Our planetary system is called the Solar System, as everything revolves around the Sun. The space that lies beyond our solar system is known as interstellar space.
Origin and Evolution of the Solar System
| Theory | Year | Proponent |
| Gaseous Hypothesis | 1755 | Immanuel Kant |
| Nebular Hypothesis | 1796 | Laplace |
| Planetesimal hypothesis | 1905 | T.C Chamberlin |
| Tidal Hypothesis | 1919; modified in 1929 | James Jeans |
| Binary Star Hypothesis | 1937 | H.N. Russel |
| Supernova Hypothesis | 1946 | F. Hoyle |
Facts About the Sun
- It is the central celestial body of our Solar System. It is a star.
- Age: It is believed to be 5 billion years old.
- Composition: Mainly composed of hydrogen and helium. It has a liquid inner section surrounded by a gaseous outer covering.
- Size: 13,92,000 km.
- Temperature: It varies from 15 million degrees Celsius found at the core to 5,500 degrees Celsius observed at its surface.
Layers of the Sun
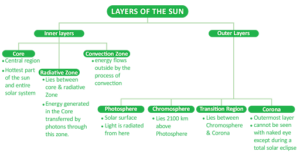
Sun’s Secrets: Key Phenomena and Their Impact on Earth
-
- Sun Spots: These are the dark patches visible on the surface of the Sun. They are dark because they are cooler than the surroundings.
- Solar Wind: It is a stream of plasma flowing outward from the Sun’s corona.
- Coronal Mass Ejection (CME): It refers to the release of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. They occur when the Sun’s magnetic field lines undergo reorganize.
- Solar Cycle: It is the cycle that the Sun’s magnetic field goes through, approximately every 11 years. Every 11 years, the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips, and the Sun’s north and south poles switch places.
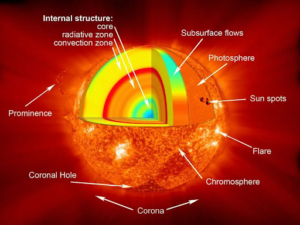
- Solar Flares: These are large explosions from the surface of the sun that emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
-
-
- They occur when the magnetic energy that is built up in the solar atmosphere is released suddenly.
- Auroras: They are formed when the charged particles released by the CME react with the different gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
- Lights seen near the North Pole are called Aurora Borealis or northern lights.
- Similarly, Aurora Australis or southern lights are the lights that occur near the South Pole.
- Most of the auroras occur at a height of 97–1000 kilometres from the earth’s surface.
- Sun’s Halo: It is also known as ’22 degrees halo’. It is an optical phenomenon which occurs when sunlight refracts millions of hexagonal ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. It forms a rainbow-coloured ring with a radius of approximately 22 degrees around the sun or the moon. Circular halos specifically are produced by cirrus clouds.
-
- Space Weather: It is a type of weather created due to the activity on the Sun’s surface. It results in the variations in the space environment between the sun and Earth.
Planets
Planets are objects that orbit around a star in an elliptical path.
- Dwarf Planets: The dwarf planets are small. They don’t have a distinct orbital path.
- There are four dwarf planets in the Kuiper Belt, viz. Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris. Another dwarf planet located in the main asteroid belt is Ceres.
- Exoplanets: These are the planets which are located outside our Solar System.
- Protoplanet: It is a celestial body orbiting around a star and thought to be developing into a planet. In 2022, the Hubble Space Telescope photographed a Jupiter-like protoplanet named AB Aurigae b.
Pluto: It is the largest among dwarf planets
|
Classification of Planets
| Inner Planets | Outer Planets |
|
|
Planets and Important Facts
| Planet | Order from the Sun | Time taken for rotation | Time Taken for revolution | No. of Moons | No. of Rings | Other Facts |
| Mercury | 1 | 59 earth days | 88 earth days | 0 | 0 | Fastest planet in our solar system that travels through space at 47 kilometres per second |
| Venus | 2 | 243 earth days. | 225 earth days | 0 | 0 |
|
| Earth | 3 | About 24 hours | About 365 days | 1 | 0 |
|
| Mars | 4 | Little over 24 hours | 687 earth days | 2-Phobos and Deimos. | 0 | Appears like a reddish ball due to iron minerals on its surface |
| Jupiter | 5 | About 10 hours | 12 earth years | 80
Ganymede is the largest |
Yes |
|
| Saturn | 6 | 10.7 hours | 29 earth years | 83
Titan is the largest |
Yes (7) | Composed of gas and does not have a solid surface |
| Uranus | 7 | 17 hours | 84 Earth years | 27 | Yes (13) | Known as the “Ice Giant” as most of its mass is a hot, dense fluid of icy materials-water, methane, and ammonia |
| Neptune | 8 | 16 hours | 165 earth years | 14 | Yes (9) | Known as Uranus’s twin because of the striking similarity in size, structure, and composition |
PYQ. Which one of the following statements is correct with reference to our solar system? (2002)
Answer: A |
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper Belt is a ring-shaped region located beyond the orbit of Neptune, spanning a distance of 30 to 55 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun.
- This region is home to numerous icy bodies known as Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs) or Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs), which are remnants from the early stages of the solar system’s formation.
Oort CloudIt is a spherical collection of comets and small icy bodies that orbit the sun. It is located beyond the Kuiper Belt, in interstellar space. |
Asteroids and Comets
| Asteroid | Comets |
Types of Asteroids:
Examples: Vesta, Eros, Bennu |
Examples: Hailey’s comet In 2021, the Bernardinelli-Bernstein comet was discovered, making it the largest comet ever observed. |
PYQ. What is the difference between asteroids and comets?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2011)
Answer: B |
Meteors, Meteoroids and Meteorites
- Meteoroids: These are rocky or metallic fragments in space, varying in size from tiny dust particles to small asteroids.
- Meteor: When a meteoroid penetrates the atmosphere of Earth or another planet, it is referred to as a meteor. Commonly called “shooting stars,” meteors emit light as they burn up due to friction caused by their interaction with atmospheric molecules.
- Meteorite: If a meteor survives its journey through the atmosphere and impacts the surface, it is classified as a meteorite.
- Meteor Shower: A meteor shower occurs when Earth passes through a region with a high concentration of meteoroids, resulting in numerous meteors appearing simultaneously.These are space rocks ranging in size from dust grains to small asteroids. Meteor showers are generally named after a star or constellation that is close to where the meteors appear to originate in the sky.
Leonids Meteor Shower
Geminids Meteor Shower
|














