GS Paper 1
Mount Ruang
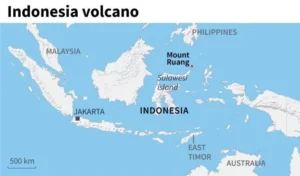
News: Indonesia’s Mount Ruang volcano has erupted for a second time in two weeks.
Location and Characteristics: It is a prominent stratovolcano situated in Indonesia’s Sulawesi Islands.
-
- It is known for its distinctive conical shape formed by successive layers of volcanic material.
Historical Activity: With a history dating back to the 16th century, Mount Ruang has experienced numerous eruptions, including the most recent one in April 2024.
Regional Context: The volcano is part of Indonesia’s vast volcanic landscape, comprising around 130 active volcanoes and positioned within the Ring of Fire.
Hazards and Risks: Eruptions of Mount Ruang have the potential to generate various hazards, including volcanic ash, pyroclastic flows, and lahars (mudflows).
Comparable Volcanoes: Mount Ruang is among several notable volcanoes in Indonesia, including Krakatau, Merapi, and Semeru, each contributing to the dynamic volcanic activity of the region.
Stratovolcano: Stratovolcano, volcanic landform characterized by a conical shape formed by layers of volcanic material deposited during successive volcanic eruptions.
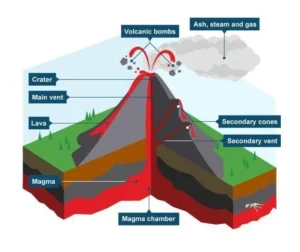
- Stratovolcanoes tend to slope gently at the base but rise quickly near the summit to form tall mountain peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
Ring of Fire (Circum-Pacific Belt): It is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
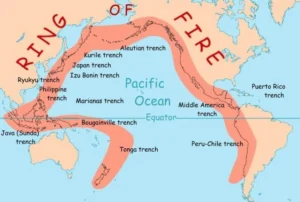
- Its length is approximately 40,000 kilometers (24,900 miles).
- It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates including the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American, and Philippine Plates.
- 75% of Earth’s volcanoes are located along the Ring of Fire.
- 90 % of Earth’s earthquakes occur along its path, including the planet’s most violent and dramatic seismic events.
GS Paper 2
Shaksgam Valley
News: The Indian Army plans to assess the military impacts of China building a road in the Shaksgam Valley.
Geographical Borders: Shaksgam Valley is also known as Trans-Karakoram Tract.
-
- The Shaksgam Valley is part of Hunza-Gilgit region of Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (POK), and is a disputed territory claimed by India but controlled by Pakistan.
- It borders Xinjiang Province of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) to the north, the Northern Areas of POK to the south and west, and the Siachen Glacier region to the east.
- It is bounded by the Kun Lun Mountains and the Karakoram peaks, it holds strategic significance.

Boundary Agreement and Dispute:
-
- Through the China-Pakistan Boundary Agreement of 1963, Pakistan unlawfully ceded control of this region to China.
- Presently, it is administered by China as part of the Xinjiang Autonomous Region.
- India does not recognize this agreement and continues to assert its claim over the valley as part of its Jammu & Kashmir territory.
National Anti- Doping Agency (NADA)
News: NADA has suspended Bajrang Punia for not giving a sample for dope test.
Autonomous Body: Set up in 2005, National Anti Doping Agency, is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
-
- It was established under the Societies Registration Act of 1860 and was provided statutory backing by the National Anti-Doping Act, 2022.
Objective: NADA India implements the anti-doping programme in India, in line with the World Anti-doping Code 2021.
Core Responsibilities:
-
- Focus on key areas such as Sample Collection (SC), Results Management (RM), Anti-Doping Education & Awareness, and Research and Intelligence & Investigations (I&I).
- With a mission to promote clean sport practices, NADA India is dedicated to fostering integrity and ethical values within the sporting community.
Types of Unemployment Cyclic Structural Frictional Seasonal Disguised | UPSC
GS Paper 3
High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS)
News: Newly published footage from the Russian government alleges to demonstrate the targeting of two Ukrainian High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS).
Overview:
- High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS) represent a formidable presence in the realm of light, multiple rocket launchers.
- Manufactured by the esteemed Lockheed Martin Corporation, HIMARS combines agility with firepower to deliver swift and precise strikes on targets.
Firepower:
- HIMARS is versatile, capable of launching either a single pod containing six rockets or deploying one MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missile.
- The ATACMS missiles boast an impressive range of up to 300 km (186 mi), offering substantial reach for strategic engagements.
Firing Speed:
- The HIMARS requires less than 20 seconds to be prepared for firing, and a full launcher load of six rockets can be fired within 45 seconds.
Survivability:
- The “Shoot-and-Scoot” capability epitomizes HIMARS’ survivability, allowing for quick firing and relocation to evade detection by enemy forces.
- Enhanced protection is provided by the Increased Crew Protection cabin, shielding the three-man crew from various hazards including launch debris, small arms fire, and plume gases.
Cocoa
News: The cost of cocoa beans, a fundamental ingredient in chocolate production, has surged dramatically.
Origin and History:
- A native of the humid tropical regions, cocoa is indigenous to the Equatorial (Amazon region) of South America.
- Cultivated over 3,000 years ago by civilizations such as the Maya, Toltec, and Aztec peoples, who crafted a beverage from the bean.

Cultivation Characteristics:
- Primarily a commercial plantation crop, cocoa is typically grown as part of a mixed crop system.
- Various varieties exist, including Criollo, Forastero, and Trinitario.
Growing Conditions:
- Cocoa pods mature continuously throughout the year, necessitating frequent harvesting cycles of every 3-4 weeks.
- Thrives predominantly in red laterite soils with an annual rainfall ranging from 1000 mm to 2000 mm.
- Optimal temperature conditions for growth fall between 15°C and 35°C.
- Cultivation can occur at altitudes of up to 1200 meters above Mean Sea Level.
- To replicate its natural habitat, commercial cocoa cultivation is best suited to plantations where approximately 50 per cent of light is available.
Cultivation in India:
- In India, cocoa cultivation is prevalent in states such as Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
KAVACH
News: Recently, the Supreme Court of India appreciated the initiatives by Indian Railways for the implementation of ‘Kavach’.
Development and Collaboration: Kavach is an indigenous Automatic Train Protection System developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) under the Ministry of Railways.
Aim: It aims to bolster safety in train operations through cutting-edge electronic technology.
Safety Features:
- Preventing Signal Violations: The primary objective of Kavach is to prevent trains from passing signals at Danger (Red), mitigating the risk of collisions.
- Technology Employed: Kavach utilizes a combination of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags installed on tracks and on-board equipment within locomotives to operate effectively.
- Automatic Braking Mechanism: In cases where the driver fails to comply with speed restrictions, Kavach automatically engages the train braking system, averting potential hazards.
- Collision Prevention: Beyond signal adherence, Kavach also serves to prevent collisions between locomotives equipped with operational Kavach systems, enhancing safety measures further.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Reliability: Recognized as one of the most cost-effective Safety Integrity Level 4 certified technologies, Kavach boasts an impressively low probability of error, estimated at 1 in 10,000 years.
Electrolysers
News: Investing in a homegrown electrolyser manufacturing infrastructure is anticipated to drive down the price of green hydrogen and enhance India’s competitive edge.
Electrolysers: Electrolysers are devices that utilize electricity to split water into clean hydrogen fuel and oxygen by passing an electric current through it, thereby separating hydrogen and oxygen molecules.
Utilization of Oxygen: Oxygen generated alongside hydrogen can either be released into the atmosphere or stored for future use, often in medical or industrial applications.
Storage and Usage of Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced by electrolysers is typically stored either as a compressed gas or liquefied, finding application in various industries or as a fuel for hydrogen fuel cells.
Types of Electrolysers:
Alkaline Electrolysers: These electrolysers employ thick membranes and nickel-based electrodes, constituting a significant portion of global electrolyser capacity.
-
- They are predominantly utilized by the fertilizer and chlorine industries.
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysers: These operate at high pressure, employing thin perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membranes.
-
- Due to the acidic environment, they require gold, titanium plated electrodes, and catalysts like platinum, iridium, and ruthenium.
- While they produce high-purity hydrogen, they are comparatively expensive.
Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell (SOEC) Electrolysers: SOEC electrolysers utilize heat to produce hydrogen from steam and are best suited for locations with available heat sources, such as nuclear or industrial facilities.
-
- Operating at high temperatures (500 – 850 degrees), they offer unique advantages in specific settings.
Standard Essential Patents (SEPs)
News: There is a possible crisis brewing in India over the manner in which certain technology companies are wielding ‘standard essential patents’ (SEP) against the telecom manufacturing sector in India.
Definition: These are patents that cover technologies which are adopted by the industry as “standards”.
Understanding SEPs: SEPs encompass patents covering technologies adopted as industry “standards,” crucial for ensuring compatibility and interoperability across different brands and devices.
Examples in Telecom Sector:
- Technologies like CDMA, GSM, and LTE serve as industry standards within the telecom sector, facilitating widespread connectivity and device compatibility.
Interoperability and Connectivity: Standards play a vital role in ensuring that various cellular phone brands, such as Apple and Samsung, can seamlessly connect to the same cellular networks, enhancing user experience and market reach.
Impact on Market Dynamics: Adoption of standards, like 4G LTE, mandates manufacturers to ensure compatibility, influencing consumer demand and market competitiveness.
Monetization and Licensing: Owners of SEPs, such as Qualcomm with 4G LTE, can gain significantly through licensing agreements, ensuring widespread adoption of their patented technologies.
Challenges:
- Patent Holdup: Lack of alternatives may empower SEP owners to demand excessive royalties or unfair licensing terms, leading to the “patent holdup” problem, as evidenced by disputes like Apple vs. Qualcomm.
- Role of Standard Setting Organizations (SSOs): SSOs, largely operated by private technology firms, play a pivotal role in setting, coordinating, and maintaining standards, aiming to address issues like patent holdup.
- Fair and Non-Discriminatory Licensing: SSOs typically mandate members contributing essential inventions to license them on fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms, ensuring equitable access to essential technologies.
Patent:
- A patent is a statutory right granted to an inventor by the Government that permits the inventor exclusive rights.
- These rights exclude others from making, selling, or using the invention without permission for a period of time.
Facts for Prelims
World Press Freedom Index 2023
News: World Press Freedom Index 2023 has been released.
World Press Freedom Index (WPFI): It is an annual assessment of countries’ press freedom levels, compiled and published by Reporters Without Borders (RSF).
Scope of Assessment: RSF evaluates 180 countries and territories, comparing the level of freedom enjoyed by journalists and media across the globe.
Evaluation Criteria
- Media Independence: It evaluates the degree to which media outlets are free from external influence or control.
- Legal Framework: The legal framework surrounding press freedom is considered, analyzing the laws and regulations governing media operations within each country.
- Safety of Journalists: RSF examines the safety of journalists as a vital indicator, assessing the level of protection and security provided to media professionals.
- Indicators for Ranking: The ranking in WPFI is based on 5 key indicators:
-
- Political Environment,
- Legislative Framework,
- Economic Conditions,
- Sociocultural Context,
- Safety of Journalists.
-

Overview of World Press Freedom Index 2023:
- Global Assessment: According to the 2023 WPFI, the situation is categorized as “very serious” in 31 countries, “difficult” in 42, “problematic” in 55, and “good” or “satisfactory” in 52 countries.
- Top Ranking Country: Norway has retained its top position in the World Press Freedom Index for the 7th consecutive year, reaffirming its commitment to press freedom.
- India’s Press Freedom Ranking: India’s press freedom ranking has declined to 161 out of 180 countries, marking a shift from “problematic” to “very bad.”
-
- This represents an 11-rank drop since the 2022 report, highlighting growing concerns regarding press freedom in the country.
- All neighboring countries of India, except Bangladesh (163), Myanmar (173), and China (179), hold higher rankings in the World Press Freedom Index.
- Bhutan ranks at 90, Nepal at 95, Sri Lanka at 135, Pakistan at 150, and Afghanistan at 152, indicating varying levels of press freedom across the region.
-
Seventh India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee (JDCC) Meeting
News: The Seventh India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee(JDCC) meeting took place in New Delhi.
Defence Cooperation: Both nations expressed satisfaction with the expanding scope of their defence cooperation, signifying a positive trajectory in bilateral relations.
Defence Industry Collaboration: The meeting emphasized intensifying defence collaboration between Indian and Indonesian defence firms, with active participation from key Indian industry players such as Bharat Forge, Mahindra Defence, and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited.
Maritime Security Collaboration: India and Indonesia underscored the importance of cooperation in maritime security, aligning with their shared vision for the Indo-Pacific region’s stability and security.
Multilateral Cooperation: Both nations actively engage in multilateral cooperation, featuring frequent high-level interactions.
- Indonesia’s pivotal role in India’s Act East Policy and broader Indo-Pacific regional dynamics was highlighted during discussions.
Collaborative Goals: The collaboration aims to bolster domestic production capabilities, enhance military capabilities, and foster stronger ties between India and Indonesia.
Addressing Common Challenges: This joint effort addresses common security challenges and contributes to the development of strategic partnerships between the two nations, promoting stability and peace in the region.

