UPSC GS 1
Brahmi Script
- News: The Brahmi script is the originator of all Indian scripts.
- Earliest Writing System:
-
- The Brahmi Script is the earliest writing system developed in India after the Indus script.
- All modern Indian scripts and several hundred scripts in Southeast and East Asia are derived from Brahmi except Kharosthi.
-
- Historical Context:
-
- The earliest known Brahmi inscriptions are from the edicts of Ashoka, the third Mauryan emperor of Magadha (ruled 268-232 BCE).
- The best-known Brahmi inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in northcentral India, dated to 250–232 BCE.
-

- Writing System Characteristics:
-
- Abugida Writing System: consonants and vowels are written together as a unit (matras or vowel diacritics used in languages like Hindi).
- Contrasted With Phoenician And Aramaic Systems (Abjads): only consonants are represented, with vowels needing to be inferred by the reader.
-
- Decipherment:
-
- Deciphered in the 19th century by James Prinsep.
- Prinsep was the secretary of the Asiatic Society of Bengal and the editor of its journal.
-
Mackenzie River
- News: The Mackenzie River is experiencing historically low water levels, stranding communities that rely on it for essential goods.
- Location:
-
- Flows through Canada’s Northwest Territories.
-
- Length:
-
- Longest river system in Canada, approximately 1,650 km (1,025 miles).
-
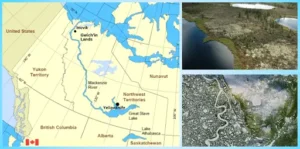
- Source and Destination:
-
- Originates from Great Slave Lake.
- Empties into the Beaufort Sea in the Arctic Ocean.
-
- Historical Significance:
-
- Crucial for transportation and natural resource extraction.
-
- Wildlife:
-
- Home to diverse wildlife, including numerous fish species, migratory birds, and mammals such as beavers and moose.
-
- Cultural and Economic Importance:
-
- Important to several Indigenous communities who have lived along its banks for thousands of years.
- Supports transportation, fishing, tourism, and hydroelectric power generation.
-
Read also: Explain Importance of Fiscal Federalism in India | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Rules Governing Civil Servants
- News: The Centre has constituted a single-member committee under the Department of Personnel and Training to examine all documents submitted by probationary IAS officer Puja Khedkar to secure her candidature in the civil services.
- All India Services:
-
- There are three All India Services: the Indian Administrative Service, the Indian Police Service and the Indian Forest Services.
- The candidates are selected by the central government with officers allotted to various state cadres.
- All India Services are governed by Article 312 of the Constitution of India.
- All India Services is a Union list subject vide Entry 70. A
- The All India Services Act, 1951 provides that the rules for the regulation,recruitment and the conditions of services for the All India Services shall be made by the Union Government after consultation with the State Governments.
-
- Governing Rules:
-
- All India Services (AIS) Conduct Rules, 1968.
- These rules were framed based on recommendations from a committee constituted by then Minister of Home Affairs Lal Bahadur Shashtri in 1962.
- This Committee on Prevention of Corruption was headed by K Santhanam, Member of Rajya Sabha.
-
- AIS (Conduct) Rule 3(1):
-
- Every member of the Service shall at all times maintain absolute integrity and devotion to duty.
-
- AIS (Conduct) Rule 4(1):
-
- Officers must not use their position or influence to secure employment for any family member with any private undertaking or NGO.
- Political neutrality needs to be maintained.
- Avoid financial obligations to individuals or organizations that may influence them.
-
- Rule 11(1):
-
- Officers may accept gifts from near relatives or personal friends with whom they have no official dealings, on occasions like weddings, anniversaries.
- Must report any gift whose value exceeds Rs 25,000 to the government (threshold updated in 2015).
- Both giving and receiving dowry is strictly prohibited.
-
- Rules for Probationers:
-
- Probation Period: Lasts for at least two years after selection, including training at LBSNAA, Mussoorie.
- Draw a fixed salary and travel allowance during probation.
- Not entitled to benefits like an official car, official accommodation, official chamber with staff, and a constable.
-
- Rule 12: Circumstances for discharge of probationers:
-
- Central government finds the probationer ineligible for recruitment or unsuitable to be a member of the service.
- Centre holds a summary enquiry before passing an order.
- Probationers are “discharged” while confirmed officers are “dismissed“.
-
- Consequences of Falsifying Certificates:
-
- Dismissal likely to be challenged in court, before Central Administrative Tribunal.
-
Foreigners’ Tribunals (FTs)
- News: The Supreme Court recently declared Assam resident Md Rahim Ali a citizen of India, throwing out the decision of a Foreigners’ Tribunal in the state.
- Definition:
-
- Foreigners’ tribunals are quasi-judicial bodies exclusive to Assam.
- Foreigners’ Tribunals were established under The Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964.
- The Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964 was issued by the Central Government under Section 3 of The Foreigners Act, 1946.
-
- Aim: To determine if a person staying illegally is a “foreigner” or not.
- Applicability:
-
- The Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964 applies to the whole of India, yet, FTs exist only in Assam as of now.
- In other states if any illegal immigrant is found, he is produced before a local court and dealt with as per the Foreigners Act, 1946.
-
- Important Amendments:
-
- State Administration can now set up tribunals to decide if a person staying illegally in India is a foreigner. Earlier, the powers to constitute tribunals were vested only with the Centre.
- Individuals can now approach the Tribunals. Previously, only the State administration could move the Tribunal against a suspect.
-
- Legality:
-
- The Supreme Court has held that the decisions of the FTs on a person’s nationality are binding.
-
- Role and Functions of Foreigners’ Tribunals (FTs):
- Detection of Suspected Foreigners: Superintendents of police (SPs) and district commissioners identify suspected foreigners. The Election Commission of India can refer cases of ‘Doubtful’ voters to the local SP, who then refers them to the FTs.
- National Register of Citizens (NRC): Individuals excluded from the final draft of the NRC (released in August 2019) can appeal to the FTs to establish their citizenship.
Rules Governing J&K
- News: MHA has amended Rules to widen the administrative role of J&K L-G.
- More on News:
-
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has widened the ambit of the administrative role of L-G of Jammu and Kashmir by amending the Transaction of Business Rules.
-
- Article 370 Revocation:
-
- On August 5, 2019, the special status granted to J&K under Article 370 was revoked.
- The former State was divided into two Union Territories: J&K and Ladakh (the latter without an assembly).
-
- Key Amendments:
- Expanded Role of Lieutenant Governor (L-G): The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) amended the Transaction of Business Rules.
- Finance Department Concurrence: Proposals regarding ‘Police’, ‘Public Order’, ‘All India Service’, and ‘Anti Corruption Bureau’ require L-G’s approval through the Chief Secretary.
- Law, Justice, and Parliamentary Affairs: Department of Law, Justice, and Parliamentary Affairs to submit proposals for appointment of Advocate-General for L-G approval through the Chief Secretary and the Chief Minister.
- Prisons, Prosecution, and Forensic Science: All matters connected with Prisons, Directorate of Prosecution, and Forensic Science Laboratory are to be submitted to the L-G.
E-FAST India Initiative
- News: NITI Aayog has announced the launch of the ‘NITI GearShift Challenge’ as part of the e-FAST India initiative.
- Overview of e-FAST India Initiative:
-
- Launched in September 2022 to support India’s commitment to achieve net zero emissions by 2070.
- Focuses on decarbonizing road-based freight transportation.
-

- Objectives:
-
- Galvanize the transition to cleaner and greener freight transportation.
- Facilitate national and international collaborations.
- Support ideation, pilot programs, and scalable technology integration.
-
- Key Stakeholders:
-
- Government, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), Logistics Service Providers (LSPs), Shippers, industry experts.
- Supported by 12 knowledge partners.
-
- NITI GearShift Challenge:
-
- Launched by NITI Aayog in collaboration with IIM Bangalore, Smart Freight Centre India, CALSTART/Drive to Zero, and WRI India.
- A pioneering hackathon focused on developing innovative business models for the adoption of zero-emission trucks (ZETs) in India.
-
- Objectives:
-
- Foster innovation in addressing financial, technical, and operational challenges related to electric truck adoption.
- Engage students, transport service practitioners, academics, and researchers.
-
- Participants:
-
- Involves e-FAST India knowledge partners, financial institutions, and industry forums.
-
- Impact:
-
- Aims to accelerate the development and adoption of electric technology in India’s freight sector at scale.
- Promotes sustainable economic and environmental practices in freight transportation.
-
UPSC GS 3
Indian Flapshell Turtle (Lissemys Punctate)
- News: The scientists at the Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) are on a mission to save an Indian flapshell turtle, whose shell cracked after an accident.
- Definition:
-
- The Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) is a freshwater species of turtle found in South Asia.
-

- Nomenclature:
-
-
- The “flap-shelled” name stems from the presence of femoral flaps located on the plastron. These flaps of skin cover the limbs when they retract into the shell.
-
- Distribution:
-
- The Indian flapshell turtle is found in Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- It has been introduced to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
-
- Habitat:
-
- It prefers shallow, quiet, often stagnant waters of rivers, streams, marshes, ponds, lakes and irrigation canals, and tanks.
-
- Diet:
-
- They are omnivores.
- It plays an important role to reduce pollution in aquatic ecosystems by feeding on snails, insects, and fragments of dead animals.
-
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Red list: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
-
Wolbachia
- News: A significant study by Shenyang Agricultural University (SAU) has revealed that Wolbachia bacteria have altered the reproductive system of the wasp Encarsia formosa, resulting in exclusively female groups.
- Commonality: Found in approximately 60% of all insects, including butterflies, bees, and beetles.
- Impact on Humans and Animals: Cannot make people or animals (e.g., fish, birds, pets) sick.
- Encarsia Formosa:
- Agricultural Importance:
-
- Efficient in controlling whiteflies, a major agricultural pest that feeds on the sap of plant leaves, causing productivity losses.
- Whiteflies belong to the insect order Hemiptera, while wasps belong to the insect order Hymenoptera.
-
- Reproductive and Behavioral Facts:
-
- The wasp lays its eggs on whitefly nymphs. The larvae hatch, penetrate the nymph, feed on its tissues, and grow to adulthood, killing the nymph in the process.
- Progeny wasps emerge from the nymph’s carcass.
- Female wasps act as a search and destroy weapon against whiteflies, while male wasps are not essential to this role.
-
Manjeera Wildlife Sanctuary
- News: The Manjeera wildlife sanctuary in Telangana is undergoing a study to potentially become the state’s first Ramsar site.
- Location:
-
- Situated in the Medak district of Telangana.
- The sanctuary follows the course of river Manjeera, a tributary of Godavari and abuts the Manjeera reservoir.
-

- General Information:
-
- Manjeera Wildlife Sanctuary was originally established as a crocodile sanctuary.
- It is home to over 70 species of birds and the vulnerable mugger crocodile.
-
- Vegetation:
-
- Dry Savannah type vegetation.
- Supports both submergent and emergent types of vegetation.
-
- Flora:
-
- Home to plant species such as Typha, Babool, Prosopis, Ipomoea, Acacia Ipomea, Vallisneria, Eichhornia, and Reeds.
-
- Fauna:
-
- Riverine habitat supporting mugger crocodiles and freshwater turtles.
- Inhabited by prawns, molluscs, and fish species including catla, rohu, murrel, eel, karugu, and chidwa.
- Also home to Indian hare, wild boar, mongoose, and jackal.
-

