UPSC GS 1
Dead Zone
- News: The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has forecasted an above-average summer “dead zone” in the Gulf of Mexico covering approximately 5,827 square miles.
- Dead Zone or Hypoxia: Refers to low-oxygen areas in the world’s lakes and oceans.
- Impact on Organisms: Few organisms can survive in hypoxic conditions, hence the name “dead zones”.
- Causes of Dead Zones:
-
- Natural Occurrence: Hypoxic zones can occur naturally.
- Human Activities: Human activities can lead to the creation of new dead zones or enhance existing ones.
-
- Formation of Dead Zones:
-
- Eutrophication Process: Dead zones occur due to eutrophication, which happens when a body of water is inundated with too many nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Cyanobacteria Role: Normally, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) feed on these nutrients. Excess nutrients cause an overgrowth of algae, known as algae blooms.
- Decomposition and Oxygen Depletion: When the algae die, they sink to the bottom.
- Bacterial Decomposition: Bacteria decompose the dead algae, stripping dissolved oxygen from the surrounding water.
-
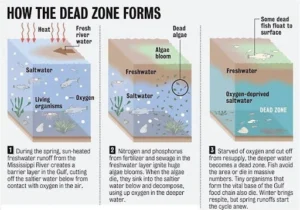
- Location: Dead zones are often near inhabited coastlines.
- Factors Influencing Dead Zones:
-
- Wind Influence: Wind can mix oxygen from the surface into deeper water, helping to break up dead zones.
- Hot Temperatures: Can worsen dead zones by warming surface water, preventing oxygen mixing with colder, denser water below.
- Heavy Rainfall: Increases the amount of pollution washed into waterways.
- Shallow Waters: Less likely to stratify and develop hypoxic conditions due to mixing by winds and tides.
- Primary Producers: Shallow, clear waters support phytoplankton, algae, and seagrasses that release oxygen during photosynthesis.
-
- Impact on Aquatic Life:
-
- Blockage of Sunlight: Dense algal blooms block sunlight, preventing underwater grasses from growing.
- Food and Shelter: Animals depending on these grasses for food and shelter suffer.
-
- Human Contributions:
-
- Pollution: Human activities cause excess nutrients to be washed into the ocean.
-
Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH)
- News: A major water crisis is emerging due to record-low snowfall in the Hindu Kush Himalaya region, threatening 12 river basins.
- Geographical Extent: The HKH region stretches 3,500 kilometers and spans eight countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
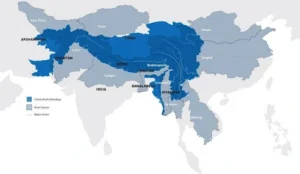
- High Peaks: Numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir (or Terichmir) at 7,708 meters (25,289 ft) in Chitral, Pakistan.
- Third Pole: Considered the Third Pole (after the North and South Poles) with significant climate implications.
- Ice and Snow Volume: Contains the largest volume of ice and snow outside the Arctic and Antarctica.
What is Cryosphere?
|
- Hydrological Significance:
-
- Source of Major Rivers: The HKH region is the source of ten large Asian river systems: the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra, Irrawaddy, Salween, Mekong, Yangtze, Yellow River, and Tarim.
- Water Supply: These river basins provide water to 1.9 billion people, constituting a fourth of the world’s population.
-
- Climate Implications:
-
- Third Pole Status: Its extensive ice and snow cover have significant impacts on global climate patterns.
-
- Vegetation:
-
- Inner Valleys: The inner valleys of the Hindu Kush see little rain and have desert vegetation.
-
- Regional Divisions: Sections of HKH:
-
- Eastern Hindu Kush: One of the three main sections.
- Central Hindu Kush: Another main section.
- Western Hindu Kush (Bābā Mountains): The third main section.
-
Read also: Indian Migrants in Gulf Countries: Opportunities and Challenges UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- News: India-IORA Cruise Tourism Conference was recently held in New Delhi.
- Foundation: Established as an inter-governmental organization in March 1997.
- Origins: Formerly known as the Indian Ocean Rim Initiative and the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC).
- Aim: To foster regional economic cooperation.
- Observer Status:
-
- UN and AU: Attained observer status at the United Nations General Assembly and the African Union in 2015.
-
- Members: 23 Member States including Australia, Bangladesh, Comoros, France, India, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Seychelles, Singapore, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, UAE, Yemen.
- Dialogue Partners: 11 Dialogue Partners including China, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Russia, Turkey, United Kingdom, USA.
- Focused Initiatives: Six priority areas include Trade and Investment, Maritime Safety and Security, Fisheries Management, Disaster Risk Management, and Blue Economy.
- Objectives:
-
- Promotion of Growth: Foster sustainable growth and balanced development within the region.
- Economic Cooperation: Emphasize economic cooperation that maximizes development opportunities, mutual interests, and shared benefits.
- Liberalization and Integration: Promote liberalization, remove barriers, and facilitate enhanced flow of goods, services, investment, and technology across the Indian Ocean rim.
-
- Location: Secretariat based in Mauritius, facilitating administrative functions.
Public Financial Management System (PFMS)
- News: It has been in news.
- Launch: Initially launched in 2009 as a Central Sector Scheme by the Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog).
- Origin: Developed and implemented by the Office of the Controller General of Accounts (CGA), Ministry of Finance.
- Primary Goals:
-
- Facilitation: To establish a robust Public Financial Management System.
- Efficiency: Create an efficient fund flow system and a payment-cum-accounting network.
-

- Scope of Coverage: Currently covers Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes, as well as other expenditures including Finance Commission grants.
- Features and Benefits
-
- Real-Time Data: Provides stakeholders with real-time, reliable, and meaningful management information.
- Decision Support: Offers an effective decision support system, aligning with the Digital India initiative.
-
- Integration and Transparency:
-
- Core Banking Integration: Integrated with the core banking system nationwide.
- Financial Transactions: Facilitates seamless financial transactions and enhances transparency and accountability in public fund management.
-
GREAT Scheme
- News: The Empowered Programme Committee (EPC) of the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM) recently approved 7 startup proposals under the GREAT scheme.
- Launch: The Central Government approved the Startup Guidelines for Technical Textiles – Grant for Research and Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) Scheme in 2023.
- Objective: GREAT Scheme aims to support young innovators, scientists, technologists, and startup ventures in the field of Technical Textiles.
- Self-Reliance: Its goal is to translate innovative ideas into commercial technologies/products to enhance India’s self-reliance in this sector.
- Funding: This scheme provides a grant-in-aid of up to Rs 50 lakh for up to 18 months. It supports development of functional prototypes or commercialization of technologies related to Technical Textiles.
- National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM):
- Initiative: Launched in 2020 by the Union Government to increase the penetration level of technical textiles in India.
- Sector Growth: Aims to leverage the rapid growth potential of the technical textiles sector.
- Objectives:
-
- Global Leadership: Position India as a global leader in Technical Textiles.
-
- Components: The mission encompasses:
-
- Research, Innovation, and Development
- Promotion and Market Development
- Export Promotion
- Education, Training, Skill Development
-
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles oversees the implementation of NTTM.
- Implementation Period: Approved for four years, from FY 2020-21 to FY 2023-24.
National Institute of Indian Medical Heritage (NIIMH)
- News: The World Health Organization (WHO) has designated the National Institute of Indian Medical Heritage (NIIMH) as a WHO Collaborating Centre (CC) for “Fundamental and Literary Research in Traditional Medicine”.
- Establishment: NIIMH was founded in 1956.
- Location: It is situated in Gaddiannaram, Dilsuknagar, Hyderabad.
- Previous Name: It was previously known as the National Center of Indian Medical Heritage (NCIMH).

- Governing Body: NIIMH operates under the administrative control of the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Affiliation: It is part of the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India.
- Mission and Activities:
-
- Focus: Dedicated to documenting and showcasing medico-historical research.
- Disciplines: Covers Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa, Homoeopathy, Biomedicine, and related healthcare disciplines in India.
- Resources: Known for its extensive collection of research materials on the history of medicine, accessible globally.
-
- Research and Resources:
-
- Audience: Supplies resource materials for historians, scientists, and researchers interested in AYUSH and modern medicine.
- Unique Position: It is the only institution of its kind in Southeast Asia dedicated to medico-historical research of traditional and modern medicine.
-
- Collections and Facilities:
-
- Manuscripts: Houses more than 500 physical manuscripts.
- Museum and Library: Features the Medical Heritage Museum and Library, with rare books and manuscripts dating back to the 15th century AD.
- Publication: The institute also publishes the Journal of Indian Medical Heritage.
-
Doctrine of Res Judicata
- News: The Supreme Court has ruled in favor of the Delhi government in several land acquisition cases. However, it recently noted that the principle of res judicata may not always apply when public interest is involved.
- Concept Evolution: Res judicata has evolved from the English Common Law System.
- Literal Meaning: Res judicata literally means “the thing has been judged”.
- Alternate Term: It is also known as claim preclusion.

- Application:
-
- Litigation: The principle applies when a litigant attempts to file a subsequent lawsuit on the same matter after receiving a judgment in a previous case involving the same parties.
- Judicial Concept: It means the issue before the court has already been decided by another court between the same parties, and courts do not allow a petition to be filed in the same or another court.
- Outcome: The court will dismiss the case as being useless.
-
- Scope:
-
- Legal Systems: Res judicata is applicable in both civil and criminal legal systems.
-
- Purpose:
-
- Preventing Injustice: To prevent injustice to the parties of a case that has supposedly been finished.
- Resource Efficiency: To avoid unnecessary waste of resources and time of the judicial system.
-
- Indian Law:
-
- Codification: Res judicata under Indian law is embodied under Section 11 of the CPC (Code of Civil Procedure), 1908.
- Illustration: If a matter is finally decided by a competent court, then the parties involved are not permitted to reopen it in subsequent litigation.
-
- Conditions for Application:
-
- Same Parties: The parties involved in the former and subsequent suits must be the same.
- Same Title: The title or subject matter must be the same as in the former suit.
- Same Issue: The issue in the matter must be the same in both the former and subsequent suits.
- Competent Court: The former suit must have been decided by a competent court.
- Final Decision: A final decision must have been provided in the former suit.
-
- Judicial Interpretation:
-
- Supreme Court Ruling: In Employee Welfare Association v. Union of India, the Supreme Court ruled that the principle of res judicata is not a technical rule but a rule of public policy.
- Acknowledged Principle: Res judicata is an essential principle of law for delivering fair justice.
-
G7 Apulia Food Systems Initiative (AFSI)
- News: The G7 leaders have launched the Apulia Food Systems Initiative (AFSI) to intensify efforts to overcome structural barriers to food security.
- The G7:
- G7: The G7 is an informal group of leading industrialised nations.
- Objective: G7 meets annually to discuss issues of global economic governance, international security, and energy policy.
- Members: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. The European Union has participated fully in the G7 since 1981 as a “nonenumerated” member.
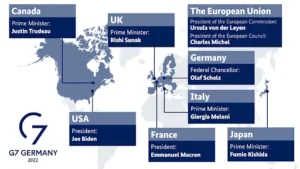
- History: The first summit was held in France in 1975.
- Presidency: The presidency of G-7 summits revolves among the seven members. Two representatives of the European Union also join.
- Secretariat: The G7 does not have a formal charter or a secretariat.
- GDP: The GDP of G7 member states makes up about 44% of the global economy in nominal terms, down from nearly 70% three decades ago.
- 50th Summit: Italy (Apulia region) is hosting the G7 summit 2024.
- Key Outcomes of G7 Summit:
- Apulia Food Systems Initiative (AFSI):
-
- Objective: Intensify efforts to overcome structural barriers to food security and nutrition.
- Focus:
- Addressing key issues within global food systems to ensure better access to food and improved nutritional outcomes.
- G7 Extraordinary Revenue Acceleration (ERA) Loans for Ukraine
- Consensus: G7 agreed to launch ERA Loans for Ukraine.
- Funding: Approximately US$50 billion in additional funding to be made available to Ukraine by the end of the year.
- Purpose: Support Ukraine amid ongoing challenges and aid in its economic stability and recovery.
-
- Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII):
-
- Funding Mobilization: Aim to mobilize up to USD 600 billion by 2027.
- Initiative: PGII is a joint initiative of the G7, launched during the 2022 G7 summit.
- Objective: Support infrastructure projects in developing countries through a combination of public and private investments.
-
- Artificial Intelligence:
-
- Announcement: Development of a brand to support the implementation of the International Code of Conduct for Organizations Developing Advanced AI Systems.
- Goal: Ensure responsible development and deployment of advanced AI technologies in accordance with international standards and ethical guidelines.
-
UPSC GS 3
Bioluminescence
- News: In the forests of Kasaragod, researchers have discovered a rare species of bioluminescent mushrooms that emit a brilliant green light in the darkness of night.
- Definition: Bioluminescence is the property of a living organism to emit light.
- Mechanism: The light emitted is produced by energy released from enzyme-catalyzed oxidation reactions in organisms.
- Chemicals Required: It requires two unique chemicals – luciferin and either luciferase or photoprotein.
- Light Emission: The spectral range of light emission in bioluminescent organisms spans from blue to red light.
- Species Exhibiting Bioluminescence: Sponges, Jellyfish, Hatchet fish, Worms, Sea walnuts, Fireflies, Fungi, Bacteria.
- Functions of Bioluminescence:
-
- Counter-illumination: Used for camouflage against predatory animals.
- Prey Attraction: Helps in luring prey.
- Intra-species Communication: Facilitates communication within the same species.
-
- Filoboletus Manipularis:
-
- Definition:
- It is a fascinating species of bioluminescent mushroom that glows a bright green at night due to a chemical reaction in their cells.
-

-
-
- Habitat:
- Thrive in tropical, humid environments.
- Typically found in dense forests with plenty of decaying organic matter, like fallen trees and leaves.
- This rich, moist environment provides the nutrients and conditions necessary for their growth and unique glowing property.
- Biochemical Process:
- The chemical reaction involves luciferin (a pigment) and luciferase (an enzyme) with oxygen.
- This reaction produces light, a trait shared with other bioluminescent organisms like fireflies and certain marine creatures.
- Advantage: The glowing mechanism is thought to attract insects, which help disperse the mushroom’s spores.
-
- Mushrooms: Mushrooms constitute secondary saprophytic fungi of the forest ecosystem.
-
- Role in Ecosystem: Secondary saprophytic fungi play a very important role in the decomposition of plant litter.
- Regional Specificity: The Western Ghats region in Kerala is rich in fungi, many of which are endemic to the region.
-
Global Environment Facility
- News: $736.4 million has been allocated for environmental protection at the Global Environment Facility (GEF) council meeting in Washington, DC, starting June 17, 2024.
- Origins: Established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit of UNFCC.
- Objective: Dedicated to addressing the world’s most pressing environmental challenges.

- Scope and Focus:
-
- Environmental Issues: Confronts biodiversity loss, climate change, pollution, and strains on land and ocean health.
- Financial Assistance: Provides funding for five major international environmental conventions:
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD)
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
-
- Member Countries: Includes 184 member countries, among them India.
- Governing Council: Main governing body comprising 32 members appointed by constituencies of GEF member countries (14 from developed, 16 from developing, and 2 from economies in transition).
- Secretariat: Based in Washington, D.C.
- GEF Trust Fund: Established to provide financial support to developing countries and economies in transition to achieve objectives of international environmental conventions and agreements.
Electromagnets
- News: Electromagnets have been in news.
- Definition: An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current.
- Control: The strength of the magnetic field is adjustable by regulating the electric current. When the current ceases, the magnetic field dissipates.
- History: Electromagnets were invented in 1824 by the British physicist William Sturgeon.
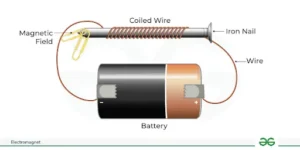
- Components:
-
- Coil and Core: Electromagnets consists of a coil of wire wound around a magnetic core made from ferromagnetic materials like iron.
- Enhancement: The magnetic core aligns magnetic domains, boosting the magnetic field’s strength.
-
- Properties and Advantages
-
- Switchability: Electromagnets can be activated or deactivated by controlling the electric current.
- Power: They are more potent than permanent magnets due to the ability to amplify the magnetic field using the magnetic core.
- Versatility: Widely utilized in motors, generators, MRI machines, and magnetic separation equipment.
-
- Applications:
-
- Industrial Use: Employed in industries for lifting heavy metal objects, material sorting, and generating mechanical motion.
- Examples: Also found in medical imaging (MRI) and consumer devices such as electric doorbells and card readers.
-
- Disadvantages:
-
- Energy Requirements: Requires a constant electric power supply to sustain the magnetic field.
- Efficiency: Less energy-efficient compared to permanent magnets.
- This structured approach covers all essential aspects of electromagnets, from their construction and advantages to their applications and drawbacks.
-
Reading between the Lines: 20 June 2024 What you should not miss from The Hindu!
Nagastra-1
- News: Nagastra-1, India’s first indigenous suicide drone has been shipped to armed forces.
- First-of-its-kind: Indian Army receives man-portable suicide drones ‘Nagastra-1’ for precision strikes.
- Objective: Designed to target enemy camps while safeguarding soldiers’ lives.
- Developed by: Nagpur-based Solar Industries, ordered through emergency procurement powers.

- Functionalities:
-
- Abort Capability: Unique feature allowing the drone to cancel attacks as needed.
- Payload: Equipped with day-and-night surveillance cameras and a 1 kg high-explosive warhead for soft-skin target neutralization.
- Capabilities: GPS-enabled precision strikes with kamikaze mode and 2-meter accuracy.
- Recovery Mechanism: Uses a parachute recovery system for abort, recover, and reuse operations.
-
- Technological Advantages:
-
- Indigenous Development: Over 75% indigenous content reduces dependency on foreign sources.
- Low Acoustic Signature: Electric propulsion system ensures minimal noise, making it hard to detect above 200 meters.
-
- Operational Specifications:
-
- Weight and Endurance: Weighs 9 kg, operates for 30 minutes with a man-in-loop range of 15 km and autonomous mode range of 30 km.
- Stealth Capabilities: Low acoustic signature enhances stealth during operations.
-
Chlorella Growth Factor (CGF)
- News: Chlorella Sorokiniana: A Protein-Rich Microalgae
- Characteristics and Reproduction:
-
- Single-Celled Algae: Chlorella sorokiniana exhibits rapid reproduction, multiplying from one cell to 24 cells within 24 hours under ample sunlight and nutrient availability.
-
- Chlorella Growth Factor (CGF):
-
- Nutritional Benefits: CGF derived from Chlorella sorokiniana is abundant in high-quality amino acids and proteins.
- Nutrient Composition: Contains essential amino acids, peptides, nucleotides, polysaccharides, vitamins, and minerals surpassing those found in commercial soy meal.
-
- Applications in Diets:
-
- Human and Animal Consumption: Promising as an alternative protein source for both human and animal diets.
- Animal Feed: Improves egg quality when added to chicken feed, indicating potential as a superior protein supplement for livestock.
-
- Advantages of Microalgae:
-
- Under-Exploited Crop: Microalgae like Chlorella sorokiniana are categorized as under-exploited crops.
- Resource Efficiency: They do not compete with traditional food crops for space and resources, offering a sustainable solution to meet growing demands for high-quality protein sources.
-

