UPSC GS 1
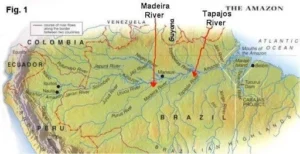
Madeira River
- News: The Madeira River has reached its lowest level since monitoring began in 1967.
- Overview of Madeira River:
-
- The Madeira River is a major tributary of the Amazon River.
- It is formed by the confluence of the Mamoré and Beni rivers at Villa Bella, Bolivia, and flows northward.
- The river forms the border between Bolivia and Brazil for about 60 miles (100 km).
-
- Madeira Basin:
-
- The Madeira River is part of the larger Madeira Basin, which covers approximately 1,300,000 square kilometers (502,000 square miles), making up about 19% of the entire Amazon Basin.
- The basin spans across Bolivia, Brazil, and Peru, with:
- 50% of its area in Bolivia
- 40% in Brazil
- 10% in Peru
-
- Significance of the Madeira River:
-
- It is a crucial waterway in South America, playing an essential role in the hydrology of the Amazon Basin.
- As the largest tributary of the Amazon River, it supports diverse flora and fauna across Bolivia and Brazil, contributing to the region’s ecosystem.
-
Sahariya Tribe
- News: Nearly 200 children are malnourished among sahariya tribes in Rajasthan.
- Sahariya Tribe:
-
- The Sahariya tribe is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) located in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Chhattisgarh.
- They are also known by various names including Seher, Sair, Sawar, Saor, and Sahara.
-
- Historical Background:
-
- The Sahariya tribe traces its origins back to the days of the Ramayana and even beyond.
- They are considered one of the most disadvantaged and vulnerable population groups in India.
-

- Settlement and Housing:
-
- Sahariyas generally live in a separate area within villages known as ‘Seharana,’ which is a cluster of houses.
- Their houses are typically constructed with stone boulders and have stone slab roofing, locally referred to as Patore. In some villages, mud structures are also used.
-
- Social Structure:
-
- In villages, the caste system is strongly adhered to, with people of the same caste living in close proximity.
-
- Religion:
-
- The Sahariya tribe practices Hinduism.
-
- Language:
-
- They speak a dialect influenced by Hindi and Brij Bhasha.
-
- Cultural Practices:
-
- The tribe is known for their traditional dance, the Saharia Swang, performed during Holi.
- The dance features a male performer dressed in female attire, dancing to the beats of the dhol, nagari, and matki, while interacting with male performers.
-
- Economy:
-
- The Sahariya tribe primarily depends on forest products, agriculture, and daily wage labor for their livelihood.
- They are particularly skilled in making catechu from khair trees.
-
Read also: Exploring the Magnificent Forts in India A Historical Journey | UPSC
UPSC GS 2
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)
- News: Union Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan has announced the revision in PMAY-G’s norms.
- Definition:
-
- The PMAY-G is a flagship central government scheme.
- The erstwhile rural housing scheme Indira Awaas yojana was restructured into Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana –Gramin in 2016.
-
- Funding: The Centre and states share expenses as:
-
- 60:40 ratio in case of plain areas,
- 90:10 for Northeastern states, two Himalayan states and the UT of J&K,
- The Centre bears 100% cost in case of other UTs including Ladakh.
-
- Scheme’s Housing Targets:
-
- The updated eligibility criteria are part of the Centre’s broader goal to construct two crore additional houses under the PMAY-G by 2028-29.
-
- Relaxation of Automatic Exclusion Criteria: The following families are now eligible to apply for the rural housing scheme:
-
- Two-wheelers,
- Motorised fishing boats, refrigerators,
- Landline phones,
- Earning up to Rs 15,000 per month.
-
- Parameters for Automatic Exclusion: Despite the relaxations, some criteria will continue to result in automatic exclusion, including:
-
- Owning motorised three/four-wheelers
- Owning mechanised three/four-wheeler agricultural equipment
- Possessing a Kisan Credit Card with a credit limit of Rs 50,000 or above
- Having a household member employed in the government
- Household with non-agricultural enterprises registered with the government
- Any family member paying income tax
- Any family member paying professional tax
- Owning 2.5 acres or more of irrigated land
-
- Benefits: Each beneficiary gets funds:
-
- Up to Rs 1.2 lakh in the plains,
- Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly states, difficult areas, and tribal and backward districts under the Integrated Action Plan (IAP).
-
NIDHI Program
- News: DST NIDHI scheme has led to over 1,200 tech-based products, 233 patents.
- Overview of NIDHI Programme:
-
- The National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI) program was launched in 2016.
- It is an umbrella program developed by the Innovation & Entrepreneurship division, Department of Science & Technology.
-
- Aim of NIDHI:
-
- To nurture start-ups by scouting, supporting, and scaling innovations.
-
- Key Stakeholders:
-
- Various departments and ministries of the central government
- State governments
- Academic and R&D institutions
- Mentors, financial institutions, angel investors, venture capitalists, and private sectors
-
- Funding:
-
- The program is funded by the National Science & Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board (NSTEDB).
-
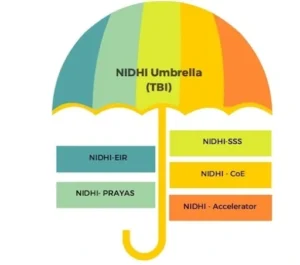
- Key Components of NIDHI:
- NIDHI-PRAYAS: This program supports young innovators by providing mentoring and financial aid to convert ideas into prototypes at the Proof-of-Concept level.
-
- NIDHI Entrepreneurs-In-Residence (EIR) Program: Offers fellowships to students opting for entrepreneurship.
- NIDHI Seed Support Program: Provides early-stage seed funding to start-ups.
- NIDHI Accelerator Program: Accelerates investment readiness for start-ups through a 3-6 month structured fast-track program.
- Infrastructure Development: The NIDHI program has been instrumental in establishing Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) and Centres of Excellence (CoE), creating cutting-edge infrastructure for incubating technology-based start-ups.
-
INDIAsize
- News: The government is set to launch the ‘INDIAsize’ initiative to create standardized measurements for Indian body types, addressing fitting issues with current US and UK standards.
- Definition:
-
- The INDIAsize initiative is launched by the Ministry of Textiles to establish standardized measurements tailored to Indian body types.
-
- Need for INDIAsize:
-
- Currently, international and domestic brands available in India use size measurements from the US or UK, such as ‘small’, ‘medium’, and ‘large’.
- Western body types differ from Indian body types in terms of height, weight, and specific body part measurements.
- This mismatch leads to frequent fitting issues and consumer dissatisfaction, as current sizes do not reflect the diversity of Indian body types.
- The Ministry of Textiles introduced the INDIAsize project to create standardized body sizes for the Indian apparel sector, addressing these disparities.
-
- Project Details:
-
- The project involves gathering anthropometric data from over 25,000 males and females, aged 15 to 65, across India.
- Data will be collected using human-safe 3D whole-body scanning technology.
-
- Significance of INDIAsize:
-
- The created body size chart will enable national and international retailers and manufacturers to produce garments that better suit Indian body types.
- This initiative will help align demand and supply for well-fitted garments.
- Once implemented, INDIAsize will serve as a benchmark for fashion brands selling in India, ensuring improved fit and customer satisfaction.
-
Sugamya Bharat App
- News: The Sugamya Bharat mobile application has received over 1,400 accessibility-related complaints.
- Definition:
-
- The Sugamya Bharat App is an initiative by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is designed to assist people with disabilities and the elderly in reporting accessibility issues in public infrastructure, transportation, and buildings.
-
- Objectives of the Sugamya Bharat App:
-
- Identification of Accessibility Issues: The app allows users to report accessibility problems in public places, capturing the location of the place using Google Maps.
- Uploading Geotagged Pictures: Users can upload geotagged images to identify the type of public place facing accessibility issues.
- Complaint Submission: Any individual facing accessibility-related challenges in India can raise their concerns or grievances through the app.
-
- Scope of Complaints:
-
- Only accessibility related issues pertaining to Buildings, Transportation System and ICT (websites and TV viewing) can be registered at App.
- ICT (Information and Communication Technology) such as websites and TV viewing Complaints are filed by uploading photos, which are then forwarded to the appropriate authorities for resolution.
-
- Future Enhancements: The government plans to upgrade the app with AI capabilities. The new version will feature:
-
- An AI-powered chatbot
- A multilingual interface
- These enhancements aim to improve the overall functionality and accessibility of the app.
-
- Collaborations for Development:
-
- The development of the AI-enabled app involves partnerships with the NGO Mission Accessibility and the research institute I-STEM.
-
UPSC GS 3
Myristica Swamp
- News: Myristica swamp forest discovered in Kumbral, Maharashtra.
- Definition:
-
- Myristica swamps are freshwater swamps dominated by evergreen trees from the Myristicaceae family.
- They are referred to as living fossils due to the primitive nature of Myristica plants.
- The swamps have an evolutionary history of about 140 million years, making them valuable for evolutionary studies.
-
- Characteristics:
-
- The forests are characterized by trees with large protruding roots extending out of waterlogged soil, which remains inundated year-round.
- Myristica swamps typically occur next to rivers, helping to retain water and act as a sponge, ensuring perennial water availability.
- They have a higher capacity to sequester carbon compared to non-swampy forests.
-

- Geographical Distribution:
-
- In India, Myristica swamps are found in the Western Ghats.
- They also have a smaller distribution in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Meghalaya.
- Historically, these swamps formed a large hydrological network throughout the Western Ghats.
-
- Climatic Conditions:
-
- The formation of Myristica swamps depends on abiotic factors such as the shape of the valley between forested hills, the amount of rainfall (typically averaging 3000 mm), and water availability throughout the year.
-
- Ecological Significance:
-
- These swamps support a variety of vertebrate and invertebrate species due to stable macroecological conditions like high humidity, moderate temperature, and the availability of macrohabitats.
- An example of the fauna found in these swamps is the Myristica Swamp Treefrog (Mercurana myristicapalustris), reported from a few pockets of the Shendurney and Peppara Wildlife Sanctuaries in Kerala.
-
INS Malpe and INS Mulki
- News: The Ministry of Defence recently stated in an official statement that the Indian Navy has launched the Malpe and Mulki.
- INS Malpe and INS Mulki:
-
- INS Malpe and INS Mulki are indigenously designed and constructed Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Watercrafts (ASWCWC) for the Indian Navy.
- They are the fourth and fifth ASWCWC being built for the Navy.
- The vessels are constructed by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- A contract to build eight ASWCWC ships was signed between the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and CSL on April 30, 2019.
- The Mahe Class vessels will replace the current Abhay Class ASW Corvettes in the Indian Navy.
-

- Features:
-
- Operational Capabilities: The vessels are designed to conduct anti-submarine operations in coastal waters, engage in low-intensity maritime and mine-laying operations, and perform sub-surface surveillance and search and rescue missions.
- Dimensions: Each vessel is 78.0 meters long, 11.36 meters wide, with a draught of about 2.7 meters.
- Displacement and Speed: The displacement is about 900 tonnes, with a maximum speed of 25 knots and an endurance of 1,800 nautical miles.
- Technology: The ships are equipped with indigenously developed, state-of-the-art SONARS for underwater surveillance.
- Armament: They are fitted with light-weight torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare rockets, a close-in weapon system, and remote-controlled guns.
-
- History:
-
- The names INS Mulki and INS Malpe have historical significance.
- Previously, ships with the same names were imported from Russia as part of a fleet of six mine-sweeping vessels.
- These ships operated between 1984 and 2003 (Mulki) and 2006 (Malpe), primarily detecting mines along the coastline before being decommissioned.
- Mulki was a key port in the state, facilitating trade between India and foreign countries.
- Small ships would travel to Mulki’s coastal waters, where they would then move inland along the Shambhavi river.
- Between the 1930s and 1960s, passenger steamers also operated in the area, and a ferry service connected Udupi and Mangaluru.
- As a result, both Mulki and Malpe appeared on British-era sea charts, cementing their significance.
-
Read also: Understanding Supreme Court Verdict on Sub-Classification of SC ,ST | UPSC
Photoelectric Effect
- News: Albert Einstein won his sole Nobel Prize for explaining the photoelectric effect.
- Definition:
-
- The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon where electrons are emitted from a material’s surface when it is exposed to light of sufficient frequency.
-
- Mechanism:
-
- When light photons hit the surface of a material, typically a metal, they transfer their energy to the electrons.
- If this energy is greater than the electron’s binding energy, known as the work function, the electrons are emitted from the material.
-
- Energy Transfer:
-
- The excess energy from the photon, after overcoming the work function, is converted into the kinetic energy of the ejected electron.
-
- Photoemissive Materials:
-
- A material that exhibits this phenomenon is termed photoemissive, and the ejected electrons are called photoelectrons.
-
- Discovery: The effect was discovered in 1887 by German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz.
- Significance:
-
- Quantum Nature of Light: The photoelectric effect is crucial in understanding the quantum nature of light, as it demonstrates that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties.
- Quantum Mechanics: This duality is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics, showing how light can exhibit characteristics of both waves and discrete particles.
- Applications: The discovery and understanding of the photoelectric effect have significant implications in scientific and technological fields, including the development of photovoltaic cells and advanced imaging technologies.
-
Yellow Food Dye
- News: Recent research has shown that tartrazine, a common food dye, can make the skin of living mice temporarily transparent.
- Yellow Food Dye:
-
- Tartrazine: Also known as Yellow No. 5, tartrazine is a synthetic food colorant classified as an azo dye.
- Appearance: It is lemon yellow in color and water-soluble.
- Uses: Commonly used in dairy products, beverages, desserts, and confectioneries.
- Highlight of the Study:
- Light Absorption:
- Tartrazine absorbs blue light strongly, which gives it its characteristic orange-to-red color when dissolved in water.
- This is due to the absorption of blue light, leaving the orange-to-red light visible.
- Transparency Effect:
- Normally, biological tissues scatter light due to their diverse composition of proteins, fats, and liquids.
- Researchers discovered that a concentrated tartrazine solution can match the refractive indices of these components, reducing light scattering and allowing light to pass through, making the skin appear transparent.
- Visualization:
- When applied, tartrazine absorbs certain wavelengths of light, particularly red light, altering how light interacts with the tissue.
- This effect allowed researchers to observe blood vessels, internal organs, and muscle contractions in real-time.
- Potential Applications: This technique could simplify blood draws, enhance laser tattoo removal, and improve early cancer detection.
-

