UPSC GS 1
Goddess Skandamata
- News: Prime Minister Modi has prayed to Goddess Skandamata on the fifth day of Navratri.
- Definition:
-
- Goddess Skandamata is the goddess of patience, purity, and peace.
- Skandamata mounts on a lion.
- According to Hindu mythology, Goddess Skandamata is the mother of Lord Skanda, also known as Lord Kartikeya.
-

-
-
- She is often depicted holding her son Skanda in her lap.
- The colour of Mother Skandamata is completely white and she sits on a lotus flower, due to which she is also called Padmasana.
-
Read also: Celebrating 10 Years of Make in India | UPSC
Chenchu Tribe
- News: The Chenchus of Penukumaduguh have got less work opportunities under the MGNREGA.
- About the Chenchu Tribe:
-
- The Chenchus are an indigenous tribe residing in the Nallamala Hills, located within the Nagarjuna Sagar Tiger Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh. They are classified as a Scheduled Tribe in the state.
- Their ancestry is linked to Lord Malikarjuna of the Srisailam temple. While primarily found in Andhra Pradesh, smaller populations of Chenchus also exist in Tamil Nadu and Odisha.
-

- Social Structure and Living Patterns:
-
- The Chenchus live in small settlements called “Penta,” consisting of clusters of huts organized around kinship ties.
- These villages are governed by a village elder known as the “Peddamanishi,” whose decisions hold the highest authority within the community.
-
- Traditional Occupation:
-
- Historically, the Chenchus depend on hunting for their sustenance. They hunt deer, wild boar, rabbits, wild cocks, and birds using bows and arrows.
- They also gather forest products such as roots, tubers, fruits, beedi leaves, mahua flowers, honey, gum, tamarind, and green leaves, which they sell to traders or government cooperatives.
-
- Livelihood:
-
- Apart from hunting and gathering, the Chenchus make leaf cups and plates from tobacco leaves.
- They also sell tamarind and mahua flowers, which are popular in local markets. Honey is particularly significant in their diet and livelihood.
-
- Marriage Customs:
-
- Chenchu society is organized into clans, with 26 distinct gotras. Marriages within the same gotra are forbidden.
- Known as “Pelli,” marriages are either arranged by elders or based on the choice of the individuals.
- The maternal uncle plays a key role in the wedding ceremony by conducting the ‘sampradaan’ (handing over the bride).
-
- Religion and Beliefs:
-
- The Chenchus primarily worship Bhagwan Taru, the sky god, and Garelamai Sama, the forest goddess who protects them.
- They also revere other deities such as Lord Shiva, Hanuman, and the Goddess of Fire.
-
- Language:
-
- The Chenchu people speak dialects of the Chenchu language, including Chenchucoolam, Chenchwar, Chenswar, and Choncharu, all of which bear a strong Telugu influence.
-
Lake Kivu
- News: A boat carrying scores of passengers capsized on Lake Kivu in eastern Congo recently.
- Location: Lake Kivu is one of East Africa’s Great Lakes, straddling the border between the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) on its western side and Rwanda on its eastern side.
- Significance:
-
- It is Rwanda’s largest lake and ranks as the sixth largest lake in Africa.
- The lake is located within the Albertine Rift, which is part of the western branch of the East African Rift system.
-
- Geography:
-
- Lake Kivu sits at an elevation of 1,460 meters above sea level and covers an area of 1,040 square miles (2,700 square kilometers).
- About 58% of the lake’s waters lie within the DRC, with the remaining portion in Rwanda.
- The lake stretches 90 kilometers in length and is 50 kilometers wide.
-
- Depth and Physical Features:
-
- It has a maximum depth of 475 meters and an average depth of 220 meters.
- Its irregular shoreline is dotted with inlets, peninsulas, and numerous waterfalls.
-
- Hydrology:
-
- The lake drains into the Rusizi River, which flows southward and ultimately empties into Lake Tanganyika.
-
- Notable Feature:
-
- Idjwi Island, the world’s tenth-largest inland island, is located within Lake Kivu.
-
Rani Durgavati
- News: Madhya Pradesh cabinet recently approved the formation of a panel to develop a memorial and garden dedicated to Gond queen Rani Durgavati for Rs 100 crore.
- Background:
-
- Rani Durgavati (1524–1564) was a descendant of the Chandela dynasty of Mahoba and the queen of the Gond kingdom of Garha-Katanga.
- She was born on 5th October 1524 in the family of the famous Chandel ruler, Keerat Rai.
-
- Chandela Dynasty:
-
- The Chandela dynasty is renowned for the valor of King Vidyadhar, who successfully defended his kingdom against Mahmud Ghazni’s invasions.
- The dynasty is also known for its architectural marvels, such as the temples of Khajuraho and the fort of Kalinjar, reflecting their love for art and sculptures.
-
- Birthplace: Rani Durgavati was born in Kalinjar (Banda, U.P.), a prominent fort in medieval India.
- Marriage and Alliance:
-
- In 1542, she married Dalpatshah, the eldest son of King Sangramshah of the Gond Dynasty, forming a close alliance between the Chandela and Gond dynasties.
- In 1545, she gave birth to her son, Vir Narayan.
-
- Assumption of Power:
-
- After Dalpatshah’s death in 1550, Rani Durgavati assumed control of the Gond kingdom as Vir Narayan was too young to rule.
- She was assisted by two ministers, Adhar Kayastha and Man Thakur, in managing the administration effectively.
-
- Strategic Move:
-
- She shifted the capital from Singaurgarh to Chauragarh, a strategically important fort located in the Satpura hill range.
- Trade flourished during her reign, leading to prosperity among her people.
-

- Territorial Expansion:
-
- Following in the footsteps of her husband’s predecessors, Rani Durgavati expanded her kingdom and unified Gondwana (Garha-Katanga) with bravery, generosity, and political acumen.
- She successfully defended her territory from Sultan Baz Bahadur of Malwa.
-
- Conflict with the Mughals:
-
- In 1562, after Akbar defeated Baz Bahadur and annexed Malwa, the borders of Gondwana came into contact with the Mughal Empire.
- Rani Durgavati is most remembered for her courageous defense of Gondwana against the Mughal forces.
-
- Legacy:
-
- Despite her eventual defeat, Rani Durgavati is celebrated as a brave warrior who fought valiantly against the Mughal Empire, embodying the spirit of resistance and leadership.
-
UPSC GS 2
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam
- News: In alignment with the “Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam” campaign, South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL) has planted a staggering 1,46,675 saplings across its operational areas in Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Campaign Overview: Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam was Initiated by the Central Government on World Environment Day, 5th June 2024.
- Led by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in partnership with State Governments and Union Territories.
- Objective: The campaign encouraged citizens to plant trees as a tribute to their mothers, fostering both ecological conservation and a sense of familial respect.
- Goals:
-
- 80 crore trees to be planted by September 2024.
- 140 crore trees to be planted by March 2025.
-
- Strategy: Utilizing a “Whole of Government” and “Whole of Society” approach, the campaign seeks to involve citizens, communities, and local authorities in a nationwide effort to enhance India’s green cover.
- Campaign Activities:
-
- Distribution of saplings.
- Awareness initiatives and events where individuals plant trees in honour of their mothers.
-
- Broader Significance: The campaign ties environmental awareness with personal and cultural values, encouraging a deeper connection to nature.
- Focus Areas: The initiative also concentrated on combating land degradation and restoring degraded lands through widespread tree plantation efforts.
- South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL):
-
- South Eastern Coalfields Limited is a Government of India Undertaking and a Miniratna Company.
- South Eastern Coalfield Limited’s Gevra mine is the largest coal mine in India.
-
National Agriculture Code (NAC)
- News: The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has begun the process of formulating a National Agriculture Code (NAC), on the lines of the existing National Building Code and National Electrical Code.
- About the National Agriculture Code (NAC):
-
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is developing the National Agriculture Code (NAC), aiming to set standardized guidelines for the entire agricultural cycle.
- These standards will cover essential aspects such as field preparation, crop selection, irrigation, harvesting, storage, and modern areas like natural and organic farming.
-
- Implementation Strategy:
-
- BIS has developed a strategic framework, forming 12-14 working panels composed of university professors and R&D organizations to address specific areas of agriculture.
-
- Purpose and Guidance:
-
- The NAC will serve as a reference guide for farmers, agricultural universities, and field officials, ensuring consistent best practices across the agriculture sector.
-
- Need for NAC:
-
- Currently, BIS sets standards for agricultural machinery and inputs (e.g., fertilizers, pesticides), but there are no standards for critical practices like field preparation, irrigation, and water management, making the NAC essential.
-
- Structure of the NAC:
-
- Part 1: General principles applicable to all crops.
- Part 2: Crop-specific standards for major crops like paddy, wheat, oilseeds, and pulses.
-
- NAC Coverage:
-
- The NAC will cover the entire agricultural cycle, including crop selection, land preparation, sowing, irrigation, soil and plant health management, harvesting, post-harvest operations, and sustainability practices.
- Standards for inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, and storage will be included. Emerging areas such as natural farming, organic farming, and IoT applications in agriculture will also be addressed.
-
- Objectives of NAC:
-
- Comprehensive Code: Develop a national code to standardize agricultural practices based on agroclimatic zones, crop types, and socio-economic diversity.
- Quality Culture: Encourage a culture of quality standards in Indian agriculture, providing guidelines for policymakers and regulators.
- Decision-Making Guide: Serve as a reference for farmers to make informed decisions about agricultural techniques.
- Integration: Align Indian agricultural standards with recommended best practices.
- Smart Farming: Focus on broader agricultural issues such as smart farming, sustainability, traceability, and documentation.
- Capacity Building: Support the growth of agricultural extension services and civil society organizations through capacity-building initiatives.
-
UPSC GS 3
Hammerhead Shark
- News: Stunning shovel-shaped hammerhead shark species have been discovered in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Definition:
-
- Hammerhead sharks, known for their uniquely shaped heads, belong to the Sphyrnidae family.
- Their flattened, hammer- or shovel-shaped heads, referred to as ‘cephalofoils,’ are a distinct characteristic.
-
- Head Structure:
-
- The cephalofoil design enhances their 360-degree vision.
- It also improves their hunting efficiency.
-

- Species:
-
- There are nine species of hammerhead sharks, each differing in length.
- The largest species is the great hammerhead, which can grow up to 20 feet long.
-
- Distribution:
-
-
- Hammerhead sharks inhabit tropical and temperate waters, typically near coastlines and continental shelves.
- They may migrate seasonally, moving towards the equator in winter and towards the poles in summer.
- During El Niño events, they can travel hundreds of kilometers beyond their usual range.
-
- Physical Features:
-
-
- Their upper bodies range in color from greyish-brown to olive-green, while their undersides are white.
- They possess sharp, triangular, serrated teeth, akin to the edge of a saw blade.
- Hammerheads have special sensory organs on their heads that help detect prey in the ocean.
-
- Reproduction and Lifespan:
-
-
- Hammerhead sharks are viviparous, giving birth to live young after carrying fertilized eggs inside their bodies.
- They have a lifespan of 20-30 years.
-
- Thermoregulation:
-
-
- Being exothermic, hammerhead sharks rely on external sources to regulate their body temperature.
-
- Conservation Status: All species, except Sphyrna gilberti, are listed as Vulnerable, Endangered, or Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
Very Short Range Air Defence System
- News: India conducted three successful flight tests of a very short range air defence missile system at Rajasthan’s Pokhran firing ranges.
- Definition: The Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) is a Man Portable Air Defence System (MANPAD) designed to neutralize low-altitude aerial threats at short distances.
- Development:
-
- VSHORADS has been indigenously designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Research Centre Imarat, Hyderabad.
- The development was done in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
-

- Key Features:
-
- The missile and launcher have been highly optimized for easy portability, requiring minimal personnel for operation.
- It incorporates advanced technologies, such as a miniaturized Reaction Control System (RCS) and integrated avionics.
- The missile is powered by a dual-thrust solid motor and has a range of up to 6 km.
-
- Deployment:
-
- As a lightweight, man-portable system, VSHORADS can be quickly deployed, particularly in mountainous regions.
- It is especially useful in areas along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China, including Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
-
Read also: University Ranking Framework: A Comprehensive Guide | UPSC
Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024
- News: India has been ranked 39th among 119 countries in the latest TTDI 2024 report published by the World Economic Forum.
- Definition:
-
- First introduced in 2022, the Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI) benchmarks and measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of the Travel & Tourism (T&T) sector, which in turn contributes to the development of a country.
- The index is a direct evolution of the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index (TTCI), which has been published biennially since 2007.
-
- Published by: The report has been published by the World Economic Forum.
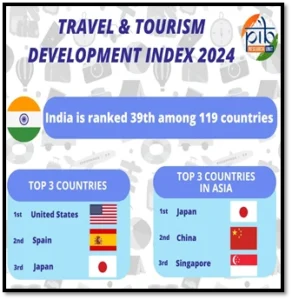
- India’s Position: India ranks 39th out of 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Key Areas of Improvement for India: India has made notable progress in several areas, particularly in the prioritization of travel and tourism, safety and security, and health and hygiene.
- Government of India’s Initiatives: The Indian government views tourism as a crucial sector for fostering social inclusion, generating employment, and driving economic growth.
-
- Tourism plays a central role in India’s vision to become a developed nation by 2047.
-
- Measures to Enhance Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs):
-
- Key efforts to boost FTAs include the promotion of adventure and niche tourism.
- The government has simplified the availability of e-visas and introduced a 24×7 multilingual tourist helpline.
- On World Tourism Day 2024, the launch of initiatives like ‘Paryatan Didi’ and ‘Paryatan Mitra’ aims to enhance the hospitality experience for tourists.
-

- Domestic Tourism Initiatives:
-
- Several programs have been introduced to boost domestic tourism, such as Dekho Apna Desh, the PRASHAD Scheme, the Vibrant Village Programme, SWADESH 2.0, and the Regional Connectivity Scheme (Udaan).

