UPSC GS 2
Union Budget
- News: Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently presented the first budget of the Narendra Modi government’s third term in Parliament.
- Key Focus Areas: The Finance Minister laid down nine priorities of the Budget:
-
- Productivity and resilience in agriculture
- Employment and skilling
- Inclusive Human resource development and social justice
- Manufacturing and services
- Support for promotion of MSMEs
- Urban development
- Energy security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, research and development
Read also: Understanding Overview of Economic Survey | UPSC
Priority 1: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
- Transforming Agriculture Research:
-
- A comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup will be undertaken to focus on raising productivity and developing climate-resilient varieties.
- Funding will be provided in a challenge mode, including to the private sector.
- Domain experts from both the government and outside will oversee the conduct of such research.
- Release of New Varieties:
-
- New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation by farmers.
- Natural Farming:
-
- In the next two years, 1 crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming supported by certification and branding.
- Implementation will be through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres will be established.

- Missions for Pulses and Oilseeds:
-
- A strategy is being put in place to achieve ‘atmanirbharta’ for oilseeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soybean, and sunflower.
- Vegetable Production & Supply Chains:
-
- Large-scale clusters for vegetable production will be developed closer to major consumption centres.
- Farmer-Producer Organizations, cooperatives, and start-ups will be promoted for vegetable supply chains, including for collection, storage, and marketing.
- Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture:
-
- Implementation of the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture for coverage of farmers and their lands will be facilitated in partnership with the states within 3 years.
- Digital crop survey for Kharif using the DPI will be taken up in 400 districts this year.
- Details of 6 crore farmers and their lands will be brought into the farmer and land registries.
- Issuance of Jan Samarth based Kisan Credit Cards will be enabled in 5 states.
- Shrimp Production & Export:
-
- Financial support for setting up a network of Nucleus Breeding Centres for Shrimp Broodstocks will be provided.
- Financing for shrimp farming, processing, and export will be facilitated through NABARD.
- National Cooperation Policy:
-
- A National Cooperation Policy will be brought out for the systematic, orderly, and all-round development of the cooperative sector.
- The policy goal will be fast-tracking the growth of the rural economy and generating employment opportunities on a large scale.
- Financial Provision
- A provision of ₹ 52 lakh crore for agriculture and allied sectors has been made this year.
Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
- Employment Linked Incentive:
-
- Three schemes under the Prime Minister’s package for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ will be implemented, based on EPFO enrolment and focusing on first-time employees and support for employees and employers.
- Scheme A: First Timers:
-
- One month’s wage as subsidy (maximum `15,000)
- Applicable to all sectors
- First timers have a learning curve before they become fully productive; subsidy is to assist employees and employers in hiring of first timers.
- Applicable to all persons newly entering the workforce (EPFO) with wage/salary less than Rs. 1 lakh per month.
- Subsidy will be paid to the employee in three instalments
- Employee must undergo compulsory online Financial Literacy course before claiming the second instalment.
- Subsidy to be refunded by employer if the employment to the first timer ends within 12 months of recruitment.
- Expected to cover approximately one crore persons per annum.
- Scheme will be for 2 years
- Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
-
- Incentivizes additional employment in the manufacturing sector, linked to first-time employees.
- All employers which are corporate entities and those non-corporate entities with a three year track record of EPFO contribution will be eligible.
- Employer must hire at least the following number of previously non-EPFO enrolled workers: 50 or 25% of the baseline (previous year’s number of EPFO employees)
- Incentive will be paid for four years partly to the employee and partly to the employer as follows:
- Employer must maintain threshold level of enhanced employment throughout, failing which subsidy benefit will stop.
- Employee must be directly working in the entity paying salary/wage (i.e. in-sourced employee).
- Employees with a wage/ salary of up to `1 lakh per month will be eligible, subject to contribution to EPFO.
- For those with wages/salary greater than `25,000/month, incentive will be calculated at `25,000/month.
- Subsidy to be refunded by employer if the employment to first timer ends within 12 months of recruitment.
- Scheme will be for 2 years
- Scheme C: Support to Employers
-
- Additional employment within a salary of ₹ 1 lakh per month will be counted.
- Government will reimburse up to ₹ 3,000 per month for 2 years towards employers’ EPFO contribution for each additional employee.
- Expected to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh persons.
- Applicable to an employer who:
- Increases employment above the baseline (previous year’s number of EPFO employees) by at least two employees (for those with less than 50 employees) or 5 employees (for those with 50 or more employees) and sustains the higher level, and
- For employees whose salary does not exceed `1,00,000/month
- New employees under this Part need not be new entrants to EPFO
- If the employer creates more than 1000 jobs:
- Reimbursement will be done quarterly for the previous quarter
- Subsidy will continue for the 3rd and 4th year on the same scale as Employer benefit in Part-B
- Scheme will be for 2 years
- Expected to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh persons.
- Participation of Women in the Workforce:
-
- Setting up working women hostels in collaboration with industry and establishing creches.
- Skilling Programme:
-
- A new centrally sponsored scheme for skilling in collaboration with state governments and industry.
- 20 lakh youth to be skilled over a 5-year period.
- 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes will be upgraded in hub and spoke arrangements with outcome orientation.
- Total outlay of ` 60,000 crore over five years
- Government of India—` 30,000 crore
- State Governments—` 20,000 crore
- Industry—` 10,000 crore (including CSR funding)
- 200 hubs and 800 spoke ITIs –all with industry collaboration
- Re-design and review of existing courses
- New courses
- 1 to 2 year courses in all 1000 ITIs
- Short term specialised courses in Hub ITIs
- Capacity augmentation of 5 national institutes for training of trainers.
- Skilling Loans:
-
- The Model Skill Loan Scheme will be revised to facilitate loans up to ₹ 5 lakh with a guarantee from a government-promoted fund.
- Expected to help 25,000 students every year.
- Education Loans:
-
- Financial support for loans up to ₹ 10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions.
- E-vouchers for annual interest subvention of 3 per cent of the loan amount will be given directly to 1 lakh students every year.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Saturation Approach:
-
- Adoption of a saturation approach to cover all eligible people through various programs for education and health.
- Empowerment by improving capabilities through schemes for craftsmen, artisans, self-help groups, scheduled caste, scheduled tribe, women entrepreneurs, and street vendors.
- Implementation of PM Vishwakarma, PM SVANidhi, National Livelihood Missions, and Stand-Up India will be stepped up.
- Purvodaya:
-
- Formulation of the Purvodaya plan for the all-round development of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Coverage includes human resource development, infrastructure, and economic opportunities.
- Support for development on the Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor, including an industrial node at Gaya.
- Development of road connectivity projects: Patna-Purnea Expressway, Buxar-Bhagalpur Expressway, Bodhgaya, Rajgir, Vaishali, and Darbhanga spurs, and an additional 2-lane bridge over river Ganga at Buxar.
- Power projects, including a new 2400 MW power plant at Pirpainti, will be undertaken.
- New airports, medical colleges, and sports infrastructure in Bihar will be constructed.
- Additional allocation for capital investments and expedited external assistance from multilateral development banks for Bihar.
- Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act:
-
- Facilitation of special financial support for the state’s capital through multilateral development agencies.
- Arrangement of ₹ 15,000 crore in the current financial year, with additional amounts in future years.
- Commitment to financing and early completion of the Polavaram Irrigation Project.
- Promotion of industrial development with funds for essential infrastructure in Kopparthy node on the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and Orvakal node on Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
- Additional allocation for capital investment and grants for backward regions of Rayalaseema, Prakasam, and North Coastal Andhra.
- PM Awas Yojana:
-
- Announcement of three crore additional houses under PM Awas Yojana in rural and urban areas, with necessary allocations.
- Women-Led Development:
-
- Allocation of more than ₹ 3 lakh crore for schemes benefitting women and girls, promoting women-led development.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan:
-
- Launch of Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan to improve the socio-economic condition of tribal communities.
- Saturation coverage for tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts, covering 63,000 villages and benefiting 5 crore tribal people.
- Bank Branches in North-Eastern Region:
-
- Establishment of more than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank in the North East region to expand banking services.
- Rural Development Provision:
-
- A provision of ₹ 66 lakh crore for rural development, including rural infrastructure, has been made.
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
- Support for Promotion of MSMEs:
-
- Special attention will be given to MSMEs and labour-intensive manufacturing through financing, regulatory changes, and technology support.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector:
-
- Term loans for MSMEs for machinery and equipment purchase without collateral.
- Operated through pooling credit risks of MSMEs.
- Self-financing guarantee fund to provide up to ₹ 100 crore guarantee cover per applicant.
- Borrower to provide an upfront guarantee fee and annual fee on the reducing loan balance.
- New Assessment Model for MSME Credit:
-
- Public sector banks to build in-house capability for MSME credit assessment.
- Development of a new credit assessment model based on MSME digital footprints.
- Model to include MSMEs without formal accounting systems.
- Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period:
-
- New mechanism for continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during stress periods.
- Support for credit availability through a government-promoted guarantee fund.
- Mudra Loans:
-
- Mudra loan limit increased to ₹ 20 lakh from ₹ 10 lakh for entrepreneurs who have successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category.
- Enhanced Scope for Mandatory Onboarding in TReDS:
-
- Turnover threshold for mandatory onboarding on TReDS platform reduced from ₹ 500 crore to ₹ 250 crore.
- Inclusion of 22 more CPSEs and 7000 more companies.
- Medium enterprises included in the scope of suppliers.
- SIDBI Branches in MSME Clusters:
-
- SIDBI to open new branches to serve all major MSME clusters within 3 years.
- 24 branches to open this year, expanding service coverage to 168 out of 242 major clusters.
- MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing:
-
- Financial support for setting up 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector.
- Facilitation of 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation.
- E-Commerce Export Hubs:
-
- E-Commerce Export Hubs to be set up in PPP mode for MSMEs and traditional artisans.
- Hubs to facilitate trade and export-related services under one roof.
- Measures for Promotion of Manufacturing & Services:
- Internship in Top Companies:
-
- Launch of a scheme for internship opportunities in 500 top companies for 1 crore youth over 5 years.
- Interns to receive ₹ 5,000 per month allowance and ₹ 6,000 one-time assistance.
- Companies to cover training costs and 10% of internship costs from CSR funds.
- Applicable to those who are not employed and not engaged in full time education.
- Youth aged between 21 and 24 will be eligible to apply.
- Cost sharing (per annum):
- Government – `54,000 towards monthly allowance (plus `6,000 grant for incidentals)
- Company – Rs 6,000 from CSR funds towards monthly allowance
- Training cost to be borne by the Company from CSR funds.
- Administrative costs to be borne by respective parties (for the Company, reasonable administrative expenses can be counted as CSR expenditure)
- Participation of companies is voluntary.
- Ineligible candidates (indicative list)
- Candidate has IIT, IIM, IISER, CA, CMA etc as qualification
- Any member of the family is assessed to Income Tax
- Any member of the family is a government employee, etc.
- At least half the time should be in actual working experience/job environment, not in classroom.
- Phase 1 of the scheme will be for 2 years followed by Phase 2 for 3 years
- Industrial Parks:
-
- Development of “plug and play” industrial parks in or near 100 cities in partnership with states and the private sector.
- Twelve industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme to be sanctioned.
- Rental Housing:
-
- Facilitation of dormitory-type rental housing for industrial workers in PPP mode with VGF support and commitment from anchor industries.
- Shipping Industry:
-
- Implementation of ownership, leasing, and flagging reforms to improve the Indian shipping industry’s share and generate employment.
- Critical Mineral Mission:
-
- Establishment of a Critical Mineral Mission for domestic production, recycling, and overseas acquisition of critical minerals.
- Mandate includes technology development, skilled workforce, extended producer responsibility framework, and suitable financing mechanism.
- Offshore Mining of Minerals:
-
- Launch of the first tranche of offshore blocks for mining, building on existing exploration.
- Digital Public Infrastructure Applications:
-
- Development of DPI applications for productivity gains, business opportunities, and innovation in credit, e-commerce, education, health, law and justice, logistics, MSME, services delivery, and urban governance.
- Integrated Technology Platform for IBC Ecosystem:
-
- Setup of an Integrated Technology Platform for improving outcomes under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
- Voluntary Closure of LLPs:
-
- Extension of C-PACE services for voluntary closure of LLPs to reduce closure time.
- National Company Law Tribunals:
-
- Reforms and strengthening of tribunals to speed up insolvency resolution.
- Establishment of additional tribunals, some to decide cases exclusively under the Companies Act.
- Debt Recovery:
-
- Reforming and strengthening debt recovery tribunals.
- Establishment of additional tribunals to speed up recovery.
Priority 5: Urban Development
- Cities as Growth Hubs:
-
- Development of ‘Cities as Growth Hubs’ through economic and transit planning.
- Orderly development of peri-urban areas using town planning schemes in collaboration with states.
- Creative Redevelopment of Cities:
-
- Formulation of a framework for enabling policies, market-based mechanisms, and regulation for brownfield redevelopment of existing cities.
- Transit-Oriented Development:
-
- Formulation of Transit-Oriented Development plans for 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh.
- Implementation and financing strategy to be included.
- Urban Housing:
-
- Addressing housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families under PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0.
- Investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore, with ₹ 2.2 lakh crore central assistance over the next 5 years.
- Provision of interest subsidy for affordable housing loans.
- Implementation of enabling policies and regulations for efficient and transparent rental housing markets.
- Water Supply and Sanitation:
-
- Promotion of water supply, sewage treatment, and solid waste management projects for 100 large cities in partnership with State Governments and Multilateral Development Banks.
- Street Markets:
-
- Scheme to support the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities each year for the next five years, building on the PM SVANidhi Scheme.
- Stamp Duty:
-
- Encouragement for states with high stamp duty to moderate rates.
- Consideration of further lowering duties for properties purchased by women.
Priority 6: Energy Security
- Energy Transition:
-
- Policy on energy transition pathways balancing employment, growth, and environmental sustainability will be introduced.
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana:
-
- Launched to install rooftop solar plants for 1 crore households to obtain free electricity up to 300 units per month.
- Scheme has generated 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications.
- Pumped Storage Policy:
-
- Promotion of pumped storage projects for electricity storage.
- Facilitation of smooth integration of renewable energy into the overall energy mix.
- Small and Modular Nuclear Reactors: Partnership with the private sector for:
-
- Setting up Bharat Small Reactors.
- Research & development of Bharat Small Modular Reactor.
- Research & development of newer technologies for nuclear energy.
- Advanced Ultra Super Critical Thermal Power Plants:
-
- Development of indigenous technology for AUSC thermal power plants completed.
- Joint venture between NTPC and BHEL to set up an 800 MW commercial plant using AUSC technology.
- Government to provide fiscal support.
- Development of indigenous capacity for high-grade steel and advanced metallurgy materials.
- Roadmap for ‘Hard to Abate’ Industries:
-
- Formulation of a roadmap for moving ‘hard to abate’ industries from ‘energy efficiency’ targets to ‘emission targets’.
- Implementation of regulations for transition from ‘Perform, Achieve and Trade’ mode to ‘Indian Carbon Market’ mode.
- Support to Traditional Micro and Small Industries:
-
- Facilitation of investment-grade energy audits in 60 clusters, including brass and ceramic.
- Provision of financial support for cleaner energy and energy efficiency measures.
- Replication of the scheme in another 100 clusters in the next phase.
Priority 7: Infrastructure
- Infrastructure Investment by Central Government:
- Fiscal Support: Commitment to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, balancing other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
- Capital Expenditure: Provision of ₹11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure, constituting 3.4% of GDP.
- Infrastructure Investment by State Governments:
-
- Support Encouragement: States encouraged to provide similar scale support for infrastructure, considering their development priorities.
- Long-term Loans: Provision of ₹5 lakh crore for long-term interest-free loans to support states’ resource allocation.
- Private Investment in Infrastructure:
-
- Promotion: Investment by the private sector promoted through viability gap funding, enabling policies, and regulations.
- Financing Framework: Introduction of a market-based financing framework.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY):
-
- Phase IV Launch: Launch of Phase IV to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations with increased population.
- Irrigation and Flood Mitigation:
-
- Bihar Flood Control: Financial support for projects estimated at ₹11,500 crore, including Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and other schemes.
- Assam Flood Assistance: Assistance for flood management and related projects.
- Himachal Pradesh Rehabilitation: Assistance for reconstruction and rehabilitation through multilateral development assistance.
- Uttarakhand Cloud Burst Relief: Assistance for losses due to cloud bursts and landslides.
- Sikkim Flash Flood Relief: Assistance for recent flash floods and landslides.
- Tourism Development:
-
- Global Tourist Destination: Positioning India as a global tourist destination to create jobs, stimulate investments, and unlock economic opportunities.
- Bihar Temples: Comprehensive development of Vishnupad Temple Corridor and Mahabodhi Temple Corridor in Bihar, modelled on Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor.
- Rajgir Development: Comprehensive initiative for Rajgir, significant for Hindus, Buddhists, and Jains.
- Nalanda: Development of Nalanda as a tourist centre and revival of Nalanda University.
- Odisha Tourism: Assistance for development of Odisha’s temples, monuments, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes, and beaches.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
- Research and Innovation:
- Anusandhan National Research Fund: Operationalization of the fund for basic research and prototype development.
- Private Sector Research: Establishment of a mechanism to spur private sector-driven research and innovation at a commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore.
- Space Economy:
- Expansion Goal: Commitment to expanding the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years.
- Venture Capital Fund: Creation of a venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore to support this expansion.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
- Economic Policy Framework:
-
-
- A new framework will be formulated to delineate the approach to economic development.
- Collaboration with States: Effective implementation of reforms will require collaboration between the Centre and states, promoting competitive federalism and incentivizing states for faster implementation of reforms through a significant portion of the 50-year interest-free loan.
- Rural Land Actions:
-
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) for all lands.
- Digitization of cadastral maps.
- Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership.
- Establishment of land registry.
- Linking to the farmers registry to facilitate credit flow and other agricultural services.
- Urban Land Actions:
-
- Digitization of land records with GIS mapping.
- Establishment of an IT-based system for property record administration, updating, and tax administration to improve the financial position of urban local bodies.
- Labour-Related Reforms:
- Services to Labour: Comprehensive integration of the e-shram portal with other portals for a one-stop solution for employment and skilling services.
-
- Open architecture databases for the labour market, skill requirements, and available job roles.
- Shram Suvidha & Samadhan Portal: Revamp of these portals to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.
- Capital and Entrepreneurship Reforms:
-
- Financial Sector Vision and Strategy: A document will be prepared to meet the financing needs of the economy, guiding the government, regulators, financial institutions, and market participants for the next 5 years.
- Climate Finance Taxonomy: Development of a taxonomy for climate finance to enhance capital availability for climate adaptation and mitigation, supporting the country’s climate commitments and green transition.
- Variable Capital Company Structure: Legislative approval will be sought for this structure to provide efficient and flexible financing for leasing aircrafts and ships, and pooled funds of private equity.
- FDI and Overseas Investment: Simplification of rules and regulations for Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investments to facilitate foreign investments, nudge prioritization, and promote the use of the Indian Rupee for overseas investments.
- NPS Vatsalya: Launch of a plan for parents and guardians to contribute to the National Pension Scheme for minors, with seamless conversion to a normal NPS account upon reaching adulthood.
- Ease of Doing Business:
-
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0: Further enhancement of the Ease of Doing Business.
- State Incentives: Incentives for states to implement their Business Reforms Action Plans and digitalization.
- Data and Statistics:
- Data Governance: Improvement of data governance, collection, processing, and management using technology tools and sectoral databases established under the Digital India mission.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS):
-
- NPS Review Committee: Progress by the committee to address relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.
- Budget Estimates 2024-25:
-
- Receipts and Expenditure: Total receipts (excluding borrowings) estimated at ₹48.07 lakh crore and total expenditure at ₹48.21 lakh crore.
- Net Tax Receipts: Estimated at ₹25.83 lakh crore.
- Fiscal Deficit: Estimated at 4.9% of GDP.
- Borrowings: Gross and net market borrowings through dated securities estimated at ₹13.01 lakh crore and ₹11.63 lakh crore, respectively.
- Fiscal Consolidation: Commitment to reach a fiscal deficit below 4.5% next year and maintain a declining Central Government debt path as a percentage of GDP from 2026-27 onwards.
Indirect Taxes
- Medicines and Medical Equipment:
-
- Cancer Medicines: Full exemption from customs duties on three additional cancer medicines: Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, Durvalumab.
- Medical X-ray Equipment: Changes in the Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on x-ray tubes and flat panel detectors for medical x-ray machines under the Phased Manufacturing Programme to synchronize with domestic capacity addition.
- Mobile Phone and Related Parts:
-
- Reduction in Basic Customs Duty (BCD): Reduction in BCD on mobile phones, mobile PCBA, and mobile chargers to 15% to benefit consumers.
- Critical Minerals:
-
- Customs Duty Exemptions: Full exemption on customs duties for 25 critical minerals, with reduced BCD on two of them (silicon quartz and silicon dioxide, BCD has been reduced from 5-7.5% to 2.5%.).
- Critical Mineral Mission: The government will set up a Critical Mineral mission for domestic production, recycling of critical minerals, and overseas acquisition of critical mineral assets.
- Solar Energy:
-
- Expanded Exemptions: Expansion of the list of exempted capital goods for manufacturing solar cells and panels.
- Customs Duty on Solar Glass and Tinned Copper: Non-extension of customs duty exemptions due to sufficient domestic manufacturing capacity.
- Marine Products:
-
- BCD Reduction: Reduction of BCD on certain broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimp, and fish feed to 5%.
- Customs Duty Exemptions: Customs duty on inputs for manufacture of shrimp, fish feed, leather goods, textile and apparel and footwear have also been exempted.
- Leather and Textile:
-
- Competitiveness Enhancement: Reduction of BCD on real down filling material from duck or goose.
- Exemptions: There will be no duty on wet white, crust, and finished leather for manufacture of garments, footwear and other leather products for exports.
- Duty Inversion Rectification: Reduction of BCD on methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) for manufacturing spandex yarn from 7.5% to 5%.
- Export Duty Structure: Simplification and rationalization of the export duty structure on raw hides, skins, and leather.
- Precious Metals:
-
- Gold and Silver: Reduction of customs duties on gold and silver to 6% and on platinum to 6.4% to enhance domestic value addition in gold and precious metal jewellery.
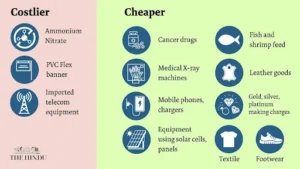
- Other Metals:
-
- Production Cost Reduction: Removal of BCD on ferro nickel and blister copper.
- Continuation of Nil BCD: Continuation of nil BCD on ferrous scrap and nickel cathode, and concessional BCD of 2.5% on copper scrap.
- Electronics:
-
- Value Addition: Removal of BCD on oxygen-free copper for manufacturing resistors, subject to conditions.
- Chemicals and Petrochemicals:
- BCD Increase: Increase in BCD on ammonium nitrate from 7.5% to 10% to support existing and new capacities in the pipeline.
- Plastics:
-
- BCD Increase: Increase in BCD on PVC flex banners from 10% to 25% to curb imports of non-biodegradable and hazardous materials.
- Telecommunication Equipment:
-
- BCD Increase: Increase in BCD from 10% to 15% on PCBA of specified telecom equipment to incentivize domestic manufacturing.
- Trade Facilitation:
-
- Export and Re-import Extensions: Extension of the export period for goods imported for repairs from six months to one year, and the time limit for re-import of goods for repairs under warranty from three to five years, to promote domestic aviation and boat & ship maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO).
See more: Budget 2024 For India By Finance Minister | UPSC
Direct Taxes:
- Simplification for Charities and TDS:
- Merging Tax Exemption Regimes: Two tax exemption regimes for charities merged into one.
-
- Merging 5% TDS rate into 2% TDS rate.
- Withdrawal of 20% TDS rate on mutual funds or UTI repurchase.
- Reduction of TDS rate on e-commerce operators from 1% to 0.1%.
- Credit of TCS in the TDS deducted on salary.
- Decriminalization of delay in TDS payment up to the due date of filing statements.
- Simplification of Reassessment:
-
- Reopening and Reassessment: Reopening beyond three years if escaped income is ₹ 50 lakh or more, up to five years.
- In search cases, reducing the time limit from ten years to six years before the year of search.
- Simplification and Rationalization of Capital Gains:
-
- Short-term Gains: Short Term Capital Gains (STCG) tax on some assets will be increased from 15% to 20%
- Long-term Gains: Long Term Capital Gains (LTCG) tax on all financial and non-financial asset will be hiked from 10 to 12.5% Increased exemption limit on capital gains on certain financial assets to ₹ 1.25 lakh per year.
- Classification as long-term Gains: Listed financial assets held for more than a year, unlisted financial assets, and non-financial assets held for at least two years.
- Tax on capital gains at applicable rates for unlisted bonds, debentures, debt mutual funds, and market-linked debentures irrespective of holding period.
- Taxpayer Services:
-
- Digitalization: All major GST taxpayer services and most Customs and Income Tax services digitalized. Remaining services to be digitalized over the next two years.
- Litigation and Appeals:
-
- Reducing Pendency: Deploying more officers for first appeals, proposing Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024.
- Monetary Limits for Appeals: Increase monetary limits for filing appeals related to direct taxes, excise and service tax in the Tax Tribunals, High Courts and Supreme Court to Rs 60 lakh, Rs 2 crore and Rs 5 crore, respectively.
- Employment and Investment:
-
- Abolishing Angel Tax: For all classes of investors to bolster the start-up ecosystem.
- Cruise Tourism: Simpler tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises. Fixed profit and gains of cruise-ship operators to 20% of aggregate amount received.
- Diamond Industry: Safe harbour rates for foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds in India.
- Corporate Tax Rate: Tax rates for foreign companies will be slashed to 35% from current tax rate of 40%.
- Deepening the Tax Base:
-
- Security Transactions Tax: The government increased the STT on sale of security option from 0.0625% to 0.1%, while tax levied on futures was increased from 0.0125% to 0.02%, in Budget 2024.
- Increase to 0.02% on futures and 0.1% on options.
- Buyback Tax: Tax income received on buyback of shares in the hands of the recipient.
- Other Proposals:
-
- NPS Contributions: NPS limit for employers in the private sector is raised from 14% to 10% of the employee’s basic salary.
- Non-reporting Penalties: Indian professionals working in multinationals get ESOPs and invest in social security schemes and other movable assets abroad. De-penalizing non-reporting of movable assets abroad up to ₹ 20 lakh under the Black Money Act.
- Finance Bill Proposals:
-
- Withdrawal of equalization levy of 2%.
- Expansion of tax benefits to certain funds and entities in IFSCs.
- Immunity from penalty and prosecution for benamidar on full and true disclosure.
- Personal Income Tax:
-
- Standard Deduction: Standard deduction to salaried individuals and pensioners is proposed to be increased from ₹ 50,000 to₹ 75,000 under the new tax regime.
- Family Pension Deduction: Deduction from family pension of Rs. 15,000 is proposed to be increased to ₹ 25,000 under the new tax regime.
- Tax Rate Structure (New Regime):

-
-
- As a result of these changes, a salaried employee in the new tax regime stands to save up to ₹ 17,500/- in income tax.




