UPSC GS 1
Lake Prespa
- News: Little Prespa Lake on the Albanian-Greek border is slowly dying, transforming from a crystal-clear lake to a marshy wasteland.
- Definition:
-
- Lake Prespa is one of the oldest tectonic lakes in Europe and the highest tectonic lake located on the Balkan Peninsula.
- The lake sits at the confluence of three significant geological formations: a granite massif in the East, a karstic massif from Galicica in the West, and the Suva Gora in the South.
- The area is geologically significant, featuring rocks dating back to the Paleozoic era as well as sediments from the more recent Neogene era.
-
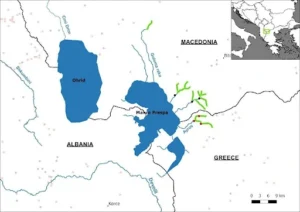
- Composition and Location:
-
- Lake Prespa is divided into two parts: Great Prespa Lake, which spans Albania, Greece, and the Republic of Macedonia, and Small Prespa Lake.
- Small Prespa Lake, also referred to as Little Prespa Lake, lies primarily within Greek territory, with only its southernmost part extending into Albania.
-
- Environmental Challenges:
-
- The lake is facing environmental stress due to rising temperatures, increasingly mild winters with reduced snowfall, and a general lack of precipitation, all of which have severely impacted the lake’s ecosystem.
-
Read also: Celebrating 10 Years of Make in India | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Classical Language Status
- News: The Union Cabinet has approved classical language status to Marathi, Bengali, Assamese, Pali, and Prakrit. This cabinet decision increases the number of recognised classical languages from six to eleven.
- Criteria for Declaring a Language as Classical:
-
- Antiquity: The language must have early texts or recorded history spanning 1500-2000 years.
- Literary Heritage: The language should have a body of ancient literature or texts considered valuable heritage by generations of speakers.
- Original Literary Tradition: The literary tradition should be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
- Distinctiveness: The classical language and its literature should be distinct from the modern form. There may be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or offshoots.
-
- Languages with Classical Status:
-
- Tamil: Declared in 2004.
- Sanskrit: Declared in 2005.
- Kannada: Declared in 2008.
- Telugu: Declared in 2008.
- Malayalam: Declared in 2013.
- Odia: Declared in 2014.
-
- Advantages of Classical Language Status:
-
- Awards: Two major annual international awards for scholars of eminence in classical Indian languages.
- Centres of Excellence: Establishment of a Centre of Excellence for studies in Classical Languages.
- Academic Support: The University Grants Commission is requested to create a certain number of Professional Chairs for the Classical Languages, at least in the Central Universities.
-
Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)
- News: India has more than 3,000 legacy waste dumpsites, with 2,424 of them having a waste load of more than 1,000 tonnes.
- Definition:
-
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM), also known as the Clean India Mission, was launched by the Central government on October 2, 2014.
-
- Aim:
-
- Eliminating open defecation and creating Open Defecation Free (ODF) villages.
- Construction of toilets across the country.
- The mission aimed to achieve this goal by October 2, 2019, coinciding with the 150th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi.
-
- Components:
-
- The mission has two components – rural (SBM-Gramin, overseen by the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and urban (SBM-Urban, overseen by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
-
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0):
-
- In 2021, the government introduced the second edition of the mission — Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0).
- This five-year campaign, running until 2026, seeks to create “garbage-free cities” and maintain the ODF status across 4,372 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
- Aim:
- 100% source segregation of waste,
- Door-to-door waste collection,
- Scientific waste management.
- Remediate legacy dumpsites and convert them into green zones while preventing the creation of new dumpsites.
-
- Progress and Achievements:
-
- Among States, Tamil Nadu has the maximum area reclaimed from dumpsites at 837 acres (42%).
- Gujarat is the best performing State with 75% area (698 out of 938 acres) of landfills reclaimed.
-
- Legacy Waste Dumpsites:
-
- Legacy waste dumpsites refer to large areas where solid waste has been dumped and stored for years in an unscientific, uncontrolled manner.
- These dumpsites accumulate waste without any proper processing or treatment.
- According to the State of India’s Environment 2023 report, India generates approximately 1,50,000 tonnes of municipal solid waste per day.
-
UK-Mauritius Treaty
- News: Recently, agreement has been signed between the Republic of Mauritius and the United Kingdom on the Status of the Chagos Archipelago.
- Chagos Archipelago:
-
- It is an isolated atoll of tiny islands in the central Indian Ocean, located about 1,000 miles (1,600 km) south of the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent.
- The chain includes the Salomon Islands, Peros Banhos, Nelson’s Island, Three Brothers Islands, Eagle Islands, Danger Island, the Egmont Islands and Diego Garcia, a strategically important US military base.
- The Chagos Archipelago consists of five atolls, including The Great Chagos Bank – the largest atoll in the world.
- Atolls are sparsely populated, low-lying islands whose white, sandy beaches and placid lagoons are ideally suited to the tourism industry.
- An atoll surrounds a body of water called a lagoon.
- Atolls develop with underwater volcanoes, called seamounts.
- The Territory is one of 14 British Overseas Territories and administered from London by the British Indian Ocean Territory Administration.
- Uninhabited until the late 18th century, the French brought African and Indian slaves to work in coconut plantations. In 1814, the Chagos islands were ceded to Britain.
- In 1965, the UK formed the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT,) with Chagos as a key part. Some BIOT islands were ceded to Seychelles after its 1976 independence.
- Though Chagos was administratively attached to Mauritius, when Mauritius gained independence in 1968, Chagos remained with Britain.
- The UK provided Mauritius with 3 million pounds for the detachment of the islands.
-
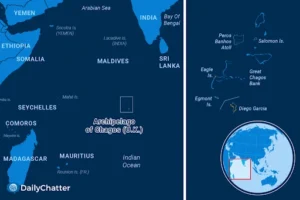
- Diego Garcia:
-
- Diego Garcia, is a coral atoll, largest and southernmost member of the Chagos Archipelago, in the central Indian Ocean.
- In 1966, Britain signed an agreement with the US which made the BIOT available for the two countries’ defence needs.
- The base’s location allows the US military to quickly access parts of Asia and Africa, and it was used to launch long-range bombing missions during the Gulf War and the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Mauritius has long claimed that the UK illegally occupies Chagos and has raised the matter many times in international fora.
-
- UK-Mauritius Treaty:
-
- Under the terms of the new agreement, the United Kingdom will agree that Mauritius is sovereign over the Chagos Archipelago, including Diego Garcia, site of a joint U.S.-UK military facility.
- In turn, the UK will exercise the sovereign rights and authorities of Mauritius with respect to Diego Garcia in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
-
SARTHIE 1.0.
- News: The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment (DoSJE), Government of India, and the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) have recently launched SARTHIE 1.0.
- SARTHIE 1.0:
-
- SARTHIE 1.0 is an initiative aimed at empowering marginalized and disadvantaged communities, including Scheduled Castes (SCs), Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Senior Citizens, Transgender Persons, Victims of Alcoholism and Substance Abuse, persons involved in Begging, Denotified and Nomadic Tribes, among others.
- The initiative aligns with the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, particularly focusing on goals that address poverty eradication, inequality reduction, and the promotion of social protection policies to foster equality.
- It seeks to bridge gaps in awareness and provide legal aid to ensure that social welfare programs are effectively implemented.
- The initiative fosters collaboration between the executive and judiciary, ensuring that the principles of social justice are strengthened.
-

- Key Facts About NALSA:
-
- Constitution: NALSA was established under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987.
- Mandate: It has the responsibility to provide legal assistance to disadvantaged and vulnerable groups, while also promoting legal literacy across society.
- Leadership: The Chief Justice of India serves as the Patron-in-Chief of NALSA, with the second senior-most judge of the Supreme Court acting as the Executive Chairman.
- Location: NALSA operates from the Supreme Court of India in New Delhi.
- State and High Court Committees: Every State has its own State Legal Services Authority, and each High Court has a corresponding High Court Legal Services Committee.
-
UPSC GS 3
Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: A catastrophic weather phenomenon devastated an estimated 50,000 trees over 332 hectares in Mulugu’s Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Definition:
-
- Eturunagaram Wildlife Sanctuary was declared a sanctuary in 1953 and is located near the border of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, and Telangana.
- It is well-known for its rich biodiversity and tribal heritage.
-
- Rivers:
-
- The sanctuary is bisected by the perennial river Dayyam Vagu, which divides it into two parts.
- Additionally, the River Godavari also flows through the sanctuary, enhancing its ecological significance.
-
- Cultural Significance:
-
- Eturunagaram is famous for the Sammakka Sarakka Jathra (Medaram Jatara), one of Asia’s largest tribal festivals, which takes place here every two years, attracting millions of devotees.
- Medaram Jatara: Medaram Jatara is the second-largest fair of India, after the Kumbh Mela, celebrated by the second-largest Tribal Community of Telangana- the Koya tribe for four days.
- As the largest tribal fair in Asia, Medaram Jathara is conducted in honour of the Goddesses Sammakka and Saralamma.
- It is celebrated once in two years in the month of ‘Magha’ (February) on the full moon day. Saralamma was the daughter of Sammakka.
- Her idol, according to the rituals, is installed in a temple at Kannepalli, a small village near Medaram.
-
- Vegetation:
-
- The sanctuary falls under the tropical dry deciduous type of vegetation. It is abundant in teak, bamboo, and other species like madhuca and terminalia.
- The region is also known for its climbers, which are a unique feature spread throughout the sanctuary.
-
- Flora:
-
- The sanctuary’s flora includes a rich variety of trees such as teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia, making it a vital ecological zone.
-
- Fauna:
-
- Eturunagaram Wildlife Sanctuary is home to several keystone species, including the Mugger crocodiles, Indian gaur and giant squirrel.
- Other species found in the sanctuary include tigers, leopards, jackals, sloth bears, panthers, wolves, wild dogs, chousingha, and sambar.
-
Monetary Policy Committee
- News: The members of the Monetary Policy Committee have been appointed by the Central government.
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934:
-
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (RBI Act) has been amended by the Finance Act, 2016 to provide for a statutory and institutionalized framework for Monetary Policy Committee.
- Under Section 45ZB of the amended RBI Act, 1934, the central government is empowered to constitute a six-member MPC.
-
- Definition of MPC:
-
- The RBI Act provides for the constitution of a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) to determine the policy rate required to achieve the inflation target.
-
- Members:
-
- Governor of the Reserve Bank of India—Chairperson, ex officio;
- Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, in charge of Monetary Policy—Member, ex officio;
- One officer of the Reserve Bank of India to be nominated by the Central Board—Member, ex officio;
- Three independent members, experts in the field of economics, banking or finance, to be selected by the Government, will hold office for a period of four years or until further orders, whichever is earlier.
-
- Management:
-
- The MPC is required to meet at least four times in a year and the quorum for the meeting of the MPC is four members.
- Each member of the MPC has one vote, and in the event of an equality of votes, the Governor of RBI has a second or casting vote.
-
Read also: Understand Indian Pension System: A Complete Overview | UPSC
Honey Badger
- News: For the first time, a honey badger has been captured on camera in Uttarakhand’s Terai East Forest Division.
- Honey Badger (Ratel):
-
- Commonly known as the Ratel, the Honey Badger is closely related to skunks, otters, ferrets, and other badgers.
- These animals are omnivorous and nocturnal, belonging to the weasel family.
- Honey badgers are recognized for their strong, curved claws, which they use for digging burrows for shelter.
- Their diet is varied, including small animals, fruits, and honey.
- Known for their solitary nature, they can skillfully twist and turn to evade predators.
-

- Distribution:
-
- Honey badgers are distributed across parts of Africa and Asia.
- In India, they have been spotted in areas such as Bannerghatta National Park (Karnataka), Chilika Lagoon (Odisha), and Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra).
-
- Ecological Significance:
-
- Honey badgers play a key role in maintaining ecological balance by preying on smaller animals and pests, which helps regulate populations and safeguard crops.
- They aid in nutrient cycling, enriching the soil through their diet and waste.
- As indicators of ecosystem health, their presence signals a diverse and thriving environment for other species.
-
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Red List: Classified as “Least Concern.”
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I, providing them with the highest level of legal protection in India.
-

