UPSC GS 1
Enemy Property in India
- News: The Indian government has begun to auction enemy properties.
- Definition: Enemy property is property left behind by people who migrated to enemy countries.
- Historical Context:
-
- Government of India took over properties and companies of those who took Pakistani nationality under the Defence of India Rules framed under The Defence of India Act, 1962.
- These properties were vested in the Custodian of Enemy Property for India.
- Similar actions were taken for property left behind by those who went to China.
- The Tashkent Declaration of January 10, 1966 included a clause that said India and Pakistan would discuss the return of the property and assets taken over by either side in connection with the conflict.
- Pakistan disposed of all such properties in 1971.
- The Enemy Property Act, enacted in 1968, provided for the continuous vesting of enemy property in the Custodian of Enemy Property for India.
- The Act ruled that the heirs of people who migrated to Pakistan and China would not have any right to succession over the property left by their ancestors .
- The central government, through the Custodian, is in possession of enemy properties spread across many states in the country.
- There are 13,252 enemy properties in India, valued at over Rs1 lakh crore.
-
- Amendments and Expansions:
-
- The 2017 amendment to the Act (Enemy Property (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2017) stated that the successors of those who migrated to Pakistan and China ceased to have a claim over the properties left behind in India.
- “Enemy subject” and “enemy firm” now include the legal heir and successor of an enemy, regardless of their citizenship.
- The succeeding firm of an enemy firm is included, irrespective of the nationality of its members or partners.
-
- Highest Enemy Property in India
-
- Uttar Pradesh (5,982) has the highest number of enemy properties, followed by West Bengal (4,354).
-
Read also: Explain Importance of Fiscal Federalism in India | UPSC
Rwanda
- News: President Paul Kagame has won in Rwanda elections with more than 99% of the vote.
- Location: Rwanda is a landlocked country lying south of the Equator in east-central Africa.
- Borders: Shares borders with Burundi, Tanzania, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Capital: Kigali
- Currency: Rwandan franc
- Population:
-
- One of Africa’s most densely populated countries with approximately a thousand people per square mile.
- Predominantly made up of the Hutu and Tutsi ethnic groups, with Christianity being the major religion.
-
- Government: Adopted a presidential system of government with a constitution in 2003.
- Major Mountain Ranges: Albertine Rift and Virunga.
- Major Rivers:
-
- The Nile and the Congo are the two major African rivers flowing through Rwanda.
- Other significant rivers: Kagera, Nyabarongo, Ruzizi, Luhwa, and Akanyaru.
- 80% of rivers drain into the Nile via Lake Victoria, and 20% drain into the Congo via the Rusizi River, the lowest point in Rwanda at 950 m.
-
- Lakes:
-
- Numerous lakes, with Lake Kivu being the largest, located on the western border with the DRC.
- Notable lakes: Burera, Cohana, Ruhondo, Muhazi, Rweru, and Ihema.
-
- Biodiversity:
-
- One of the most ecologically diverse regions in Africa.
- The Albertine Rift region in western Rwanda is home to about a third of Africa’s birds, 40 percent of its mammals, and 20 percent of the continent’s amphibians and plants.
-
UPSC GS 2
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- News: UPSC Chairperson Manoj Soni has resigned five years before term ends.
- Definition: The UPSC is a constitutional body as mandated under Article 315-323 Part XIV Chapter II of the Constitution of India.
- History:
-
- The Lee Commission constituted by the British in 1924 had suggested in its report for the creation of an unprejudiced and independent Public Service Commission.
- Under the Chairmanship of Sir Ross Barker, it was established on October 1, 1926 as Public Service Commission and was later reconstituted as the Federal Public Service Commission in 1935.
- After the independence in 1947, the agency got renamed as the Union Public Service Commission.
- It was also given a Constitutional status with the promulgation of the Constitution of India on January 26, 1950.
-
- Important Constitutional Provisions:
-
- Article-315. Public Service Commissions for the Union and for the States.
- Article-316. Appointment and term of office of members.
- Article-317. Removal and suspension of a member of a Public Service Commission.
- Article-318. Power to make regulations as to conditions of service of members and staff of the Commission.
- Article-319. Prohibition as to the holding of offices by members of Commission on ceasing to be such members.
- Article-320. Functions of Public Service Commissions.
- Article-321. Power to extend functions of Public Service Commissions.
- Article-322. Expenses of Public Service Commissions.
- Article-323. Reports of Public Service Commissions.
-
- Composition:
-
- The UPSC consists of a chairman and ten members.
- The President of India appoints the UPSC Chairman and other members.
- Each member holds office for a tenure of 6 years or till he becomes the age of 65 years.
-
- Resignation:
-
- A member of the Union Public Service Commission may resign from his/her office by submitting the written resignation to the President of India.
-
- Functions/Mandate of UPSC under Article 320 and 321 of the Constitution of India:
-
- Recruitment by conducting competitive examinations and selection through interviews
- Advising on the suitability of officers for appointment on promotion as well as transfer-on –deputation
- Advising the Government on any matter referred to the Commission by the President of India
- Handling disciplinary cases relating to civil services
- Miscellaneous matters relating to grant of extra-ordinary pensions, reimbursement of legal expenses
- Assisting the government on any matter referred to the Commission by the President of India
- On the request of the Governor of a State, to serve all or any of the needs of a State relating to recruitment, with the approval of the President
-
Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI)
- News: The Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh recently inaugurated Asia’s first health research-related “Pre-clinical Network Facility” under the Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI).
- About: CEPI (Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations) was launched in 2017 as a partnership between public, private, philanthropic, and civil organizations.
- Founders: CEPI was founded by the governments of Norway and India, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the World Economic Forum.
- Mission: The mission of CEPI is to accelerate the development of vaccines and other biological countermeasures against epidemic and pandemic threats, ensuring they are accessible to everyone in need.
- Achievements
-
- Vaccine Development: CEPI has supported the development of over 50 vaccine candidates or platform technologies.
- Targeting High-Risk Pathogens: Focuses on known high-risk pathogens and potential future threats, referred to as “Disease X”.
- Key Initiative – 100 Days Mission: The ‘100 Days Mission’ aims to reduce the time needed to develop safe, effective, and globally accessible vaccines to just 100 days.
-
- India and CEPI
-
- Ind-CEPI Mission: The Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India, supports the Ind-CEPI Mission.
-
- Focus:
-
- The Ind-CEPI Mission concentrates on rapid vaccine development for epidemic preparedness.
- It is managed through a dedicated Program Management Unit (PMU) at the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
-
Section 294 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC)
- News: The Supreme Court recently observed that an accused cannot be considered a witness against himself if he is asked to admit or deny the genuineness of documents produced by the prosecution under Section 294 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- Filing of Documents:
-
- Section 294 of the CrPC deals with the filing of documents by either the prosecution or the accused.
- It mandates that the particulars of every document filed by either party must be included in a list.
-
- Admission or Denial:
-
- This section requires the opposing party or their pleaders to be given the opportunity to admit or deny the genuineness of each document presented.
-
- Applicability:
-
- Section 294 applies to all documents filed by the prosecution or the accused, regardless of their nature and character.
- However, it does not apply to witnesses who wish to directly produce additional documents during the trial or while recording their evidence.
- It is specifically limited to documents filed by the prosecution or the accused, and not by third parties like witnesses.
-
- Genuineness of Documents:
-
- The genuineness of the documents is a critical aspect, and without proper proof, reliance cannot be placed on them.
-
- Purpose:
-
-
- The primary purpose of Section 294 of the CrPC is to accelerate the pace of the trial by avoiding the waste of time in recording unnecessary evidence.
- It allows for the admission of documents whose genuineness is not disputed by the opposing party.
-
- Benefits:
-
-
- This section aims to ensure transparency and fairness in the judicial process by allowing both the prosecution and the accused to present relevant documents effectively.
-
Voicebox Programme
- News: NFDC and Netflix partner will launch ‘The Voicebox’ upskilling programme for voice-over artists in India.
- Overview:
-
- The Voicebox Programme offers Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) training specifically for voice-over artists.
- This training focuses on eight languages: English, Hindi, Marathi, Bengali, Malayalam, Tamil, Telugu, and Gujarati.
-

- Eligibility:
-
- The program is open to professionals, preferably women, who have more than two years of experience in the media and entertainment sector and are keen to enhance their voice-over skills.
-
- Funding:
-
- The programme is sponsored by the Netflix Fund for Creative Equity, which has committed $100 million annually for five years to support underrepresented communities in the TV and film industries through global programs.
-
- Program Structure:
-
- Workshops: Structured workshops will be conducted, including training sessions with guest lectures and mentoring, followed by an assessment.
- Locations: The workshops will take place in seven major Indian cities: New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Chennai, and Kochi.
- Participant Selection: Each batch will accommodate up to 30 candidates, with a total of 210 participants selected through preliminary screening. At least 50% of the participants will be women.
-
- Training Partner:
-
- Pearl Academy, a leading design institute in India, will act as the Training Partner for this program.
-
- Special Project:
-
- Seven top participants from each batch will be chosen to contribute to Netflix’s special project, “Azaadi ki Amrit Kahaniya.” These participants will lend their voices to narrate stories that reflect the Indian independence movement.
-
See more: Foundation Course For IAS/IPS/UPSC: The Ultimate Guide
UN Water Convention
- News: Ivory Coast joined the United Nations Water Convention, becoming the 10th African nation to do so.
- Overview:
-
- The UN Water Convention, formally known as the Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes, was adopted in Helsinki in 1992 and entered into force in 1996.
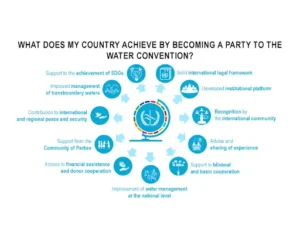
- It is a legally binding instrument aimed at promoting the sustainable management of shared water resources, implementing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), preventing conflicts, and fostering peace and regional integration.
-
- History:
-
- Initially negotiated as a regional framework for the pan-European region.
- An amendment procedure in March 2016 allowed all UN Member States to accede to the convention.
- Chad and Senegal became the first African Parties in 2018.
- Iraq joined in March 2023 as the first country from the Middle East.
- Namibia joined in June 2023 as the first country from Southern Africa.
- Panama joined in July 2023 as the first country from Latin America.
-
- Requirements for Parties:
-
- Parties must prevent, control, and reduce transboundary impacts.
- Transboundary waters must be used in a reasonable and equitable way.
- Parties must ensure the sustainable management of transboundary waters.
- Countries sharing the same transboundary waters must cooperate through specific agreements and joint bodies.
-
- Framework Agreement:
-
- The convention does not replace bilateral and multilateral agreements for specific basins or aquifers.
- It promotes the establishment, implementation, and further development of such agreements.
-
- Significance:
-
- The UN Water Convention is a powerful tool for promoting and operationalizing the achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its SDGs.
- The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) services the UN Water Convention.
-
- Ivory Coast:
-
- It is located on the coast of western Africa.
- Its capital is Abidjan.
- It is bounded to the north by Mali and Burkina Faso, to the east by Ghana, to the south by the Gulf of Guinea, to the southwest by Liberia, and to the northwest by Guinea.
- It is the largest producer of cocoa in the world, producing over 2 million tons a year.
-
Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) Programme
- News: Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme is set to get a fresh boost under the leadership of the Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour & Employment.
- Ministry: Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Aim: A nation-wide programme under the Khelo India mission aims at identifying talent among school-going athletes aged 9 to 18 years.
- Objective:
-
- To hunt talent from every nook and corner of the country.
- To use sports as a tool to curb addiction towards drugs and other gadgetry distractions.
-
- Implementation Strategy:
-
- KIRTI aims to conduct 20 lakh assessments across the country throughout the year to identify talent through notified Talent Assessment Centres.
-

- Features:
-
- KIRTI’s athlete-centric programme has a transparent selection methodology based on Information Technology.
- Data analytics based on Artificial Intelligence are being used to predict the sporting acumen in an aspiring athlete.
- Taking the help of scientific tools, KIRTI will involve physical education teachers and experts in scouting talent.
- In the first phase, 10 Khelo India disciplines – archery, athletics, boxing, football, hockey, kabaddi, kho-kho, volleyball, weightlifting and wrestling have been identified.
-
- Importance:
-
- India aims to become a top 10 sports nation in the world by 2036 and among the top five by 2047.
- India aims to build a culture of sports and also create a cradle of talent that can win India medals at global competitions like the Olympics and Asian Games.
-
- Khelo India Mission:
-
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
- It aims at infusing sports culture and achieving sporting excellence in the country.
- Under the “Sports Competitions and Talent Development” vertical of the Khelo India Scheme, the “Talent Identification and Development” component is dedicated to identification and development of athletes to develop the sports ecosystem in the country.
-
UPSC GS 3
Phlogacanthus Sudhansusekharii
- News: Researchers from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI) have discovered a new plant species called ‘Phlogacanthus Sudhansusekharii’, from a wildlife sanctuary in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Definition:
-
- Phlogacanthus Sudhansusekharii is a newly discovered plant species which belongs to the family ‘Acanthaceae’ and the ‘Phlogacanthus’ genus.
- The genus ‘Phlogacanthus’ comprises 13 species in India and is spread over mainly the northeastern and eastern Himalayan states.
-

- Nomenclature: The species is named to honor Dr Sudhansu Sekhar Dash, a scientist at the BSI, for his “significant contribution” to plant and ecological research in the Indian Himalayan region.
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
- News: The government wants to increase the capital base of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development, or NaBFID, to ₹1 trillion through support from banks.
- About:
-
- The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) was established in 2021 under the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- It is a Development Finance Institution (DFI) in India, primarily focused on long-term infrastructure financing.
- NaBFID is regulated and supervised by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
-
- Objective: NaBFID aims to increase its capital base to 1 trillion INR with support from banks.
- Purpose: The main purpose of NaBFID is to provide specialized financing for infrastructure development in India.
- Goals:
-
- Addressing Financing Gaps: NaBFID aims to address gaps in long-term non-recourse finance for infrastructure projects.
- Development of Financial Markets: It seeks to strengthen the development of bonds and derivatives markets in India.
-
- Economic Boost: NaBFID is focused on boosting India’s economy sustainably through infrastructure development.

