UPSC GS 1
Aleppo
- News: Syrian government forces lost control of Aleppo for the first time in the ongoing civil war after an Islamist-led rebel alliance launched a successful offensive.
- Historical Significance:
-
- Aleppo, also known as “Halab” in Arabic, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with references to it appearing in Egyptian texts dating back to the 20th century BC.
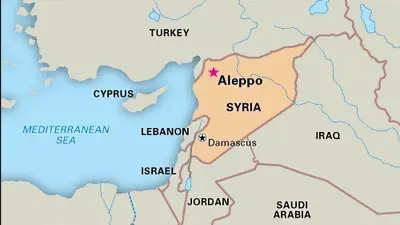
- Geographical Location:
-
- Aleppo is a key city in northern Syria, located approximately 30 miles (50 km) south of the Turkish border.
- It is around 60 miles (100 km) from both the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Euphrates River to the east.
- The city sits on a plateau at an elevation of about 1,300 feet (400 meters).
- Historical and Cultural Importance:
- Throughout its history, Aleppo has been a significant trade center due to its strategic position at the crossroads of several trade routes, dating back to the 2nd millennium BC.
- Over the centuries, Aleppo has been ruled by various civilizations, including the Hittites, Assyrians, Arabs, Mongols, Mamelukes, and Ottomans.
- Landmarks and Features:
- The city’s most iconic feature is the medieval citadel, which stands on a partly man-made hill at the city’s center, rising about 130 feet (40 meters) above the surrounding area.
- The Quwayq River flows through Aleppo, though it has occasionally run dry, particularly due to heavy water consumption in Turkey, where the river originates.
- Modern History and Conflict:
- Aleppo became a focal point of the Syrian Civil War from 2012 to 2016.
- In 2016, opposition fighters in Aleppo surrendered the city to government forces, marking a significant event in the conflict.
Read also: India-Bangladesh Relations: Key Insights for UPSC Preparation
UPSC GS 2
Indian Navy Day
- News: Every year on December 4th, Indian Navy Day is celebrated to honour the brave men and women who serve and protect our nation and its waters.
- More on News: The Indian Navy displayed its operational prowess and capabilities through an ‘Operational Demonstration’ that covered many facets of naval operations by ships, submarines, aircraft, marine commandos and Indian Army personnel at the pristine Blue Flag Beach, Puri, Odisha, on 04 Dec 24.

- History:
-
- The Indian Navy celebrates Navy Day on 04 December to commemorate Operation Trident, the audacious attack on Karachi harbour during the Indo-Pak War in 1971.
- The operation was carried out by a squadron of Indian Navy ships that included missile boats and anti-submarine corvettes.
- The operation earned several gallantry awards, including the Maha Vir Chakra, India’s second-highest gallantry award for the operation’s commandant, Commander (and later Commodore) BB Yadav.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act
- News: The Union government recently informed the Lok Sabha that increasing cases registered under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act are attributed to “growing awareness, wider publicity, and enhanced capacity building of police personnel.”
- About the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989:
- The Act aims to prevent atrocities against members of the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) by individuals not belonging to these communities.
- It prescribes punishments for crimes of atrocities committed against SCs and STs.
- The Central Government is empowered to draft rules for implementing the Act’s objectives.
- Implementation is carried out by State Governments and Union Territory Administrations, which receive central assistance under a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Offences under the Act:
- Crimes committed between SCs and STs or within the same group are not covered under this Act.
- It lists 37 offences that disrupt the dignity, rights, and esteem of SC and ST communities, including denial of economic, democratic, and social rights, along with misuse and exploitation of the legal system.
- Investigation Process:
- All offences under the Act are cognizable.
- Only officers at the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) or higher can investigate cases under this Act.
- Investigations must be completed within 30 days, and the findings are to be reported directly to the state police director.
- Special Courts:
- The Act mandates the establishment of Special Courts for trying cases related to atrocities against SCs and STs.
- State Governments, with approval from the Chief Justice of the High Court, must designate a Court of Session in each district as a Special Court for these cases.
- Special Courts conduct trials on a day-to-day basis to ensure speedy justice.
- A Special Public Prosecutor or an advocate with at least seven years of experience is appointed for each Special Court to handle cases under the Act.
- Punishments:
- The Act prescribes a minimum punishment of six months’ imprisonment, with a maximum sentence of five years and a fine in most cases.
- In specific offences, the minimum punishment is enhanced to one year, and the maximum penalty includes life imprisonment or the death sentence.
- Section 4 penalizes public servants, excluding SCs and STs, who willfully neglect their duties under the Act, with imprisonment up to six months.
- Provision for Immediate Relief:
-
- As per the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Rules, 1995, relief is provided to victims, their families, and dependents by the District Magistrate, Sub-Divisional Magistrate, or any other Executive Magistrate.
- This relief may include cash or essential items such as food, water, clothing, shelter, medical aid, and transport facilities to meet immediate needs.
Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024
- News: The Rajya Sabha recently approved the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024, through a voice vote.
- Objective:
- The bill seeks to amend the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, to attract investments in oil and gas exploration and production.
- It aims to regulate the exploration and extraction of petroleum and natural gas.

- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- The amendment broadens the definition of mineral oils to include petroleum and natural gas.
- Additionally, naturally occurring hydrocarbons, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil are categorized under mineral oils.
- However, coal, lignite, and helium are explicitly excluded from this definition.
- Provisions for Leases:
- The bill introduces provisions for mining leases, covering activities such as exploration, prospecting, production, making mineral oils merchantable, and their disposal.
- Prospecting, an initial step in identifying potential oil and gas reserves, is included.
- Mining leases will now be replaced with petroleum leases, though existing mining leases under the 1948 Act will remain valid.
- Empowerment of the Central Government:
- The central government is authorized to frame rules on:
- Regulating the grant of leases.
- Determining lease terms, including the area size and duration.
- Conservation and development of mineral oils.
- Methods for oil production and procedures for collecting royalties, fees, and taxes.
- The bill also allows for rules on:
- Merging and combining petroleum leases.
- Sharing production and processing facilities.
- Lessee obligations for environmental protection and emission reduction.
- Alternative mechanisms for resolving disputes regarding petroleum leases.
- The central government is authorized to frame rules on:
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
-
- The bill decriminalizes certain provisions of the original 1948 law by introducing penalties, adjudication processes, and appeals mechanisms.
- The penalty for violating rules has been increased significantly, from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 25 lakhs.
- Unauthorized exploration, prospecting, or production will attract a penalty of Rs. 25 lakhs, with continued violations incurring Rs. 10 lakh per day.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism:
- An officer of the rank of Joint Secretary or above will be appointed by the central government to adjudicate penalties.
- Appeals against the adjudicating officer’s decisions can be submitted to the appellate tribunal established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Board Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- News: The Parliament recently announced that approximately 1.45 crore households have registered under the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, with 6.34 lakh installations successfully completed.
- Launch and Objective:
- The scheme was launched on February 15, 2024, with the goal of providing free electricity to households across India.
- It aims to encourage rooftop solar panel installations by offering financial assistance.
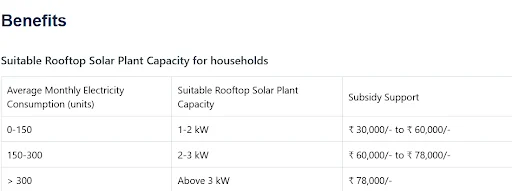
- Subsidy Details:
- Households can receive a subsidy covering up to 40% of the total cost of solar panels.
- Beneficiary families can save up to Rs 18,000 annually by receiving 300 units of free electricity per month.
- Cost Savings and Budget:
- The scheme is expected to reduce government expenditure on electricity by Rs 75,000 crore annually.
- It has a financial outlay of Rs 75,021 crore and will be implemented until the fiscal year 2026–27.
- Benefits:
- Free electricity for eligible households.
- Reduction in government electricity expenses.
- Promotion of renewable energy usage.
- Decrease in carbon emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
- The household should own a house with a rooftop suitable for solar panel installation.
- A valid electricity connection is required.
- Applicants who have previously received subsidies for solar panels are not eligible.
- Role of DISCOMs:
- State Implementation Agencies (SIAs):
- DISCOMs are designated as SIAs to oversee the scheme’s implementation.
- Their responsibilities include ensuring net meter availability, conducting timely inspections, and commissioning solar installations.
- Incentives to DISCOMs:
- DISCOMs will receive incentives for achieving additional grid-connected rooftop solar capacity installations beyond a predefined baseline.
- A total of Rs 4,950 crore has been allocated for the incentives component.
Ayush Oushadhi Gunavatta evam Uttpadan Samvardhan Yojana (AOGUSY)
- News: Ministry of Ayush has implemented a Central Sector Scheme Ayush Oushadhi Gunavatta evam Uttpadan Samvardhan Yojana (AOGUSY), to promote Ayush System of medicines.
- Definition:
- This scheme is a Central Sector initiative formulated by the Ministry of Ayush.
- It focuses on regulating Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and Homeopathy (ASU&H) medicines in India using the framework established by the Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940, and its associated rules.

- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Enhancing Manufacturing and Exports: Strengthen India’s manufacturing capabilities and boost the export of traditional medicines and health promotion products under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Infrastructure and Technology Upgradation: Support infrastructural and technological advancements in public and private sectors to standardize, manufacture, and test Ayush drugs and materials.
- Regulatory Framework Strengthening: Bolster regulatory mechanisms at the Central and State levels to ensure effective quality control, safety monitoring, and prevention of misleading advertisements for Ayush drugs.
- Promoting Synergies and Standards: Encourage collaborations, synergies, and convergence for enhancing the standards and quality of Ayush drugs and materials.
- Key Components:
-
- Upgrading Ayush Pharmacies and Laboratories: Improve and upgrade Ayush Pharmacies and Drug Testing Laboratories to meet higher quality standards.
- Drug Safety and Advertisement Surveillance: Monitor the safety of ASU&H drugs through pharmacovigilance programs and keep surveillance on misleading advertisements.
- Regulatory Framework Strengthening: Strengthen Central and State regulatory frameworks by building technical human resources and conducting capacity-building programs for Ayush drugs.
- Standards and Certification Support: Facilitate the development of standards and the accreditation or certification of Ayush products and materials in collaboration with institutions like BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards), QCI (Quality Council of India), scientific bodies, and industrial R&D centers.
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
- News: International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development has unveiled an Air Quality Dashboard, a public platform offering real-time and forecasted data on air pollution.
- Overview:
- ICIMOD is an intergovernmental knowledge and learning center dedicated to the people of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
- It was officially established and inaugurated on 5 December 1983.
- Mission:
- The center aims to generate and share knowledge that influences regional policy and actions.
- It also attracts investments to help the diverse countries and communities in the HKH region transition toward greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
- Member Countries:
- ICIMOD includes the following member countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Functions:
- ICIMOD supports the region by generating and sharing information and knowledge to find innovative solutions to critical mountain challenges.
- It bridges the gap between science, policies, and practical on-the-ground solutions.
- The center offers a regional platform where experts, policymakers, planners, and practitioners can exchange ideas and collaborate to achieve sustainable mountain development.
- Headquarters: Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Key Points About the Air Quality Dashboard:
- Data Integration: The Air Quality Dashboard integrates data from ground sensors and satellite imagery to provide a comprehensive overview of air pollution at local, sub-regional, and regional levels.
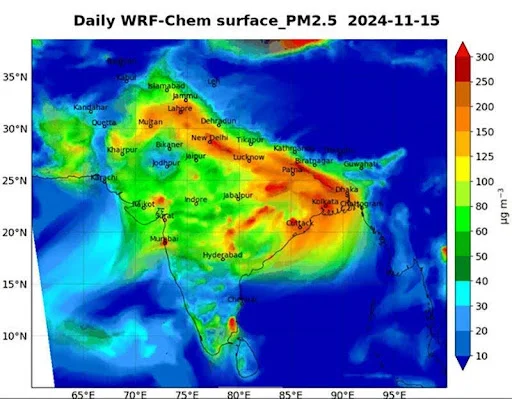
-
- Timelapse Tool:
- One of the key features of the dashboard is its dynamic timelapse, powered by the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem).
- This model highlights the alarming spread of PM2.5 plumes across the region, including pollution hotspots like Lahore, New Delhi, and Kolkata.
- Model Insights: The WRF-Chem model on the dashboard enables users to explore the interaction between weather patterns and air pollution sources, offering valuable insights into pollution outbreaks and trends.
- Emissions Data: The dashboard incorporates emissions data at both local and regional levels, helping to paint a clearer picture of pollution dynamics across borders.
- Forecasting Capabilities: Users can access two-day forecasts through the dashboard, enabling communities, policymakers, and researchers to predict and prepare for changes in air quality.
See more: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): Origin & Mandate | UPSC
UPSC GS 3
Aravali Green Wall
- News: At a UN climate event that is part of CoP16 in Riyadh, India showcased its ‘Aravali Green Wall’ and underscored the need to implement such innovative initiatives for restoring degraded forest lands.
- Scope and Vision:
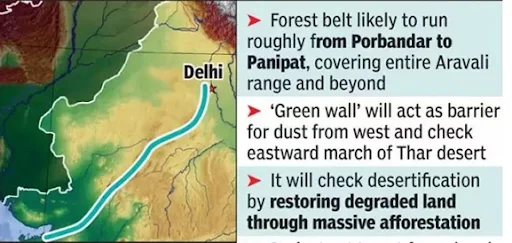
- This initiative aims to develop a green buffer zone extending 5 km around the Aravalli Hills.
- It is part of the Union Environment Ministry’s broader strategy to create green corridors across India to address land degradation and desertification.
- Coverage Area:
- The project encompasses Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Delhi, covering the expansive 6 million hectares of the Aravalli hills landscape.
- Implementation Measures:
- The project involves planting native tree and shrub species on scrubland, wasteland, and degraded forest areas.
- It focuses on the rejuvenation and restoration of surface water bodies such as ponds, lakes, and streams.
- Agroforestry and pasture development are integral components aimed at improving local community livelihoods.
- Objectives:
- Enhancing Ecological Health:
- The project is designed to improve the ecological stability of the Aravalli Hills, countering environmental degradation.
- Combatting Desertification:
- It aims to prevent the eastward expansion of the Thar Desert by creating green barriers.
- These barriers will help reduce soil erosion, desertification, and the occurrence of dust storms.
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- By increasing carbon sequestration, the project will contribute to climate change mitigation.
- Planting native tree species will enhance biodiversity, ecosystem services, and provide vital habitats for wildlife.
- Promoting Sustainable Development:
- The initiative involves local communities in activities such as afforestation, agroforestry, and water conservation.
- These efforts are expected to generate income, employment, and food security, offering significant social and economic benefits.
- International Commitments: The project supports India’s commitments to global conventions, including:
- UNCCD (United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification).
- CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity).
- UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change).
Linen Inspection and Sorting Assistant (LISA) System
- News: Recently, the Union Railway Minister inaugurated the Linen Inspection and Sorting Assistant (LISA) system.
- Definition:
-
- This system, known as LISA, utilizes Artificial Intelligence for inspecting and sorting linens like bed sheets and towels provided to passengers in air-conditioned train coaches.
- LISA is an advanced AI-based automated machine designed to ensure a 100% quality inspection of bed sheets used in trains.
- It thoroughly checks linens to detect and segregate substandard ones, ensuring high standards of hygiene and service.
- Advanced AI algorithms enable precise and reliable inspection results, improving the accuracy of the process.
- The system processes large volumes of linens efficiently, enhancing operational productivity.
- Developed by the Pune division of Indian Railways, LISA has been installed at the Ghorpadi Integrated Coaching Complex (GICC).

- Features of LISA System:
-
- Quality Assurance: Ensures 100% quality checks on bed sheets and other linens used in trains.
- Advanced Technology: Employs sophisticated AI algorithms for thorough and dependable inspections.
- Efficiency: Handles large-scale linen processing quickly, significantly boosting operational efficiency.

