UPSC GS 1
Juneteenth
- News: It is celebrated on June 19 annually in the US.
- Introduction:
-
- Juneteenth, short for “June Nineteenth,” is a holiday in the United States that celebrates the end of slavery and commemorates African American freedom and achievements.
-
- Historical Significance:
-
- Union General’s Announcement: Juneteenth marks June 19, 1865, when Union General Gordon Granger arrived in Galveston, Texas, and proclaimed the end of the Civil War and the emancipation of enslaved African Americans.
- Emancipation Proclamation: Despite President Abraham Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, which legally freed slaves in Confederate states, enforcement was delayed, particularly in Texas.
-
- Activities: Juneteenth is celebrated with a variety of activities including parades, cultural events, educational workshops, and family gatherings.

- Reflection: It serves as a time to reflect on African American heritage, freedom, and accomplishments, while acknowledging ongoing struggles for equality.
- Significance: Juneteenth has gained recognition as a pivotal cultural and historical event in the United States.
- Federal Holiday: In 2021, Juneteenth was designated a federal holiday, solidifying its importance in American history and culture.
Stonehenge
- News: The UK police recently arrested two people, including an Indian-origin man, for spraying an orange substance on Stonehenge.
- Location: Situated in Wiltshire, England, Stonehenge is a prehistoric stone circle monument and archaeological site.
- Structure: Composed of approximately 100 massive upright stones arranged in a circular layout.
- Early History: Originally built about 5,000 years ago as an early henge monument.
- Stone Circle: The unique stone circle was erected in the late Neolithic period around 2500 BC.
- Bronze Age Additions: In the early Bronze Age, numerous burial mounds were constructed in the vicinity.

- Purpose and Significance
-
- Symbol of Power: It also symbolized the authority and wealth of the chieftains, aristocrats, and priests responsible for its construction.
- Part of a Sacred Landscape: Stonehenge is just one component of a larger sacred landscape that included other stone and wooden structures, as well as burial sites.
- Astronomical Alignments: Aligned with the movements of the Sun and possibly the Moon, suggesting its use in celestial observations and tracking seasonal changes for agricultural purposes.
-
- UNESCO World Heritage Designation:
-
- Alongside over 350 nearby monuments and henges, including the temple complex at Avebury, Stonehenge was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1986.
-
Delos Island
- News: A remarkable ancient site on the tiny Greek island of Delos is “doomed to disappear” within decades due to rising sea levels and geological processes.
- Sanctuary Importance: Delos Island is one of the most significant sanctuaries of the ancient Greek and Roman world.
- Location: Situated in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea.
- Early Settlement: First settled in the 3rd millennium B.C.
- UNESCO Status: Designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Famous For: The island is famous as the birthplace of the twin gods Apollo and Artemis.
- Key Facts About the Aegean Sea:
-
- Location and Geography: Positioned in the East Mediterranean Basin.
- Geographic Boundaries: Bordered by the Greek peninsula to the west and Anatolia (the Asian side of Turkey) to the east.
- Connecting Straits: Linked to the Black Sea by the Bosphorus Strait and to the Marmara Sea by the Dardanelles Strait.
- Island Ownership: Most Aegean Islands belong to Greece, with Turkey possessing Imbros (Gökçeada) and Tenedos (Bozcaada) in the northeastern part of the sea.
-
- Climate:
-
- Mediterranean Climate: Characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- Hot-Summer Mediterranean: Experiences drier and hotter summers, particularly in Western Turkey and Greece.
- Northern Aegean Climate: Classified as cold semi-arid, with cooler summers.
- Etesian Wind Influence: The weather in the Aegean basin is largely influenced by the Etesian winds, which help moderate the summer temperatures.
-
Read also: Understanding and Addressing the Risks of Spurious Liquor | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Pro-tem Speaker
- News: President Droupadi Murmu recently appointed seven-term MP from Odisha Bhartruhari Mahtab as the pro-tem Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- Introduction:
-
- The Pro-tem Speaker is a temporary Speaker appointed to perform certain duties until a new Speaker is elected.
- The term “Pro-tem” means “for the time being” or “temporarily.”
-
- Constitutional Basis:
-
- Constitutional Mention: The Constitution does not explicitly mention the post of Pro-tem Speaker.
- Official Guidelines: The official ‘Handbook on the Working of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs’ outlines the ‘Appointment and Swearing in of Speaker pro tem.’
-
- Selection of the Pro-tem Speaker:
-
- Appointment: When the Speaker post is vacant before a new Lok Sabha, the duties are assigned to a Member of the House appointed by the President as the Pro-tem Speaker.
- Selection Criteria: Normally, the senior-most members of the Lok Sabha (based on years of membership) are chosen, though exceptions can occur.
- Preparation of List: After the new government is formed, the Legislative Section prepares a list of the senior-most Lok Sabha members.
- This list is submitted to the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs or the Prime Minister for identifying the Pro-tem Speaker and three other members for administering oaths.
- Consent and Approval: The Minister of Parliamentary Affairs obtains the consent of the selected members.
- A note is then submitted to the President for approval of the appointments and the date and time of the swearing-in ceremony.
- Notification: Once approved by the President, the Ministry informs the Pro-tem Speaker and the other three members about their appointments.
-
- Duties of Pro-tem Speaker:
-
- Administering Oaths to New MPs: The primary duty is to administer the oath or affirmation to newly elected Members of Parliament (MPs).
- Under Article 99 of the Constitution, every Member must make and subscribe to an oath before the President or a person appointed by him.
- Oath Administration by Other Members: Three other elected members are also appointed by the President for MPs to take the oath before them.
- These members are generally senior-most members of the Lok Sabha.
- Swearing-in Ceremony: The President administers the oath to the Pro-tem Speaker at the Rashtrapati Bhawan.
- The Pro-tem Speaker then administers the oath to the other three members in the Lok Sabha.
- Session Timing: The swearing-in of the Pro-tem Speaker usually takes place at 9:30 am on the same day the Lok Sabha session starts. The Lok Sabha’s timing typically begins at 11 am, subject to the President’s convenience.
- Administering Oaths to New MPs: The primary duty is to administer the oath or affirmation to newly elected Members of Parliament (MPs).
-
Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)
- News: Chairman of the Economic Advisory Council (EAC) to the Prime Minister, Bibek Debroy, has emphasized the need for a new poverty line.
- Overview:
-
- The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) is an independent body constituted in 2017.
- It aims to provide advice on economic and related issues to the Government of India, specifically to the Prime Minister.
-
- Terms of Reference:
-
- Advisory Role: Analyzing any issue, economic or otherwise, referred to it by the Prime Minister and advising him thereon.
- Macroeconomic Focus: Addressing issues of macroeconomic importance and presenting views thereon to the Prime Minister.
- Suo-Motu Analysis: Initiating analyses and advice on its own (suo-motu) or on reference from the Prime Minister or anyone else.
- Special Tasks: Attending any other task as may be desired by the Prime Minister from time to time.
-
- Regular Reporting and Monitoring:
-
- Monthly Reports: Preparing a monthly report on economic developments at home and abroad for the Prime Minister.
- Trend Monitoring: Monitoring economic trends on a regular basis, bringing important developments to the PM’s attention, and suggesting suitable policy responses.
-
- Interaction and Communication:
-
- Stakeholder Engagement: Regularly interacting with stakeholders and the public.
- Public Communication: Communicating findings and recommendations through reports, presentations, and public events.
-
- Composition:
-
- Leadership: Headed by the Chairman.
- Membership: Includes a mix of economists and experts from academia, research institutions, and the private sector.
- Flexibility: No fixed definition of the exact number of members and staff; the Council is often reconstituted with different organizational structures and leaders of recognized international eminence.
-
- Administrative Support:
-
- Nodal Agency: For administrative, logistic, planning, and budgeting purposes, the NITI Aayog serves as the nodal agency for the EAC-PM.
-
Nature Restoration Plan
- News: The EU adopts its new Nature Restoration Law.
- Approval: The European Union has approved the Nature Restoration Law (NRP), a pioneering continent-wide and comprehensive law.
- Component: This law is a key component of the EU’s European Green Deal, which aims for net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
- Objectives:
-
- The NRP includes binding restoration targets aimed at the long-term recovery of nature in the EU’s land and sea areas.
-

- Goals:
-
- 2030: Recover at least 20% of the EU’s land and sea areas.
- 2050: Restore all ecosystems in need of restoration.
-
- Implementation:
-
- National Restoration Plans: Each EU country will implement the NRP through their respective National Restoration Plans.
-
e-Shram Portal
- News: The Indian delegation to the 112th International Labour Conference (ILC) showcased the e-Shram portal and its present achievements on 4th June 2024 at Geneva, Switzerland.
- Introduction:
-
- The e-Shram Portal was launched by the Ministry of Labour and Employment in 2021 to register and create a comprehensive National Database of Unorganized Workers (NDUW).
- It serves as a “One-Stop-Solution” for unorganized workers across the country.
-
- Registration and Occupations:
-
- Self-Declaration Basis: Unorganized workers can register themselves on the portal through self-declaration.
- Occupations: Covers 400 occupations within 30 broad occupation sectors.
- Aadhaar Verification: The registration is fully Aadhaar verified and Aadhaar seeded.
-
- Objectives and Benefits:
-
- Social Security Access: Facilitates access to various social security schemes implemented by different Ministries/Departments for the benefit of unorganized workers.
-

- Integration with Other Portals:
-
- National Career Service (NCS) Portal
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH)
- myScheme Portal
- Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Mandhaan (PMSYM) Scheme
-
- Unorganized Worker:
-
- The term ‘unorganised worker’ has been defined under the Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008 as ‘a home based-worker, self employed worker or a wage worker in the unorganised sector and includes a worker in the organised sector who is not covered by any of the Acts mentioned in scheduled II of its Act.
-
UPSC GS 3
5G Intelligent Village Initiative
- News: The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has announced a proposal for ‘5G Intelligent Village’ showcasing the advantages of 5G connectivity, for which it has selected 10 villages from different states.
- 5G Intelligent Village Initiative: It aims to harness the transformative power of 5G technology to uplift rural communities, ensuring equitable technological advancement.
- Utilization of 5G: Focuses on the effective use of Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) in selected villages.

- Key Pillars:
-
- Agriculture
- Education
- Healthcare
- Governance
- Sustainability
-
- Demonstration: Showcases the advantages and impact of 5G connectivity in rural areas.
- Quantum Encryption Algorithm (QEA):
-
- Definition: It seeks to develop an India-specific Quantum Encryption Algorithm (QEA), leveraging quantum mechanics to secure digital communication channels.
- Key Features:
- Unparalleled Security: Provides the highest level of security.
- Advanced Encryption Capabilities: Utilizes cutting-edge encryption methods.
- Ultrafast and Efficient Encryption: Ensures rapid and efficient encryption.
- Funding: Proposals will be supported by the Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) scheme of the Department of Telecom (DoT).
-
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF):
-
- Definition: It is established under the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF) of the Department of Telecom (DoT), Government of India.
- Purpose: Promotes research, design, prototyping, proof of concept testing, IPR creation, field testing, security, certification, and manufacturing of telecom products.
- Support: Encourages the development of a robust telecom technology ecosystem through various funded activities.
-
Casimir Effect
- News: Scientists have discovered how to control the casimir effect—and supercharge tiny machines.
- Overview of the Casimir Effect:
-
- The Casimir effect is a phenomenon in quantum field theory where two uncharged, closely spaced conducting plates experience an attractive force, known as the Casimir force.
- This force emerges from quantum vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field between the plates.
-
- Quantum Vacuum Fluctuations:
-
- In quantum field theory, the vacuum is not truly empty but is filled with transient virtual particles and electromagnetic field fluctuations.
- Although the space between the plates appears empty, it is actually occupied by virtual particles that continually appear and vanish.
- These particles affect the electromagnetic field, resulting in an overall attraction between the plates.
-
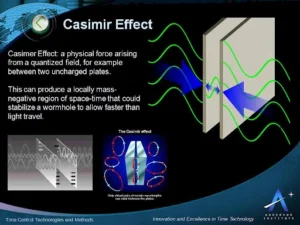
- Historical Context:
-
- Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir first predicted this effect in 1948 during his research on colloidal solutions.
-
- Experimental Verification and Applications: The Casimir effect has been experimentally confirmed and finds applications in various domains, such as:
-
- Nanotechnology
- Condensed Matter Physics
-
- Impact on Fundamental Physics:
-
- The Casimir effect has enhanced our understanding of fundamental physics, including the nature of vacuum energy.
- Experimental physicists have noted its significance in micromachined devices, and advancements in instrumentation have enabled more precise measurements of the force.
-
- Example of Casimir Effect:
-
- When colloidal particles are suspended in a vacuum, they are influenced by the Casimir force due to their proximity to other surfaces.
- Attractive and Repulsive Forces: This force can be either attractive or repulsive depending on the separation distance and the dielectric properties of the surrounding medium.
- Effect on Colloidal Particles: The Casimir force affects the movement and interactions of the colloidal particles.
- For instance, if two particles are sufficiently close, they may experience an attractive Casimir force that draws them together, leading to aggregation.
-
Sustainable Development Report 2024
- News: The U.N.’s annual Sustainable Development Report 2024 has been released.
- Definition: The Sustainable Development Report (SDR) reviews the annual progress made towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) since their adoption by the 193 UN Member States in 2015.
- Publication: The report is published annually by the Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN).
- Highlights of SDR 2024:
- Theme: “The SDGs and the UN Summit of the Future.”
- Index on Multilateralism: Introduces a new index measuring countries’ support for UN-based multilateralism.
- Sustainable Food and Land Systems: Discusses long-term strategies to achieve sustainable food and land systems.
- Global Rankings
-
- Leading Nations: Finland, Sweden, and Denmark top the rankings in this year’s report.
-
- Global Progress:
-
- Achievement Status: Only 16% of the SDG targets are on track to be achieved by 2030, while 84% show limited progress or regression.
- Progress Variation: Progress towards the SDGs varies significantly across different country groups.
- Nordic Countries: Continue to lead in SDG achievement.
- BRICS Countries: Demonstrating strong progress.
- Vulnerable Nations: Lagging far behind.
-

- India:
-
- India is ranked 109th out of 166 countries.
- India records on track performance in Poverty reduction and Quality Education targets.
-
- Challenges and Recommendations
-
- Investment Challenge: Sustainable development remains a long-term investment challenge.
- Global Financial Architecture: The need for reforming the global financial architecture is more urgent than ever.
- Global Cooperation: Emphasizes the necessity of global cooperation to tackle global challenges.
- Commitment to Multilateralism: Barbados ranks highest in commitment to UN-based multilateralism, whereas the United States ranks last.
-
- Focus on Food and Land Systems: Off-Track Targets
-
- Critical Areas: SDG targets related to food and land systems are significantly off-track.
- FABLE Pathways: The report presents new FABLE (Food, Agriculture, Biodiversity, Land, and Energy) pathways to support sustainable food and land systems.
-
- Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN):
-
- The Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) was launched in 2012 by UN.
- It aims to mobilize global scientific and technological expertise to promote practical problem solving for sustainable development and implement the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
-
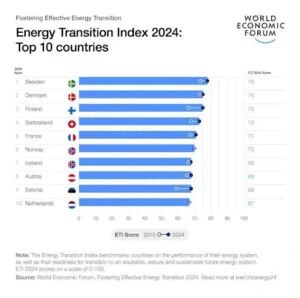
Energy Transition Index (ETI) 2024
- News: Countries across the world have reached record highs in their Energy Transition Index scores.
- Energy Transition Index 2024: The Energy Transition Index tracks progress and preparedness for an equitable, secure and sustainable energy future.
- Published Annually by : World Economic Forum
- Aim: The Energy Transition Index (ETI), benchmarks 120 countries on their current energy system performance and on the readiness of their enabling environment.
- Key Points of ETI 2024:
- Leading Countries: European countries lead: Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Switzerland, and France lead the rankings.
- Notable Progress: Emerging economies like Brazil and China have made significant strides.
- India’s Position: Ranked 63rd in ETI-2024.
- Clean Energy Infrastructure: India recognized for substantial progress in its clean energy infrastructure.
- Energy System Performance: Despite overall progress, 83% of countries regressed in at least one of the three energy system performance dimensions: security, equity, and sustainability.
- Narrowing Gap: Disparities in energy transition performance between advanced and developing economies are shrinking.
- Challenges: Challenges remain in balancing different facets of energy transition, despite progress over the past decade.
- Pace of Transition: While 107 of the 120 countries benchmarked in the report demonstrated progress on their energy transition journeys in the past decade, the overall pace of the transition has slowed and balancing its different facets remains a key challenge.
- India’s Clean Energy Landscape:
-
- Renewable Energy: India’s power generation capacity includes 42% from renewable energy and biomass.
- Global Ranking: Fourth-largest renewables market globally, showcasing significant growth and investment in renewable energy sectors.
-
See this: A List of Major Freedom Fighters of India (1857-1947)
INS Sunayna
- News: INS Sunayna visits Port Victoria in Seychelles, aims to strengthen two navies with SAGAR vision.
- Introduction:
-
- INS Sunayna is the second vessel in the Saryu-class patrol series of the Indian Navy.
-

- Design and Construction:
-
- Builder: Goa Shipyard Limited
- Class: Saryu-class patrol vessel
- Launch Year: 2009
-
- Capabilities and Features:
-
- Speed: Capable of achieving speeds of up to 25 knots.
- Power Management: Equipped with an automatic power management system.
- Navigation and Communication: Fitted with the latest navigation, communication, and electronic support systems.
-
- Operational Roles:
-
- Fleet Support Operations: Designed to provide logistical and operational support to naval fleets.
- Patrolling: Engages in both coastal and offshore patrolling to ensure maritime security.
- Ocean Surveillance: Monitors sea lines of communication and offshore assets.
- Escort Duties: Provides escort services for various naval and civilian vessels.
-
- Other Saryu-Class Vessels:
-
- INS Sumitra
- INS Sumedha
-
- SAGAR:
-
- SAGAR stands for Security and Growth for All in the Region.
- It is a label used by the Prime Minister and Government of India for India’s vision and geopolitical framework of maritime cooperation in the Indian Ocean region.
-
Facts for Prelims
World Refugee Day
- News: World Refugee Day is annually celebrated globally on June 20th.
- Date and Purpose: World Refugee Day is observed globally on June 20th each year.
- Aim: This day is dedicated to raising awareness about the millions of people who have been forced to flee their homes due to conflict, persecution, or natural disasters.
- Theme for 2024: “Everyone is Welcome.”
- History and Evolution:
- UN Refugee Rights Definition: In 1951, the United Nations defined the rights of refugees.
- Africa’s Initiative: In 1970, Africa established a day to honor refugees.
- Global Recognition: Recognizing the global nature of the refugee crisis, the UN General Assembly declared June 20th as World Refugee Day in 2000.
Blue Planet Prize
- News: Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) has received the 2024 Blue Planet Prize.
- Awarding Body: The Blue Planet Prize is awarded by Japan’s Asahi Glass Foundation.
- Purpose: The prize recognizes outstanding achievements in scientific research and its application that have contributed to solving global environmental problems.
- Monetary Award: The prize includes an award of $500,000.

- Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
-
- Formation: IPBES was established in Panama City in 2012 by 94 governments.
- Status: It is an independent intergovernmental body, not part of the United Nations.
- Objectives:
- Science-Policy Interface: Aims to strengthen the connection between scientific research and policy-making for biodiversity and ecosystem conservation.
- Sustainability and Well-being: Focuses on the sustainable use of biodiversity, long-term human well-being, and sustainable development.
- Member States: IPBES currently has over 145 member states.
- Observers: Various NGOs and civil society groups participate as observers in the formal IPBES process.
- Global Assessment Report: In its Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, IPBES identified invasive alien species as one of the primary direct drivers of biodiversity loss worldwide.
- Secretariat: Located in Bonn, Germany.
-

