UPSC GS 1
Konda Reddi Tribe
- News: Isolated from the modern world, the Konda Reddis rely on age-old traditions to sustain their livelihoods.
- Definition: The Konda Reddis are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) residing along the banks of the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh.
- Language: The Konda Reddis primarily communicate in Telugu, characterized by their distinct accent.
- Religion: Their primary religious practice is Folk Hinduism, which includes local traditions and the worship of community-level deities.

- Family and Marriage:
- Family Structure: The Konda Reddis follow a patriarchal and patrilocal family system.
- Marriage Practices: Monogamy is the norm, though polygamous families are also found. Marriage arrangements include negotiation, love and elopement, service, capture, and exchange, all of which are socially acceptable within the community.
- Political Organization:
- Social Control: The tribe governs itself through a traditional institution known as the ‘Kula Panchayat.’
- Village Leadership: Each village has a hereditary headman referred to as the ‘Pedda Kapu.’ The headman also serves as the Pujari (priest) for the village’s deities.
- Livelihood:
- Primary Activities:
- The Konda Reddis engage in shifting cultivation and depend heavily on forest flora and fauna for their sustenance.
- Their staple crop is jowar, which forms the basis of their diet.
- Commercial Crops: They cultivate cashew, niger, chili, and cotton using the Podu (shifting) cultivation method.
- Role of Cattle: Cows are central to their livelihood and sustenance practices.
- Housing and Architecture:
-
- Traditional Homes: The Konda Reddi houses retain a distinct architectural style that has been preserved over generations.
- Circular Architecture: Their homes feature circular mud walls and thatched roofs, resembling the Bhunga-style architecture of Gujarat’s Kachchh region.
Read also: Railways (Amendment) Bill 2024 – Key Highlights for UPSC Prep
Durgadi Fort
- News: A civil court in Kalyan has ruled in favour of the Hindu side over the disputed Durgadi Fort, where the Shiv Sena unfurled a saffron flag in September 1968.
- Definition:
- Durgadi Fort is located in Kalyan, a town near Mumbai in Maharashtra.
- Positioned along the banks of the Ulhas River, the fort offers panoramic views of the river, the surrounding landscape, and the city of Kalyan.

- Historical Significance of Kalyan:
- Kalyan has been a significant junction and an important location since ancient times.
- During the Satavahana era, Kalyan was a well-developed international harbor, highlighting its strategic importance.
- Construction and Role in Maratha Navy:
- The fort was constructed by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, marking the beginning of the Maratha Navy.
- Shivaji Maharaj captured Kalyan and Bhiwandi from Adilshah on 24th October 1654.
- He built the fort near the creek to provide support for Kalyan and utilized it as a dockyard for shipbuilding.
- Religious Significance:
-
- The fort is named after Goddess Durga, and a temple dedicated to her is located within the fort premises.
UPSC GS 2
‘Jalvahak’ Scheme
- News: The Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW), Shri Sarbananda Sonowal recently unveiled a major scheme for Cargo Promotion – ‘Jalvahak’ Scheme.
- Definition: The Jalvahak Scheme has been introduced to incentivize a shift from road and rail freight transportation to inland waterways, drawing inspiration from Europe’s Marcopolo initiative.
- Rationale for the Scheme:
- Aims to encourage the use of inland waterways as a sustainable and efficient mode of transportation.
- Seeks to promote modal shifts from the better-funded and more developed road and rail sectors.

- Duration of the Scheme: The scheme will be operational for a period of three years.
- Implementing Agency: Inland and Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL) and Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Shipping, Ports, and Inland Waterways.
- Scheme Design:
- Financial incentives will be provided directly to cargo owners who transition from road/rail to inland waterways.
- The incentives will cover up to 35% of the actual operational expenditure incurred on waterways transport.
- Only applicable for long-haul cargo movement over distances exceeding 300 kilometers.
- Fixed Day Scheduled Sailing Services between key locations like Kolkata, Patna, Varanasi, and Pandu (Assam).
- Applicability of Incentives: Initially, incentives are available for cargo movement along:
-
- National Waterway 1 (River Ganga).
- National Waterway 2 (River Brahmaputra).
- National Waterway 3 (River Barak).
- Launch: The policy was inaugurated in Kolkata, where Minister Sonowal lagged off three vessels:
- MV AAI carrying 1,000 tonnes of gypsum to Patna.
- MV Homi Bhaba transporting 200 tonnes of coal to Varanasi.
- MV Trishul, along with two barges, carrying 1,500 tonnes of cement to Pandu, Guwahati.
DAE- Homi Bhabha Chair for Distinguished Scientist/Professors
- News: Union Minister of State for Science & Technology recently informed the Parliament about DAE- Homi Bhabha Chair for Distinguished Scientist/Professors Scheme.
- Definition: The DAE-Homi Bhabha Chair Scheme is administered by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Aim:
- It recognizes and provides opportunities to distinguished scientists and engineers, including those who are retired or superannuated, for their significant contributions in developing sensitive or critical technologies.
- The scheme enables these experts to conduct research and development in areas of their expertise and of relevance to the Department of Atomic Energy.

- Eligibility and Tenure:
- The scheme is intended for distinguished scientists/professors and engineers.
- It includes retired or superannuated individuals with significant contributions to sensitive or critical technological advancements.
- The tenure under the scheme is flexible, ranging from one to five years, as determined by the Selection Committee.
- Honorarium and Allowances:
- Monthly Honorarium: Awardees receive an honorarium of ₹2,00,000 per month. If the honorarium, combined with the pension, exceeds the last drawn pay, the honorarium is capped at the last drawn pay.
- Contingency Grant: A grant of ₹76,000 per annum is provided to cover expenses such as secretarial assistance, telephone bills, and stationery.
- Equipment Allowance: A one-time equipment allowance of up to ₹1,25,000 is provided for the entire tenure. This allowance includes ₹10,000 specifically for purchasing books.
- Transport Allowance: A fixed monthly transport allowance is provided if the awardee is not allocated an official vehicle.
Samarth Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- News: Recently the Rajya Sabha was informed about the SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Scheme.
- Definition:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative is spearheaded by the Ministry of Heavy Industry & Public Enterprises, Government of India.
- It is part of the scheme for Enhancing Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
- This initiative involves key stakeholders such as manufacturers, vendors, and customers.

- Objectives and Purpose:
- SAMARTH Udyog aims to create experiential and demonstration centers for Industry 4.0 to raise awareness among Indian manufacturing industries.
- The initiative focuses on integrating smart technologies within industries, especially to facilitate the transformation of Indian manufacturing towards Industry 4.0 standards.
- SAMARTH Centres:
- Four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been established:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab in Pune.
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing at IIT Delhi.
- I-4.0 India @ IISc in Bengaluru.
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell at CMTI, Bengaluru.
- Support and Activities Provided by SAMARTH Centres:
- These centers assist industries, including MSMEs, to enhance workforce skills and build awareness of Industry 4.0 technologies through:
- Organizing seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events on Industry 4.0.
- Conducting training programs to help industries understand and adopt Industry 4.0 principles.
- Offering consultancy services in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics.
- Providing incubation support to start-ups and MSMEs exploring Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Key Features:
-
- No financial assistance is provided directly to any industry, including MSMEs, for adopting Industry 4.0 technologies under the SAMARTH Centre initiative.
- The focus is on awareness-building, skill development, and consultancy support to encourage Industry 4.0 adoption.
UPSC GS 3
Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)
- News: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released the results of the November 2024 round of its bi-monthly consumer confidence survey (CCS).
- Definition: The Consumer Confidence Survey is conducted and released bi-monthly by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Aim: It serves as a measure of consumers’ optimism or pessimism regarding their anticipated financial circumstances.
- Insights from the Survey:
- Consumer optimism typically translates to increased spending, whereas lack of confidence may result in reduced consumption.
- Lower consumption patterns can potentially trigger economic slowdowns or recessions.
- Key Indicators of the Survey:
- Current Situation Index (CSI): Reflects the consumer sentiment about the present economic conditions.
- Future Expectation Index (FEI): Represents the consumers’ outlook on their financial situation and the overall economy in the future. This survey offers vital insights into consumption trends and helps policymakers gauge economic activity.
Dulcibella Camanchaca
- News: Scientists have discovered a new amphipod in the Atacama Trench. This new species is named Dulcibella camanchaca and has drawn comparisons to alien-like features.
- Definition:
- Dulcibella camanchaca is a newly discovered predatory amphipod species.
- It was identified at a depth of 7,902 meters in the Atacama Trench.
- The species belongs to the Eusiridae family and represents a newly identified genus, making it a notable addition to deep-sea biodiversity records.

- Distinctive Features:
- It measures slightly under 4 centimeters, making it larger than its closest relatives.
- This species exhibits specialized raptorial appendages, known as gnathopods, which it uses to hunt smaller organisms.
- Unlike most amphipods found in trenches that are scavengers, this species is an active predator that preys on other amphipods, playing an essential role in the deep-sea food chain.
- The amphipod is a fast swimmer and was named after the concept of “darkness” in the languages of the Andean peoples.
- Adaptations for Deep-Sea Survival:
- The species displays pale coloring, a common adaptation among deep-sea organisms to thrive in the absence of light.
- Its features and behavior are optimized for survival in the extreme, pitch-black environment of the trench.
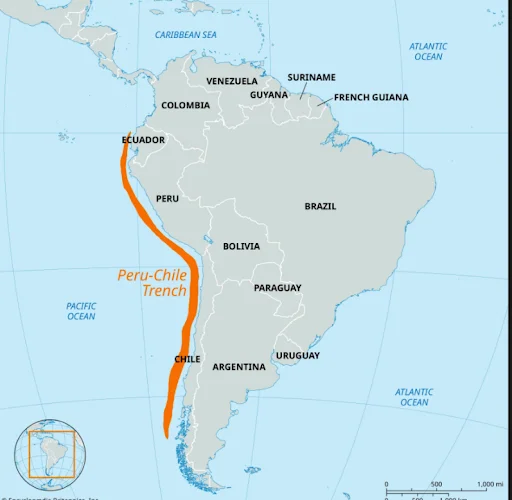
- Atacama Trench (Peru-Chile Trench):
-
- The Atacama Trench is a hadal zone, a term used to describe the deepest parts of the ocean ranging from 6,000 to 11,000 meters.
- Hadal areas are incredibly challenging to study due to their depth and the extreme conditions, but they are home to highly specialised and often unique species.
- It stretches approximately 3,666 miles (5,900 km) in length, running parallel to the coasts of Peru and Chile.
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Scheme
- News: The National Dam Safety Authority is likely to submit its final report on the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Scheme soon, excluding the aspect of conducting geo-technical tests.
- Definition:
- KLIP is a multi-purpose irrigation project located on the Godavari River in Kaleshwaram, Bhupalpally, Telangana, India.
- The project is intended to meet both irrigation and drinking water needs, covering about 45 lakh acres in 20 out of the 31 districts in Telangana, including Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
- It holds the distinction of being the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.

- Geographic and Hydrological Context:
- The project’s upstream reach begins at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari rivers.
- The Pranahita River is a union of smaller tributaries, such as the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers, which together form the seventh-largest drainage basin in the Indian subcontinent.
- Scale and Structure:
- KLIP comprises 7 links and 28 packages, extending over a distance of approximately 500 km across 13 districts.
- The project uses a canal network of over 1,800 km, making it a remarkable feat of engineering and planning.
- Water Production and Allocation: The project is designed to produce a total water output of 240 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic feet), sourced as follows:
- 195 TMC from the Medigadda Barrage.
- 20 TMC from the Sripada Yellampalli project.
- 25 TMC from groundwater resources.
- The distribution of water is planned as:
- 169 TMC for irrigation.
- 30 TMC for municipal water needs in Hyderabad.
- 16 TMC for various industrial purposes.
- 10 TMC for drinking water supply to nearby villages.
- The remaining quantity accounts for evaporation losses.
Sultanpur National Park
- News: Recently, birders in Delhi-NCR were in for an exciting treat as they spotted several rare vagrant bird species at Sultanpur National Park.
- Definition:
- Sultanpur National Park is located in the Gurgaon district of Haryana, approximately 46 km from Delhi.
- Previously known as the Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary, the park spans an area of 1.42 sq. km, primarily consisting of marshy lakes and floodplains.
- The park’s core area, covering 1.21 sq. km, includes the main feature, Sultanpur Lake/Jheel.

- Sultanpur Lake (Jheel):
- Sultanpur Jheel is a seasonal freshwater wetland, with water levels varying throughout the year.
- The lake is mainly replenished by water from the Gurgaon canal of the Yamuna River and excess water from nearby agricultural lands.
- Conservation Recognition:
- In 2021, Sultanpur National Park was designated as a Ramsar site, highlighting its international importance as a wetland.
- It has also been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International, further emphasizing its ecological value.
- Flora of Sultanpur:
- The park’s vegetation is predominantly tropical and dry deciduous, comprising various grasses and tree species.
- Notable flora includes dhok, khair, tendu, jamun, neem, berberis, and different species of Acacia.
- Fauna of Sultanpur:
-
- Sultanpur is home to over 320 bird species, serving as a crucial wintering ground for migratory birds.
- It is part of the Central Asian Migratory Flyway, attracting thousands of birds from countries like Russia, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Europe during the winter season.
- Prominent bird species include the Common Hoopoe, Purple Sunbird, Black Francolin, Little Cormorant, Indian Cormorant, Siberian Crane, and Greater Flamingo.
- Seasonal migratory visitors include species like the Common Teal, Common Greenshank, and Ruff.
- Besides birds, the park is home to several terrestrial animals, including Nilgai, Sambar, Golden Jackals, Wild Dogs, Striped Hyenas, Indian Porcupines, and Mongooses.
See more: Railways (Amendment) Bill 2024 – Key Highlights for UPSC Prep
CE20 Cryogenic Engine
- News: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully carried out the sea level hot test of its CE20 cryogenic engine.
- Definition:
- The CE20 Cryogenic Engine is an indigenously developed engine by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre of ISRO.
- It is the main power source for the upper stage of the LVM3 launch vehicle, qualified to operate at a thrust level of 19 tonnes.
- Applications and Recent Upgrades:
- The engine has successfully powered the upper stage of six LVM3 missions to date.
- For the Gaganyaan mission, it has been qualified to deliver a thrust level of 20 tonnes.
- The thrust level has also been uprated to 22 tonnes for the future C32 stage, which will enhance the payload capability of the LVM3 launch vehicle.

- Features of CE20:
- It incorporates a Nozzle Protection System, addressing earlier complexities in engine testing.
- It is equipped with a nozzle area ratio of 100, ensuring better performance.
- The engine uses a multi-element igniter, tested successfully by activating only the first element during evaluations.
- Key Achievements:
- Successful demonstration of engine performance with high nozzle area ratio.
- Validation of engine and facility performance under standard operational conditions.
- Significance of the CE20 Test:
-
- This test is a milestone in ISRO’s indigenous cryogenic engine development.
- It demonstrates ISRO’s capability to overcome complex challenges in rocket propulsion technology, marking progress towards self-reliance in space exploration.

