UPSC GS 1
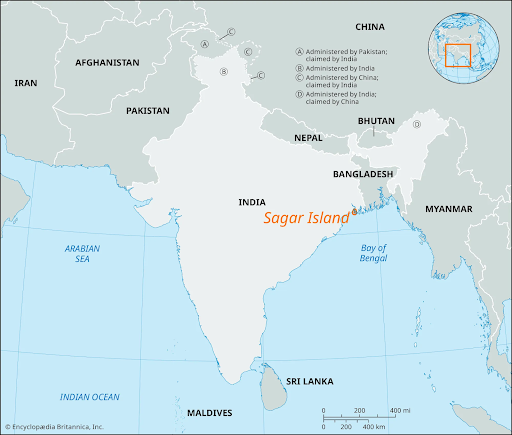
Sagar Island
- News: Sagar Island in West Bengal, renowned for hosting the iconic Gangasagar Mela every January, is experiencing the effects of climate change.
- Location and Geography:
- Also referred to as Ganga Sagar or Sagardwip, the island is situated in the Ganges delta on the continental shelf of the Bay of Bengal.
- It comprises 43 villages and is separated from Mahisani Island by the Muriganga Batala River.
- Sagar, Mahisani, and Ghoramara Islands are categorized under the sand group classification.
- Religious and Cultural Significance:
- The island is a sacred destination for Hindus, where pilgrims gather to celebrate the Makar Sankranti festival in reverence to the Sun.
- It is home to the Kapil Muni temple, a revered pilgrimage site.
- Who is Kapil Muni?
-
- Kapila, or Maharishi Kapila, is a Vedic sage traditionally regarded as the founder of the Samkhya school of Indian philosophy.
- His period is estimated to be around the 6th or 7th century BCE in the Indian subcontinent.
- Kapila is renowned for his teachings on bhakti yoga, a spiritual path emphasizing devotion as a means of liberation.
UPSC GS 2
Youth Co:Lab National Innovation Challenge for 2024-2025
- News: The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog, and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), in partnership with Citi Foundation, have officially launched the seventh edition of the Youth Co:Lab National Innovation Challenge for 2024-2025.
- About Youth Co:Lab:
-
- Youth Co:Lab was established in 2017 as a joint initiative by the UNDP and Citi Foundation.
- Its primary goal is to empower and invest in young people to drive the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through leadership, social innovation, and entrepreneurship.
- In India, the initiative was launched in 2019 in partnership with Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog.
- By the end of 2024, Youth Co:Lab has facilitated six national, theme-based youth dialogues focused on social innovation and entrepreneurship, under this collaboration.
- The Youth Co:Lab National Innovation Challenge 2024–2025 is being conducted in collaboration with AssisTech Foundation (ATF).
- This year’s challenge emphasizes empowering young entrepreneurs, including entrepreneurs with disabilities, who are innovating solutions to enhance access and opportunities for Persons with Disabilities.

- Focus: The focus is on three key sub-categories:
- Inclusive and Accessible Assistive Technology (AT)
- Inclusive Educational Technology and Skilling Solutions
- Accessible and Inclusive Care Models
- Key Facts About Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) was established in 2016 as a flagship initiative of NITI Aayog.
- Its primary objective is to foster an environment conducive to innovation and entrepreneurship across educational institutions, research organizations, industries, and MSMEs.
- Functions:
- AIM promotes entrepreneurship by providing financial assistance and mentorship to encourage innovators to transition into entrepreneurs.
- It also facilitates innovation by creating platforms where individuals with similar ideas can collaborate and develop innovative solutions.
- Key Initiatives: AIM has developed four main programs to achieve its objectives:
- Atal Tinkering Labs: Focused on nurturing creativity and innovation among school students.
- Atal Incubation Centres: Designed to support start-ups by providing necessary resources and mentorship.
- Atal New India Challenges: Aimed at fostering innovations that address national-level challenges.
- Atal Grand Challenges: Focused on finding solutions to significant global and local issues.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: All AIM programs are systematically monitored using real-time Management Information Systems (MIS) and dynamic dashboards. To ensure continuous improvement, these initiatives undergo regular reviews by third-party agencies.
U.N. Internal Justice Council
- News: Former Supreme Court judge Justice Madan B. Lokur was appointed Chairperson of the United Nations Internal Justice Council for a term ending on November 12, 2028.
- Definition:
- The United Nations Internal Justice Council (IJC) was established by the UN General Assembly as part of a reformed internal justice system.
- Its primary purpose is to promote independence, professionalism, and accountability in administering justice within the United Nations.
- Members of the IJC are appointed by the UN Secretary-General.

- Composition of the IJC: The council consists of five members, including:
- A staff representative.
- A management representative.
- Two eminent external jurists, one nominated by the staff and one by management.
- A chairperson, chosen by consensus from among the other four members, who is a distinguished jurist.
- Functions of the IJC:
- Selection of Judges: The IJC identifies and evaluates suitable candidates for judicial positions in the UN Dispute Tribunal (UNDT) and the UN Appeals Tribunal (UNAT) when vacancies arise.
- Recommendation to the General Assembly: It recommends two or three candidates for each judicial vacancy to the UN General Assembly, ensuring geographical representation is considered.
- Oversight and Reporting: The council provides its views and assessments on the functioning of the UN’s justice system to the General Assembly, aiding in its improvement.
- Appointment Process: Judges for the UN Dispute Tribunal and the UN Appeals Tribunal are appointed by the General Assembly based on the IJC’s recommendations.
No-detention Policy
- News: The Union Government has ended no-detention policy in KVs & JNVs, 5 years after diluting RTE Act; decision to impact 3,000 schools
- Policy Update on Detention for Classes 5 and 8:
- The Ministry of Education has introduced new regulations allowing students in Classes 5 and 8 in approximately 3,000 central schools, including Kendriya Vidyalayas and Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas, to be detained if they fail to pass examinations.
- Re-Examination:
- Students who fail the initial exam will have the opportunity to retake it within two months.
- If they fail the re-examination, they may be detained in the same class.
- Detention Criteria:
- Students failing the re-exam may be detained, but no child can be expelled before completing Class 8.
- Teacher and School Roles:
- Teachers and school leaders will focus on providing personalized assistance and monitoring student progress.
- Record-Keeping:
- Comprehensive records will be maintained for students who are detained, ensuring close monitoring of their progress.
- Context of the Decision:
- The decision comes after the Centre amended the Right to Education (RTE) Act five years ago, granting states and the Centre the authority to decide on detention policies for Classes 5 and 8.
- Since the amendment, some states have chosen to discard the no-detention policy.
- The ‘No-Detention’ Policy:
-
- The no-detention policy was a key provision of the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009.
- It mandated free and compulsory education for children aged 6 to 14 and prohibited holding back or expelling students up to Class 8.
- Section 16 of the Act stated that “No child admitted in a school shall be held back in any class or expelled from school till the completion of elementary education.”
UPSC GS 3
Kashmiri Papier-Mache
- News: 343 years after its extinction, Kashmir artisans give wings to the dodo in papier mache.
- About Kashmiri Papier-mâché:
-
- Kashmiri Papier-mâché is a renowned traditional craft originating from the Kashmir Valley.
- This art form was introduced to the region in the 14th century by Mir Sayyid Ali Hamadani, a Muslim saint from Persia.
- It is characterized by intricate designs and the use of paper pulp to create vibrantly decorated items.
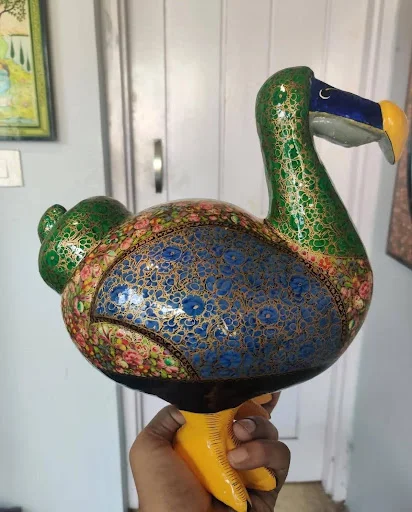

- Features of Kashmiri Papier-mâché:
- Materials and Craftsmanship: The primary material used is paper pulp, which is skillfully crafted by artisans in homes and workshops, predominantly in Srinagar and other parts of the Kashmir Valley.
- Common Products: Popular items include vases, bowls, cups (sometimes adorned with metal rims), boxes, trays, and lamp bases. Recently, papier-mâché models of extinct birds like the dodo have also gained popularity.
- Artistic Details: Designs often feature floral patterns, forest-themed prints, and intricate motifs that reflect cultural and ecological elements.
- Market Reach: Kashmiri Papier-mâché products enjoy a strong domestic demand and are highly sought after in international markets, including Europe and Mauritius.
- Legal and Cultural Recognition:
- The craft is safeguarded under the Geographical Indication (GI) Act of 1999, ensuring authenticity and promoting cultural heritage.
- It has been officially registered by the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks.
- The Dodo Connection:
- Cultural and Commercial Relevance: For Christmas, over 50,000 papier-mâché dodo models were exported to European and Mauritian markets. The dodo, which became extinct in 1681, is the national emblem of Mauritius, lending significant cultural importance to these creations.
Bio-Bitumen
- News: Union minister for road transport and highways, Nitin Gadkari, recently inaugurated a 1km stretch of Asia’s first highway with a bio-bitumen blended surface.
- About Bio-bitumen:
-
- Bio-bitumen is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional bitumen, commonly known as asphalt.
- Unlike conventional bitumen, it is free from petroleum and derived from renewable resources, making it a sustainable choice for road construction.
- Bio-bitumen can be produced using vegetable oils, synthetic polymers, or a combination of both, offering a long-term model for reducing dependence on non-renewable materials.

- Advantages of Bio-bitumen:
- Sustainable Resource: Bio-bitumen is produced from renewable materials, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based bitumen, which relies on finite resources.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Since bio-bitumen is made from organic materials that absorb carbon dioxide during growth, it often results in a lower overall environmental impact compared to traditional bitumen.
- Enhanced Environmental Performance: It contains fewer heavy metals and toxic pollutants than conventional bitumen, reducing its environmental toxicity and overall harm.
- Versatility in Applications: Bio-bitumen is adaptable and can be used in various applications, including:
- Road paving
- Roofing
- Waterproofing
- What is Bitumen?
- Bitumen is a dense and highly viscous hydrocarbon derived from petroleum.
- It is found naturally in deposits such as oil sands and pitch lakes (referred to as natural bitumen) or as a by-product of crude oil distillation.
Cephalopods
- News: Cephalopods as a group may be similar in intelligence to vertebrates as a group, and may deserve humane treatment.
- About Cephalopods: Cephalopods are the most morphologically and behaviorally advanced class within the phylum Mollusca.

- Characteristics of Cephalopods:
- Cephalopods have a completely fused head and foot, encircled by a ring of arms and/or tentacles.
- Their arms, tentacles, and funnel are derived from the foot.
- Movement is primarily achieved through jet propulsion, enabling quick and efficient travel.
- All cephalopods are carnivorous, with many being adept hunters, while others feed passively on floating organic matter.
- They possess highly developed nervous systems and complex sensory organs, facilitating advanced behaviors.
- Their epidermis contains pigment-rich cells surrounded by cells with contractile fibers.
- Many cephalopods display intricate visual camouflage by manipulating tiny pigment sacs beneath their skin, revealing specific colors and patterns.
- Some cephalopods inhabit solitary environments in the dark depths of the ocean, while others thrive socially on vibrant coral reefs.
- Certain cephalopods demonstrate complex learning capabilities, such as reversal learning, where they adapt their behavior based on changing stimuli and rewards.
- The Australian giant cuttlefish (Sepia apama) uses its chromatophores to communicate, producing patterns to attract mates or deter aggressors.
- Camouflage abilities are also utilized for ambush hunting, as they blend seamlessly into their surroundings or lure prey.
- Types of Cephalopods: Cephalopods include coleoids such as cuttlefish, octopuses, and squids, along with the chambered nautilus.
See more: Food Processing Industry: Overview and Growing Demand in India | UPSC
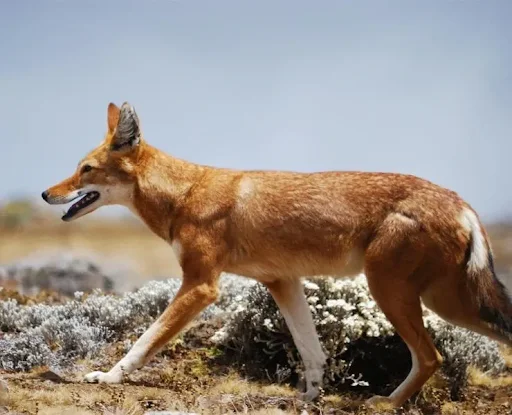
Ethiopian Wolf
- News: Recent studies have identified the Ethiopian wolf as a rare carnivore that feeds on nectar, potentially playing a role in plant pollination.
- Specialized Habitat and Ecological Role:
- The Ethiopian wolf is a highly specialized rodent predator inhabiting Afroalpine ecosystems in Africa’s high-altitude regions.
- These ecosystems, primarily found in the Ethiopian Highlands, exist at elevations of 3,200 meters or more above sea level, characterized by cold and harsh climatic conditions.

- Physical Characteristics:
- The wolf is comparable in size to a large dog, featuring a reddish coat, white markings on the throat and chest, and a bushy black tail.
- Population Status:
- With fewer than 500 individuals left, the Ethiopian wolf holds the distinction of being the most endangered carnivore in Africa.
- Habitat Specificity:
- It inhabits isolated “sky islands” — high-altitude areas above tropical forests surrounded by vastly different lowland terrains.
- Ethiopian Wolf’s Role as a Pollinator:
- Interaction with Ethiopian Red Hot Poker Flower:
- The wolf has been observed feeding on the nectar of the Ethiopian red hot poker flower, a plant known for its red and yellow blooms and sweet nectar that attracts various pollinators.
- As the wolf moves between flowers, its muzzle becomes dusted with pollen, potentially facilitating pollination.
- Behavioral Observations:
- Researchers recorded wolves spending considerable time in flower fields. For instance, one wolf was seen visiting 30 flower heads within 1.5 hours.
- This behavior suggests that the Ethiopian wolf actively seeks nectar, a unique trait among large carnivores.

