UPSC GS 1
Denali Fault
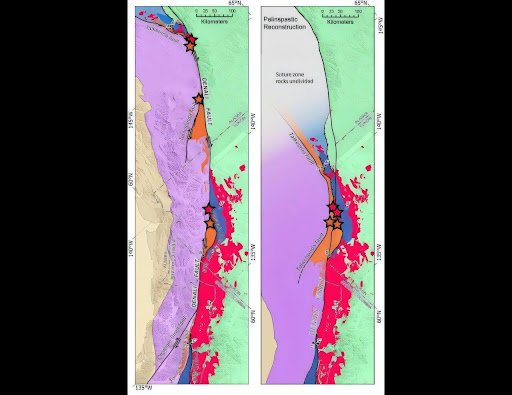
- News: New research shows that three sites spread along an approximately 620-mile portion of today’s Denali Fault were once a smaller united geologic feature indicative of the final joining of two land masses.
- Key Findings on the Denali Fault:
- Geological Significance:
- The Denali Fault, located in southern Alaska, has been a significant factor in shaping Earth’s geological history.
- A recent study reveals that three sites along the Denali Fault were once part of a single geological feature, symbolizing the final union of two landmasses millions of years ago.
- Tectonic Activity and Movement:
- Over the course of millions of years, tectonic forces caused horizontal movement along the fault, resulting in a separation of this unified feature by over 483 kilometers.
- These movements reflect the intense tectonic activity that has shaped the region’s geological structure.
- Terminal Suture Zone:
- The three locations along the fault once formed a terminal suture zone, marking the last phase of tectonic plate integration into a larger landmass.
- What are Fault Lines?
-
- Fault is a gently curved fracture in the rocks of Earth’s crust, where compressional or tensional forces cause relative displacement of the rocks on the opposite sides of the fracture.
- Faults may be vertical, horizontal, or inclined at any angle.

Sahitya Akademi Awards
- News: The Sahitya Akademi recently announced the winners of its annual Sahitya Akademi Awards, which are recommended by jury members in 21 languages.
- About the Sahitya Akademi Awards
- The Sahitya Akademi Award is presented for the most distinguished books of literary merit published in any of the major Indian languages recognized by the Akademi.
- In addition to the 22 languages listed in the Constitution of India, the Akademi has also recognized English and Rajasthani as eligible languages for its award program.
- Awardees are given a plaque, a shawl, and a monetary award of ₹1 lakh.
- Key Facts about Sahitya Akademi:
- The Akademi was officially inaugurated by the Government of India on 12 March 1954.
- It was registered as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- The Sahitya Akademi serves as the central institution for literary dialogue, publication, and promotion in India. It is the only organization in the country that undertakes literary activities in 24 Indian languages, including English.
- Ministry: The Sahitya Akademi operates as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Culture.
- Head Office: Located in New Delhi.
Read also: Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR) in India | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
National Farmers’ Day (Kisan Diwas)
- News: The National Farmers’ Day, or Kisan Diwas, is celebrated on December 23 annually in India.

- Definition:
-
- Observed annually on December 23, National Farmers’ Day honors the birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Chaudhary Charan Singh.
- This day recognizes farmers as the backbone of the Indian economy and highlights their vital contribution to the nation’s socio-economic progress.
- States such as Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh, where agriculture plays a predominant role, actively celebrate this occasion.
- Key Government Initiatives for Farmers’ Welfare:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):
- Launched on February 24, 2019, this flagship scheme supplements the financial needs of land-owning farmers, subject to certain exclusions.
- Under the scheme, ₹6,000 is transferred annually in three instalments via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) to eligible farmers’ families.
- As of the 18th instalment, released in October 2023, over ₹3.45 lakh crore has been disbursed, benefiting more than 11 crore farmers nationwide.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY):
- Introduced in 2016, this scheme offers affordable crop insurance to protect farmers from non-preventable natural risks.
- Farmers’ premiums are capped at 2% for Kharif crops, 1.5% for Rabi crops, and 5% for commercial and horticultural crops.
- As of August 2023, ₹1,63,519 crore (98%) has been paid out against a total claim amount of ₹1,67,475 crore.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY):
- Launched on September 12, 2019, this scheme provides social security to small and marginal farmers.
- Beneficiaries receive a monthly pension of ₹3,000 after reaching the age of 60.
- Farmers aged 18 to 40 contribute ₹55-200 per month until turning 60 to qualify for the pension.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF):
- Announced under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Package, the fund addresses infrastructure gaps in agriculture.
- The scheme provides medium- and long-term financing for post-harvest management and community farming projects, supported through interest subvention and credit guarantees.
- A ₹1 lakh crore fund is being disbursed from FY 2020-21 to FY 2025-26, with support extended until FY 2032-33.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS):
- This initiative offers concessional short-term agriculture loans for crop cultivation, animal husbandry, dairying, and fisheries.
- Loans up to ₹3 lakh are provided at a 7% annual interest rate for one year.
- Farmers who repay promptly receive an additional 3% interest subvention, reducing the effective rate to 4% per annum.
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme:
- Approved recently by the central government, this scheme aims to provide drones to women-led Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- With a total allocation of ₹1,261 crore for FY 2023-24 to FY 2025-26, 15,000 drones are set to be distributed.
- The package includes mandatory pilot training and additional instruction for agricultural applications.
- In the first phase for FY 2024-25, 3,090 SHGs will receive drones, with 500 drones already procured by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY):
- This scheme focuses on developing pre- and post-harvest infrastructure for agriculture and allied sectors.
- It enhances access to quality inputs, market facilities, and other services for farmers.
- States are granted flexibility and autonomy to design and implement projects based on the specific needs of their local farmers.
Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer
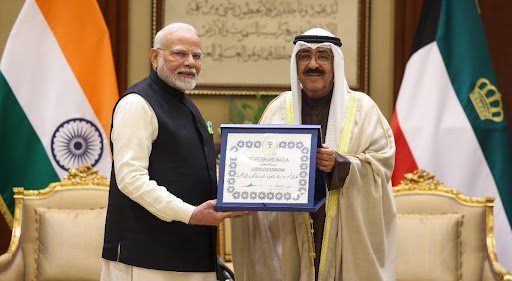
- News: Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been awarded the Wisam Mubarak al-Kabeer, or the Order of Mubarak the Great, by Sheikh Meshal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah.
- What is the Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer?
-
- The Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer is Kuwait’s highest national award, conferred by the Kuwaiti government.
- It is awarded to Heads of State, foreign Sovereigns, and members of royal families as a gesture of friendship and goodwill.
- Past Recipients of the Award:
-
- Queen Elizabeth II of England.
- Former US Presidents George HW Bush and Bill Clinton.
- King Salman of Saudi Arabia.
- Former French President Nicolas Sarkozy, among others.
- Historical Background:
- Instituted in 1974 in memory of Mubarak Al Sabah, also known as Mubarak al-Kabeer or Mubarak the Great, who ruled Kuwait from 1896 to 1915.
- During his reign, Kuwait gained more autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
- In 1899, Mubarak signed a treaty with Britain, making Kuwait a British protectorate to safeguard it from Turkey.
- Mubarak is credited with shaping Kuwait’s future trajectory.
- The design of the award was revised in 1992 after Kuwait’s liberation from Iraq in 1991.
- India-Kuwait Relations:
- PM Modi is the first Indian Prime Minister to visit Kuwait since Indira Gandhi in 1981.
- Kuwait is among India’s top trading partners, with bilateral trade valued at $10.47 billion in 2023-24.
- Kuwait is India’s sixth-largest crude oil supplier, fulfilling 3% of India’s energy needs.
- Indian exports to Kuwait reached $2 billion for the first time, while investments by the Kuwait Investment Authority in India exceed $10 billion.
- India and Kuwait share strong historical ties, with links dating back to pre-oil Kuwait when maritime trade with India was central to Kuwait’s economy.
- The Indian rupee was legal tender in Kuwait until 1961.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) Programme
- News: The Indian government and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) have signed a landmark $350 million policy-based loan under the second subprogramme of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) programme.
- Definition:
-
- The Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) is a programmatic policy-based loan (PBL) aimed at supporting the government’s reforms in India’s logistics sector.
- The initiative is designed to enhance India’s manufacturing sector and improve the resilience of the nation’s supply chains.
- The SMILE programme is a collaborative effort between the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) under the Ministry of Finance, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, and the Asian Development Bank (ADB).

- Key Pillars of the SMILE Programme:
-
- Strengthening Institutional Frameworks: Focus on developing the capacities at national, state, and city levels to ensure the seamless integration of multimodal logistics infrastructure.
- Standardising Warehousing: Efforts are underway to establish uniform standards for warehousing, aiming to streamline supply chains and attract private investment.
- Improving Trade Logistics: Aimed at enhancing the efficiency of India’s external trade operations, making logistics processes more effective.
- Promoting Smart, Low-Emission Systems: Encouraging the use of advanced technologies to improve logistics efficiency while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
UPSC GS 3
Quantum Satellite
- News: Recently, Chairman of the Mission Governing Board of the nascent National Quantum Mission, said India plans to launch a quantum satellite in “2-3 years for quantum communications”.
- Definition: A quantum satellite is a communications satellite designed to harness quantum physics principles to ensure secure signal transmission.

- Purpose:
- Enhanced Signal Security: Safeguards against emerging threats posed by quantum computing.
- Support for Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Enables unbreakable encryption through the application of QKD.
- Quantum Cryptography and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD):
- Quantum Cryptography: Involves leveraging the fundamental principles of quantum physics to secure communication channels.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD):
- Objective: Facilitates the secure exchange of encryption keys while ensuring that any unauthorized interception is detected.
- Mechanisms of QKD:
- Quantum Measurement Principle: Observing or measuring a photon alters its quantum state, exposing any eavesdropping attempt.
- Quantum Entanglement: Involves the use of entangled photon pairs, where a change in the state of one photon is instantaneously reflected in its pair, ensuring secure and tamper-proof key distribution.
India State of Forest Report
- News: Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Bhupender Yadav recently released the ‘India State of Forest Report 2023’ (ISFR 2023) at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun.
- Definition:
-
- The India State of Forest Report is published biennially by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) and has been in circulation since 1987.
- It provides a comprehensive assessment of the nation’s forest and tree resources using satellite-based Remote Sensing data and field-based National Forest Inventory (NFI).
- The 2023 edition marks the 18th report in this series.
- The report covers key aspects such as forest cover, tree cover, mangrove cover, growing stock, carbon stock, forest fire incidents, and Agroforestry.

- Highlights of India State of Forest Report 2023:
- Forest and Tree Cover: The total Forest and Tree cover is 8,27,357sq km, which is 25.17 percent of the geographical area of the country. The Forest Cover has an area of about 7,15,343sq km (21.76%) whereas the Tree Cover has an area of 1,12,014 sq km (3.41%).
- A positive increase in forest and tree cover has been observed compared to the 2021 assessment.
- States with Maximum Gains in Cover:
- Forest and Tree Cover Gains: Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan have shown the highest increase.
- Forest Cover Gains: Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha top the list in terms of maximum increase.
- Top States in Forest and Tree Cover Area-Wise:
- Largest Forest and Tree Cover: Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Largest Forest Cover: Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
- Forest Cover as Percentage of Total Geographical Area:
- Lakshadweep has the highest forest cover at 91.33%, followed by Mizoram and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- A total of 19 states and union territories have over 33% of their geographical area under forest cover.
- Of these, eight states/UTs, including Mizoram, Lakshadweep, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Manipur, have forest cover exceeding 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- The total mangrove cover in the country stands at 4,992 square kilometers.
- Bamboo Bearing Area:
- The bamboo-bearing area has shown an increase since the previous assessment in 2021.
- Carbon Stock:
- India’s carbon stock has risen compared to the last assessment, reaching 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- This progress indicates an additional carbon sink of 2.29 billion tonnes since 2005, moving closer to the target of 2.5 to 3.0 billion tonnes by 2030.
Automated & Intelligent Machine-aided Construction (AIMC) System
- News: The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) has expedited the use of Automated & Intelligent Machine-aided Construction (AIMC) system for National Highways construction.
- Definition:
- The AIMC system is a cutting-edge approach in construction that integrates automation, robotics, and intelligent systems to enhance efficiency, precision, and safety in building projects.
- It leverages advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation to support various construction processes.

- Key Features:
- Automation in Construction: AIMC systems use automated machinery and robotics to handle repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, reducing human labor and improving productivity.
- Intelligent Systems: AI and machine learning algorithms are employed to optimize construction processes, predict project outcomes, and enhance decision-making.
- Improved Precision: Automation in the AIMC system leads to highly precise construction, minimizing errors and improving the quality of the final product.
- Enhanced Safety: By automating dangerous tasks, the system reduces the risk of accidents and injuries on construction sites.
- Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation allows faster completion of tasks, reducing project timelines and costs.
- Cost Reduction: With less need for manual labor and fewer errors, AIMC helps cut overall construction costs.
- Sustainability: AIMC can help in the efficient use of resources, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Quality Control: The precision of intelligent machine-aided systems ensures consistent quality throughout the construction process.
- Applications:
-
- Building Construction: AIMC systems are used for tasks such as bricklaying, cement mixing, and painting.
- Infrastructure Projects: The system can be applied in roads, bridges, and tunnels, where automation can aid in tasks like excavation, material transportation, and structural assembly.
- Renovation and Maintenance: Intelligent machines can assist in the renovation of existing structures by carrying out assessment and repair tasks with minimal human intervention.
See more: Understanding Jet Streams: Formation, Types, Distribution, and Effects | UPSC
Dinga Dinga
- News: A mysterious illness—locally referred to as Dinga Dinga which means shaking like dancing—has wreaked havoc in Uganda, affecting over 300 people in Bundibugyo district.
- Definition:
- Locally known as ‘Dinga Dinga’, which translates to ‘shaking like dancing,’ this disease primarily affects women and girls.
- It is characterized by fever and excessive body shaking, with the severity of symptoms varying.
- Symptoms of Dinga Disease
-
- Uncontrollable Body Shaking: The most notable symptom is violent, involuntary shaking that resembles dancing.
- Fever and Extreme Weakness: Patients often experience high fever and feel extremely weak, making daily activities difficult.
- Paralysis-like Immobility: In severe cases, individuals report a sensation similar to paralysis, with simple actions like walking becoming impossible.
- Cause and Diagnosis
- The exact cause of Dinga Dinga remains unclear, with health experts struggling to identify the virus or pathogen responsible for the disease.
- Despite extensive efforts, no specific source of the illness has been pinpointed yet.
- Treatment
- Currently, antibiotics are being used to treat the illness, although the effectiveness of this treatment remains uncertain without a clear diagnosis.

