UPSC GS 1
Belgaum Congress Session
- News: Karnataka Chief Minister Siddaramaiah recently unveiled a statue of Mahatma Gandhi at the Veera Soudha memorial, the venue of the 1924 Belgaum Congress session, in Belagavi.
- Definition:
- The centenary of the historic 1924 Belagavi Session of the Indian National Congress (INC) is being commemorated in Belagavi, Karnataka.
- This session, the 39th of the INC, was held on December 26-27, 1924, in Belagavi and holds a unique place in India’s history.

- Key Highlights of the 1924 Session:
- Presidency of Mahatma Gandhi: Mahatma Gandhi presided over the session, marking the only time he held the position of Congress President.
- Notable Participants: The session was attended by prominent leaders such as Jawaharlal Nehru, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Sarojini Naidu, and Khilafat leaders Muhammad Ali Jauhar and Shaukat Ali, among others.
- Significance of the Session:
- Promotion of Self-Reliance:
- The emphasis on Khadi symbolized Gandhi’s vision for a self-sufficient India.
- Gandhi urged citizens to embrace spinning and weaving as a means to reduce dependence on British textiles and promote economic independence.
- Advocacy for Communal Harmony:
- Gandhi emphasized the importance of communal harmony as a foundation for India’s freedom and unity.
- He promoted mutual respect among all communities, regardless of religion.
- Organizational Reforms:
- To make the Congress movement more inclusive, Gandhi reduced membership fees by 90%.
- This initiative encouraged greater participation from people across different economic backgrounds.
Read also: Preventing Stampedes in India: Key Insights for UPSC
Brahmaputra River
- News: China has approved the construction of the world’s largest dam, stated to be the planet’s biggest infra project costing USD 137 billion, on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in riparian states – India and Bangladesh.
- Definition: The Brahmaputra is a transboundary river flowing through India, originating from the Chemayungdung glacier in the Kailash range near Lake Mansarovar.
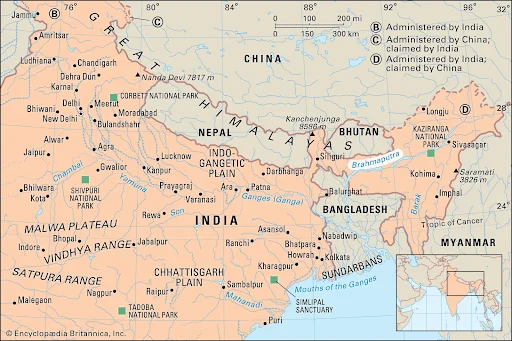
- Course of the River:
- Source and Initial Course: Originates from the Chemayungdung glacier in Tibet and flows eastward for approximately 1,200 kilometers, where it is known as the Tsangpo.
- Entry into India:
- The river enters India near Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- After receiving its major left-bank tributaries, Lohit and Dibang, it is referred to as the Brahmaputra.
- Final Destination:
- In Bangladesh, the Brahmaputra merges with the Ganga River, forming the Sundarbans Delta.
- Major Tributaries of the Brahmaputra:
- Left Bank Tributaries:
- Burhi Dihing
- Dhansari
- Lohit
- Dibang
- Kopili
- Right Bank Tributaries:
- Subansiri
- Kameng
- Manas
- Sankosh
Veer Baal Diwas
- News: The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi recently participated in Veer Baal Diwas at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- Date of Observation: Veer Baal Diwas is observed annually on December 26, starting from the year 2022.
- Purpose: The day is dedicated to honoring the martyrdom of Baba Fateh Singh and Zorawar Singh, the Sahibzade (sons) of Guru Gobind Singh Ji, who sacrificed their lives for their faith.
- Background:
- Escape from Anandpur Fort: Guru Gobind Singh, along with his family and followers, was forced to flee from Anandpur Fort as the Mughal forces surrounded it.
- Capture of Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh: During the turmoil, Guru Gobind Singh’s youngest sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh, were captured by the Mughal army.
- Martyrdom: Despite their young age, the brothers stood firm in their faith and refused to renounce it. As a result, Wazir Khan ordered them to be bricked alive around December 26, 1705.
- Government Recognition: In 2022, the Government of India declared December 26 as Veer Baal Diwas to honor and remember the bravery and sacrifice of the Sahibzade.

- Who is Guru Gobind Singh?
- Position: Guru Gobind Singh was the 10th Sikh Guru, succeeding his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, who was the 9th Sikh Guru.
- Contributions to Sikhism
- Foundation of Khalsa: Guru Gobind Singh is widely recognized for establishing the Khalsa, a community of initiated Sikhs, and for outlining the five key symbols of Khalsa, known as the Five ‘K’s:
- Kesh (uncut hair)
- Kanga (wooden comb)
- Kara (iron or steel bracelet)
- Kirpan (dagger)
- Kachera (short breeches)
- Battle Against the Mughals: Guru Gobind Singh fought against the Mughal Empire, notably participating in the Battle of Muktsar in 1705.
- Guru Granth Sahib: In 1708, before his passing, Guru Gobind Singh declared the Guru Granth Sahib as the eternal Guru of Sikhs, solidifying its role as Sikhism’s holy scripture.
UPSC GS 2
United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF)
- News: UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has paid tributes to Brigadier General Amitabh Jha of India, who was serving with the UNDOF at Golan Heights.
- Establishment: UNDOF was created following the approval of UN Security Council resolution 350 (1974) on May 31, 1974. The force was set up after the signing of the disengagement agreement between Israel and Syria.

- Mandate:
- Primary Role: The primary mission of UNDOF is to maintain the ceasefire between Israel and Syria and to supervise two key areas:
- Area of Separation: A demilitarized buffer zone between the two countries.
- Area of Limitation: A zone where restrictions are imposed on Israeli and Syrian military personnel and equipment.
- Renewal of Mandate: The mandate of UNDOF is reviewed and renewed every six months, with the current extension valid until June 2025.
- Financing: UNDOF is financed through a separate account that is approved annually by the UN General Assembly.
- India’s Contribution: India is one of the top contributors of troops and police to the mission, ranking as the third-largest contributor overall.
- Headquarters: The headquarters of UNDOF is situated at Camp Faouar, located in the Golan Heights.
SVAMITVA Scheme
- News: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will distribute over 50 lakh property cards under SVAMITVA Scheme to property owners in over 46,000 villages.
- Introduction:
- The Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas (SVAMITVA) is a central government initiative introduced in 2020.
- Its primary goal is to promote economic development in rural areas by providing property ownership documentation to households residing in village settlement areas.
- The scheme employs advanced drone-based survey technology to achieve its objectives.

- Objectives of the SVAMITVA Scheme:
- Enhancing financial stability: By enabling rural citizens to use their properties as collateral for loans and other financial services.
- Accurate land records: Establishing precise land records to aid in rural planning and development.
- Property tax determination: Facilitating the calculation of property tax, directly benefiting Gram Panchayats (GPs) in states where tax collection is devolved or contributing to the state exchequer.
- Survey infrastructure creation: Developing robust survey infrastructure and GIS-based maps that various government departments can utilize.
- Improved Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs): Supporting the creation of high-quality GPDPs using detailed GIS maps.
- Conflict resolution: Reducing property-related disputes and minimizing legal cases through clear ownership documentation.
- Key Features:
- Use of advanced technology: The scheme leverages drone technology for precise mapping and surveying of village properties.
- Documentation of property rights: Provides ‘Record of Rights’ to rural households, offering legal recognition of property ownership.
- Focus on rural development: Aims to streamline property management and rural governance through accurate mapping and data.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) oversees the implementation of the SVAMITVA Scheme, ensuring alignment with its goals and objectives.
UPSC GS 3
Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) 2023-24
- News: The Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) for 2023-24 (October-September) reveals significant growth in India’s unincorporated non-agricultural sector, comprising non-corporate entities.
- Definition: The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has published the Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) 2023-24, covering the reference period from October 2023 to September 2024.
- Objective: The Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) 2023-24 was conducted to assess various economic and operational characteristics of unincorporated non-agricultural establishments in India.
- Coverage and Scope:
- Geographical Coverage: Includes rural and urban areas across India, excluding villages in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
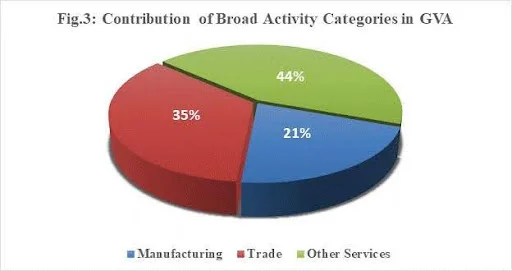
- Sectors Covered: Encompasses unincorporated establishments operating in:
- Manufacturing
- Trade
- Other services (excluding construction)
- Data Collection: The survey gathered critical information, including:
-
- Number of workers employed
- Gross Value Added (GVA)
- Emoluments paid to workers
- Fixed assets owned
- Type of ownership
- Registration status
- Purpose:
-
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking.
- Supports the compilation of National Accounts Statistics.
- Addresses the informational needs of industries.
- Enables informed, data-driven decision-making for economic development.
- Key Highlights of ASUSE 2023-24:
-
- Increase in Establishments: The number of establishments grew from 6.50 crore in 2022-23 to 7.34 crore in 2023-24, marking a significant 12.84% increase.
- Growth in Gross Value Added (GVA): GVA rose by 16.52%, primarily due to a 26.17% growth in the other services sector. GVA per worker increased by 5.62%, reaching ₹1,49,742 in 2023-24 (at current prices).
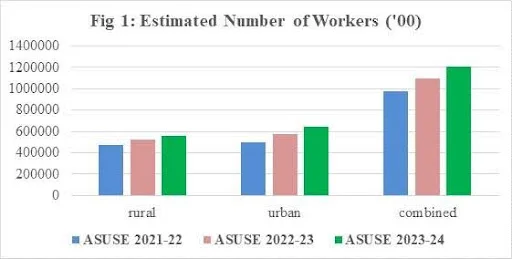
- Employment Expansion: More than 12 crore workers were employed between October 2023 and September 2024, indicating a robust labour market performance.
- Female Entrepreneurship: The percentage of female-owned proprietary establishments increased from 22.9% in 2022-23 to 26.2% in 2023-24, highlighting rising female participation in business ownership.
- Improved Digital Adoption: The percentage of establishments using the internet increased from 21.1% in 2022-23 to 26.7% in 2023-24, reflecting a growing trend toward digital transformation.
Kaveri Engine
- News: The Kaveri engine developed by the Gas Turbine Research Establishment under the Defence Research and Development Organisation has been cleared for inflight testing.
- Definition:
- The Kaveri engine project was initiated in the late 1980s to provide indigenous propulsion for the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas.
- It represents a significant milestone in India’s efforts to achieve self-reliance in advanced aerospace technology.

- Development and Key Stakeholders: The engine is being developed by the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), a unit of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Features of the Kaveri Engine:
- Thrust Generation:
- The dry version of the engine produces a thrust of approximately 49-51 kN.
- This level of thrust makes it well-suited for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) applications, such as the Ghatak stealth UCAV program.
- Plans are underway to integrate an afterburner to enhance the thrust to 73-75 kN for more demanding operational requirements.
- Testing and Modifications:
- The engine has undergone extensive ground testing and high-altitude simulations, both in India and abroad (e.g., in Russia).
- These evaluations showcased improvements in reliability, thrust performance, and operational stability.
- It has successfully met the benchmarks for inflight testing.
- Significance of the Kaveri Engine:
- Self-Reliance in Aero-Engine Technology:
- The Kaveri engine is a pivotal step in reducing India’s dependence on foreign technologies for military aviation.
- Its development strengthens India’s capabilities in designing and producing advanced engines for UAVs and other aircraft.
- Support for Indigenous Programs:
- The engine is integral to India’s stealth UCAV initiative, particularly the Ghatak program, further advancing the nation’s defense ecosystem.
Kanha Tiger Reserve
- News: Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh, Mohan Yadav has announced the translocation of 15 tigers to the states of Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha. The selected tigers will be moved from the renowned Bandhavgarh, Pench, and Kanha tiger reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Kanha Tiger Reserve (KTR):
- Location: Kanha Tiger Reserve is situated across the Mandla and Balaghat districts, within the Maikal range of the Satpura mountains, which is part of the Central Indian Highlands.
- Establishment: The reserve was designated as a national park on June 1, 1955, and later became a Tiger Reserve in 1973.
- Cultural Significance: The landscape of Kanha Tiger Reserve served as the inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s famous work, The Jungle Book.
- Mascot: Kanha is notable for being the first in India to introduce an official mascot, Bhoorsingh the Barasingha, a symbol of the reserve’s conservation efforts.
- Flora: The park’s lowland forests are primarily composed of sal trees (Shorea robusta) and a variety of mixed forest species, with meadows scattered throughout. The highland forests feature tropical moist deciduous trees and bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus) on the slopes.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a significant population of Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and Indian wild dogs. It is globally recognized for saving the Barasingha, the state animal of Madhya Pradesh, from near extinction.
See more: Fifth Schedule Vs Sixth Schedule | UPSC
Wealth Tax
- News: At a recent panel discussion in New Delhi, French economist Thomas Piketty suggested that a wealth and inheritance tax be imposed on the super-rich in India, which, in turn, could fund health and education.
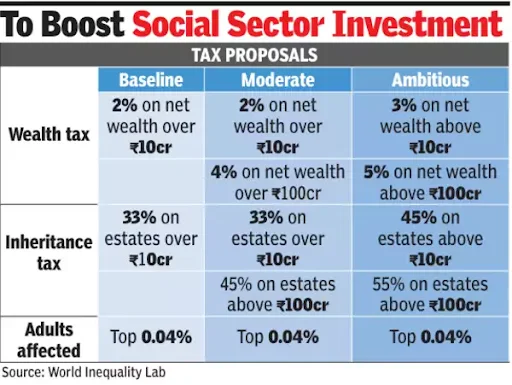
- Wealth Tax:
-
- Definition: Wealth tax is a tax levied on the net market value of an individual’s assets, which can include cash, bank deposits, shares, fixed assets, personal cars, and real property.
- Global Context: Several countries, such as France, Portugal, and Spain, have implemented wealth taxes as a part of their tax structures.
- Objective: The main aim of wealth tax is to target assets that are deemed unproductive or non-essential, encouraging individuals to invest in more productive avenues.
Other Relevant Tax Concepts
|
- Wealth Tax in India:
- Introduction: The Wealth Tax Act was introduced in India in 1957, following the recommendations of the Kaldor Committee (1955), as a measure for tax rationalization.
- Tax Rate: Initially, the tax rate was set at 1% for individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), and companies with earnings exceeding ₹30 lakh per year.
- Abolition: In 2015, the wealth tax was abolished due to challenges such as extensive litigation, an increased compliance burden, and high administrative costs.
- Replacement Measures: Following the abolition, the government increased the surcharge on the super-rich, with individuals earning more than ₹1 crore and companies earning over ₹10 crore now facing a surcharge increase from 2% to 12%.

