UPSC GS 1
Mount Fuji
- News: A town in Japan is taking steps to stop tourists from causing trouble while attempting to capture the perfect picture of Mount Fuji.
- Overview of Mount Fuji:
-
- Mount Fuji is the tallest peak in Japan, soaring to an elevation of 3,776 meters.
- Situated approximately 100 kilometers west of Tokyo, the capital city of Japan, it is located on Honshu Island, near the Pacific Coast.
-
- Geological Characteristics:
-
- Unlike many other renowned high-elevation mountains worldwide, Mount Fuji does not form part of an extensive mountain range.
- Rather, it is characterized as a solitary stratovolcano.
- Constructed from numerous basaltic lava flows, each several meters thick, Mount Fuji features a prominent summit crater.
- It exhibits a smooth slope and expansive base, culminating in a majestic peak.
-

- Volcanic Activity and Formation:
-
- Mount Fuji’s volcanic activity is primarily attributed to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Philippine Plate, resulting in the accumulation of magma beneath the Earth’s surface.
- Despite its volcanic nature, the mountain’s summit remains snow-covered throughout much of the year, contributing to its iconic imagery and allure.
-
- UNESCO World Heritage Site Designation:
-
- Recognizing its cultural and natural significance, Mount Fuji was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2013.
-
Cascadia Subduction Zone
- News: Cascadia Subduction Zone, one of Earth’s top hazards, has come into sharper focus.
- Overview of the Cascadia Subduction Zone (CSZ):
-
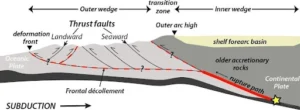
- The Cascadia Subduction Zone (CSZ) is a prominent geological feature situated off the western coast of North America, spanning from northern California to southern British Columbia.
- It represents an active convergent boundary where the Juan de Fuca Plate undergoes subduction beneath the North American Plate.
-
- Geological Significance:
-
- The CSZ plays a pivotal role in shaping the geological landscape of the region, facilitating the movement and interaction of tectonic plates.
- Its subduction process leads to significant implications for seismic activity and geological hazards in the surrounding area.
-
- Earthquake and Tsunami Risks:
-
- The CSZ has the potential to generate massive earthquakes, some of which may reach magnitudes of 9.0 or greater.
- Eg: A comparable fault off the coast of Japan was responsible for the catastrophic Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011.
-
UPSC GS 2
Proportional Representation (PR)
- News: India follows the First Past the Post System (FPTP) in elections to the Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies.
- Election System in India : The method of election prescribed by the Indian Constitution is as follows:
-
- Plurality System or First Past the Post System (FPTP):
- Under this system, the entire country is divided into 543 constituencies.
- Each constituency elects one representative; and the candidate who secures the highest number of votes in that constituency is declared elected.
- FPTP has been adopted in India as it can be easily understood by common voters who have no specialized knowledge about politics and elections.
- Proportional Representation (PR):
- In this system of election, once the votes are counted, each party is allotted the share of seats in the Parliament in proportion to its share of votes.
- In India, PR system is prescribed for the election of President, Vice President, and for the election to the Rajya Sabha and Vidhan Parishads.
-
| FPTP | PR |
| The country is divided into small geographical units called constituencies or districts. | Large geographical areas are demarcated as constituencies. The entire country may be a single constituency. |
| Every constituency elects one representative. | More than one representative may be elected from one constituency. |
| Voter votes for a candidate. | Voter votes for the party. |
| A party may get more seats than votes in the legislature. | Every party gets seats in the legislature in proportion to the percentage of votes that it gets. |
| Candidate who wins the election may not get the majority (50%+1) votes . | Candidate who wins the elections gets majority of votes. |
| The voters know who their own representative is and can hold him or her accountable. | Voters choose a party and the representatives are elected on the basis of party lists. Hence, there is no one representative who represents and is responsible for one locality. |
| It gives the largest party or coalition some extra bonus seats, more than their share of votes would allow. | It may not produce a clear majority because seats in the legislature would be divided on the basis of share of votes. |
| FPTP makes it possible for parliamentary government to function smoothly and effectively by facilitating the formation of a stable government. | PR based election may not be suitable for giving a stable government in a parliamentary system. |
| FPTP encourages voters from different social groups to come together to win an election in a locality. | In a diverse country like India, a PR system would encourage each community to form its own nation-wide party. |
| Examples: U.K., India | Examples: Israel, Netherlands |
- Mixed Member Proportional Representation (MMPR):
-
- To balance stability and proportionate representation, the Mixed Member Proportional Representation (MMPR) system can be considered in India.
- Under MMPR, there is one candidate elected through FPTP from each territorial constituency, and additional seats are allocated to parties proportionally based on their vote share.
- Example: Germany, and New Zealand
-
Santiago Network for Loss and Damage
- News: The third Glasgow Dialogue on Loss and Damage recently took place in Bonn, Germany.
- Definition: Santiago Network is a global initiative aimed to support developing countries in averting, minimizing, and addressing loss and damage caused by climate change.
- Launch: The Santiago Network was established at COP 25 in Madrid.
-
- It was established as part of the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage associated with Climate Change Impacts under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
-
- Key Objectives:
-
- Technical Assistance:
- The Santiago Network provides technical assistance to developing countries, facilitating their efforts to address climate change-related loss and damage.
- This assistance encompasses access to knowledge, resources, and expertise.
- Capacity Building:
- The network aims to enhance capacity by connecting vulnerable nations with a range of technical assistance providers.
- These providers include academic institutions, organizations, civil society entities, and the private sector.
- Facilitation of Loss & Damage Fund:
- The network plays a crucial role in ensuring the effective utilization of the Loss & Damage Fund established during COP28.
- This involves coordinating and facilitating access to the fund for developing countries.
- Technical Assistance:
-
Read also: Paper Leaks in India: Reasons, Consequences and Solutions | UPSC
National Health Claim Exchange
- News: The Health Ministry along with the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) are launching the National Health Claim Exchange (NHCX).
- National Health Claim Exchange (NHCX):
-
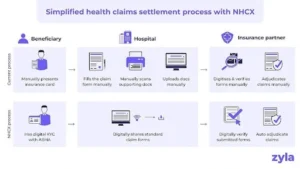
- It is a digital platform designed to integrate insurance companies, healthcare service providers, and government insurance scheme administrators.
- It serves as a gateway for the exchange of claims-related information among various stakeholders within the healthcare and health insurance ecosystem.
-
- Key Features and Benefits:
-
- Seamless Interoperability:
- The integration with NHCX is expected to enable seamless interoperability of health claims processing.
- This enhancement will improve efficiency and transparency in the insurance industry, providing significant benefits to both policyholders and patients.
- Alignment with Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission:
- The NHCX aligns with the goals of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, which seeks to simplify the health insurance claims procedure.
- The mission aims to create a unified digital platform for healthcare services, and the NHCX plays a crucial role in achieving this objective by streamlining the claims process.
- Seamless Interoperability:
-
Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS)
- News: PM Modi along with 71 ministers, including 30 Cabinet ministers, 5 ministers of state (Independent charge) and 36 Ministers of State (MoS) were recently sworn in.
- Overview of the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS):
-
- The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) is a high-level committee chaired by the Prime Minister of India.
- It serves as the apex body for deliberating on matters pertaining to national security, defence policy, and expenditure.
-
- Composition
-
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister
- Members: Ministers of Defence, Home Affairs, Finance, and External Affairs
-
- Functions of the CCS:
- Decision-Making on National Security:
-
- The CCS deliberates on appointments of officials in national security bodies, making it the apex authority in this regard.
- It plays a crucial role in formulating and implementing defence policy and expenditure decisions, as well as matters related to India’s overall security.
-
- Addressing Defence and Security Issues:
-
- The CCS addresses a wide array of issues concerning the defence and security of India, ensuring comprehensive coverage in strategic planning.
- It also deals with law and order matters, recognizing their significance in maintaining national security.
-
- Enhancing National Security:
-
- The committee discusses and evaluates various initiatives aimed at enhancing the national security apparatus of India, ensuring a proactive approach to security challenges.
-
- Foreign Policy Implications
-
- In addition to domestic matters, the CCS handles policy matters of foreign affairs with potential security implications, including agreements with other countries on security-related issues.
-
- Political Considerations:
-
- The CCS engages in discussions regarding political issues that could impact the security landscape of the nation, ensuring a holistic approach to national security management.
-
UPSC GS 3
Green Ammonia Production
- News: The Solar Energy Corporation of India has initiated competitive bidding for total available capacity of 5.39 lakh MT/annum of Green Ammonia intended for production and supply.
- More on News: This move is under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Programme, managed by the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Programme:
- Definition: The SIGHT Programme is a major financial measure under the National Green Hydrogen Mission, managed by the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- Aim: The programme consists of two distinct financial incentive mechanisms:
-
- Component I: Provides incentives for domestic electrolyser manufacturing with a total outlay of INR 4,440 crore.
- Component II: Focuses on green hydrogen production with a financial outlay of INR 13,050 crore.
-
- Implementing Agency:
-
- The Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) is the implementing agency for the SIGHT Programme.
- SECI has issued a Request for Selection (RfS) to identify and select producers for the production and supply of Green Ammonia in India.
-
- Green Ammonia:
-
- What is ammonia?
- Ammonia is a compound of hydrogen and nitrogen.
- It is a colourless gas with a distinct smell produced naturally in the environment.
- In the environment, ammonia is part of the nitrogen cycle and is produced in soil from bacterial processes.
- Ammonia is also produced naturally from decomposition of organic matter, including plants and animals.
- It is also produced by industry for use in agriculture as fertiliser, a refrigerant gas, for purification of water supplies and in the manufacture of plastics, textiles, dyes and other chemicals.
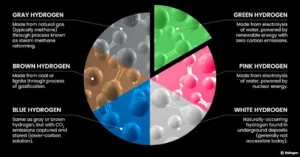
- What is green ammonia?
- Green ammonia is made by using hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air.
- These are then fed into the Haber process (also known as Haber-Bosch), all powered by sustainable electricity.
- In the Haber process, hydrogen and nitrogen are reacted together at high temperatures and pressures to produce ammonia, NH3.
- What is ammonia?
-
- Green Hydrogen Production:
-
- Green Hydrogen is produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrolyser powered by electricity generated from renewable energy sources.
-
- National Green Hydrogen Mission:
-
- Launched on January 4, 2023, the National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to promote the production and usage of Green Hydrogen.
- It has a total outlay of Rs. 19,744 crores up to FY 2029-30.
- This mission will significantly contribute to India’s goal of becoming Aatmanirbhar (self-reliant) through clean energy, serving as an inspiration for the global clean energy transition.
- It aims to achieve substantial decarbonization of the economy, reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports, and position India as a leader in Green Hydrogen.
-
White Phosphorous Bombs
- News: Israel continues to use white phosphorus munitions in south Lebanon, causing lasting damage and driving villagers away.
- Characteristics of White Phosphorus:
-
- Physical Properties: White phosphorus is a waxy substance with a yellowish to clear appearance and a pungent, garlic-like odor.
- Combustibility: It is highly combustible, burning quickly and brightly when exposed to air.
-
- Military Applications:
-
- Use in Incendiary Weapons: White phosphorus is used in incendiary weapons by militaries around the world.
- Its applications include illuminating targets at night and inflicting damage on enemies.
- Function of Incendiary Weapons: These weapons are designed to set fire to objects or cause burns to people through the action of flame, heat, or both, resulting from a chemical reaction of a flammable substance like napalm or white phosphorus.
- Use in Incendiary Weapons: White phosphorus is used in incendiary weapons by militaries around the world.
-

- Combustion Properties:
-
- Burning Temperature: White phosphorus burns at a temperature of 800°C and can spontaneously ignite at temperatures up to 1,300°C when exposed to oxygen.
- Smoke Production: It produces dense white smoke when ignited, which is used by armies to create smokescreens in sensitive zones.
- Fire Spread: It can cause fast-moving and widespread fires on the ground.
- Difficulty in Extinguishing: Once ignited, white phosphorus is very difficult to extinguish as it clings to various surfaces, including skin and clothing. Its wax-like nature makes it hard to remove, and it can reignite when bandages are removed.
-
- Legal Status and Regulation:
-
- Regulation of Use: Although white phosphorus munitions are not banned under international law, their use is supposed to be tightly regulated due to their incendiary effects.
- Chemical Weapons Convention: White phosphorus is not considered a chemical weapon under the Chemical Weapons Convention.
-
See this: A List of Major Freedom Fighters of India (1857-1947)
Facial Authentication Technology for EPS Pensioners
- News: More than 6.6 lakh pensioners made use of the ‘Facial Authentication Technology’ in 2023-24 to verify their digital life certificates for pension provided under the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
- Facial Authentication Technology (FAT) for EPS Pensioners:
- To enhance ‘Ease of Living’, EPFO adopted Digital Life Certificate (DLC) for its pensioners in 2015.
- EPFO accepts DLCs based on biometric authentication from the EPS pensioners.
- To minimize difficulties among elderly on account of having to physically visit a bank/ post office etc. the MeitY and UIDAI developed FAT whereby face recognition technology can be used for proof of life certificate.
- The use of facial authentication method requires installation of two applications, viz. “Aadhaar Face RD” and the “Jeevan Pramaan” in their smartphones.
- Once the scan is completed, the DLC submission is confirmed on the mobile screen along with the Jeevan Pramaan ID and PPO number, completing the process conveniently from home.
- About Facial Recognition Technology:
-
- Facial recognition technology identifies or verifies a person using an image, video, or any audiovisual element of their face.
- It is a method of biometric identification that utilizes facial and head measurements to authenticate an individual’s identity.
-
- How Facial Recognition Technology Works:
-
- Facial recognition technology captures unique biometric data from each person’s face and facial expressions.
- This collected data is then used to identify, verify, and authenticate individuals.
-
- Benefits of Facial Recognition:
-
- Fast and Smooth Remote Identity Verification: Facial recognition technology offers rapid and seamless remote identity verification.
- Enhanced User Experience: The technology provides a unique, smooth, and fast user experience, reducing the necessity for in-person visits or video conferences.
- Enhanced Security: Each face possesses unique and inimitable characteristics, enhancing security through biometric comparison.
- Standard for High-Risk Operations: Facial recognition technology is recognized as a standard for remote identity verification in high-risk operations, such as opening bank accounts and signing contracts.
-
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) Report
- News: India witnessed a fall in spending inequality in 2022-23 compared to 2011-12, according to a detailed report on Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES).
- HCES:
-
- The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) is conducted by the National Statistical Office (NSO) every 5 years.
- The data of HCES provides budget shares of different commodity groups that is used for preparation of the weighting diagram for compilation of official Consumer Price Indices (CPIs).
- It is released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
-
- Key Findings:
-
- Food Consumption Expenditure:
- Households in both rural and urban areas spent the highest share of consumption expenditure on ‘beverages, refreshments, and processed food’.
- Some states, however, showed a preference for other items such as ‘milk and milk products’ and ‘egg, fish & meat’.
- Non-Food Consumption Expenditure:
- Households in both rural and urban areas spent the most on conveyance.
- This was followed by expenditure on durable goods, miscellaneous goods, and entertainment.
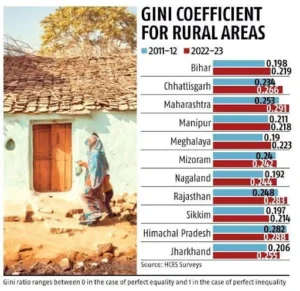
- Increase in Rural Gini Coefficient:
- Overall Increase: The Gini coefficient increased in rural areas of 11 states between 2011-12 and 2022-23.
- Affected States: The states where the Gini coefficient rose include Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- Increase in Urban Gini Coefficient:
- The Gini coefficient for consumption expenditure rose in urban areas of three states: Meghalaya, Himachal Pradesh, and Manipur.
- Food Consumption Expenditure:
-
-
-
- National Trends:
- Rural Areas: Nationally, the Gini coefficient for rural areas declined from 0.283 in 2011-12 to 0.266 in 2022-23.
- Urban Areas: For urban areas, the Gini coefficient decreased from 0.363 to 0.314 during the same period.
- Note: A lower Gini coefficient indicates reduced spending inequality.
- National Trends:
-
- About the Gini Coefficient:
-
- Definition: The Gini coefficient is an indicator of income or wealth inequality, derived from the Lorenz curve.
- Calculation: It is calculated by dividing the area between the perfect equality curve and the actual income distribution curve by the area under the perfect equality curve.
- Range and Interpretation:
- The Gini coefficient ranges from 0 (0%) to 1 (100%):
- 0: Represents perfect equality, where every resident in a country has the same income.
- 1: Represents perfect inequality, where one resident earns all the income, and the rest earn nothing.
-
Pump And Dump Scheme
- News: The Securities Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) recently slapped a fine of Rs 7.75 crore on 11 individuals for allegedly operating a ‘pump and dump’ scheme.
- Understanding Pump and Dump Scheme:
-
- A pump and dump scheme is a manipulative tactic in the stock market involving artificially inflating the price of a stock through false and misleading information.
- The stock is sold at the inflated price to leave investors with significant losses.
-
- Process of Pump and Dump:
-
- Acquisition of Stocks: Fraudsters acquire a significant amount of stock in a small or thinly traded company, often referred to as ‘penny stocks’.
- Aggressive Promotion: The stock is aggressively promoted through various means such as mass emails, newsletters, and misleading social media posts to create hype and attract investors.
- Increased Demand: As the promotion gains traction, more investors buy into the stock, driving up its price due to increased demand. Coordinated buying may further boost the price during this phase.
- Sell-Off: Once the stock price is sufficiently pumped up, the fraudsters start selling off their holdings at the inflated prices, causing the stock price to plummet.
-

- Impact on Investors and the Market:
-
- Investors who bought the stock at inflated prices face significant losses when the stock price crashes, undermining confidence in the financial markets.
- Legitimate investors become wary of potential fraud, affecting market integrity.
-
- Regulations Around Pump and Dump:
-
- Under the Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) guidelines, pump and dump schemes are completely banned.
- SEBI’s Crackdown: SEBI has ordered crackdowns on YouTube-run share pump-and-dump operations and is in the process of framing regulations on financial influencers (finfluencers).
- Rise of Financial Influencers: The rise of influencers in India providing financial advice without qualifications has been detrimental, especially in the case of recent start-up listings.
- Regulators face challenges in monitoring social media platforms like Telegram and Instagram.
-
World Oceans Day 2024
- News: World Oceans Day was recently celebrated at UN Headquarters in New York.
- Overview of World Oceans Day:
-
- World Oceans Day is an annual event observed on June 8th, with the primary objective of raising awareness about the significant role oceans play in the global ecosystem.
-
- Theme for 2024: “Awaken New Depth”
- History and Recognition:
-
- The concept of World Oceans Day was initially proposed at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992, also known as the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED).
- Recognizing the critical importance of oceans, the UN officially designated June 8th as World Oceans Day in 2008.
-
- Importance of Oceans:
-
- Oceans cover more than 70% of the Earth’s surface and play a vital role in regulating the planet’s climate, providing essential resources such as food and oxygen, and supporting a diverse range of marine life.
- They also contribute significantly to human livelihoods by sustaining industries such as fishing, tourism, and shipping.
-
Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLHEP)
- News: A Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) has been signed for the implementation of a comprehensive Fisheries Management Plan at the 2000 MW Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLP) located in Assam.
- Overview of Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLHEP):
-
- Location: The Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLHEP) is an under-construction gravity dam situated on the Subansiri River in northeastern India, straddling the borders of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Capacity: With a capacity of 2000 MW (8×250 MW), it is poised to become the largest hydroelectric plant in India upon completion.
- Development: This run-of-river project is being developed by the National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC), a state-run entity.
-
- Key Facts about the Subansiri River:
-
- The Subansiri River is a trans-Himalayan river and a right-bank tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- Known locally as the Gold River due to its historical gold dust content, it flows through Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China.
- The river originates from the Himalayas in China and flows eastward and southeastward into India, eventually joining the Brahmaputra River in the Lakhimpur district of Assam.
- The Subansiri River stretches approximately 518 km in length, with a drainage basin covering 32,640 square kilometers (12,600 square miles).
- It is the largest tributary of the Brahmaputra River, contributing 7.92% of the Brahmaputra’s total flow.
- The river’s high topographic variation makes it a significant potential zone for hydropower generation, underscoring its importance for regional energy projects such as the SLHEP.
-

