UPSC GS 1
Lake-effect Snowfall
- News: Lake-effect snow warnings have been issued across parts of Ohio, New York, and Pennsylvania.
- About Lake-Effect Snow:
-
- Definition: Lake-effect snow is a localized weather phenomenon caused by the interaction of cold air moving over warmer lake water, resulting in snow being deposited in specific regions downwind of the lake.
- Common Regions: This phenomenon frequently occurs in the Great Lakes region during late fall and winter.
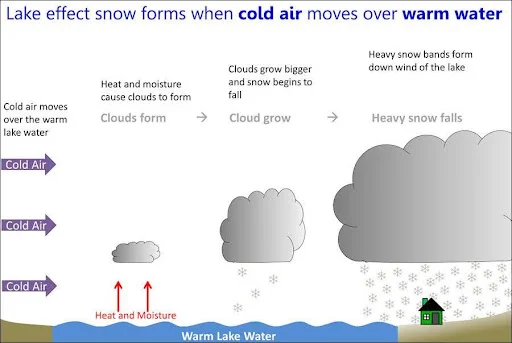
- Formation of Lake-Effect Snow:
- Cold Air Over Warm Waters:
- Lake-effect snow develops when cold air, often originating from Canada, flows across the open and relatively warm waters of the Great Lakes.
- The temperature contrast leads to the transfer of warmth and moisture from the lake’s surface to the lower atmosphere.
- Cloud Formation:
- As the moisture-laden air rises, clouds form and develop into narrow snow bands capable of producing intense snowfall, with rates of 2 to 3 inches or more per hour.
- Factors Influencing Lake-Effect Snow:
- Wind Dynamics:
- The direction and speed of the wind determine the snow band’s width, length, and location.
- Changes in wind direction can shift snowfall to different areas, while stronger winds can create broader snow bands.
- Topography:
- Variations in terrain can affect snowfall intensity and accumulation rates, amplifying or diminishing the snow band in specific areas.
Read also: International Day of Persons with Disabilities | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Anna Chakra
- News: The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution recently launched ‘Anna Chakra’, and SCAN (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA) portal.
- About Anna Chakra:
-
- Definition: Anna Chakra is a supply chain optimization tool designed for the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- Objective: Spearheaded by the Department of Food and Public Distribution, it enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the PDS logistics network across India.
- Development: Created in collaboration with the World Food Programme (WFP) and the Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT) at IIT-Delhi.

- Working:
- Advanced Algorithms: The tool uses sophisticated algorithms to determine optimal routes and streamline the transportation of food grains through various supply chain nodes.
- Complex Operations: Managing a vast supply chain involves multiple stakeholders, including farmers, transporters, and Fair Price Shops (FPS).
- Scale: The initiative covers 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops and approximately 6,700 warehouses involved in the PDS supply chain.
- Interstate Route Optimization: A specialized tool is used to optimize PDS movement between states, integrated with the Railways’ FOIS (Freight Operations Information System) via the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
- Integration with PM Gati Shakti: The tool integrates with the PM Gati Shakti platform, utilizing geo-locations of FPSs and warehouses across states for better logistics planning.
- Advantages:
- Cost Savings: Optimization efforts across 30 states indicate a potential annual savings of approximately ₹250 crores.
- Enhanced Efficiency: It accelerates the delivery process for the world’s largest food security program, which supports 81 crore beneficiaries.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces fuel consumption, logistics costs, and carbon emissions due to decreased transportation needs.
- About SCAN Portal (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA):
-
- Purpose: Provides a unified platform for states to submit subsidy claims, with scrutiny and approval by the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD).
- Workflow Automation: Ensures end-to-end automation for processing and settling food subsidy claims using a rule-based system.
- Expeditious Settlements: Facilitates faster submission, review, and release of subsidies, ensuring a seamless operational workflow.
International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience
- News: The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC) have jointly launched the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience.
- International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience:
- Launch: Jointly established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC).
- Objective: Focuses on bolstering the resilience of submarine cables, which form the backbone of the global digital economy.

- Members:
- Composition: Includes 40 members worldwide, such as ministers, heads of regulatory bodies, and senior telecommunications experts, ensuring a diverse global representation.
- Meetings: The Advisory Body convenes twice a year to discuss international policies, infrastructure challenges, and best practices for enhancing the resilience of submarine cables.
- Functions:
- Promoting Best Practices: Encourages governments and industries to adopt practices that improve the resilience of submarine cables, minimize risks of damage, and facilitate their timely repair and deployment.
- Support for Stakeholders: Leverages the collective expertise of its members to cater to the needs of individuals reliant on submarine cables and those involved in their deployment, maintenance, and protection.
- Strategic Guidance: Provides recommendations to tackle issues such as increasing data traffic, aging infrastructure, and environmental threats to these critical systems.
- What is the International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC)?
-
- Establishment: Founded in 1958 as a global platform for governments and commercial entities engaged in the submarine cable industry.
- Mission: Aims to enhance the security and protection of undersea cables by facilitating the exchange of technical, legal, and environmental knowledge.
National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET)
- News: In a landmark development, National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET) has officially recognized Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) as an Awarding Body (Dual).
- About National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET):
-
- Establishment: Formed by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Government of India, on December 5, 2018, as a regulatory authority to ensure quality in the Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) sector.
- Predecessors: It assumed the responsibilities previously carried out by the National Skill Development Agency (NSDA) and the earlier National Council of Vocational Training (NCVT).
- Operational Timeline: Became fully operational on August 1, 2020.
- Role: Serves as the national regulator responsible for setting standards and drafting regulations for the vocational education, training, and skilling ecosystem, ensuring improved quality and outcomes.

- Objectives and Focus:
- Regulatory Integration: Aims to consolidate fragmented regulatory frameworks while introducing quality assurance across the vocational education and training landscape.
- Skill Development: Works to enhance the quality and performance of vocational education providers, fostering a workforce with advanced skills for greater employability and economic growth.
- Standardization: Establishes minimum operational standards for vocational education entities involved in both short-term and long-term training programs.
- Functions of NCVET:
- Awarding Bodies: Recognizes, monitors, disciplines, and de-recognizes awarding bodies.
- Assessment Agencies: Recognizes, monitors, disciplines, and de-recognizes agencies conducting assessments.
- Skill Information Providers: Recognizes, monitors, disciplines, and de-recognizes entities providing skill-related information.
- Approval of Qualifications: Develops guidelines for approving qualifications and ensures their approval in accordance with these guidelines.
- Grievance Redressal: Establishes and oversees a system to address grievances related to recognized entities.
SVAGRIHA Rating
- News: The Intermodal Terminal (IMT) at Kalughat in Bihar, developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), has been awarded a five-star SVAGRIHA rating by the GRIHA Council.
- About SVAGRIHA Rating:
- Full Form: SVAGRIHA stands for Simple Versatile Affordable GRIHA and promotes the adoption of green buildings and sustainable practices under the Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA).
- Purpose: It is a guidance-cum-rating system specifically developed for small standalone buildings such as residences, commercial offices, motels, dispensaries, and schools.
- Objective: The system aims to minimize the environmental impact of small-scale developments.
- Rating System:
- Applicability: The SVAGRIHA rating is only applicable to projects with a built-up area of less than 2500 square meters.
- Criteria: The system includes 14 criteria grouped into five broad subcategories:
- Architecture and Energy
- Water and Waste
- Materials
- Landscape
- Lifestyle
- Mandatory Points: Certain points are mandatory to attempt within each subcategory.
- Scoring: Projects can achieve a total of 50 points, and ratings are assigned on a 1 to 5-star scale.
- Evaluation Tool: Designed as a user-friendly online tool, it provides guiding parameters to evaluate a project’s performance under SVAGRIHA in a straightforward and accessible manner.
UPSC GS 3
CGIAR Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands (GSRD)
- News: CGIAR has launched its visionary 2030 Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands to transform farming in the world’s driest regions and ensure sustainable food systems for generations to come.
- About Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands:
- Initiative Leadership: Spearheaded by CGIAR centers, the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) and the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
- Purpose: Provides a comprehensive roadmap to strengthen food security, conserve biodiversity, and build resilient livelihoods for 2.7 billion people living in dryland regions, with a focus on Asia and Africa.
- Launch Event: Introduced at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) held in Riyadh.
- Collaborative Development: Created through extensive consultations with national research institutions, governments, private sector partners, and civil society, ensuring region-specific strategies tailored to diverse drylands.

- What is Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR)?
- Establishment: Founded in 1971, it is a global partnership involving diverse donors supporting 15 international research centers.
- Collaborative Reach: Works in close partnership with hundreds of government bodies, civil society organizations, and private enterprises worldwide.
- Vision: Aims to alleviate poverty and hunger, enhance human health and nutrition, and boost ecosystem resilience through cutting-edge international agricultural research, partnerships, and leadership.
- Objectives of CGIAR:
-
- Food for People: Foster sustainable increases in productivity and production of nutritious food, particularly benefiting impoverished communities.
- Environment for People: Safeguard and sustainably utilize natural resources and biodiversity to improve livelihoods, addressing climate change and other environmental challenges.
- Policies for People: Advocate for institutional and policy reforms that drive agricultural growth and ensure equity, with a focus on empowering rural women and disadvantaged groups.
Sonai-Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: The Assam forest department confirmed the Royal Bengal Tigers’ presence in the Sonai-Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary, with the first photographic evidence captured in the Sonitpur district.
- About Sonai-Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary:
-
- Location: The sanctuary is situated in Assam, India, along the foothills of the Great Himalayan Range.
- Area and Establishment: Spanning 175 sq. km, it was designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1998.
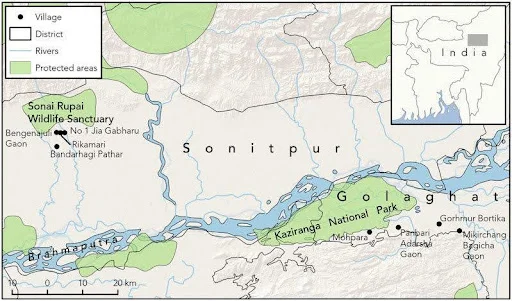
- Geographic Boundaries:
- Eastern Boundary: Marked by the Gabhoru River.
- Western Boundary: Defined by the Panchnoi River, with the Rowta Reserve Forest further west.
- Northern Boundary: Shares an interstate boundary with the Kameng Reserve Forest in the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Southern Area: Encompasses the Charduar Reserve Forest and several villages.
- Water Bodies:
- Rivers: Four perennial rivers—Dolsiri, Gabharu, Gelgeli, and Belsiri—flow through the sanctuary.
- Wetlands: Numerous seasonal wetlands, locally known as bheels, appear during the monsoon when heavy rains cause floods and river overflows.
- Climate:
- Type: Sub-tropical climate with hot, humid summers.
- Rainfall: Heavy summer rains often result in flooding and overflowing rivers.
- Vegetation:
- Forest Types: Comprises tropical evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests.
- Flora: Prominent tree species include Hollock, Koroi, Nahar, Titasapa, Simul, Sal, Ajar, and Hatipeta.
- Wildlife:
-
- Key Attractions: Renowned for Indian bison, elephants, and the one-horned rhinoceros.
- Other Fauna: Hosts species like sambar deer, barking deer, hog deer, Himalayan crestless porcupines, large Indian civets, small Indian civets, black bears, and sloth bears.
See more: Fifth Schedule Vs Sixth Schedule | UPSC
Cape Buffalo
- News: A study in Tanzania’s Ngorongoro Conservation Area (NCA) has provided valuable insights into the causes of human-Cape buffalo conflicts, a recurring issue across sub-Saharan Africa.
- About Cape Buffalo:
-
- Scientific Name: Syncerus caffer.
- Description: Known for its strength and aggression, it is a formidable species among African wildlife.

- Subspecies: There are four subspecies of African buffalo:
- Cape buffalo (southern savanna buffalo).
- Forest buffalo.
- West African savanna buffalo.
- Central African savanna buffalo.
- Appearance:
- Body Structure: They have long, stocky bodies with short, sturdy legs, giving them a comparatively short standing height.
- Horns: The adult buffalo’s horns are distinct, with fused bases that form a continuous bone shield across the head, called a “boss.”
- Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Found in swamps, floodplains, mopane grasslands, and African mountain forests.
- Range of Habitats: Thrive in areas with dense cover, including reeds and thickets, but are also seen in open woodlands, montane grasslands, savannas, and moist lowland rainforests.
- Activity: Active both day and night, they are highly social animals living in herds. Herds typically consist of related females and their offspring, organized in a linear dominance hierarchy.
- Distribution:
- Found primarily in the savannas of eastern and southern Africa.
- Diet:
- Feeding Habits: They are strictly herbivorous, consuming a wide range of grasses, sedges, leaves, and other plants.
- Swimming Abilities: Excellent swimmers, often crossing rivers to access better grazing areas.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Listing: Classified as Near Threatened.
Punatshangchhu-II Hydropower Project
- News: India and Bhutan recently reviewed hydropower projects, including the 1020 MW Punatsangchhu-II Hydropower Project, expressing satisfaction over its progress, as it is approaching completion.
- About Punatsangchhu-II Hydropower Project:
-
- Capacity: A 1 GW run-of-the-river hydroelectric power-generating facility currently under construction.
- Location: Situated on the right bank of the Punatsangchhu River in Wangdue Phodrang district, Western Bhutan.
- Development: The project is being executed by the Punatsangchhu II Hydroelectric Project Authority, established under an Inter-Government Agreement (IGA) between the Royal Government of Bhutan and the Government of India.

- Funding Arrangement:
- The project is financed by the Government of India (GoI) with a structure of 30% grant and 70% loan.
- The loan carries an annual interest rate of 10%, repayable in 30 semi-annual installments starting one year after the mean operational date.
- Operational Transition:
- The project authority will be dissolved within two years of commissioning. Afterward, the project will be handed over to the Royal Government of Bhutan.
- Project Infrastructure:
- Dam Construction: Includes a concrete gravity dam that is 91m in height and 223.8m in length.
- Diversion Tunnel: Features an 877.46m-long, 12m-diameter tunnel with a discharge capacity of 1118 cubic meters per second.
- Cofferdams:
- An upper cofferdam measuring 168.75m in length and 22m in height.
- A downstream cofferdam of 102.02m in length and 13.5m in height.
- Power Generation:
- Upon completion, the Punatsangchhu-II plant is projected to produce approximately 4,357 million units of electricity annually, significantly contributing to Bhutan’s hydropower capacity.

