined for hundreds of years.
- In the early 1900s, diamonds were discovered in several parts of Namaqualand, including Sperrgebiet in Namibia and the Richtersveld in South Africa.
-
- What are Termites?
-
- Termites are underground insects that feed on wood, frequently damaging homes and other buildings.
-

-
-
- Termites are sometimes called “white ants” because of their pale coloring and physical similarities to ants.
- Most termite species are found in the tropics, but several dozen species are found throughout the United States, including Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Alaska is the only U.S. state without termites.
- Termites obtain nutrients from wood and plant materials, but they can’t digest their food on their own. Instead they have symbiotic protozoa and bacteria in their guts to break down the tough plant fibers.
- These insects live in colonies with their own hierarchies.
- Each colony has three kinds of termites: royalty, soldiers, and workers.
- Termites can be beneficial because they decompose dead plant matter and return the nutrients to the ecosystem, just like earthworms and fungi.
- Ants are among the biggest predators of termites.
-
UPSC GS 2
Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
- News: The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a significant deliverable of India’s G-20 Presidency, launched by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2024.
- Launch and Objective: The GIDH was launched by WHO with the aim of accelerating the implementation of the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- Function:
-
- Collaboration Platform: GIDH serves as a collaborative platform bringing together governments, international organizations, and private entities working in the field of digital health.
- Knowledge Sharing: It facilitates the exchange of digital health goods and knowledge to promote equitable access to digital health technologies.
-
- Goal:
-
- Health Outcomes Improvement: GIDH aims to support countries in leveraging digital technologies to enhance health outcomes and strengthen healthcare systems.
- Equitable Access: The initiative focuses on promoting equitable access to digital health solutions, ensuring that advancements in digital health benefit all populations.
-
Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC)
- News: The Supreme Court recently refused to entertain a writ petition seeking revocation of the CBFC certification given to the Annu Kapoor starter film ‘Hamare Baarah’.
- Definition: The Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC), commonly referred to as the Censor Board, is a statutory body under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting in India.
- Regulatory Authority: The CBFC regulates the public exhibition of films in India based on the Cinematograph Act, 1952.
- Certification Requirement: Films can only be publicly exhibited in India after receiving certification from the CBFC.
- Legal Framework: The process follows the Cinematograph Act, 1952, the Cinematograph (Certification) Rules, 1983, and guidelines issued by the Central Government.
- Membership: The CBFC consists of a chairperson and other members, with a minimum of 12 and a maximum of 25 members appointed by the Central Government.
- Advisory Panels: Each regional office is assisted by Advisory Panels whose members are nominated by the Central Government from various walks of life for a two-year term.
- Categories of Film Certification: The CBFC classifies films into 4 categories based on their content:
-
- U (Universal): Suitable for viewers of all age groups.
- U/A: Universal, but children under the age of 12 require adult supervision.
- A (Adult): Restricted to adult audiences.
- S (Special): Restricted to specialized audiences, such as professionals like doctors and farmers.
-
- Activities and Responsibilities:
-
- Seminars and Surveys: The CBFC conducts seminars involving film critics, writers, and industry professionals. It also performs national surveys to gauge public reaction, which helps in forming guidelines for film certification.
-
- Headquarters: Located in Mumbai.
- Regional Offices: There are nine regional offices located in Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Thiruvananthapuram, Hyderabad, New Delhi, Cuttack, and Guwahati.
National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme (NFIES)
- News: The Union Government has approved the Central Sector Scheme “National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme (NFIES) with a total financial outlay of Rs. 2254.43 crore.
- Definition: It is a Central Sector Scheme with a substantial financial allocation of Rs 2,254.43 crore for the period spanning from 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- Aim: Its primary objective is to bolster forensic infrastructure across India.
- Ministry: This initiative is being spearheaded by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Components of NFIES:
- Establishment of NFSU Campuses:
-
- The scheme aims to establish campuses of the National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) across various locations in India.
- This expansion will enhance the academic and research capabilities in forensic sciences.
-
- Establishment of CFSLs:
-
- Central Forensic Science Laboratories (CFSLs) will be set up in strategic locations nationwide.
- These laboratories play a crucial role in conducting scientific analysis and providing expert opinion in criminal investigations.
-

- Enhancement of Delhi Campus of NFSU:
-
- The existing infrastructure of the NFSU campus in Delhi will be improved to accommodate increased capacity and upgraded facilities.
-
- Need for NFIES:
- Legislative Mandate:
-
- The enactment of new criminal laws mandates forensic investigation for offenses punishable with seven years or more.
- This legislative requirement is expected to significantly increase the workload of forensic laboratories across the country.
-
- Shortage of Trained Manpower:
-
- There is a notable scarcity of trained forensic professionals in India’s Forensic Science Laboratories (FSLs).
- The expansion of NFSU campuses and establishment of new CFSLs will address this shortage by providing specialized training and education in forensic sciences.
-
- Case Load and Pendency:
-
- Existing forensic laboratories are burdened with high caseloads and pending cases.
- The expansion under NFIES aims to alleviate this pressure by increasing forensic capacity and efficiency.
-
- Government’s Conviction Rate Goal:
-
- Aligning with the Government of India’s objective to achieve a conviction rate exceeding 90%, NFIES seeks to strengthen forensic capabilities crucial for securing justice through robust scientific investigation and evidence analysis.
-
Read also: Indian Migrants in Gulf Countries: Opportunities and Challenges UPSC
International Hydrographic Organisation
- News: On 21 June every year, the International Hydrographic Organisation (IHO) celebrates the World Hydrography Day to raise awareness about hydrography.
- Overview:
-
- The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to ensuring that all the world’s seas, oceans, and navigable waters are thoroughly surveyed and charted.
-
- Founded: 1921
- Purpose:
-
- To coordinate the activities of national hydrographic offices,
- promote uniformity in nautical charts and documents,
- issue best practices for surveys,
- provide guidelines to maximize the use of hydrographic survey data, and
- develop hydrographic capabilities in Member States.
-
- Member States: 100 countries
-
- India has been an active member of the IHO since 1955.
- Membership: Indian Naval Hydrographic Department (INHD): Established in 1874 in Kolkata (formerly known as the Marine Survey of India), it serves as the nodal agency for hydrographic surveys in India.
-
- Host: The IHO Secretariat is hosted by the Principality of Monaco.
- Functions and Activities: The IHO coordinates national hydrographic offices to:
-
- Promote uniformity in the creation and distribution of nautical charts and documents.
- Issue guidelines and best practices for conducting hydrographic surveys.
- Ensure that hydrographic survey data is used effectively.
- Enhance the hydrographic capabilities of its Member States through training and development.
-
- World Hydrography Day:
-
- It is celebrated annually on June 21.
- The theme for 2024 is “Hydrographic Information – Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Sustainability in Marine Activities”.
-
Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Programme (FTI-TTP)
- News: The Union Home Minister of India recently inaugurated the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Programme (FTI-TTP) at the Indira Gandhi International Airport in Delhi.
- Overview:
-
- It is an initiative by the Central Government aimed at providing faster, smoother, and safer immigration clearance.
-
- Objectives:
-
- The program aims to reduce congestion at airports by offering expedited emigration and immigration clearance for pre-verified travelers.
-
- Collaboration:
-
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has collaborated with the Ministry of Civil Aviation and the Bureau of Immigration to implement the FTI-TTP.
-
- Comparison:
-
- FTI-TTP is similar to the Global Entry Program offered by the United States, allowing pre-approved and low-risk travelers to benefit from expedited immigration and security clearance upon arrival.
-
- Implementation:
-
- Phase One: The program was initially launched at airports in New Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Kochi, and Ahmedabad.
- Phase Two: The first phase covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders, while the second phase will include foreign travelers.
-
- Features:
-
- E-gates: The program runs on e-gates or automated border gates, minimizing human intervention in the immigration clearance process.
- Online Portal: The FTI-TTP will be implemented through an online portal, with the Bureau of Immigration acting as the nodal agency.
- Enrollment: Applicants must register online with their details and documents. Once approved, they can bypass long immigration queues upon arrival in India.
- Validity: FTI registration is valid for up to five years or until the passport’s validity, whichever comes first.
-
- Process:
-
- Arrival at E-gate: The registered passenger scans their boarding pass at the e-gate to retrieve flight details.
- Passport and Biometrics: The passport is scanned, and the passenger’s biometrics are authenticated at the e-gate.
- Clearance: Once identity and biometrics are verified, the e-gate opens, and immigration clearance is granted.
-
UPSC GS 3
The Trinity Challenge (TTC)
- News: A project by the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology, Delhi (IIIT-Delhi), has won the joint second prize in Trinity Challenge’s second competition.
- Purpose: TTC is a charity that supports the development of data-driven solutions to protect against global health threats.
- Partnership: It comprises over 40 leading global organizations from the private, public, and social sectors, united to use data and advanced analytics for health innovation and preparedness.
- Initiation: Launched in response to the Covid-19 pandemic to improve global readiness for health emergencies.
- Activities:
-
- Public Challenges: TTC launches, supports, and funds public challenges to foster innovative solutions.
- Initial Challenge: Focused on delivering data-driven solutions to predict, respond to, and recover from pandemics, awarding £5.7 million to successful teams.
- Second Challenge: The Trinity Challenge on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) invites global minds to create data-driven solutions to protect the efficacy of antibiotics.
-
- Key Project: AMRSense:
- Leadership: Led by IIIT-Delhi in collaboration with CHRI-PATH, 1mg.com, and ICMR.
- Objective: AMRSense aims to empower communities by addressing challenges in engaging, motivating, and training community health workers (CHWs) in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance and management.
- Challenges Addressed:
-
- Lack of a comprehensive data ecosystem.
- Insufficient analytics capabilities for effective AMR management.
-
- Focus: Building a proactive One Health ecosystem to improve AMR surveillance and management.
- Goals of The Trinity Challenge:
-
- Inclusive Innovations: Using data and analytics to create solutions that are inclusive and improve health outcomes globally.
- Enhanced Preparedness: Building a world that is better prepared for health emergencies through collaborative efforts and innovative solutions.
- Support and Funding: Providing financial support to promising projects and ideas that address critical health challenges.
-
Iberian lynx
- News: The Iberian lynx has rebounded from “endangered” to “vulnerable,” as per a new study by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
- Definition: The Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus) is a critically endangered carnivore endemic to Europe, known for its distinctive pointed ears, long legs, and leopard-like spotted fur.
- Characteristics and Behavior:
- Sexual Dimorphism: Like other cat species, Iberian lynx exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males typically being larger and heavier than females.
- Nocturnal Behavior: They are primarily nocturnal, with activity patterns closely synchronized with their main prey, which is the rabbit.

- Habitat Requirements: Iberian lynx prefer variable terrain below 1300 meters, characterized by a mix of closed Mediterranean scrubland and open grassland patches, often near marshes.
- Historical and Current Distribution: Once widespread throughout the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal), the species is now sparsely distributed in limited areas of these countries.
- Human-Related Threats: The main threats to the Iberian lynx include poaching, habitat destruction due to human activities, illegal hunting, and a reduction in their primary food source, the rabbit.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Red List: The Iberian lynx is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- CITES: It is also listed under Appendix II of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora).
-
Russell’s Viper
- News: With a spike in the snakebite cases in Bangladesh, all health centres have been ordered to ensure ample stock of anti-venom. In rural areas, hospitals have reported a rise in snakebites, particularly from the Russell’s viper.
- Overview:
-
- Russell’s Viper, scientifically known as Daboia russeli, is a highly venomous terrestrial snake belonging to the family Viperidae.
- It is named after Patrick Russell, a Scottish herpetologist who first described many of India’s snakes in the 1790s.
-
- Significance:
-
- It is one of the “big four” deadliest snakes in India, alongside the Common krait (Bungarus caeruleus), the Indian Cobra (Naja naja), and the Saw-scaled viper (Echis carinatus).
-

- Distribution: Russell’s vipers are found across various regions in Asia, including:
-
- India
- Sri Lanka
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- Myanmar
- Thailand
- Pakistan
- Cambodia
- Tibet
- China (Guangxi, Guangdong)
- Taiwan
- Indonesia
-
- Habitat: Russell’s vipers are primarily found in:
-
- Open, grassy, or bushy areas
- Second-growth forests (scrub jungles)
- Forested plantations
- Farmland
- They tend to avoid dense forests but are often found in areas where human contact and rodent prey are abundant, such as farmlands.
- Despite their presence in these areas, they generally avoid human contact and do not actively seek to bite people.
- Most bites occur when humans inadvertently step on or try to handle the snake, with fatalities often resulting from delayed medical treatment.
-
- Features:
-
- Size: Russell’s vipers can grow up to 1.5 meters in length.
- Appearance: They are identified by their distinctive reddish-brown spots outlined in black and white.
- They have a wide, triangular head with small, overlapping scales, large nostrils, and small eyes with vertical pupils.
-
- Behavior: Mainly nocturnal, these snakes become active as the sun fades. They are quite sedentary, often staying in one place for several days unless disturbed.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
-
Barda Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: Forest Department in Gujarat has started translocating spotted deer (cheetal) and sambars from Gir Forest to the Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS).
- Location:
-
- Barda Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the state of Gujarat, India.
-
- Rivers and Dams:
-
- The sanctuary is nourished by two waterways, the Bileshvary River and the Joghri River, and features two dams, Khambala and Fodara.
-
- Inhabitants:
-
- Ethnic groups such as the Maldharis, Bharvads, Rabaris, and Gadhvis inhabit this region.
-
- Conservation Efforts:
-
- To develop Barda as a secondary habitat for the Asiatic lion, the state government initiated the ‘Gir-Barda Project’ in 1979.
-
- Flora: Some notable plants include Rayan, Babul, Ber, Jamun, Amli, Gorad, Bamboo, Dhav, Dhudhlo etc.
- Fauna: Leopard, Hyena, Wild boar, wolf, Jackal, blue bull, rare and endangered spotted eagle, crested hawk eagle etc.
- Asiatic Lions:
-
- It is endemic to Gir landscape of Gujarat, the Asiatic Lion (Scientific name – Panthera leo persica) is one of five pantherine cats native to India.
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I
- CITES : Appendix I
-
Space Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM)
- News: A part of the Long March 2-C rocket, carrying the China-France SVOM satellite, fell near a residential area and exploded shortly after its launch from Xichang Satellite Launch Centre.
- Overview of Space Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM):
-
- The Space Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM) is a collaborative French-Chinese satellite mission designed to detect and study gamma-ray bursts (GRBs).
-
- Launch Vehicle: Long March-2C rocket
- Launch Site: Xichang Satellite Launch Center, Sichuan Province, China
- Weight: 930 kilograms
- Instruments: Four in total – two French and two Chinese
- Orbit: Over 600 kilometers above Earth
- Designed Life: 5 years (potential operational life up to 20 years)
- Primary Goal: To detect and study gamma-ray bursts, the brightest and most energetic events in the universe.

- Potential Achievements:
-
- Detecting the most distant GRBs, corresponding to the earliest GRBs in the universe.
- Providing data to test the laws of physics under extreme conditions.
- Offering insights into the dynamics and evolution of the universe.
-
- Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs):
- Origin: GRBs generally occur from the explosion of massive stars (over 20 times the mass of the sun) or the fusion of compact stars.
- Energy Release: They emit energy equivalent to over a billion billion suns.
- Observational Significance: Observing GRBs is like looking back in time, as the light from these events takes a long time to reach Earth.
- Challenges: GRBs are hard to catch because they can appear anywhere in the sky and last for just a few seconds.
-
- They are absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, necessitating space-based observations.
-
- Scientific Importance:
-
- Historical Insight: The rays from GRBs carry traces of the gas clouds and galaxies they pass through, providing valuable data on the history and evolution of the universe.
- Physics Testing: The data gathered by SVOM will help test the laws of physics under conditions that cannot be replicated on Earth.
- Understanding Universe Dynamics: Insights into the dynamics of the universe will be enhanced through the study of GRBs.
-
State of Global Air (SoGA) Report 2024
- News: Air pollution is having an increasing impact on human health, becoming the second leading global risk factor for death, according to the fifth edition of the State of Global Air (SoGA) report.
- The State of Global Air (SoGA) Report:
-
- It is an important annual publication released by the Health Effects Institute (HEI) in partnership with UNICEF.
- The report provides comprehensive data and analysis on air quality and its health impacts globally.
-
- Key Findings:
- Air Pollution as a Leading Risk Factor:
-
- Air pollution has become the second-leading global risk factor for death, overtaking tobacco and diabetes and second only to hypertension.
-
- Impact on Non-Communicable Diseases:
-
- Nearly 90% of the disease burden from air pollution is due to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
-
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Dominance:
-
- Six out of ten deaths attributed to air pollution are caused by the tiny PM2.5 particles.
- Ozone and household air pollution account for 38% and 6% of air pollution-related deaths, respectively.
-
- Global Death Toll:
-
- Air pollution claimed 8.1 million lives worldwide in 2021, with a significant burden observed in India and China.
- India accounted for one in four of these deaths.
-
- Country-Specific Data:
-
- India and China together represented 54% of the global disease burden due to air pollution in 2021.
- Air pollution in India caused 21 lakh (2.1 million) deaths, while in China, it led to 23 lakh (2.3 million) deaths.
-
- Child Mortality:
-
- More than 700,000 deaths in children under five were linked to air pollution, making up 15% of all global deaths in this age group.
- Lower respiratory infections (LRIs) were the leading cause of death among children under five due to air pollution.
- India recorded the highest number of deaths in this demographic, with 169,400 children under five dying due to air pollution in 2021, translating to approximately 464 child deaths daily.
-
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
-
- In 2021, nearly 50% of all ozone-related COPD deaths occurred in India (237,000 deaths), followed by China (125,600 deaths) and Bangladesh (15,000 deaths).
-
Fire Dragon 480
- News: A new study by the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has claimed that China’s tactical ballistic missile, the Fire Dragon 480, possesses the capability to sink a US Ticonderoga-class cruiser patrolling the Red Sea.
- Definition: The Fire Dragon 480 is a significant Chinese long-range rocket developed by China’s Norinco Group primarily for export purposes.

- Specifications:
-
- Type: It is a 750-mm tactical ballistic missile.
- Precision-guidance: Equipped with precision-guidance sensors, allowing it to accurately target and strike moving objects.
- Platform: Launched from a high-speed wheeled platform designed to operate effectively in harsh environments.
- Warhead: It carries a warhead that exceeds 400 kg, making it more potent compared to conventional anti-ship missiles.
- Impact Velocity: Capable of achieving speeds exceeding 500 meters per second, ensuring significant destructive power upon impact.
- Range: Initially believed to have a range limit of 290 km (180 miles). Chinese researchers suggest its practical range could potentially exceed 500 km.
- Adoption: Adopted by the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) in 2019, indicating its integration into China’s military capabilities.
- Export Deal: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) secured the only publicly disclosed export deal for the Fire Dragon 480, amounting to a significant $245 million agreement.
-
Read also: Western Disturbances: Origin, Spread, Effects and Climate Change | UPSC
Encephalartos Woodii
- News: Scientists are using remote sensing technologies and artificial intelligence to assist the search for a female to Encephalartos woodii plant in the Ngoye Forest.

- Definition:
-
- Encephalartos woodii, commonly known as Wood’s cycad, is a distinctive plant native to South Africa and a member of the cycad family.
-
- Appearance:
-
- Encephalartos woodii is characterized by thick trunks and large, stiff leaves that form a majestic crown.
- Its appearance is striking and contributes to its popularity in horticulture.
-
- Reproductive Strategy:
-
- Like all cycads, Encephalartos woodii reproduces through cones rather than flowers.
- The male cones produce pollen, which is carried by insects (such as weevils) to the female cones for fertilization.
-
- Sexual Differentiation:
-
- Differentiating between male and female cycads is challenging until they mature and produce cones.
- Female cones are typically wide and round, while male cones are elongated and narrower.
-
- Cycads as “Living Fossils”:
-
- Evolutionary History: Cycads are often referred to as “living fossils” due to their ancient lineage dating back to the Carboniferous period, approximately 300 million years ago.
- They thrived during the Mesozoic era, also known as the Age of Cycads.
- Gymnosperms: Cycads belong to the group of gymnosperms, which includes conifers and ginkgos. They reproduce using cones, unlike flowering plants (angiosperms).
-
- Conservation Status and Threats:
- Endangered Status:
-
- Despite their ancient lineage and resilience, cycads, including Encephalartos woodii, are among the most endangered living organisms on Earth.
- The slow growth and reproductive cycles (taking ten to 20 years to mature) contribute to their vulnerability.
-
- Threats:
-
- The primary threats to cycads include habitat loss due to deforestation, grazing, and collection for horticultural purposes.
- Their striking appearance and ancient lineage make them desirable in exotic ornamental horticulture, leading to illegal trade and further endangerment in the wild.
-
World Investment Report 2024
- News: The UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) recently released the World Investment Report 2024.
- Definition:
-
- The World Investment Report, published by the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
- It provides a comprehensive analysis of global trends in foreign direct investment (FDI) and its implications for development.
-
- Focus of the Report:
- Global FDI Trends:
-
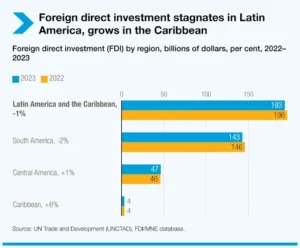
- Overall, global FDI experienced a slight decline of 2% in 2023.
-
- FDI in Developing Countries:
-
- FDI flows to developing countries decreased by 7% to $867 billion. This decline was primarily driven by an 8% decrease in FDI to developing Asia.
-
- China’s FDI:
-
- China, the world’s second-largest recipient of FDI, saw a rare decline in inflows.
-
- Sectoral Trends:
-
- There was reduced investment in infrastructure and the digital economy sectors. However, sectors like manufacturing and critical minerals, which are integral to global value chains, experienced strong growth.
-
- Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
-
- International investment in sectors crucial for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in developing countries declined in 2023.
-
Claude 3.5 Sonnet
- News: Anthropic, OpenAI’s biggest rival, has launched its latest AI model called Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
- Definition:
-
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet, developed by Anthropic as part of their generative pre-trained transformers, represents a notable advancement in large language models (LLMs).
-
- Development and Model Family:
-
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet is the successor to Claude 3 Sonnet, belonging to Anthropic’s series of generative pre-trained transformers.
- These models are trained on vast text datasets to predict the next word, facilitating natural language understanding and generation.
-
- Performance Advancements:
-
- Speed and Efficiency: Claude 3.5 Sonnet is reported to be twice as fast as Claude 3 Sonnet, enhancing efficiency in processing tasks.
- Task Performance: It sets new benchmarks across various domains:
- Excelling in coding tasks evaluated by HumanEval.
- Performing well in graduate-level reasoning tests like GPQA (Graduate-Level Physics Question Answering).
- Demonstrating strong knowledge at the undergraduate level based on MMLU (Modern Multilingual Language Understanding) metrics.
-
- Capabilities:
- Naturalness and Relatability: Claude 3.5 Sonnet shows improvements in understanding subtle nuances, humor, and complex instructions.
-
- It excels in generating high-quality content that is natural and relatable, enhancing its utility in diverse applications.
-
- Benchmark Performance:
-
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet has outperformed several prominent models in seven out of eight overall benchmarks.
- Notable competitors include GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Meta’s Llama 3 400B, underscoring its superiority in various evaluation metrics.
-
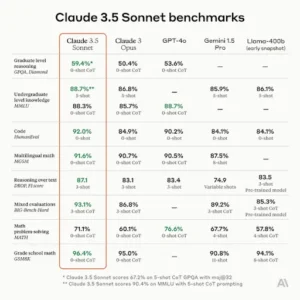
- Vision Capabilities:
-
- As a vision model in AI, Claude 3.5 Sonnet excels in understanding and analyzing visual information, including images and videos.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet shows notable improvements in tasks requiring visual reasoning, such as decoding charts, graphs, and other visual data representations.
- It can accurately extract and interpret text even from unclear or imperfect images, showcasing enhanced capabilities in optical character recognition (OCR).
- The model can quickly identify and interpret information from visual cues, such as reading text from posters or distant walls. This capability highlights its efficiency in real-time applications where rapid visual processing is essential.
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet’s ability to transcribe text from images is particularly beneficial across industries such as retail, logistics, and financial services.
-
- What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
-
- A large language model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) program that can recognize and generate text, among other tasks.
- LLMs are trained on huge sets of data—hence the name “large.”
-

