UPSC GS 1
Abhidhamma Divas
- News: PM Modi is attending an event to mark Abhidhamma Divas during which he will also share his insights on the importance of the Pali language.
- About Abhidhamma Divas:
-
- Abhidhamma Divas, or Abhidhamma Day, is an important Buddhist observance marking the Buddha’s descent from Tāvatiṃsa Heaven after imparting the Abhidhamma teachings.
-
- Symbolism:
-
- It commemorates the Buddha’s return to the human realm to share advanced teachings with his disciples.
-
- Coincidence with Pavāraṇā Festival:
-
- The day aligns with the Pavāraṇā Festival, which marks the conclusion of the first Rainy Retreat (Vassa).
-
- Teachings in Tāvatiṃsa Heaven:
-
- As per tradition, after attaining enlightenment, the Buddha spent three months in the Tāvatiṃsa Heaven, teaching the Abhidhamma to his mother, Māyā, who had been reborn there.
-
- Connection with Buddhist Lent (Vassa):
-
- This period overlaps with the Vassa, a time of meditation and study, during which monks remain in monasteries.
-
- Lunar Month and Observance:
-
- Abhidhamma Divas is celebrated on the full moon day of the seventh lunar month, marking the end of Vassa.
- Devotees in Theravāda Buddhist countries like Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Sri Lanka celebrate the day with devotion.
-
- Religious Practices: Devotees engage in religious activities such as:
-
- Offering alms to monks and nuns
- Reciting scriptures and attending sermons focused on the Abhidhamma
- Meditating and reflecting on the teachings of the Buddha
-
Read also: The Gig Economy in India: Growth, Challenges & Insights | UPSC
- Cultural and Spiritual Practices:
-
- Deepening Understanding of Teachings:
- The day provides an opportunity to explore the Abhidhamma, which delves into Buddhist philosophy and psychology.
- Cultivating Virtues:
- Devotees aim to develop qualities such as generosity, wisdom, and loving-kindness through their actions.
- Acts of Charity:
- Many Buddhists participate in charitable activities, including donating food, clothing, or financial support to monasteries, charitable organizations, and those in need.
-
- Significance in Modern Times:
-
- Encouraging Mindfulness and Self-Reflection:
- Abhidhamma Divas promotes personal growth by encouraging mindfulness and spiritual reflection.
- Reinforcing Buddhist Values:
- The observance emphasizes core principles such as compassion, wisdom, and the pursuit of inner peace.
- Connecting with Buddha’s Teachings:
- It reminds individuals of the importance of aligning with the Buddha’s teachings to live a purposeful and peaceful life.
-
Global Hunger Index 2024
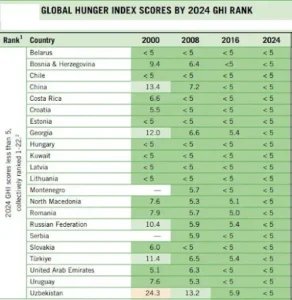
- News: India ranked 105th out of 127 countries in Global Hunger Index 2024.
- What is the Global Hunger Index (GHI)?
-
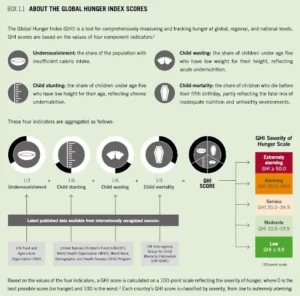
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is an annual peer-reviewed publication that provides a comprehensive measurement and tracking of hunger at global, regional, and national levels.
- It is a joint initiative between Welthungerhilfe and Concern Worldwide.
-
- Highlights of the 2024 Global Hunger Index (19th Edition):
-
- Theme: The theme for the 2024 GHI is “How gender justice can advance climate resilience and zero hunger.”
- Global Hunger Statistics:
- The current GHI score is 18.3, showing a slight improvement from a score of 18.8 in 2016.
- Approximately 2.8 billion people are unable to afford a healthy diet.
- Regional Disparities in Hunger:
- Sub-Saharan Africa: This region exhibits the highest rates of malnutrition and child mortality globally, with ongoing conflicts in Somalia and Sudan worsening hunger crises.
- South Asia: Countries like Afghanistan, India, and Pakistan are facing significant hunger challenges.
-
- Key Issues:
-
- Sustainable Development Goal 2: The GHI 2024 indicates that 42 countries experience alarming or serious hunger levels, reflecting stagnation in the fight against hunger despite decades of progress.
- Gender Disparity: Women are especially vulnerable to food insecurity due to discriminatory norms and violence, which limit their access to resources.
- Underlying Causes of Hunger:
- Climate change and environmental degradation impact food production and threaten the foundations of economies and agriculture.
- Armed conflicts lead to displacement and disruptions in food systems.
- Lower-income countries struggle with debt, diverting funds from critical developmental needs.
-
- Success Stories:
-
- Countries like Mozambique and Nepal have achieved significant improvements in their GHI scores since 2016, demonstrating that progress is attainable.
-
- India-Specific Findings in the GHI 2024:
-
- Alarming Child Malnutrition Rates:
- Approximately 35.5% of children under five are stunted, indicating chronic undernutrition, while 18.7% are wasted, reflecting acute malnutrition.
- These figures point to a significant lack of adequate nutrition during crucial developmental periods, severely affecting children’s physical and cognitive growth.
- Additionally, around 13.7% of the overall population suffers from undernourishment, a persistent issue.
- Child Mortality Rates:
- There has been some progress in reducing child mortality, with 2.9% of children dying before their fifth birthday.
- However, the overall hunger situation remains dire, highlighting the need for immediate action.
-
- India’s Performance Trends in the GHI:
-
- Minimal Improvement Over the Decade:
- India’s score has shown stagnation, moving from 29.3 in 2016 to 27.3 in 2024.
- While there have been gains in certain areas, such as child mortality rates, the overarching issue of hunger persists.
-
- India vs. Neighbours:
-
- In comparison to neighbouring countries like Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bangladesh—each with fewer economic resources—India’s GHI performance is particularly alarming.
- This suggests that economic growth alone does not necessarily translate to improved nutritional outcomes.
-
Mount Adams
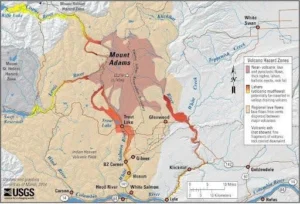
- News: Mount Adams, Washington’s largest volcano, is experiencing increased seismic activity.
- Volcano Type:
-
- Mount Adams is a stratovolcano, though it is currently dormant.
- Its last major eruption occurred around 1,000 years ago.
-
- Location:
-
- The volcano is situated in the Cascade Range in Washington, USA.
- It lies approximately 31 miles (50 km) east of Mount St. Helens and about 55 miles (89 km) north of the Columbia River.
-
- Elevation:
-
- With a peak reaching 12,281 feet (3,743 meters), Mount Adams is the second-highest mountain in Washington State, after Mount Rainier.
-
- Geological Composition:
-
- The volcano is primarily formed of andesite and basaltic andesite lava flows.
- By volume, it is among the largest stratovolcanoes in the Cascade Range.
-
- Glaciers:
-
- Several glaciers are found on Mount Adams, with the largest being Adams Glacier on the northern slope.
- Other notable glaciers include White Salmon Glacier, Avalanche Glacier, and Klickitat Glacier.
-
- Flora and Fauna:
-
- The mountain is part of the Gifford Pinchot National Forest, which hosts a variety of wildlife, including deer, elk, black bears, and numerous bird species.
- Vegetation around the area includes both subalpine and alpine plant species, adding to the ecological diversity.
-
- Climate:
-
- The climate varies with elevation; the lower slopes experience temperate conditions, while the upper regions have colder temperatures throughout the year and heavy snowfall in winter.
-
- Cultural Significance:
-
- Known as Pahto or Klickitat by Indigenous tribes, Mount Adams holds spiritual and cultural importance for Native American communities such as the Yakama Nation, who consider it a sacred site.
-
Roopkund Lake
- News: Uttarakhand’s Roopkund lake, known as the “lake of skeletons” is experiencing adverse impacts due to climate change.
- About Roopkund Lake: Roopkund, often referred to as the “Lake of Skeletons,” is a glacial lake located in Uttarakhand, India.
- Elevation and Location: Positioned at an altitude of 16,500 feet above sea level, it lies at the base of Mt. Trishul in the Garhwal Himalayas.
- Physical Characteristics:
-
- The lake is relatively small, measuring approximately 130 feet in width, and remains frozen for much of the year.
- It is surrounded by towering snow-capped peaks and vibrant green meadows.
-

- Skeletal Remains:
-
- Roopkund is known as the “Lake of Skeletons” due to the numerous human skeletons, some still possessing preserved flesh, that lie beneath its waters.
- These remains become visible when the snow melts during warmer months.
-
- Historical Context:
-
- The skeletal remains have been dated to around the 9th century AD, leading to various theories regarding the circumstances of their deaths.
-
- Recent Research Findings:
-
- A study conducted in 2019 by scientists from India, the US, and Germany questioned the longstanding belief that the skeletons belonged to a single group who died in one event.
- Instead, the research suggested that the remains are from genetically diverse individuals who perished over a period of up to 1,000 years.
-
UPSC GS 2
Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra
- News: Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) has inaugurated a new ‘Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK)’ of the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO), at the National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Disabilities (NIEPVD), Dehradun.
- Initiative Overview: The Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK) is a specialized program aimed at empowering individuals with disabilities, particularly those who are visually impaired.
- Location: The center is situated at the National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Disabilities (NIEPVD) in Dehradun.
- Purpose: PMDK serves as an essential resource for improving the quality of life and expanding opportunities for Divyangjans (persons with disabilities).
- Objectives and Services:
-
- Empowerment Through Rehabilitation: The PMDK is committed to providing comprehensive rehabilitation services to visually impaired individuals, facilitating their journey towards independence and self-sufficiency.
- Assistive Technologies: The center is equipped with state-of-the-art technologies, including prosthetics, orthotics, and Braille devices, to support individuals in their daily activities and improve their mobility.
- Skill Development: The initiative prioritizes skill development by offering various training programs that equip beneficiaries with vocational skills, paving the way for employment and self-employment opportunities.
- Community Engagement: By promoting community involvement, PMDK seeks to enhance awareness of the abilities of persons with disabilities and encourage inclusivity.
-
- Facilities and Infrastructure:
-
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Lab: A specialized laboratory that provides customized assistive devices to improve mobility and functionality for users.
- Audiology Room: Facilities dedicated to auditory assessments and interventions, catering to individuals with combined visual and hearing impairments.
- Braille Workshop: A designated area for the production of Braille materials and assistive devices, fostering literacy and educational opportunities for visually impaired individuals.
-
e-Migrate Portal
- News: India recently launched a revamped e-Migrate portal and mobile app with the objective of facilitating Indians to travel overseas legally with safety.
- Overview: The e-Migrate Portal is an online platform initiated by the Government of India to assist and manage the migration of Indian workers seeking employment overseas.
- Objectives: The primary goal of the portal is to provide a safe and transparent framework for migrant workers. It offers various services, including:
-
- Access to information
- Assistance with documentation
- Helpline support
- Integration with other services
- Awareness campaigns
-
- Promoting Safe Mobility:
-
- The portal advocates for safe and legal mobility channels for Indian migrants.
- It aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 10, which emphasizes orderly and responsible migration.
-
- Features:
- Helpline Support:
-
- The upgraded platform includes a 24/7 multilingual helpline to address issues faced by workers abroad, particularly in the Gulf region.
- A feedback feature ensures timely resolution of concerns raised by users.
-
- Document Submission Integration:
-
- The revamped system integrates with Digilocker, facilitating secure and paperless document submission.
-
- Expansion of Services:
-
- Through a partnership with Common Service Centres (CSCs), the portal aims to broaden immigration services to rural areas, providing information in local languages to enhance accessibility.
-
- Job-Seeker Support:
-
- The platform serves as a one-stop marketplace for overseas employment opportunities, supporting job seekers in finding suitable positions abroad.
-
Hibakusha
- News: Nihon Hidankyo, a Japanese group of atomic bomb survivors, has won the 2024 Nobel Peace Prize.
- Definition: Hibakusha is a Japanese term used to describe the survivors of the atomic bombings that occurred in 1945 in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- Historical Context:
-
- On August 6, 1945, the United States dropped the atomic bomb known as Little Boy on Hiroshima, Japan.
- Just three days later, a second bomb, called Fat Man, was dropped on Nagasaki, Japan.
- By the end of 1945, the bombings resulted in the deaths of over 200,000 individuals.
-

- Survivors:
-
- Many individuals survived the bombings but sustained injuries, and they became known as hibakusha, which translates to “bomb-affected people.”
- The term “niju hibakusha” refers to more than 160 people who were present during both attacks in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
-
- Current Statistics:
-
- As of now, the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare officially recognizes 106,825 living hibakusha, with an average age of 85.6 years.
-
- Government Assistance:
-
- The Japanese government provides various forms of support to hibakusha, including medical allowances to assist with health-related issues stemming from the bombings.
-
- Ongoing Discrimination:
-
- Despite the support, discrimination persists against hibakusha and their descendants.
- There is a widespread belief that these individuals may suffer from hereditary effects of radiation or that their conditions could be contagious, leading to stigma affecting their children and grandchildren.
-
Read also: Israel-Lebanon War: Causes, and Global Impact | UPSC
UPSC GS 3
Bone Ossification Test
- News: Following the high-profile murder of Nationalist Congress Party leader Baba Siddique, a bone ossification test confirmed that one of the accused, who had claimed to be a minor, is in fact an adult.
- Definition:
-
- Ossification is the natural process through which bones develop, starting in early fetal stages and continuing into late adolescence.
- The rate of ossification varies among individuals.
-
- Purpose:
-
- The test helps estimate a person’s age based on the maturity level of their bones.
-
- Process:
-
- X-rays of specific bones, such as those in the hand and wrist, are captured to assess skeletal growth.
- These X-ray images are compared against established reference charts to determine biological age.
-
- Scoring System:
-
- Experts evaluate bone development by matching it with standardized growth charts tailored for the specific population group.
-
- Application in the Criminal Justice System:
-
- Juvenile Justice Act (JJA):
- Individuals below 18 years of age are classified as minors under the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
- The Act emphasizes rehabilitation rather than punishment for minors.
- Juvenile Justice Board (JJB):
- Minors involved in legal violations are presented before the JJB, which includes a magistrate and two social workers.
- The JJB may impose measures like community service or placement in special homes to facilitate the minor’s reform.
- Trials for Heinous Crimes:
- After a 2021 amendment, juveniles aged 16 to 18 accused of serious offenses carrying a minimum sentence of seven years undergo a preliminary assessment.
- This evaluation determines whether the juvenile possesses the mental and physical capacity to understand their actions, guiding whether they should be tried as adults.
-
- Legal Considerations for Age Determination:
-
- Section 94 of the JJA:
- If there is uncertainty about a person’s age, the Board initially looks for school certificates or birth records as primary evidence.
- When such documentation is unavailable, ossification or other medical tests are ordered for age verification.
- Judicial Precedents:
- Courts emphasize that ossification tests should only be used as a last resort if no official records are available.
- These tests are considered supplementary and cannot override valid age-related documents.
-
- Supreme Court Directive:
-
- The Supreme Court has advised that ossification tests hold lesser priority and should only be conducted after exhausting all documentary evidence.
-
- Reliability and Accuracy of Bone Ossification Tests:
-
- Variability in Development:
- Ossification varies across individuals, so the tests cannot provide precise results. They typically estimate an age range, such as 17 to 19 years.
- Margin of Error:
- Courts often allow for a margin of error, especially in delicate cases.
- For example, under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, the Delhi High Court recommends taking the upper age in the estimated range and allowing an additional margin of up to two years to ensure fairness.
-

