UPSC GS 1
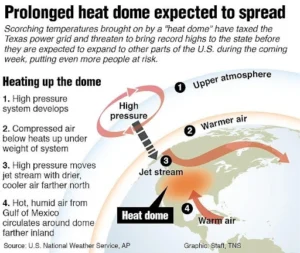
Heat Dome
- News: Record-high temperatures in the western US are being caused by ‘heat domes’.
- What is a Heat Dome?
-
- High-Pressure System: A heat dome is a high-pressure system that forms over a large area in the atmosphere, causing extremely hot and dry weather conditions.
- Trapping of Hot Air: This system traps hot air, preventing it from rising and cooling.
- Compression of Air: As a result, the air becomes compressed and heats up, forming a dome-shaped area of hot air that can persist for several days or weeks.
-
- Causes of a Heat Dome:
-
- Sinking Air: Created by sinking air that warms as it descends.
- Stagnant Air: Under a heat dome, the air can become stagnant, allowing heat to build up and intensify.
- Excess Sunlight: High-pressure systems bring clear skies, leading to more sunlight absorption and heat.
- Geographical Factors: Locations with lots of land and dry air, such as plains and deserts, are favorable for heat domes.
- Climate Change: Warmer background temperatures and drier conditions contribute to the formation and intensity of heat domes.
-
- Impact of Heat Domes:
-
- Vulnerable Populations: Elderly individuals, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions are particularly at risk.
- Outdoor Workers: Construction workers, farmers, and agricultural workers face increased risks of heat-related illnesses due to prolonged exposure.
- Low-Income Communities: Homes in poverty-stricken areas often have heat-trapping surfaces like concrete and asbestos.
- Heat-Related Illnesses: Prolonged exposure can lead to heat exhaustion, characterized by dehydration, dizziness, and nausea, and can progress to heat stroke, which can cause organ damage and death.
- Cardiopulmonary Stress: Extreme heat stresses the heart and lungs, particularly for those with conditions like asthma or heart disease.
- Droughts and Wildfires: Hot and dry conditions lead to droughts and increase the risk of wildfires.
-
- Mitigation Strategies
-
- Reducing Greenhouse Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation.
- Investing in Green Infrastructure: Cities can invest in parks, green roofs, and tree planting to reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Implementing Building Codes and Standards: Ensuring new buildings are designed to withstand extreme heat and maintain indoor comfort.
- Reducing Heat–Trapping Surfaces: Decreasing the amount of asphalt and concrete in urban areas.
-
Read also: UPSC Current Affairs: Siang River, Denisovans, Equity Mutual Funds, and More
World Population Prospects Report 2024
- News: The United Nations released the World Population Prospects 2024 report recently.
- Definition: The World Population Prospects Report presents population estimates from 1950 to the present for 237 countries underpinned by analyses of historical demographic trends.
- Released by: United Nations
- Key Highlights:
- Global Population Projections:
-
- The world population is projected to reach 10.3 billion by 2080 and will then decline towards the end of the century to 10.2 billion.
- As of 2024, the global population stands at 8.2 billion.
-
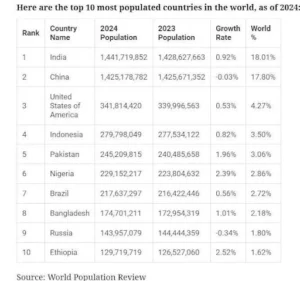
- India’s Population Projections:
-
- Surpassing China, India is the world’s most populated country.
- India’s population in 2024 is projected at 1.45 billion.
- The population is expected to peak at 1.69 billion in 2054.
- India will remain the most populous nation on Earth throughout the century.
-
- World Population Day:
-
- World Population Day is an annual event, observed on July 11 every year, which seeks to raise awareness of global population issues.
- The day came to be established by the United Nations and was first observed in the year 1989.
- Theme 2024: Leave no one behind, count everyone.
-
UPSC GS 2
Supreme Court Verdict On Muslim Women’s Maintenance
- News: The Supreme Court has recently ruled that a divorced Muslim woman is entitled to a claim of maintenance.
- Legal Entitlement to Maintenance:
-
- Affirmed that all married and divorced women, including those divorced through “triple talaq”, have the right to claim maintenance under Section 125 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- This entitlement is independent of personal laws and serves as a social justice measure to prevent destitution.
-
- Relationship with the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act, 1986:
-
- Recognized that rights granted by the 1986 Act do not supersede the right to seek maintenance under Section 125 CrPC.
- Upheld the constitutional validity of both Section 125 CrPC and the 1986 Act, ensuring that Muslim women can assert their rights under either law.
-
- Constitutional Principles Upheld:
-
- Emphasized the prohibition of discrimination based on religion under Article 15(1) of the Constitution, highlighting that denying maintenance under Section 125 CrPC to divorced Muslim women would violate this principle.
- Stressed the importance of maintenance under Section 125 CrPC in providing a dignified life for women, irrespective of their marital status or religious affiliation.
-
- Scope and Application:
-
- Clarified that women can claim maintenance under Section 125 CrPC even while married, not exclusively after divorce.
- Applicable to all women unable to support themselves, including divorced Muslim women facing financial hardship post-divorce.
-
- Judicial Interpretation and Legislative Intent:
-
- Interpreted the CrPC and the 1986 Act to ensure adequate protection and justice for divorced Muslim women, aligning with constitutional mandates.
- Ensured that all divorced Muslim women, regardless of their marriage type, can access maintenance under Section 125 CrPC to avoid legal loopholes in protective measures.
-
UPSC GS 3
Salvinia Molesta
- News: An exotic beetle, Cyrtobagus salvinia, has completely eliminated ‘Chinese Jhalaar’ in 18 months from Satpura dam in Madhya Pradesh.
- Salvinia Molesta:
-
- In Madhya Pradesh, the Sarani reservoir on the Tawa River, has been battling an invasive aquatic fern, Salvinia molesta.
- It known locally as “Chinese Jhalaar” and globally as Kariba weed.
-
- Characteristics of Salvinia molesta:
-
- Invasive Nature: A highly detrimental, free-floating aquatic fern that does not attach to the soil but remains buoyant on water surfaces.
- Habitat: Thrives in slow-moving, nutrient-rich waters such as lakes, ponds, streams, and oxbows.
-

-
-
- Environmental Impact: Causes oxygen depletion and light obstruction, severely impacting aquatic life and biodiversity.
- Potential Benefits: Some studies suggest its potential for treating blackwater effluent.
-
- Biological Control: Cyrtobagus salvinia
- Introduction: The South American beetle Cyrtobagus salvinia has been employed to combat the invasive Salvinia molesta.
- Diet and Lifecycle: Solely feeds on Salvinia molesta and dies once its food source is exhausted, posing no further environmental threat.

- Reproduction: Females lay eggs in the lower leaves and rhizomes of the Salvinia plant.
- Larvae: Burrow through rhizomes and feed voraciously on new buds, leading to warping, stunting, and eventual sinking of the plant.
- Adults: Feed on buds and leaves but cause less damage compared to larvae.
Squalus Hima
- News: Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India have discovered a new species of deep-water dogfish shark Squalus hima in Kerala along the Arabian Sea.
- Definition:
-
- Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae that are commonly known as spurdogs.
- Spurdog are named so due to their tendency to hunt in dog-like packs.
-

- Features:
-
- These sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines.
- Teeth in upper and lower jaws similar in size.
- They have angular short snouts and a small mouth almost as wide as the snout.
- They have the first dorsal fin origin behind the pectoral fins.
- Their body is without any spots.
- The species of this family are generally small sharks.
- Like all sharks, dogfish grow slowly, mature late in life, and live a long time (35 to 40 years).
- Females grow larger and mature later than males.
- Female spurdog sharks have one of the longest pregnancies of any vertebrate, lasting between 18-22 months.
- The spurdog is a predator that feeds on bony fish, and sometimes even smaller sharks.
- It is a migratory species that spends the winter months in deep water, and the summer months in warm coastal waters.
-
- Distribution:
-
- Found in the Irish Sea and Northeast Atlantic, and in temperate waters world-wide.
-
- Importance and Exploitation:
-
- Species belonging to the genus Squalus and Centrophorus are exploited for their liver oil that contains high levels of squalene (or squalane is when it is processed for products).
- It is in high demand for pharmaceutical industries particularly for making high end cosmetic products and anti cancerous products.
-
Sambhar Deer (Rusa Unicolor)
- News: In Central India, changes in land use and roads are disrupting the populations of gaur and sambar. This fragmentation threatens their genetic diversity.
- Native Range: Sambhar Deer can be found in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Size: One of the largest members of the deer family

- State Animal: Odisha.
- Characteristics:
-
- Color: Light brown to dark with a grayish/yellowish tinge; paler underparts.
- Coat: Dark, coarse short hair with creamy white to light brown hair on the undersides.
- Behavior: Nocturnal.
- Social Structure: Males live alone most of the year; females live in small herds.
- Herbivorous: Eats grasses, foliage, fruits, leaves, water plants, herbs, berries, bamboo, stems, and various shrubs and trees.
-
- Habitat:
-
- Tropical seasonal forests, subtropical mixed forests, tropical rainforests.
- Rarely found far from water.
-
- Ecological Role:
-
- Seed Dispersal: Important for dispersing seeds throughout their native range.
-
- Main Threats: Habitat fragmentation, habitat loss, illegal poaching.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN: Vulnerable.
- WPA, 1972: Schedule I.
-
Makhana Cultivation
- News: Fox Nuts are in demand as a ‘super snack’, with its prices soaring in domestic and international markets since 2019.
- Definition:
-
- Makhana (Hindi) Fox nut & Gorgon Nut (English) & Euryale ferox ( Biological name) belong to the Family of ‘Nymphaeaceae’.
- Also known as ‘ Black Diamond’ due to its multi-purpose use in medicine, healthcare, nutrition.
- It is a non-cereal food.
- It is a perennial aquatic cash crop.
-

- Climate Suitable for Cultivation:
-
- Makhana is a plant that is mostly found and grown in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Temperature: Between 20 to 35 degree Celsius
- Relative humidity: 50%-90%
- Annual rainfall: 100-250 cm.
- Pond Ecosystem: The plant flourishes well in stagnant perennial water bodies (including various ponds, land depressions, oxbow lakes, swampy lands and ditches).
-
- Botanical Traits:
-
- It is a seed propagated plant.
- It has a thick rhizomatous stem.
- It is a self-pollinated plant.
-
- Major Producers:
-
- Largest: India is the largest producer, accounting for approximately 70-80% of the global yield.
- Countries including Japan, Korea, China, Bangladesh and Russia also grow Makhana in wild form.
- States: At around 80%, Bihar accounts for the highest production of makhana in the country. It is also grown in Assam and Bengal.
-
- Importance:
-
- Makhana contains a good amount of carbs in each serving and is also rich in several micronutrients, including calcium, magnesium, iron, and phosphorus.
- Mithila Makhana is a GI-tagged product.
- The Mallahs of Mithila in Bihar are involved in its processing that provides them with livelihood.
- Makhana is a product approved under the Union government’s One District One Product scheme, under which subsidies are provided to food processors for branding, marketing, and developing infrastructure.
-
See this: India’s Demographic Dividend- Significance and Challenges | UPSC
Key Largo Tree Cactus (Pilosocereus Millspaughii)
- News: A new study suggests the Key Largo tree cactus, discovered roughly three decades ago in North America, has gone extinct locally.
- Definition: Key Largo Tree Cactus is a rare cactus that was discovered in the Florida Keys in 1992 and had been monitored since then.
- Regions: It grows in parts of the Bahamas, northern Cuba, a few Caribbean islands, and Florida.
- Physical Characteristics:
-
- Height: Can exceed 20 feet (six meters).
- Flowers: Cream-colored with a garlic scent, gleaming in the moonlight.
- Fruits: Red and purple, attractive to mammals and birds.
-

- Pollination: Pollinators: The garlic-scented flowers attract bats.
- Preferred Locations: Exposed hilltops in Dry Broadleaf Evergreen Formation-Woodland/Shrublands.
- Threats:
-
- Saltwater intrusion.
- Soil depletion from hurricanes and high tides.
- Herbivory by local mammals.
-
Shield-Tail Snake (Uropeltis Caudomaculata)
- News: A new species of shield tail snake has been discovered in Meghamalai-Munnar hill region in the Western Ghats.
- Name Origin: The snake has been named ‘Tail-spot shield tail after the yellow spot on each side of the base of its tail.
- Comparison: Differs from its closest relative, Uropeltis pulneyensis, which has a stripe instead of a spot.
- Key Feature: It has increased number of ventral scales.
- Distribution: Uropeltis caudomaculata is found in only three localities:
-
- Meghamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu,
- Periyar Tiger Reserve and Yellapetty,
- Munnar in Kerala.
-

- Shield-Tail Snakes (Uropeltidae)
- Name Origin: Derived from Greek words “ura” (tail) and “pelte” (shield), indicating the large keratinous shield at the tip of the tail.
- Characteristics:
-
- They are primitive, nonvenomous, burrowing snakes.
- Shieldtail snakes are small, typically growing to between 25 and 50 cm (10 and 20 inches) in length.
- Most species appear black, purple, or brown, red, orange, or yellow spots.
- Shieldtails are nocturnal and live at higher elevations in loose soil.
- Their diet is principally made up of earthworms.
- They give birth to 3–9 living young.
-
- Native Regions: They are endemic to peninsular India and Sri Lanka.
National Gopal Ratna Award
- News: The nomination process of National Gopal Ratna Award-2024 will start from July 15.
- Award: This award is given under The “Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM)”.
- Objective:
-
- The Department aims for the effective development of the Animal Husbandry and Dairy sector to provide sustainable livelihoods for farmers.
- Special Award for North Eastern Region (NER) States to boost dairy development activities.
-

- Award Categories for NGRA 2024:
-
- Best Dairy Farmer rearing indigenous cattle/buffalo breeds (list of registered breeds annexed).
- Best Dairy Cooperative Society (DCS)/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization (FPO).
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT).
-
- Award Details: Best Dairy Farmer and Best DCS/FPO/MPCs will receive Certificate of merit, a memento and monetary prize:
-
- Rs. 5,00,000/-(Rupee five lakh only) -1st rank
- Rs. 3,00,000/- (Rupee three lakh only) -2nd rank and
- Rs. 2,00,000/- (Rupee two lakh only) -3rd rank
- Rs. 2,00,000/- (Rupee two lakh only) -Special Award for North Eastern Region (NER)
- No cash prize will be provided in the Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT) Category. Only Certificate of merit and a memento shall be given.
-
- Occasion: Awards to be conferred on National Milk Day (26th November 2024)

