It is a vast expanse of space where everything in existence lies.
Different Views on the Universe
| Geocentric View | It places our Earth at the centre of the Universe |
| Heliocentric View | It regards our Sun at the centre of the Universe |
Big Bang Theory: Origins and Evidence
It was given by George Lemaitre.
- It states that the universe came into existence around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe started as just a single point called the singularity – infinite mass with zero volume.
- During the Big Bang, the single point inflated and exploded violently which resulted in expansion of the universe.
Evidences Supporting Big Bang
- Distance between galaxies increased (Red Shifting of Galaxies)
- Faint glow of light present in the Universe (Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation)
Galaxies
It is a huge collection of dust, gas, and billions of stars and their solar systems which are held together by gravity.
Types of Galaxies
| Spiral Galaxies | Elliptical Galaxies | Irregular Galaxies |
|
|
|
Milky Way Galaxy: Structure and Neighbors
- Location: Our solar system is located in this galaxy.
- Size: Around 1,00,000 light-years across
- Age: Around 13.6 billion years.
- Type: Spiral Galaxy.
- Structure:
- Sagittarius A*: It is a supermassive black hole in the middle of our Milky Way galaxy. Everything in our galaxy revolves around this black hole.
- Galactic Bulge: It is a tightly packed region of gas, dust, and stars in the immediate surrounding of the Sagittarius A*.
- Galactic Disc: It is located beyond the galactic bulge. It hosts billions of stars, including our Sun.
- Nearest Neighbour: Andromeda
Science of Stars
Stars are a giant, glowing ball of gas and dust which are held together by gravity.
Characteristics:
- Mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
- Vary in size, mass and temperature.
- The colour of the star is determined by its temperature. The hottest stars are generally blue, while the coldest stars appear red.
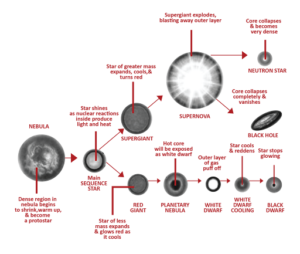
Life Cycle of a Star
Constellation
A group of stars with a constant shape.
- Visibility of a particular constellation depends on the location and time.
- Generally named after objects, animals, and even mythological figures.
- At present, there are 88 officially recognized constellations.
- Used to name stars, meteor showers, and navigation.
- Examples: Ursa Major, Orion, Hunter, Ursa Minor, and The Little bear.














