UPSC GS 1
Lonar Lake
- News: The Maharashtra Government plans to submit a proposal to the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to include the famous Lonar Lake in Buldhana district in the UNESCO World Heritage Sites list.
- Location and Formation: Lonar Lake is a lagoon located in the Buldhana district of Maharashtra, India. It was created as a result of a meteorite impact.

- Unique Characteristics:
-
- It is the only known saline crater lake in the world, formed approximately 50,000 years ago by the impact of a meteorite.
- The water of the lake is notably seven times saltier than seawater.
- Physical Dimensions: The lake has a diameter of 1.2 kilometers and a depth of 150 meters. It is encircled by a rim of hills that rise up to an angle of 75 degrees.
- Color Changes and Microorganisms:
- One of the lake’s most remarkable features is its changing color, which shifts from green to pink depending on the season and water conditions.
- This color change is caused by the presence of microorganisms that flourish in the lake’s saline and alkaline environment.
Read also: PRAGATI Portal for UPSC Preparation – Overview & Benefits
UPSC GS 2
UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs
- News: India has been chosen to Chair the 68th Session of the Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND).
- Definition: The United Nations Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND) is the primary policy-making body for drug-related issues within the United Nations system.

- Mandate and Responsibilities:
- The CND is tasked with monitoring global drug trends, assisting Member States in developing balanced drug policies, and overseeing the implementation of major international drug control conventions.
- It has the authority to decide on the scope of control of substances under three key international drug control conventions: the 1961, 1971, and 1988 Conventions.
- Establishment:
- The Commission was established in 1946 by a resolution of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- It is one of ECOSOC’s functional commissions and serves as the governing body for the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
- Membership and Structure:
- The CND consists of 53 Member States, which are elected by ECOSOC.
- The Commission is chaired by a Bureau, with one representative from each regional group.
- It also includes five subsidiary bodies: the Heads of National Drug Law Enforcement Agencies from Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia and the Pacific, Africa, and the Subcommission in the Near and Middle East.
- Meetings and Sessions:
- The CND meets annually to adopt decisions and resolutions, with intersessional meetings convened throughout the year.
- Towards the end of each year, it holds a reconvened session to discuss budgetary and administrative matters in its role as the governing body of the United Nations drug programme.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria.
Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH)
- News: The Supreme Court recently ordered the Archaeological Survey of India and the UNESCO’s Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH) for the restoration of two heritage buildings in Mysore city.
- Establishment and Purpose: Founded in 1984, INTACH is an autonomous non-profit organization focused on preserving India’s extensive natural, built, and cultural heritage.

- Scope and Reach:
- It is the largest non-profit membership organization in India dedicated to the protection and conservation of the country’s tangible and intangible heritage.
- Recognized globally as one of the largest heritage organizations, INTACH has over 228 chapters throughout India.
- Volunteer Network: INTACH operates as a volunteer-driven entity, with its dedicated volunteers playing a key role in spreading awareness about India’s rich cultural heritage across cities, towns, and villages.
- Headquarters and Operations: New Delhi.
- Divisions: It operates through multiple specialized divisions, including:
- Architectural Heritage.
- Natural Heritage.
- Art and Material Heritage.
- Intangible Cultural Heritage.
- Heritage Education and Communication Services (HECS).
- Heritage Crafts and Community.
- Heritage Tourism.
- Listing Cell.
- INTACH Knowledge Centre.
- INTACH Heritage Academy.
India Internet Governance Forum
- News: The India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) 2024 will be held on December 9-10, 2024, at the Bharat Mandapam Convention Center, Pragati Maidan, New Delhi.
- Definition:
-
- The India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) is the Indian chapter of the United Nations Internet Governance Forum (UN IGF).
- It serves as a global, multi-stakeholder platform aimed at fostering dialogue on public policy issues related to the Internet.

- Establishment and Goals:
- Established in 2021, the IIGF seeks to maximize the opportunities presented by the Internet while addressing the associated challenges and risks.
- Collaboration and Inclusivity:
- IIGF promotes collaborative discussions among a wide range of stakeholders, including representatives from government, civil society, industries, technical communities, think tanks, and industry associations.
- It is supported by a 14-member multi-stakeholder committee and is known for its inclusive and collaborative approach.
- Role in Policy Shaping:
- The forum plays a vital role in shaping policies for an open, secure, and accessible Internet. Key areas of focus include cybersecurity, digital inclusion, data privacy, and emerging technologies.
- Highlights of IIGF 2024:
- Support and Organization: The IIGF 2024 is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI).
- Purpose and Focus: This initiative aims to explore critical aspects of Internet governance, foster meaningful dialogue, and showcase India’s leadership in the global digital ecosystem.
- Key Themes:
- The forum will focus on creating balanced, growth-oriented legal and regulatory frameworks that strengthen Internet governance.
- Another important focus will be Responsible AI, promoting the ethical and effective use of artificial intelligence for societal benefit.
UPSC GS 3
Copernicus Programme
- News: A brand-new Copernicus Sentinel -1C satellite was successfully launched from the European Spaceport in French Guiana on board a Vega C rocket operated by Arianespace.
- Purpose: The Copernicus Programme is a European initiative that monitors the Earth and its environment to benefit European citizens.

- Satellite System:
- The programme is supported by a dedicated fleet of Sentinel satellites and contributing missions.
- Sentinel satellites are specifically designed to meet the data requirements of Copernicus information services and their users.
- Since the launch of Sentinel-1A in 2014, the European Union has been working on deploying a full constellation of nearly 20 satellites in orbit by 2030.
- Data Collection and Sources:
- Integrated Systems: Copernicus relies on a complex system that gathers data from multiple sources, including:
- Earth observation satellites.
- In-situ sensors such as ground stations, airborne, and sea-borne sensors.
- Thematic Areas Addressed: The programme delivers services in six thematic domains:
- Atmosphere.
- Marine.
- Land.
- Climate.
- Emergency response.
- Security.
- Management and Accessibility:
- Governance and Funding:
- Copernicus is funded, coordinated, and managed by the European Commission in collaboration with partners such as the European Space Agency and other EU agencies.
- Data Accessibility:
- A significant portion of Copernicus data is freely available to users.
- The data is processed and transformed into services to meet diverse needs.
Indian Star Tortoise
- News: Recent research has identified two genetically distinct groups within the Indian star tortoise species: the northwestern and southern groups.
- About Indian Star Tortoise:
- Name and Appearance:
- The Indian star tortoise is named for the distinctive star-like patterns on its high-domed shell, which make it easily recognizable.
- Its unique shell shape and striking patterns have made it a popular species in the global exotic pet trade.

- Habitat:
- The Indian star tortoise is adaptable to various habitats, thriving in semi-arid lowland forests, thorn scrub forests, semi-desert areas, and arid grasslands.
- This species is well-suited for environments that experience seasonal wet and dry periods, with many populations living in areas with a monsoon season followed by extended dry spells.
- Distribution:
- Endemic to the Indian subcontinent, the Indian star tortoise can be found in the arid regions of northwest India (bordering Pakistan), South India, and Sri Lanka.
- However, due to the pet trade, it has been found in homes as far away as Canada and the U.S.
- The tortoise is generally crepuscular, meaning it is most active during the early morning and late afternoon, particularly in dry, hot weather conditions.
- Diet:
- Indian star tortoises are primarily herbivores, feeding on grasses, herbaceous leaves, and flowers.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN: Listed as Vulnerable.
- CITES: Included in Appendix I, indicating a high level of protection.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Listed in Schedule I, offering the highest level of protection under Indian law.
Nova
- News: Astronomers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have spotted far ultra violet (FUV) emissions from novae for the first time in the neighbouring Andromeda galaxy.
- Definition and Nature: A nova is a transient astronomical event where a bright, new star suddenly appears and gradually fades over weeks or months following its outburst.
- Occurrence: Novae typically happen in binary star systems, where a dense white dwarf star, roughly the size of Earth, orbits closely with a Sun-like companion.
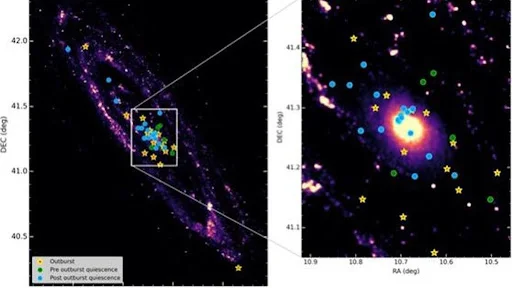
- Mechanism:
- The white dwarf’s intense gravitational force pulls material from its companion star, causing a buildup of matter on the white dwarf’s surface.
- This accumulation triggers powerful thermonuclear reactions, leading to a bright burst of energy, known as a nova.
- Luminosity: The nova reaches its maximum brightness within hours of the outburst and can continue to shine intensely for several days.
- Significance of the Research:
- Researchers have detected ultraviolet emissions from 42 novae in the Andromeda galaxy, marking a significant milestone in nova research.
- Among these, four novae were observed during their outburst, offering an unprecedented opportunity to study the different phases of binary star systems.
- This discovery allows scientists to observe novae at various stages of their life cycle, from accumulating material from their companion star to expelling it into space.
- Key Facts about the Andromeda Galaxy:
- The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31 or M31, is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way.
- It lies 2.5 million light years away from Earth and is a prominent member of the Local Group, which includes the Milky Way and several other galaxies.
- Like the Milky Way, the Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy, named for the bar-like structure formed by stars at its center.
Damselfish
- News: A small team of ichthyologists at the California Academy of Sciences has discovered a new species of damselfish living off the shores of the Maldives.
- Species and Habitat:
-
- Damselfish refers to approximately 250 species of small, predominantly tropical marine fish belonging to the family Pomacentridae (order Perciformes). These fish are found in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific oceans.

- Physical Characteristics:
-
- Damselfishes are characterized by their deep bodies and forked tails. They closely resemble cichlids and share some physical traits, such as having a single nostril on each side of their head and an interrupted lateral line.
- They also possess two anal spines, which is a distinct feature.
- Coloration and Size:
- Many damselfish species are known for their vibrant coloration, which can include shades of red, orange, yellow, or blue.
- Most species grow to a length of about 15 cm (6 inches), making them relatively small in size.
- Behavior:
- Damselfishes are known for their energetic and swift movements. They are typically very territorial and can display aggressive behavior towards other fish.
- Diet:
- Some species primarily consume plant matter or small animals suspended in the water, while others are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources.
- Habitat Preferences:
- While most damselfishes live around coral reefs, certain species, notably the anemone fishes, are known for inhabiting the stinging tentacles of sea anemones, where they find protection and food.
Moths
- News: Moths can hear sounds emitted by plants and rely on them to choose on which plant to lay their eggs, according to a new study.
- Classification and Diversity:
-
- Moths are insects that belong to the order Lepidoptera, which they share with butterflies.
- There are approximately 160,000 known species of moths, vastly outnumbering the number of butterfly species.

- Adaptability and Habitat:
-
- Moths are highly adaptable creatures and can be found in nearly all habitats, except for polar regions.
- Size and Appearance:
- Moths vary significantly in size, with their wingspans ranging from as small as 4 mm (0.16 inches) to as large as 30 cm (about 1 foot).
- Typically, moths have duller colors compared to butterflies, which provides them with effective camouflage. However, some species, such as the luna moth and atlas moth, are known for their vibrant colors.
- Antennae:
- Moths are distinguished from butterflies by their antennae, which are often feathery, in contrast to the thin, clubbed antennae of butterflies.
- Activity Patterns:
- While most moths are nocturnal, there are some species that are active during the day.
- Feeding Habits and Economic Impact:
- Both moth larvae and adults primarily feed on plants. The larvae, in particular, can cause significant damage to ornamental trees, shrubs, and various economically important plants.
See more: Integrated Theatre Commands | UPSC Prep
Business 4 Land Forum
- News: At the Business 4 Land forum during the COP16 conference, the private sector was encouraged to incorporate the sustainable management of land into corporate and financial strategies.
- About the Business 4 Land Initiative:
- Origin and Purpose:
- The Business 4 Land (B4L) initiative is a key program by the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) designed to engage the private sector in promoting sustainable land and water management.
- Focus Areas:
- The initiative supports companies and financial institutions in managing risks and identifying opportunities linked to land degradation and drought.
- Goal:
- The primary goal of the B4L initiative is to restore 1.5 billion hectares of land by 2030, contributing to the global commitment of achieving Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN), which aims for net-zero land degradation by 2030. Additionally, B4L seeks to improve drought resilience.
- Three Core Pillars:
- Business Operations and Value Chains: Promote sustainable practices and encourage businesses to set specific targets for minimizing land-related impacts throughout their operations.
- Finance: Foster the development of sustainable financial solutions focused on land restoration and increasing resilience to drought.
- Advocacy: Advocate for the creation of policies that cultivate a supportive business environment for sustainable land and water management.

